Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsConstitution of India 1
Constitution of India 1
Uploaded by
pratapsinghashutosh12The constitution of India is the supreme law of the country. It was adopted by the constituent assembly on November 26, 1949 and came into effect on January 26, 1950. The constitution establishes the framework of the government, outlines the fundamental rights of citizens and the directive principles. It is divided into 22 parts that describe the different branches of government and their powers and duties. Key aspects that are covered include fundamental rights like equality, freedom of religion and speech, and fundamental duties of citizens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Life - Pre - Intermediate - Student - S - Book - Second 1 PDFDocument195 pagesLife - Pre - Intermediate - Student - S - Book - Second 1 PDFJavier BrezigarNo ratings yet
- Canada Packers - Exhibits + Valuation - FionaDocument63 pagesCanada Packers - Exhibits + Valuation - Fiona/jncjdncjdn100% (1)
- Quiz On Economic GlobalizationDocument2 pagesQuiz On Economic GlobalizationKc SevillaNo ratings yet
- Because of An Acorn Teacher GuideDocument7 pagesBecause of An Acorn Teacher GuideChronicleBooksNo ratings yet
- Important Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74Document8 pagesImportant Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74MohanNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument70 pagesConstitutionakshay100% (1)
- COI - Reference PointersDocument177 pagesCOI - Reference Pointersshahidshaikh9936No ratings yet
- Parts Articles and Schedules - GS POL - 15.7.21Document51 pagesParts Articles and Schedules - GS POL - 15.7.21AlokNo ratings yet
- Articles in The Indian ConstitutionDocument12 pagesArticles in The Indian Constitutiontapasranjanbiswal123No ratings yet
- Imp Articles, Parts & ScheduleDocument7 pagesImp Articles, Parts & ScheduleAkash PatelNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution 2020 47e939c5Document12 pagesIndian Constitution 2020 47e939c5KriNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesParts of The Indian Constitutionserryserry362No ratings yet
- ArticleDocument7 pagesArticleshivankur sharmaNo ratings yet
- NTSE Sheet 3 PDFDocument8 pagesNTSE Sheet 3 PDFVed bukhariyaNo ratings yet
- Points ConstitutionDocument6 pagesPoints Constitutionchoosypandit81No ratings yet
- Indian Constitution - Parts, Fundamental Rights and SchedulesDocument5 pagesIndian Constitution - Parts, Fundamental Rights and SchedulesShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument6 pagesIndian ConstitutionKavalla Bhimarao67% (3)
- Parts of Indian ConstitutionDocument1 pageParts of Indian Constitutionvishalbeniwal1712No ratings yet
- eBOOK 22091914205956Document42 pageseBOOK 22091914205956Kuwar NikhilNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution .Document18 pagesIndian Constitution .kiranbarki63No ratings yet
- 1702739581Document86 pages1702739581Aasif ProchaNo ratings yet
- Must Know Articles of Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesMust Know Articles of Indian Constitutionnur mdNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument1 pageConstitution of IndiaDeva GnanamNo ratings yet
- Bbaa2d9b D1da 4f8b 9eea 54cad7ca97ef GKMaterialDocument2 pagesBbaa2d9b D1da 4f8b 9eea 54cad7ca97ef GKMaterialHarsh SaravatNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity NotesDocument31 pagesIndian Polity NotesPremNo ratings yet
- Parts and Important Articles of The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesParts and Important Articles of The Constitutioncoolsumitan100% (1)
- Rts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument6 pagesRts of The Indian ConstitutionshreenathNo ratings yet
- INDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)Document6 pagesINDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)workprofile440No ratings yet
- Parts Subject Matter Articles Covered I II III IV Iv-A VDocument10 pagesParts Subject Matter Articles Covered I II III IV Iv-A Vrakesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Hands OutDocument9 pagesIndian Polity Hands OutRitwik PatraNo ratings yet
- National Commission For Scheduled Tribes: Why in News?Document3 pagesNational Commission For Scheduled Tribes: Why in News?gitalel223No ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Parts Vs Corresponding ArticlesDocument3 pagesIndian Constitution Parts Vs Corresponding ArticlesTharun CloudNo ratings yet
- CITIZENSHIPDocument2 pagesCITIZENSHIPAakrati gargNo ratings yet
- Parts of Indian ConstitutionDocument2 pagesParts of Indian Constitutionjharbifno0% (1)
- Important Articles of Indian Constitution, Complete ListDocument12 pagesImportant Articles of Indian Constitution, Complete ListJacob JrNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument44 pagesConstitution of Indiasoumya612No ratings yet
- TestDocument5 pagesTestGolden GlobeNo ratings yet
- Weekely Assignment Test 3Document6 pagesWeekely Assignment Test 3anjaliNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights (Q)Document60 pagesFundamental Rights (Q)AnshuNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Fundamental RightsDocument10 pagesMCQ On Fundamental RightsDebkanta DasNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument13 pagesIndian ConstitutionUjjwal VermaNo ratings yet
- Important Articles of The Constitution of India in PDFDocument8 pagesImportant Articles of The Constitution of India in PDFYashasvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Parts of ConstitutionDocument4 pagesParts of ConstitutionFake MailNo ratings yet
- Part B 1. About India-C-EDocument39 pagesPart B 1. About India-C-ESaYani SamaDdarNo ratings yet
- IMP Articles of Indian ConstitutionDocument8 pagesIMP Articles of Indian ConstitutionNandita NanditaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law II - ContentDocument13 pagesConstitutional Law II - ContentKrishan TewaryNo ratings yet
- MCQ 12Document4 pagesMCQ 12Ripin KhannaNo ratings yet
- Fundamendal LawDocument12 pagesFundamendal Lawsmart prabhuNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Pakistan: PreambleDocument7 pagesConstitution of Pakistan: Preamblejawad hanifNo ratings yet
- c7afa36089584986f45498d3142f1845Document6 pagesc7afa36089584986f45498d3142f1845balasonu745No ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument9 pagesArticlespankajpankaj18112002No ratings yet
- Fundamental RightsDocument2 pagesFundamental RightsSamar PathaniaNo ratings yet
- 663cb536d904f4001885e970 ## Higher Education 08 D 240511 002406Document27 pages663cb536d904f4001885e970 ## Higher Education 08 D 240511 002406gautam kumarNo ratings yet
- Wbcs 2019 Mains Indian Polity (Paper - V) Answer Key: Academic AssociationDocument10 pagesWbcs 2019 Mains Indian Polity (Paper - V) Answer Key: Academic AssociationLiton GhoshNo ratings yet
- Uttarakhand Judicial Service 2013Document38 pagesUttarakhand Judicial Service 2013n2167475No ratings yet
- Articles India ConstitutionDocument3 pagesArticles India ConstitutionYash KumbleNo ratings yet
- POLITY 1.0 by Abhas SainiDocument39 pagesPOLITY 1.0 by Abhas SainiKeshav BhartiNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument134 pagesConstitution of IndiarajdeeppawarNo ratings yet
- List of Important Articles of The Constitution of India - GK Notes PDF!Document12 pagesList of Important Articles of The Constitution of India - GK Notes PDF!Akash BhowalNo ratings yet
- NnnppppaaaaDocument33 pagesNnnppppaaaayashuyash33No ratings yet
- Polity Most Important QuestionDocument9 pagesPolity Most Important QuestionAryan kumar KeshariNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs Merged PDFDocument157 pagesCurrent Affairs Merged PDFabesh sinhaNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- American Architecture by Omoge Oluwole TemitopeDocument36 pagesAmerican Architecture by Omoge Oluwole TemitopeOmoge Oluwole TemitopeNo ratings yet
- 2017 Contamination of Coliform Bacteria in Water and Fishery Resources in Manila Bay Aquaculture FarmsDocument30 pages2017 Contamination of Coliform Bacteria in Water and Fishery Resources in Manila Bay Aquaculture FarmsIsabelNo ratings yet
- Establishing The Agile PMO PDFDocument6 pagesEstablishing The Agile PMO PDFA ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Martin Intertextuality - An IntroductionDocument5 pagesMartin Intertextuality - An IntroductionEkru0% (1)
- Trigonometric Substitution PDFDocument7 pagesTrigonometric Substitution PDFStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- SNC Supplier Collaboration at PepsiCoDocument23 pagesSNC Supplier Collaboration at PepsiCopraty888No ratings yet
- DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved For Public Release Distribution Is UnlimitedDocument189 pagesDISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved For Public Release Distribution Is UnlimitedStein Hjalmar Hansen100% (1)
- Southeast Texas GivesDocument16 pagesSoutheast Texas GivesbeaumontenterpriseNo ratings yet
- Autism HandoutDocument2 pagesAutism Handoutapi-300851874100% (1)
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Case PresentationDocument52 pagesOsteogenesis Imperfecta: Case PresentationEricka B. Banaszczuk100% (3)
- "Can I Touch It?" Playbill, Company One TheatreDocument15 pages"Can I Touch It?" Playbill, Company One TheatretylerprendergastNo ratings yet
- Torts FinalsDocument15 pagesTorts FinalsRon AceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Greek LiteratureDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Greek LiteratureMuneeb Jan7802509No ratings yet
- Project Proposal For AetaDocument3 pagesProject Proposal For AetaZander Aaron CorpusNo ratings yet
- LS2 - Science - SG01 (V3.2)Document27 pagesLS2 - Science - SG01 (V3.2)als midsayap1No ratings yet
- Daftar Obat IcuDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat Icuendang puji lestariningsih100% (1)
- Woldia University - 3 Year Cs Section 1 Group 5Document85 pagesWoldia University - 3 Year Cs Section 1 Group 5Yitayal GebruNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesSummative Test 2nd QuarterHenry Canon LumangtadNo ratings yet
- Quiz in MapehDocument1 pageQuiz in MapehCathy PartidasNo ratings yet
- United States v. Andrew Jones, JR., 952 F.2d 397, 4th Cir. (1991)Document2 pagesUnited States v. Andrew Jones, JR., 952 F.2d 397, 4th Cir. (1991)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Portable EMG Data Acquisition Module For Upper Limb Prosthesis ApplicationDocument8 pagesPortable EMG Data Acquisition Module For Upper Limb Prosthesis ApplicationHoàng ThắngNo ratings yet
- Mendoza Vs IACDocument2 pagesMendoza Vs IACDarrell Magsambol100% (1)
- Course Outline Conversational/journal Style. Ateneo Law Journal UP Law Journal Harvard Law Journal Proposal: Amendment of Compensation LawDocument6 pagesCourse Outline Conversational/journal Style. Ateneo Law Journal UP Law Journal Harvard Law Journal Proposal: Amendment of Compensation LawJosef GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Arts 7 Q3testDocument3 pagesArts 7 Q3testMary GraceNo ratings yet
- Prist University: Question BankDocument4 pagesPrist University: Question BankGanesan NkNo ratings yet
- Tan 2020 - School Leadership Meta-AnalysisDocument22 pagesTan 2020 - School Leadership Meta-AnalysisGustavo MoreiraNo ratings yet
Constitution of India 1
Constitution of India 1
Uploaded by
pratapsinghashutosh120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views7 pagesThe constitution of India is the supreme law of the country. It was adopted by the constituent assembly on November 26, 1949 and came into effect on January 26, 1950. The constitution establishes the framework of the government, outlines the fundamental rights of citizens and the directive principles. It is divided into 22 parts that describe the different branches of government and their powers and duties. Key aspects that are covered include fundamental rights like equality, freedom of religion and speech, and fundamental duties of citizens.
Original Description:
My creations are very beautiful
Original Title
constitution of india 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe constitution of India is the supreme law of the country. It was adopted by the constituent assembly on November 26, 1949 and came into effect on January 26, 1950. The constitution establishes the framework of the government, outlines the fundamental rights of citizens and the directive principles. It is divided into 22 parts that describe the different branches of government and their powers and duties. Key aspects that are covered include fundamental rights like equality, freedom of religion and speech, and fundamental duties of citizens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views7 pagesConstitution of India 1
Constitution of India 1
Uploaded by
pratapsinghashutosh12The constitution of India is the supreme law of the country. It was adopted by the constituent assembly on November 26, 1949 and came into effect on January 26, 1950. The constitution establishes the framework of the government, outlines the fundamental rights of citizens and the directive principles. It is divided into 22 parts that describe the different branches of government and their powers and duties. Key aspects that are covered include fundamental rights like equality, freedom of religion and speech, and fundamental duties of citizens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
constitution of india
What is the constitution of India ?
The constitution of India is the supreme law of India
The document lays down the framework
demarcates fundamental political code ,structure,
procedures , powers and duties of government
institutions and sets out fundamental rights ,
directive principles and the duties of citizens
When it was adopted and become effective?
Constitution was adopted by the
constituent of assembly of India on
26 November 1949 and become
effective on 26 January 1950
What are the parts of the Indian
constitution ?
The parts of the Indian constitution are :-
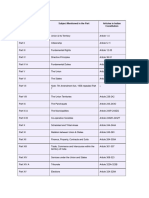
Part Subject Article
(1) The Union and its territory Article 1 to 4
(2) Citizenship Article 5 to 11
(3) Fundamental Rights Article 12 to 35
(4) Directive Principles Article 36 to 51
(4a) Fundamental Duties Article 51 A
(5) The Union Article 52 to 151
(6) The States Article 152 to 237
(7) Repealed by constitution (7th Amendment) Act ,1956
(8) The Union Territories Article 239 to 242
(9) The Panchayats Article 243 to 243O
(9a) The Municipalities Article 243P to 243ZG
(9b) Co-operative Societies Article 243H to 243ZT
(10) The Scheduled and Tribal Areas Article 244 to 244A
(11) Relation Between the Union and the States Article 245 to 263
(12) Finance, Property, Contracts and Suits Article 264 to 300A
(13) Trade, Commerce and Intercourse within the Territory of India Article 301 to 307
(14) Services under the Union and the states Article 308 to 323
(14A) Tribunals Article 323A to 323B
(15) Elections Article 324 to 329A
(16) Special provisions relation to certain classes Article 330 to 342
(17) Official Language Article 343 to
351
(18) Emergency Provision Article 352 to
360
(19) Miscellaneous Article 361 to 367
(20) Amendment of the Constitution Article 368
(21) Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions Article 369 to 392
(22) Short title, commencement , Article 393 to 395
authoritative text in Hindi and repeals
Fundamental Rights
What is fundamental Right ?
Fundamental Rights are the group of rights that have been recognized by a
high degree of protection from encroachment These rights are specifically
identified in a constitution , or have been found under due process of law
What are the Fundamental rights ?
Fundamental rights in India are the rights guaranteed under
Part 3 (Article 12- 35 ) of the Constitution of India
There six Fundamental Rights of the constitution are:-
(1) The Right to Equality (Articles 14-18)
(2) The Right to Freedom (Articles 19-20)
(3) The Right against Exploitation (Articles 23-24)
(4) The Right to Freedom of Religion (Articles 25-28)
(5) Cultural and Education Rights (Articles 29-30)
(6) The Right to Constitutional Remedies ( Article 32 and 226)
Fundamental Duties
What is fundamental duties ?
Duties basically imply moral obligation of all citizens of a country, there
are 11 fundamental duties in India which are written in Part 4A of the
Constitution , to promote patriotism and strengthen the unity of India
What are the fundamental duties ?
The 11 fundamental duties are :-
(1)Abide by the Constitution and respect (8) Develop scientific
national flag and national anthem temper
(2)Follow ideals of the freedom struggle (9) Safeguard public
(3)Protect sovereignty and integrity of India property
(4)Defend the country and render national (10) Strive for excellence
services when called upon (11) Duty for all parents /
(5)Spirit of common brotherhood guardians to send their
(6)Preserve composite culture children in the age group
(7)Preserve natural environment of 6-14 years to school
You might also like
- Life - Pre - Intermediate - Student - S - Book - Second 1 PDFDocument195 pagesLife - Pre - Intermediate - Student - S - Book - Second 1 PDFJavier BrezigarNo ratings yet
- Canada Packers - Exhibits + Valuation - FionaDocument63 pagesCanada Packers - Exhibits + Valuation - Fiona/jncjdncjdn100% (1)
- Quiz On Economic GlobalizationDocument2 pagesQuiz On Economic GlobalizationKc SevillaNo ratings yet
- Because of An Acorn Teacher GuideDocument7 pagesBecause of An Acorn Teacher GuideChronicleBooksNo ratings yet
- Important Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74Document8 pagesImportant Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74MohanNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument70 pagesConstitutionakshay100% (1)
- COI - Reference PointersDocument177 pagesCOI - Reference Pointersshahidshaikh9936No ratings yet
- Parts Articles and Schedules - GS POL - 15.7.21Document51 pagesParts Articles and Schedules - GS POL - 15.7.21AlokNo ratings yet
- Articles in The Indian ConstitutionDocument12 pagesArticles in The Indian Constitutiontapasranjanbiswal123No ratings yet
- Imp Articles, Parts & ScheduleDocument7 pagesImp Articles, Parts & ScheduleAkash PatelNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution 2020 47e939c5Document12 pagesIndian Constitution 2020 47e939c5KriNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesParts of The Indian Constitutionserryserry362No ratings yet
- ArticleDocument7 pagesArticleshivankur sharmaNo ratings yet
- NTSE Sheet 3 PDFDocument8 pagesNTSE Sheet 3 PDFVed bukhariyaNo ratings yet
- Points ConstitutionDocument6 pagesPoints Constitutionchoosypandit81No ratings yet
- Indian Constitution - Parts, Fundamental Rights and SchedulesDocument5 pagesIndian Constitution - Parts, Fundamental Rights and SchedulesShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument6 pagesIndian ConstitutionKavalla Bhimarao67% (3)
- Parts of Indian ConstitutionDocument1 pageParts of Indian Constitutionvishalbeniwal1712No ratings yet
- eBOOK 22091914205956Document42 pageseBOOK 22091914205956Kuwar NikhilNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution .Document18 pagesIndian Constitution .kiranbarki63No ratings yet
- 1702739581Document86 pages1702739581Aasif ProchaNo ratings yet
- Must Know Articles of Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesMust Know Articles of Indian Constitutionnur mdNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument1 pageConstitution of IndiaDeva GnanamNo ratings yet
- Bbaa2d9b D1da 4f8b 9eea 54cad7ca97ef GKMaterialDocument2 pagesBbaa2d9b D1da 4f8b 9eea 54cad7ca97ef GKMaterialHarsh SaravatNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity NotesDocument31 pagesIndian Polity NotesPremNo ratings yet
- Parts and Important Articles of The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesParts and Important Articles of The Constitutioncoolsumitan100% (1)
- Rts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument6 pagesRts of The Indian ConstitutionshreenathNo ratings yet
- INDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)Document6 pagesINDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)workprofile440No ratings yet
- Parts Subject Matter Articles Covered I II III IV Iv-A VDocument10 pagesParts Subject Matter Articles Covered I II III IV Iv-A Vrakesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Hands OutDocument9 pagesIndian Polity Hands OutRitwik PatraNo ratings yet
- National Commission For Scheduled Tribes: Why in News?Document3 pagesNational Commission For Scheduled Tribes: Why in News?gitalel223No ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Parts Vs Corresponding ArticlesDocument3 pagesIndian Constitution Parts Vs Corresponding ArticlesTharun CloudNo ratings yet
- CITIZENSHIPDocument2 pagesCITIZENSHIPAakrati gargNo ratings yet
- Parts of Indian ConstitutionDocument2 pagesParts of Indian Constitutionjharbifno0% (1)
- Important Articles of Indian Constitution, Complete ListDocument12 pagesImportant Articles of Indian Constitution, Complete ListJacob JrNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument44 pagesConstitution of Indiasoumya612No ratings yet
- TestDocument5 pagesTestGolden GlobeNo ratings yet
- Weekely Assignment Test 3Document6 pagesWeekely Assignment Test 3anjaliNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights (Q)Document60 pagesFundamental Rights (Q)AnshuNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Fundamental RightsDocument10 pagesMCQ On Fundamental RightsDebkanta DasNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument13 pagesIndian ConstitutionUjjwal VermaNo ratings yet
- Important Articles of The Constitution of India in PDFDocument8 pagesImportant Articles of The Constitution of India in PDFYashasvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Parts of ConstitutionDocument4 pagesParts of ConstitutionFake MailNo ratings yet
- Part B 1. About India-C-EDocument39 pagesPart B 1. About India-C-ESaYani SamaDdarNo ratings yet
- IMP Articles of Indian ConstitutionDocument8 pagesIMP Articles of Indian ConstitutionNandita NanditaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law II - ContentDocument13 pagesConstitutional Law II - ContentKrishan TewaryNo ratings yet
- MCQ 12Document4 pagesMCQ 12Ripin KhannaNo ratings yet
- Fundamendal LawDocument12 pagesFundamendal Lawsmart prabhuNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Pakistan: PreambleDocument7 pagesConstitution of Pakistan: Preamblejawad hanifNo ratings yet
- c7afa36089584986f45498d3142f1845Document6 pagesc7afa36089584986f45498d3142f1845balasonu745No ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument9 pagesArticlespankajpankaj18112002No ratings yet
- Fundamental RightsDocument2 pagesFundamental RightsSamar PathaniaNo ratings yet
- 663cb536d904f4001885e970 ## Higher Education 08 D 240511 002406Document27 pages663cb536d904f4001885e970 ## Higher Education 08 D 240511 002406gautam kumarNo ratings yet
- Wbcs 2019 Mains Indian Polity (Paper - V) Answer Key: Academic AssociationDocument10 pagesWbcs 2019 Mains Indian Polity (Paper - V) Answer Key: Academic AssociationLiton GhoshNo ratings yet
- Uttarakhand Judicial Service 2013Document38 pagesUttarakhand Judicial Service 2013n2167475No ratings yet
- Articles India ConstitutionDocument3 pagesArticles India ConstitutionYash KumbleNo ratings yet
- POLITY 1.0 by Abhas SainiDocument39 pagesPOLITY 1.0 by Abhas SainiKeshav BhartiNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument134 pagesConstitution of IndiarajdeeppawarNo ratings yet
- List of Important Articles of The Constitution of India - GK Notes PDF!Document12 pagesList of Important Articles of The Constitution of India - GK Notes PDF!Akash BhowalNo ratings yet
- NnnppppaaaaDocument33 pagesNnnppppaaaayashuyash33No ratings yet
- Polity Most Important QuestionDocument9 pagesPolity Most Important QuestionAryan kumar KeshariNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs Merged PDFDocument157 pagesCurrent Affairs Merged PDFabesh sinhaNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- American Architecture by Omoge Oluwole TemitopeDocument36 pagesAmerican Architecture by Omoge Oluwole TemitopeOmoge Oluwole TemitopeNo ratings yet
- 2017 Contamination of Coliform Bacteria in Water and Fishery Resources in Manila Bay Aquaculture FarmsDocument30 pages2017 Contamination of Coliform Bacteria in Water and Fishery Resources in Manila Bay Aquaculture FarmsIsabelNo ratings yet
- Establishing The Agile PMO PDFDocument6 pagesEstablishing The Agile PMO PDFA ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Martin Intertextuality - An IntroductionDocument5 pagesMartin Intertextuality - An IntroductionEkru0% (1)
- Trigonometric Substitution PDFDocument7 pagesTrigonometric Substitution PDFStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- SNC Supplier Collaboration at PepsiCoDocument23 pagesSNC Supplier Collaboration at PepsiCopraty888No ratings yet
- DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved For Public Release Distribution Is UnlimitedDocument189 pagesDISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved For Public Release Distribution Is UnlimitedStein Hjalmar Hansen100% (1)
- Southeast Texas GivesDocument16 pagesSoutheast Texas GivesbeaumontenterpriseNo ratings yet
- Autism HandoutDocument2 pagesAutism Handoutapi-300851874100% (1)
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Case PresentationDocument52 pagesOsteogenesis Imperfecta: Case PresentationEricka B. Banaszczuk100% (3)
- "Can I Touch It?" Playbill, Company One TheatreDocument15 pages"Can I Touch It?" Playbill, Company One TheatretylerprendergastNo ratings yet
- Torts FinalsDocument15 pagesTorts FinalsRon AceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Greek LiteratureDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Greek LiteratureMuneeb Jan7802509No ratings yet
- Project Proposal For AetaDocument3 pagesProject Proposal For AetaZander Aaron CorpusNo ratings yet
- LS2 - Science - SG01 (V3.2)Document27 pagesLS2 - Science - SG01 (V3.2)als midsayap1No ratings yet
- Daftar Obat IcuDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat Icuendang puji lestariningsih100% (1)
- Woldia University - 3 Year Cs Section 1 Group 5Document85 pagesWoldia University - 3 Year Cs Section 1 Group 5Yitayal GebruNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesSummative Test 2nd QuarterHenry Canon LumangtadNo ratings yet
- Quiz in MapehDocument1 pageQuiz in MapehCathy PartidasNo ratings yet
- United States v. Andrew Jones, JR., 952 F.2d 397, 4th Cir. (1991)Document2 pagesUnited States v. Andrew Jones, JR., 952 F.2d 397, 4th Cir. (1991)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Portable EMG Data Acquisition Module For Upper Limb Prosthesis ApplicationDocument8 pagesPortable EMG Data Acquisition Module For Upper Limb Prosthesis ApplicationHoàng ThắngNo ratings yet
- Mendoza Vs IACDocument2 pagesMendoza Vs IACDarrell Magsambol100% (1)
- Course Outline Conversational/journal Style. Ateneo Law Journal UP Law Journal Harvard Law Journal Proposal: Amendment of Compensation LawDocument6 pagesCourse Outline Conversational/journal Style. Ateneo Law Journal UP Law Journal Harvard Law Journal Proposal: Amendment of Compensation LawJosef GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Arts 7 Q3testDocument3 pagesArts 7 Q3testMary GraceNo ratings yet
- Prist University: Question BankDocument4 pagesPrist University: Question BankGanesan NkNo ratings yet
- Tan 2020 - School Leadership Meta-AnalysisDocument22 pagesTan 2020 - School Leadership Meta-AnalysisGustavo MoreiraNo ratings yet