Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsHaccp 1
Haccp 1
Uploaded by
guzman.regina.lauriaThe document discusses Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), a systematic approach for identifying and preventing food safety hazards. It describes the 7 principles of HACCP: 1) conduct a hazard analysis and identify potential risks, 2) determine critical control points, 3) establish critical limits, 4) establish procedures to monitor critical control points, 5) establish corrective actions, 6) establish verification procedures, and 7) establish record-keeping. Key aspects include identifying microbiological, chemical, physical and allergen hazards, determining critical control points using a decision tree, establishing critical limits for each control point, and monitoring procedures to ensure control points remain under control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Develop and Implement A Food Safety PlanDocument15 pagesDevelop and Implement A Food Safety Planneha75% (4)
- Pda TR 54Document79 pagesPda TR 54Claudia Marcela Gómez100% (1)
- Haccp ExamDocument10 pagesHaccp ExamWendy Tandy100% (1)
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control PointDocument37 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control PointMark Nikko ManginsayNo ratings yet
- DRRR-Week 2Document7 pagesDRRR-Week 2Ren Andaleon Cortez100% (1)
- HACCPDocument28 pagesHACCPShafakatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Food Safety and Quality SystemDocument45 pagesChapter 4 Food Safety and Quality SystemIman Fatihah100% (1)
- 4.0 Food Safety and Quality SystemDocument44 pages4.0 Food Safety and Quality SystemSiti Aisyah MahamudNo ratings yet
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point)Document11 pagesHACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point)Aarzoo DbHlxrBFTl100% (1)
- 1305_HACCP,TQM,GMP,RISK_ASSESMENT_compressedDocument12 pages1305_HACCP,TQM,GMP,RISK_ASSESMENT_compressedakramsharek84No ratings yet
- Principles of Haccp: Principle 1 - Conduct A Hazard AnalysisDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Haccp: Principle 1 - Conduct A Hazard AnalysisAttia MunawerNo ratings yet
- Implement Food Hygiene ProceduresDocument59 pagesImplement Food Hygiene ProceduresShirmeenanwer100% (1)
- 12 Steps To Develop A HACCP PlanDocument8 pages12 Steps To Develop A HACCP PlanDeavoNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument29 pagesHACCPPrasad MgNo ratings yet
- History of The Haccp SystemDocument18 pagesHistory of The Haccp SystemScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- QA Lect 3 Good MNF Practices and HACCPDocument11 pagesQA Lect 3 Good MNF Practices and HACCPShaunNo ratings yet
- Test Food Safety 2Document7 pagesTest Food Safety 2Danial Iqhwan100% (1)
- The Principles of HACCPDocument51 pagesThe Principles of HACCPBruno100% (1)
- Leila Kakko Tampere University of Applied Science Traditional Food in Combating Foodborne Pathogens 2011Document57 pagesLeila Kakko Tampere University of Applied Science Traditional Food in Combating Foodborne Pathogens 2011harichandradeshmukh17No ratings yet
- Haccp SystemDocument28 pagesHaccp SystemAaron RoxasNo ratings yet
- The HACCP System and ApplicationDocument48 pagesThe HACCP System and ApplicationNabilah Ong100% (1)
- HACCPDocument29 pagesHACCPCherry Ann Garcia Durante100% (1)
- HACCPDocument59 pagesHACCPbieche43No ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point 1 (Haccp)Document30 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control Point 1 (Haccp)Ann Rose PayumoNo ratings yet
- GMP N HACCPDocument3 pagesGMP N HACCPrhib47957No ratings yet
- Eating Establishment RegulationsDocument9 pagesEating Establishment RegulationsThelano RapizNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument35 pagesTerm PaperAyesha CampbellNo ratings yet
- KakkoL GMP in Food PDFDocument0 pagesKakkoL GMP in Food PDFErwin Koko TkciNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument43 pagesHACCPleah.donyaNo ratings yet
- 10-HACCP Lecture EnglishDocument61 pages10-HACCP Lecture Englishmena 2No ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis and Cri Hazard AnalysisDocument11 pagesHazard Analysis and Cri Hazard Analysisanto132zokaNo ratings yet
- Haccp TrainingDocument2 pagesHaccp TrainingMBAZIIRA HATIMNo ratings yet
- HACCP Basic CourseDocument28 pagesHACCP Basic CourseVasilicaNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument11 pagesHACCPAyaaaa OmeyyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point Concept in Sea Food IndustryDocument8 pagesAssignment 1: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point Concept in Sea Food IndustryRISHIKANo ratings yet
- Group 6 THC 2Document46 pagesGroup 6 THC 2John Carlo VLOGSNo ratings yet
- HACCP Principles PracticeDocument67 pagesHACCP Principles PracticeEbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- Haccp GMP Ssop 2007Document7 pagesHaccp GMP Ssop 2007aidaNo ratings yet
- Lucr ST PublicataDocument6 pagesLucr ST PublicataSincu AlexandraNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument47 pagesHACCPAnonymous El6p9Bl100% (1)
- Final Inception ReportDocument7 pagesFinal Inception Reportjahn teherNo ratings yet
- HACCPImp GuideDocument9 pagesHACCPImp Guidem.monir.saNo ratings yet
- HACCP FormsDocument10 pagesHACCP FormskavehNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point HaccpDocument14 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control Point HaccpLLEGUE, John Edward A.No ratings yet
- Haccp Izstrades VadlinijasDocument2 pagesHaccp Izstrades VadlinijasAgnese DziguneNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument6 pagesHACCPamrutha tkNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument21 pagesHACCPAINA SAHIRAH ABDUL AZISNo ratings yet
- HACCP and Kitchen SafetyDocument12 pagesHACCP and Kitchen SafetycecedrakeNo ratings yet
- HACCP Manual Cart D orDocument21 pagesHACCP Manual Cart D orejub6447100% (1)
- Chapter 4 HaccpDocument41 pagesChapter 4 HaccpSPMUSER9ANo ratings yet
- HACCP in Milk Industry: Ankara University, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Department of Food Hygiene and TechnologyDocument18 pagesHACCP in Milk Industry: Ankara University, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Department of Food Hygiene and TechnologyGeorgette RepunteNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument8 pagesHACCPKaye NicolasNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point 1Document12 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control Point 1Francis BigualNo ratings yet
- Haccp PPP - 2Document14 pagesHaccp PPP - 2solivan_051704No ratings yet
- Approaches To Safe Meat F 8754301Document23 pagesApproaches To Safe Meat F 8754301adminNo ratings yet
- Haccp: The HACCP Seven PrinciplesDocument1 pageHaccp: The HACCP Seven PrinciplesAnonymous LJ9JdSBKHNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument61 pagesHACCPAbd-alruhman HossnyNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument21 pagesHACCPNur Athirah Muhamad SobriNo ratings yet
- GMP HaccpDocument43 pagesGMP HaccpMohammad Ashraf PaulNo ratings yet
- Difference Between HACCP and GMPDocument27 pagesDifference Between HACCP and GMPqtryst71% (7)
- Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points PrinciplesDocument1 pageHazard Analysis of Critical Control Points PrinciplesAsandaNo ratings yet
- Effective microbiological sampling of food processing environments (1999)From EverandEffective microbiological sampling of food processing environments (1999)No ratings yet
- Supplemental Slides For Module 1Document7 pagesSupplemental Slides For Module 1guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 UtilitiesDocument29 pagesModule 3.1 Utilitiesguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument12 pagesRoot Cause Analysisguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Week8 - Earth's Lithosphere - Phil RA 9003Document23 pagesWeek8 - Earth's Lithosphere - Phil RA 9003guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Ferment 3Document14 pagesFerment 3guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 QMSDocument23 pagesModule 2 QMSguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Human Security and Refugee RightsDocument1 pageHuman Security and Refugee Rightsguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Ferment 2Document15 pagesFerment 2guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document45 pagesLesson 7guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Feminist EthicsDocument17 pagesFeminist Ethicsguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document30 pagesLesson 5guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document19 pagesLesson 4guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 MT1Document11 pagesChapter 9 MT1guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Tabel Perbedaan ISO 45001 Dan OHSAS 18001Document5 pagesTabel Perbedaan ISO 45001 Dan OHSAS 18001sudarno20No ratings yet
- A Mobile and Android-Based Application For Local Disaster Risk Reduction and MonitoringDocument6 pagesA Mobile and Android-Based Application For Local Disaster Risk Reduction and MonitoringInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/22Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/22Sameera MNo ratings yet
- 01 Incident - Accident Investigation ReportDocument2 pages01 Incident - Accident Investigation ReportSasi KssNo ratings yet
- City of Portland Complaint FinalDocument39 pagesCity of Portland Complaint FinalNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- 5-Risk Assessment Methods For Vapour-Cloud ExplosionsDocument10 pages5-Risk Assessment Methods For Vapour-Cloud ExplosionsNojus DekerisNo ratings yet
- 9 Hazard Identification Risk AssessmentDocument10 pages9 Hazard Identification Risk Assessmentvasanth pugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- Demobilization and Demolition Activies of Porta Cabins and Containers For Laydown AreaDocument10 pagesDemobilization and Demolition Activies of Porta Cabins and Containers For Laydown AreaNasrullahNo ratings yet
- Part V (C) - Risk Management - JSA & SOP (Day 2)Document22 pagesPart V (C) - Risk Management - JSA & SOP (Day 2)kwong siongNo ratings yet
- Fire Hazard PowerpointDocument19 pagesFire Hazard PowerpointDahlia Mi Villanueva100% (4)
- Lesson 4: Practice Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresDocument16 pagesLesson 4: Practice Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresAl Brelzhiv SarsalejoNo ratings yet
- Chemical SafetyDocument4 pagesChemical Safetyarfredbileg08No ratings yet
- TSA-017 - Lifting Using Split BoxDocument2 pagesTSA-017 - Lifting Using Split BoxMusadiq HussainNo ratings yet
- Manual: Movifit FC - Function Level "Technology" With PROFINET IO InterfaceDocument36 pagesManual: Movifit FC - Function Level "Technology" With PROFINET IO InterfaceJhonnie Rosete LuquezNo ratings yet
- A 14-Step Strategy of HACCP System Implementation in Snack Food ManufacturingDocument13 pagesA 14-Step Strategy of HACCP System Implementation in Snack Food Manufacturinganishor87No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Hazards and The Risk of Thermal Runaway PDFDocument6 pagesChemical Reaction Hazards and The Risk of Thermal Runaway PDFGuz UchihaNo ratings yet
- Role of Donor Agencies in Disaster Management: International Journal of Multidisciplinary Education and ResearchDocument5 pagesRole of Donor Agencies in Disaster Management: International Journal of Multidisciplinary Education and ResearchYathiraj YathirajNo ratings yet
- Cahilap Aj MacroDocument5 pagesCahilap Aj Macrosamu hayesNo ratings yet
- Induction Furnace Hazard RegisterDocument3 pagesInduction Furnace Hazard RegisterVALENTINE T NHOPINo ratings yet
- DRRR Week 2 Module 1Document11 pagesDRRR Week 2 Module 1Jacob Tabula67% (3)
- Derelict Hospital 1 - Denburgh Insane Asylum - Online Location ScoutDocument2 pagesDerelict Hospital 1 - Denburgh Insane Asylum - Online Location ScoutsimsoawesomeNo ratings yet
- Basic Occup0ational Safety and HealthDocument93 pagesBasic Occup0ational Safety and HealthGabriel Galiza100% (1)
- TIS0002908.001 en-US-PV-351-SOP-CRI-PTZ CameraDocument24 pagesTIS0002908.001 en-US-PV-351-SOP-CRI-PTZ CameraPedro DebiaNo ratings yet
- B96280ABDocument158 pagesB96280ABMunya BengezaNo ratings yet
- HACCP Plan For Aluminum Foil LidsDocument2 pagesHACCP Plan For Aluminum Foil LidsRao WaqarNo ratings yet
- TR-Electronics Front-Of-Line Operation NC IIDocument71 pagesTR-Electronics Front-Of-Line Operation NC IIAmhier MokamadNo ratings yet
- Hazard PayDocument14 pagesHazard PayMark BuendiaNo ratings yet
- PSF Proponent HandbookDocument52 pagesPSF Proponent HandbookCarlo BernardoNo ratings yet
Haccp 1
Haccp 1
Uploaded by
guzman.regina.lauria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views20 pagesThe document discusses Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), a systematic approach for identifying and preventing food safety hazards. It describes the 7 principles of HACCP: 1) conduct a hazard analysis and identify potential risks, 2) determine critical control points, 3) establish critical limits, 4) establish procedures to monitor critical control points, 5) establish corrective actions, 6) establish verification procedures, and 7) establish record-keeping. Key aspects include identifying microbiological, chemical, physical and allergen hazards, determining critical control points using a decision tree, establishing critical limits for each control point, and monitoring procedures to ensure control points remain under control.
Original Description:
Original Title
HACCP 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), a systematic approach for identifying and preventing food safety hazards. It describes the 7 principles of HACCP: 1) conduct a hazard analysis and identify potential risks, 2) determine critical control points, 3) establish critical limits, 4) establish procedures to monitor critical control points, 5) establish corrective actions, 6) establish verification procedures, and 7) establish record-keeping. Key aspects include identifying microbiological, chemical, physical and allergen hazards, determining critical control points using a decision tree, establishing critical limits for each control point, and monitoring procedures to ensure control points remain under control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views20 pagesHaccp 1
Haccp 1
Uploaded by
guzman.regina.lauriaThe document discusses Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), a systematic approach for identifying and preventing food safety hazards. It describes the 7 principles of HACCP: 1) conduct a hazard analysis and identify potential risks, 2) determine critical control points, 3) establish critical limits, 4) establish procedures to monitor critical control points, 5) establish corrective actions, 6) establish verification procedures, and 7) establish record-keeping. Key aspects include identifying microbiological, chemical, physical and allergen hazards, determining critical control points using a decision tree, establishing critical limits for each control point, and monitoring procedures to ensure control points remain under control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
Industrial Microbiology
Food Safety and Food Plant
Sanitation - HACCP
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP)
system
- food safety program developed for astronauts
- prevent hazards that could cause food-borne illnesses
- traditional way: spot-checks and random sampling of
products
advantages:
-based on sound science
-more efficient and effective (record keeping)
-help food companies compete more effectively in the
world market
Hazard Analysis Critical Control
point (HACCP) System
- Is a system that should lead to the production of
microbiologically safe foods
- A systematic approach to controlling foodborne hazards
- Proper implementation of HACCP in food service
establishments and the home = decrease in foodborne
illness.
Hazard Analysis Critical Control point
(HACCP) System
PREREQUISITE PROGRAMS – concerns and aspects of the entire
food environment before the HACCP system is initiated
1. Suitability of facilities
2. Control of suppliers
3. Safety and maintenance of production equipment
4. Cleaning and sanitation of equipment and facilities
5. Personal hygiene of employees
6. Control of chemicals, pest control and the like.
- Good manufacturing practices
Hazard Analysis Critical Control point
(HACCP) System
Principles
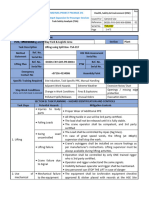
1. Assess the hazards and risks.
2. Determine the critical control point(s) (CCP).
3. Establish the critical limits.
4. Establish procedures to monitor CCPs.
Hazard Analysis Critical Control point
(HACCP) System
Principles
5. Establish corrective actions.
6. Established procedures for verification that the HACCP
system is working correctly.
7. Establish effective record-keeping systems that document
the HACCP plan.
Assess Hazards and Risks
-quality is differentiated from safety concerns
Types of Hazards*
*will cause injury/illness in the absence of its control
-Microbiological: e.g., bacteria, yeasts, molds and viruses.
-Chemical: e.g., water, food contact materials, cleaning
agents, pest control substances, contaminants, pesticides,
biocides and food additives
-Physical: e.g., packaging, pest droppings, screws, etc.
-Allergens
Examples of questions considered when conducting a hazard
analysis
Stage 3: Determine Control Measures: For each
identified hazard, the HACCP team must establish control
measures to mitigate or eliminate the hazard.
Stage 4: Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs):
Critical Control Points (CCPs) are specific points in the
process where control measures can be effectively
applied to prevent, reduce, or eliminate the identified
hazard to an acceptable level.
Hazard analysis summary
Determine Critical Control Point(s)
-a step at which control can be applied and is essential:
a. To prevent or eliminate a food safety hazard
b. To reduce it to an acceptable level
Examples:
1. Heat process steps where time-temperature relations must
be maintained
2. Freezing and time to freezing before pathogens can multiply
3. Maintenance of the pH of a food product at a level that
prevents the growth of pathogens
4. Employee hygiene
Example of CCP Decision Tree
Establish the critical limit
-a maximum and/or minimum value to distinguish between
safe and unsafe operating conditions at a CCP
-not the same as operational limits, which are meant other
than food safety (e.g., quality)
-each CCP have one or more control measures with critical
limits
Critical limits may be based on:
-moisture, humidity, water activity, temperature, pH, time,
salt concentration, available chlorine, viscosity, preservative,
aroma, and visual appearance.
Establish the critical limit
Establish the critical limit
Establish Procedures to Monitor CCPs
-a planned sequence of observations or measurements to
assess whether a CCP is under control
-to produce an accurate record for future use in verification
-monitoring results will be documented (e.g., chart recorder)
-Microbial analyses are not used to monitor
You might also like
- Develop and Implement A Food Safety PlanDocument15 pagesDevelop and Implement A Food Safety Planneha75% (4)
- Pda TR 54Document79 pagesPda TR 54Claudia Marcela Gómez100% (1)
- Haccp ExamDocument10 pagesHaccp ExamWendy Tandy100% (1)
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control PointDocument37 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control PointMark Nikko ManginsayNo ratings yet
- DRRR-Week 2Document7 pagesDRRR-Week 2Ren Andaleon Cortez100% (1)
- HACCPDocument28 pagesHACCPShafakatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Food Safety and Quality SystemDocument45 pagesChapter 4 Food Safety and Quality SystemIman Fatihah100% (1)
- 4.0 Food Safety and Quality SystemDocument44 pages4.0 Food Safety and Quality SystemSiti Aisyah MahamudNo ratings yet
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point)Document11 pagesHACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point)Aarzoo DbHlxrBFTl100% (1)
- 1305_HACCP,TQM,GMP,RISK_ASSESMENT_compressedDocument12 pages1305_HACCP,TQM,GMP,RISK_ASSESMENT_compressedakramsharek84No ratings yet
- Principles of Haccp: Principle 1 - Conduct A Hazard AnalysisDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Haccp: Principle 1 - Conduct A Hazard AnalysisAttia MunawerNo ratings yet
- Implement Food Hygiene ProceduresDocument59 pagesImplement Food Hygiene ProceduresShirmeenanwer100% (1)
- 12 Steps To Develop A HACCP PlanDocument8 pages12 Steps To Develop A HACCP PlanDeavoNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument29 pagesHACCPPrasad MgNo ratings yet
- History of The Haccp SystemDocument18 pagesHistory of The Haccp SystemScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- QA Lect 3 Good MNF Practices and HACCPDocument11 pagesQA Lect 3 Good MNF Practices and HACCPShaunNo ratings yet
- Test Food Safety 2Document7 pagesTest Food Safety 2Danial Iqhwan100% (1)
- The Principles of HACCPDocument51 pagesThe Principles of HACCPBruno100% (1)
- Leila Kakko Tampere University of Applied Science Traditional Food in Combating Foodborne Pathogens 2011Document57 pagesLeila Kakko Tampere University of Applied Science Traditional Food in Combating Foodborne Pathogens 2011harichandradeshmukh17No ratings yet
- Haccp SystemDocument28 pagesHaccp SystemAaron RoxasNo ratings yet
- The HACCP System and ApplicationDocument48 pagesThe HACCP System and ApplicationNabilah Ong100% (1)
- HACCPDocument29 pagesHACCPCherry Ann Garcia Durante100% (1)
- HACCPDocument59 pagesHACCPbieche43No ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point 1 (Haccp)Document30 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control Point 1 (Haccp)Ann Rose PayumoNo ratings yet
- GMP N HACCPDocument3 pagesGMP N HACCPrhib47957No ratings yet
- Eating Establishment RegulationsDocument9 pagesEating Establishment RegulationsThelano RapizNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument35 pagesTerm PaperAyesha CampbellNo ratings yet
- KakkoL GMP in Food PDFDocument0 pagesKakkoL GMP in Food PDFErwin Koko TkciNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument43 pagesHACCPleah.donyaNo ratings yet
- 10-HACCP Lecture EnglishDocument61 pages10-HACCP Lecture Englishmena 2No ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis and Cri Hazard AnalysisDocument11 pagesHazard Analysis and Cri Hazard Analysisanto132zokaNo ratings yet
- Haccp TrainingDocument2 pagesHaccp TrainingMBAZIIRA HATIMNo ratings yet
- HACCP Basic CourseDocument28 pagesHACCP Basic CourseVasilicaNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument11 pagesHACCPAyaaaa OmeyyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point Concept in Sea Food IndustryDocument8 pagesAssignment 1: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point Concept in Sea Food IndustryRISHIKANo ratings yet
- Group 6 THC 2Document46 pagesGroup 6 THC 2John Carlo VLOGSNo ratings yet
- HACCP Principles PracticeDocument67 pagesHACCP Principles PracticeEbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- Haccp GMP Ssop 2007Document7 pagesHaccp GMP Ssop 2007aidaNo ratings yet
- Lucr ST PublicataDocument6 pagesLucr ST PublicataSincu AlexandraNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument47 pagesHACCPAnonymous El6p9Bl100% (1)
- Final Inception ReportDocument7 pagesFinal Inception Reportjahn teherNo ratings yet
- HACCPImp GuideDocument9 pagesHACCPImp Guidem.monir.saNo ratings yet
- HACCP FormsDocument10 pagesHACCP FormskavehNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point HaccpDocument14 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control Point HaccpLLEGUE, John Edward A.No ratings yet
- Haccp Izstrades VadlinijasDocument2 pagesHaccp Izstrades VadlinijasAgnese DziguneNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument6 pagesHACCPamrutha tkNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument21 pagesHACCPAINA SAHIRAH ABDUL AZISNo ratings yet
- HACCP and Kitchen SafetyDocument12 pagesHACCP and Kitchen SafetycecedrakeNo ratings yet
- HACCP Manual Cart D orDocument21 pagesHACCP Manual Cart D orejub6447100% (1)
- Chapter 4 HaccpDocument41 pagesChapter 4 HaccpSPMUSER9ANo ratings yet
- HACCP in Milk Industry: Ankara University, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Department of Food Hygiene and TechnologyDocument18 pagesHACCP in Milk Industry: Ankara University, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Department of Food Hygiene and TechnologyGeorgette RepunteNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument8 pagesHACCPKaye NicolasNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point 1Document12 pagesHazard Analysis Critical Control Point 1Francis BigualNo ratings yet
- Haccp PPP - 2Document14 pagesHaccp PPP - 2solivan_051704No ratings yet
- Approaches To Safe Meat F 8754301Document23 pagesApproaches To Safe Meat F 8754301adminNo ratings yet
- Haccp: The HACCP Seven PrinciplesDocument1 pageHaccp: The HACCP Seven PrinciplesAnonymous LJ9JdSBKHNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument61 pagesHACCPAbd-alruhman HossnyNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument21 pagesHACCPNur Athirah Muhamad SobriNo ratings yet
- GMP HaccpDocument43 pagesGMP HaccpMohammad Ashraf PaulNo ratings yet
- Difference Between HACCP and GMPDocument27 pagesDifference Between HACCP and GMPqtryst71% (7)
- Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points PrinciplesDocument1 pageHazard Analysis of Critical Control Points PrinciplesAsandaNo ratings yet
- Effective microbiological sampling of food processing environments (1999)From EverandEffective microbiological sampling of food processing environments (1999)No ratings yet
- Supplemental Slides For Module 1Document7 pagesSupplemental Slides For Module 1guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 UtilitiesDocument29 pagesModule 3.1 Utilitiesguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument12 pagesRoot Cause Analysisguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Week8 - Earth's Lithosphere - Phil RA 9003Document23 pagesWeek8 - Earth's Lithosphere - Phil RA 9003guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Ferment 3Document14 pagesFerment 3guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 QMSDocument23 pagesModule 2 QMSguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Human Security and Refugee RightsDocument1 pageHuman Security and Refugee Rightsguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Ferment 2Document15 pagesFerment 2guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document45 pagesLesson 7guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Feminist EthicsDocument17 pagesFeminist Ethicsguzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document30 pagesLesson 5guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document19 pagesLesson 4guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 MT1Document11 pagesChapter 9 MT1guzman.regina.lauriaNo ratings yet
- Tabel Perbedaan ISO 45001 Dan OHSAS 18001Document5 pagesTabel Perbedaan ISO 45001 Dan OHSAS 18001sudarno20No ratings yet
- A Mobile and Android-Based Application For Local Disaster Risk Reduction and MonitoringDocument6 pagesA Mobile and Android-Based Application For Local Disaster Risk Reduction and MonitoringInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/22Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/22Sameera MNo ratings yet
- 01 Incident - Accident Investigation ReportDocument2 pages01 Incident - Accident Investigation ReportSasi KssNo ratings yet
- City of Portland Complaint FinalDocument39 pagesCity of Portland Complaint FinalNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- 5-Risk Assessment Methods For Vapour-Cloud ExplosionsDocument10 pages5-Risk Assessment Methods For Vapour-Cloud ExplosionsNojus DekerisNo ratings yet
- 9 Hazard Identification Risk AssessmentDocument10 pages9 Hazard Identification Risk Assessmentvasanth pugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- Demobilization and Demolition Activies of Porta Cabins and Containers For Laydown AreaDocument10 pagesDemobilization and Demolition Activies of Porta Cabins and Containers For Laydown AreaNasrullahNo ratings yet
- Part V (C) - Risk Management - JSA & SOP (Day 2)Document22 pagesPart V (C) - Risk Management - JSA & SOP (Day 2)kwong siongNo ratings yet
- Fire Hazard PowerpointDocument19 pagesFire Hazard PowerpointDahlia Mi Villanueva100% (4)
- Lesson 4: Practice Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresDocument16 pagesLesson 4: Practice Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresAl Brelzhiv SarsalejoNo ratings yet
- Chemical SafetyDocument4 pagesChemical Safetyarfredbileg08No ratings yet
- TSA-017 - Lifting Using Split BoxDocument2 pagesTSA-017 - Lifting Using Split BoxMusadiq HussainNo ratings yet
- Manual: Movifit FC - Function Level "Technology" With PROFINET IO InterfaceDocument36 pagesManual: Movifit FC - Function Level "Technology" With PROFINET IO InterfaceJhonnie Rosete LuquezNo ratings yet
- A 14-Step Strategy of HACCP System Implementation in Snack Food ManufacturingDocument13 pagesA 14-Step Strategy of HACCP System Implementation in Snack Food Manufacturinganishor87No ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Hazards and The Risk of Thermal Runaway PDFDocument6 pagesChemical Reaction Hazards and The Risk of Thermal Runaway PDFGuz UchihaNo ratings yet
- Role of Donor Agencies in Disaster Management: International Journal of Multidisciplinary Education and ResearchDocument5 pagesRole of Donor Agencies in Disaster Management: International Journal of Multidisciplinary Education and ResearchYathiraj YathirajNo ratings yet
- Cahilap Aj MacroDocument5 pagesCahilap Aj Macrosamu hayesNo ratings yet
- Induction Furnace Hazard RegisterDocument3 pagesInduction Furnace Hazard RegisterVALENTINE T NHOPINo ratings yet
- DRRR Week 2 Module 1Document11 pagesDRRR Week 2 Module 1Jacob Tabula67% (3)
- Derelict Hospital 1 - Denburgh Insane Asylum - Online Location ScoutDocument2 pagesDerelict Hospital 1 - Denburgh Insane Asylum - Online Location ScoutsimsoawesomeNo ratings yet
- Basic Occup0ational Safety and HealthDocument93 pagesBasic Occup0ational Safety and HealthGabriel Galiza100% (1)
- TIS0002908.001 en-US-PV-351-SOP-CRI-PTZ CameraDocument24 pagesTIS0002908.001 en-US-PV-351-SOP-CRI-PTZ CameraPedro DebiaNo ratings yet
- B96280ABDocument158 pagesB96280ABMunya BengezaNo ratings yet
- HACCP Plan For Aluminum Foil LidsDocument2 pagesHACCP Plan For Aluminum Foil LidsRao WaqarNo ratings yet
- TR-Electronics Front-Of-Line Operation NC IIDocument71 pagesTR-Electronics Front-Of-Line Operation NC IIAmhier MokamadNo ratings yet
- Hazard PayDocument14 pagesHazard PayMark BuendiaNo ratings yet
- PSF Proponent HandbookDocument52 pagesPSF Proponent HandbookCarlo BernardoNo ratings yet