Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measurement of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Films Using DIC
Measurement of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Films Using DIC
Uploaded by
Biagio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views8 pagesThe document investigates using digital image correlation (DIC) to determine the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of thin films. DIC extracts average normal strains from images to calculate CTE as films are heated. The technique is tested on a copper sample and PI/SiO2 composite films, ranging from 40-50 micrometers thick. Results show the composite film expands uniformly and its CTE values match previous reports, validating the DIC method. While less precise than other interferometry methods, DIC has advantages of simple setup, wide sensitivity range, and automatic processing for practical CTE measurement of films.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document investigates using digital image correlation (DIC) to determine the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of thin films. DIC extracts average normal strains from images to calculate CTE as films are heated. The technique is tested on a copper sample and PI/SiO2 composite films, ranging from 40-50 micrometers thick. Results show the composite film expands uniformly and its CTE values match previous reports, validating the DIC method. While less precise than other interferometry methods, DIC has advantages of simple setup, wide sensitivity range, and automatic processing for practical CTE measurement of films.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views8 pagesMeasurement of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Films Using DIC
Measurement of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Films Using DIC
Uploaded by
BiagioThe document investigates using digital image correlation (DIC) to determine the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of thin films. DIC extracts average normal strains from images to calculate CTE as films are heated. The technique is tested on a copper sample and PI/SiO2 composite films, ranging from 40-50 micrometers thick. Results show the composite film expands uniformly and its CTE values match previous reports, validating the DIC method. While less precise than other interferometry methods, DIC has advantages of simple setup, wide sensitivity range, and automatic processing for practical CTE measurement of films.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
Measurement of coefficient of thermal
expansion of films using digital image
correlation method
Applications of the digital image correlation method (DIC) for the determination the
coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of films is investigated in this paper. The average
normal strains in the x and y direction from the region of interest are then extracted
for the determination of CTE.
What kind of material can we test with
traditional technique?
Conventional techniques, such as thermal-mechanical analysis, strain
gauges and quartz tube dilatometer. Techniques are suitable only for
bulk materials. The CCD imaging technique proposed by Wang et al. [1]
can extract the average thermal expansion strain between the two
edges of the film sample. Correspondingly, it can only be utilized to
determine the CTE of isotropic film materials [2]. Full-field optical
techniques, such as phase-shifting interferometry [3] and Electronic
Speckle Pattern Interferometry (ESPI) [4] have been proposed to
determine the whole field thermal expansion of thin film under thermal
loading.
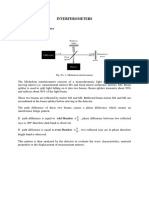
Which is the experimental set-up?
Which is the experimental set-up?
Which material are then tested with DIC?
• A pure copper sample of size 30x30x0.5 mm was used as a reference.
• As an application to polymers, thermal expansion and CTE of PI/SiO2
composite films were determined by the proposed method. The semi-
transparent PI/SiO2 composite film contains 18% weight SiO2. The
test sample was of size 20 20 mm, which was cut from original
samples using a razor blade. The thickness of the sample was 40-50
um.
Validation of the technique
It can be concluded from the figure on the
next slide that the PI/SiO2 composite film is
an isotropic material, because the sample
expands uniformly around the center point
when temperature increases. Measured CTE
data of four samples are presented in Table
1. It is observed that the CTE values in the x
direction approximate those in the y
direction. The CTE of PI/SiO2 composite film
is significantly diminished by adding SiO2
fillers. These results are also in good
accordance with the reported results in Ref.
[2], which further verifies the validity of the
proposed technique.
Validation of the technique
Conclusion
The corresponding precision of CTE determined by forward difference is
about 1.33 106 / C. Certainly, this accuracy is a little lower than that
measured by phase-shifting ESPI, which was said to be 0.1 106 / C in
Ref. [4]. Nevertheless, considering the advantages of simple
experimental set-up, low environmental vulnerability, wide range of
measurement sensitivity and automatic data processing, the DIC
technique is worthy of employment for practical CTE measurement of
films
You might also like
- Using FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy To Teach The Internal Standard MethodDocument3 pagesUsing FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy To Teach The Internal Standard MethodEdgar VegaNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of CTDocument6 pagesQuality Control of CTFrancisco HernandezNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Microtomography SlideshareDocument16 pagesX-Ray Microtomography SlidesharehafizalNo ratings yet
- Improvement On Measurement Accuracy of High-Temperature DICDocument7 pagesImprovement On Measurement Accuracy of High-Temperature DICXiongJie CheNo ratings yet
- Reflectance Application ExamplesDocument16 pagesReflectance Application ExamplessemiconsoftNo ratings yet
- Zheng 2015Document6 pagesZheng 2015dalhr198No ratings yet
- Belkhanchi 2021Document10 pagesBelkhanchi 2021dilla zainudinNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0142941805001029 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0142941805001029 MainCarlos CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Film Coating Thickness and Surface Area of Pharmaceutical Pellets Using Fluorescence Microscopy and Image AnalysisDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Film Coating Thickness and Surface Area of Pharmaceutical Pellets Using Fluorescence Microscopy and Image AnalysisSchwanStyNo ratings yet
- Mechanism and Compensation of Measurement Error Induced by Thermal Deformation of Digital Camera in Photo MechanicsDocument21 pagesMechanism and Compensation of Measurement Error Induced by Thermal Deformation of Digital Camera in Photo MechanicsTestingAccNo ratings yet
- Articulo 1Document13 pagesArticulo 1Nuñez Salvador ArianaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Young's Modulus of Metallic and Composite Materials by Digital Image CorrelationDocument6 pagesDetermination of Young's Modulus of Metallic and Composite Materials by Digital Image Correlationshamsukarim2009No ratings yet
- Polymers 11 00523Document11 pagesPolymers 11 00523Rogério JuniorNo ratings yet
- True Stress-Logarithmic Strain Curves Test of Pipeline Steels Using 3D Digital Image CorrelationDocument9 pagesTrue Stress-Logarithmic Strain Curves Test of Pipeline Steels Using 3D Digital Image Correlationsourabh mahanaNo ratings yet
- Determining The Poisson's Ratio of Thin ®LM Materials Using Resonant MethodDocument7 pagesDetermining The Poisson's Ratio of Thin ®LM Materials Using Resonant Methodxulub1No ratings yet
- TermografiaDocument23 pagesTermografiaDaniel AriasNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General: Dept. of Civil Engineering GeckDocument16 pages1.1 General: Dept. of Civil Engineering GeckAnithaNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Endoscopy For Inspection of Tube-To-Tube Sheet WeldsDocument7 pagesX-Ray Endoscopy For Inspection of Tube-To-Tube Sheet WeldsLeandro LimaNo ratings yet
- Jkps 66 1308Document9 pagesJkps 66 1308johan NGONTIENo ratings yet
- Title: Version of RecordDocument21 pagesTitle: Version of RecordDwi UtamiNo ratings yet
- A Simulation-Based Assessment of The Revised NEMA NU-2 70-cm Long Test Phantom For PETDocument5 pagesA Simulation-Based Assessment of The Revised NEMA NU-2 70-cm Long Test Phantom For PETMarcelo ToledoNo ratings yet
- A NIM PETCT Phantom For Evaluating The PET Image Quality of Micro Lesions and The Performance Parameters of CTDocument13 pagesA NIM PETCT Phantom For Evaluating The PET Image Quality of Micro Lesions and The Performance Parameters of CTp110054No ratings yet
- Digital Image Correlation For Tensile TestDocument9 pagesDigital Image Correlation For Tensile TestAli AbbarNo ratings yet
- High-Temperature Deformation Field Measurement by Combining TransientDocument8 pagesHigh-Temperature Deformation Field Measurement by Combining TransientXiongJie CheNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument5 pagesPolymerYossy RyanantaNo ratings yet
- Ae Mag-Isa 2013-3Document8 pagesAe Mag-Isa 2013-3Vivo 1906No ratings yet
- Optical ElectricalPropertiesAnDocument9 pagesOptical ElectricalPropertiesAnIvan Alves de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Testing System Development For Creep Characterization of PolymersDocument6 pagesTesting System Development For Creep Characterization of PolymersJames UgoNo ratings yet
- Thickness and Surface Measurement of Transparent Thin-Film Layers Using White Light Scanning Interferometry Combined With ReflectometryDocument8 pagesThickness and Surface Measurement of Transparent Thin-Film Layers Using White Light Scanning Interferometry Combined With ReflectometryChang MingNo ratings yet
- Bcv6NQAZhflnBaB6 zFbJdv66YQjFsmKDocument7 pagesBcv6NQAZhflnBaB6 zFbJdv66YQjFsmKshahrzad qafouriNo ratings yet
- Anisotropic thermal conductivity measurement of organic thin film with bidirectional 3ω methodDocument7 pagesAnisotropic thermal conductivity measurement of organic thin film with bidirectional 3ω methodTriều Huỳnh NhậtNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fracture Mechanics: I. Jandejsek, L. Gajdoš, M. Šperl, D. Vavr ÍkDocument14 pagesEngineering Fracture Mechanics: I. Jandejsek, L. Gajdoš, M. Šperl, D. Vavr ÍkTibebu MerideNo ratings yet
- Infrared Thermography and Calibration Techniques For Gas Turbine Applications, A ReviewDocument57 pagesInfrared Thermography and Calibration Techniques For Gas Turbine Applications, A Reviewomar900314No ratings yet
- Optical Properties and Structure of Drawn Polyethyleneterephtalate-poly-ETHYLENE FILMSDocument6 pagesOptical Properties and Structure of Drawn Polyethyleneterephtalate-poly-ETHYLENE FILMSdorian_pictNo ratings yet
- Defect and Porosity Determination of Fibre Reinforced Polymers by X-Ray Computed TomographyDocument12 pagesDefect and Porosity Determination of Fibre Reinforced Polymers by X-Ray Computed TomographyAlessandro PosillicoNo ratings yet
- Heating Rate Effects On Thermal Analysis Measurement of T in Composite MaterialsDocument10 pagesHeating Rate Effects On Thermal Analysis Measurement of T in Composite MaterialssamiNo ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional Particle Image Velocimetry: Experimental Error Analysis of A Digital Angular Stereoscopic SystemDocument11 pagesThree-Dimensional Particle Image Velocimetry: Experimental Error Analysis of A Digital Angular Stereoscopic Systemsamik4uNo ratings yet
- EI2021 Nikolic PolanskyDocument4 pagesEI2021 Nikolic PolanskyValentino NikolićNo ratings yet
- Residual Stress Measurement in Steel Beams Using The Incremental Slitting TechniqueDocument8 pagesResidual Stress Measurement in Steel Beams Using The Incremental Slitting TechniqueTimmy VoNo ratings yet
- 2Document10 pages2NamanMishraNo ratings yet
- J JMMM 2015 07 079Document10 pagesJ JMMM 2015 07 079anesaNo ratings yet
- BulganDocument10 pagesBulganIkh nahia Ikh Nakhia PharmNo ratings yet
- Puablication 2020 Mag-IsaDocument4 pagesPuablication 2020 Mag-IsaVivo 1906No ratings yet
- 14 Xiem Full 8Document8 pages14 Xiem Full 8Phan Thanh NhanNo ratings yet
- International Conf. On X-Ray - SlideshareDocument10 pagesInternational Conf. On X-Ray - SlidesharehafizalNo ratings yet
- Qwab 033Document16 pagesQwab 033Srimanthula SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Voids in Fibre Reinforced Composite MaterialsDocument6 pagesCharacterization of Voids in Fibre Reinforced Composite Materialsabilio_j_vieiraNo ratings yet
- Measure Intermetallic Layer Thickness IpcDocument12 pagesMeasure Intermetallic Layer Thickness IpcAdair NettoNo ratings yet
- On The Measurement of Phase Billmeyer1985Document6 pagesOn The Measurement of Phase Billmeyer1985The Quotes9No ratings yet
- PPXV An Elegant and Fast Method To Predict The Slow Crack Growth Behaviour of High Density Polyethylene Pipe MaterialsDocument7 pagesPPXV An Elegant and Fast Method To Predict The Slow Crack Growth Behaviour of High Density Polyethylene Pipe MaterialsMehboob ulHaqNo ratings yet
- Research On Ultrasonic Velocity Imaging of Metal Matrix Composites With TIRP MethodDocument7 pagesResearch On Ultrasonic Velocity Imaging of Metal Matrix Composites With TIRP MethodPraveen ChathurangaNo ratings yet
- Applied SciencesDocument15 pagesApplied Scienceschaminda nayanajithNo ratings yet
- Silva Et Al - 2009 PDFDocument9 pagesSilva Et Al - 2009 PDFSayantani RoyNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Single Mode Pressure SensorDocument3 pagesIntrinsic Single Mode Pressure Sensorsubhra3sNo ratings yet
- Tensile and Bending Test of Carbonepoxy and CarbonDocument8 pagesTensile and Bending Test of Carbonepoxy and CarbonKareem El MariaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Scratch Resistance in Multiphase PP Blends PDFDocument10 pagesEvaluation of Scratch Resistance in Multiphase PP Blends PDFsonchemenNo ratings yet
- CCL GD MeP 2Document8 pagesCCL GD MeP 2David MarcoeNo ratings yet
- Ae Mag-Isa 2014-1Document6 pagesAe Mag-Isa 2014-1Vivo 1906No ratings yet
- Topics On Optical and Digital Image Processing Using Holography and Speckle TechniquesFrom EverandTopics On Optical and Digital Image Processing Using Holography and Speckle TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Full-Field Measurements and Identification in Solid MechanicsFrom EverandFull-Field Measurements and Identification in Solid MechanicsMichel GrediacNo ratings yet
- P1 Mechanics: P1.1 Measuring Methods P1.3 Translational Motions of A Mass PointDocument14 pagesP1 Mechanics: P1.1 Measuring Methods P1.3 Translational Motions of A Mass PointccmejiaNo ratings yet
- Michelson Interefrometer Viva QuestionsDocument2 pagesMichelson Interefrometer Viva QuestionsDhruv NagarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Our Subject: Theory and PmcticeDocument2 pages1.1 Our Subject: Theory and PmcticeTesh SiNo ratings yet
- Direction Finding PresentationDocument35 pagesDirection Finding PresentationFoolraserNo ratings yet
- Negative-Index Metamaterial at 780 NM WavelengthDocument3 pagesNegative-Index Metamaterial at 780 NM WavelengthdickNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Smart Structures: Eric UddDocument8 pagesFiber Optic Smart Structures: Eric UddGoutham KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Metrology Chapter 3Document19 pagesMetrology Chapter 3venkeekuNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Humidity Measurement, Volume 1 Spect 3516704Document391 pagesHandbook of Humidity Measurement, Volume 1 Spect 3516704Hafshah DeviNo ratings yet
- FTIR 7800: SpectrophotometerDocument8 pagesFTIR 7800: SpectrophotometerAfzal SarfarazNo ratings yet
- 8 Electromagnetic Methods of Lightning LocationDocument17 pages8 Electromagnetic Methods of Lightning LocationMellina LisboaNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of Spie: Determination of Residual Stress in Low-Temperature PECVD Silicon Nitride Thin FilmsDocument13 pagesProceedings of Spie: Determination of Residual Stress in Low-Temperature PECVD Silicon Nitride Thin FilmsbehzadjaziNo ratings yet
- Integrating Quantum Algorithms With Gravitational-Wave Metrology For Enhanced Signal DetectionDocument18 pagesIntegrating Quantum Algorithms With Gravitational-Wave Metrology For Enhanced Signal DetectionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- 0 The Microwave Interferometer On J-TEXT TokamakDocument2 pages0 The Microwave Interferometer On J-TEXT TokamakAbhishek BasakNo ratings yet
- Use of Sentinel-1 Data For Earthquake Damage Assessment in Cases of Amatrice and Sarpol-E ZahabDocument5 pagesUse of Sentinel-1 Data For Earthquake Damage Assessment in Cases of Amatrice and Sarpol-E Zahabjacob mooreNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Engineering Physics-146-187Document42 pagesA Textbook of Engineering Physics-146-187mayzarNo ratings yet
- Ibi-Fb / Ids Georadar / Rockpoint Servicios GeotecnicosDocument2 pagesIbi-Fb / Ids Georadar / Rockpoint Servicios GeotecnicosturoNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy in Colloid and Interface ScienceDocument298 pagesFourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy in Colloid and Interface ScienceAnderson CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Govpub C13Document330 pagesGovpub C13Vishal ShindeNo ratings yet
- 1 8 173Document8 pages1 8 173Kinjal PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Shimadzu FTIR 8400s ManualDocument16 pagesShimadzu FTIR 8400s ManualMohammed HamzahNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument18 pagesElectrical EngineeringthanhNo ratings yet
- T.Y.B.Sc. (Physics) 06.07.2021Document83 pagesT.Y.B.Sc. (Physics) 06.07.2021KIRAN GOUTAMNo ratings yet
- Types of InterferometersDocument5 pagesTypes of InterferometersSameer R. KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Refractometry - Book PartialDocument18 pagesChapter7 Refractometry - Book PartialVallik TadNo ratings yet
- Interference Michelson InterferometerDocument6 pagesInterference Michelson InterferometerAsa mathewNo ratings yet
- Phased Array ASNTDocument92 pagesPhased Array ASNTMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Uv-Vis Absorption SpectrosDocument13 pagesUv-Vis Absorption Spectrosrubensfisico100% (1)
- Unit - 4 Flow VisualizationDocument21 pagesUnit - 4 Flow VisualizationAkshay SNo ratings yet
- Metrology Measurement Unit-5Document27 pagesMetrology Measurement Unit-5R NAVEEN KUMAR MECHNo ratings yet