Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Tenses
English Tenses
Uploaded by
Nnoor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views30 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views30 pagesEnglish Tenses
English Tenses
Uploaded by
NnoorCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 30
Tenses are the form taken by a verb to show
the time of an action or the state of an
event.
There are three
tenses : The Present
Tense
The Past Tense
The Future
Tense.
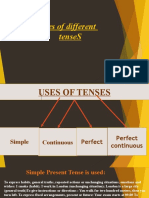
Each of the three tenses has four forms or sub-
divisions to show continuity or completeness
of the action and time. These are :
1. Indefinite
2. Continuous or Imperfect
3. Perfect
4. Perfect Continuous
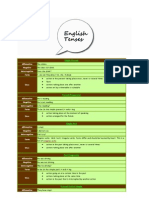
Table Of English
Tense
s
Tense Indefinite Continuo Perfect Perfect
us Continuo
us
Present Play (s) Is / Am / Are Has / Has / Have
Playing Have been Playing
Playe
d
Past Played Was / Were Had Had been
Playing Playe Playing
d
Future Will / Shall Will / Shall Will / Will / Shall
Play be Playing Shall have been
o The Indefinite Tense does not indicate whether
the action is complete or not.
o The Continuous (Imperfect) Tense that the action
is still going on.
o The Perfect Tense indicates that the action
is complete , finished or perfect.
o The Perfect Continuous Tense indicates that
the action began in the past and is still
continuing.
Subject + Verb1 + Object
Expresses a general truth or an action that
is occurring now
Eg : The sun rises from the east.
Expresses an action that occurs regularly
or habitually
Eg : She goes to the school regularly.
Affirmative Sentences : They play.
Negative Sentences : They do not play.
Interrogative Sentences : Do they play ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Do they not
play ?
Subject + Is/Am/Are + V1 + ing +
Object.
The present continuous tense is
used to express an action which
is happening at a particular time
in the present or extending over
a period of present time.
Affirmative Sentences : You are playing.
Negative Sentences : You are not playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Are you playing ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Are you not
playing ?
Subject + has/have + V3 + Object.
Has -> Singular , Have -> Plural.
The present perfect tense denotes an action
that was started in the past and has just
been completed.
Affirmative Sentences : I have played.
Negative Sentences : I have not played.
Interrogative Sentences : Have I played ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Have I not
played ?
Subject + has/have + been + V1 + ing + Object
The present perfect tense is used when an
action that started in the past is still
continuing.
Affirmative Sentences : We have been playing.
Negative Sentences : We have not been playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Have we been
playing
?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Have we not
been playing ?
Subject + V2 +
Object.
The simple past tense is used for an action
which happened at a particular time in the
past.
Affirmative Sentences : I played.
Negative Sentences : I did not play.
Interrogative Sentences : Did I play ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Did I not
played ?
Subject + was/were + V1 + ing + Object.
The past continuous tense is used for an action
which was happening at a particular time in
the past.
Affirmative Sentences : Boys were playing.
Negative Sentences : Boys were not playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Were boys
playing ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Were boys
not playing ?
Subject + had + V3 + Object.
The past perfect tense is used to express an
action that was completed before another
action started in the past. It is used with the
earlier of the two actions. The simple past
tense is used with the other action.
Affirmative Sentences : Sheila had played.
Negative Sentences : Sheila had not played.
Interrogative Sentences : Had Sheila played?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Had Sheila
not played ?
Subject + had + been + V1 + Object.
The past perfect continuous tense is used for an
action that began before a certain point in the
past and continued up to that point.
Affirmative Sentences : Ria had been playing.
Negative Sentences : Ria had not been playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Had Ria been playing?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Had Ria not been
playing ?
Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object.
The simple future tense is used for an action
that will take place at particular time in the
future.
Affirmative Sentences : Ravi will play.
Negative Sentences : Ravi will not play.
Interrogative Sentences : Will Ravi play ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Will Ravi not
play ?
Subject + will/shall + be +V1 + ing + Object
The future continuous tense is used to express
an action which will be in progress at a
particular time in the future.
Affirmative sentences : I will be playing.
Negative sentences : I will not be playing.
Interrogative sentences : Shall I be playing?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Shall I
not be playing?
Subject + shall/will + have + V3 + Object.
Future perfect tense is used to indicate the
completion of an action by a certain period
of time in the future.
Affirmative Sentences : She will have played.
Negative Sentences : She will not have played.
Interrogative Sentences : Will she have played?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Will she not
have played?
Subject + shall/will +have been + V1 +
ing + Object.
The future perfect tense is used when an action
is to continue up to a certain point of time in
the future.
Affirmative Sentences : Raj will have been
playing.
Negative Sentences : Raj will not have been
playing.
Interrogative Sentences : Will Raj have been
playing ?
Negative Interrogative Sentences : Will Raj not
have been playing ?
You might also like
- Swahili TensesDocument3 pagesSwahili TensesMartyneJohn100% (6)
- 12 Tenses in English GrammarDocument14 pages12 Tenses in English Grammargilgal kidsNo ratings yet
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- French Awesome WordsDocument109 pagesFrench Awesome WordsEn OvNo ratings yet
- Guía de Tiempos Verbales en InglésDocument4 pagesGuía de Tiempos Verbales en InglésMarianela LeonardelliNo ratings yet
- Identify The Transition Words PDFDocument2 pagesIdentify The Transition Words PDFMohamed OuladNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Explanation ExercisesDocument36 pagesPresent Simple Explanation ExercisesRafael Ramon Bastidas Bastidas100% (1)
- Tenses 130625073753 Phpapp01Document30 pagesTenses 130625073753 Phpapp01Syed Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument29 pagesTensesAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Tenses 130625073753 Phpapp01Document32 pagesTenses 130625073753 Phpapp01Khairil HidayahNo ratings yet
- Simple TensesDocument10 pagesSimple TensesDanae GallegoNo ratings yet
- Ge PresentationDocument17 pagesGe Presentationsaniya072202No ratings yet
- On TenseDocument42 pagesOn TenseSUNIL DWIVEDINo ratings yet
- Tenses Basics VKDocument19 pagesTenses Basics VKVinayak VKNo ratings yet
- Tenses 1Document25 pagesTenses 1godevil752No ratings yet
- InglesDocument20 pagesInglesJesús RamsésNo ratings yet
- PastDocument7 pagesPastDIEGO ixcotNo ratings yet
- I Saw A Great Film Yesterday. (Simple Past: S+ V2+O) 2. I Have Seen A Great Film Yesterday. (Present Perfect: S+has/have+V3+O)Document5 pagesI Saw A Great Film Yesterday. (Simple Past: S+ V2+O) 2. I Have Seen A Great Film Yesterday. (Present Perfect: S+has/have+V3+O)krishnasri ghantasala145No ratings yet
- 16 TensesDocument10 pages16 TensesOscariza AristyasNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Yet-Already-JustDocument40 pagesPresent Perfect Yet-Already-JustSantiagoCaisaguanoNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesAffirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentyvbamuNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument29 pagesVerb TensesMa. Fatima DorotanNo ratings yet
- Makalah 16 TensesDocument17 pagesMakalah 16 TensesMuhammad HairullahNo ratings yet
- English GrammerDocument14 pagesEnglish GrammerDino DinoNo ratings yet
- Uses of TensesDocument17 pagesUses of TensesMsPushpanjali PatilNo ratings yet
- Meeting 8Document13 pagesMeeting 8Fitri DelitaNo ratings yet
- Manual Lizbeth H FDocument18 pagesManual Lizbeth H Fapi-239674320No ratings yet
- Group 4purposive CommunicationDocument19 pagesGroup 4purposive Communicationbmiranda.stiNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Written ReportDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Written ReportPRECIOUS KAYE MARIE BANTIGUENo ratings yet
- Future Perfect and Future Perfect Progressive by Audina Dewi IrmayantiDocument9 pagesFuture Perfect and Future Perfect Progressive by Audina Dewi IrmayantiAudina DewiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument9 pagesPresent Perfect TenseDost JanNo ratings yet
- BinggDocument16 pagesBinggDiandra EmanuellaNo ratings yet
- Gramática InglesaDocument17 pagesGramática InglesaMaria GarciaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous: Janna Fabré 2022/2023 3rDDocument9 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous: Janna Fabré 2022/2023 3rDdani.seguranyesNo ratings yet
- Present Tense: Happens Regularly in The PresentDocument3 pagesPresent Tense: Happens Regularly in The PresentNuviettaNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesAffirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentIvana PlenčaNo ratings yet
- Past ContinousDocument5 pagesPast Continousramizeed30No ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple - Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3Document5 pagesPresent Perfect Simple - Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3Igor NircaNo ratings yet
- 12 Tenses in EnglishDocument5 pages12 Tenses in EnglishEvelin CastroNo ratings yet
- How Many Tenses Are There in EnglishDocument9 pagesHow Many Tenses Are There in EnglishSusarla SuryaNo ratings yet
- Tenses Notes DocumentDocument16 pagesTenses Notes DocumentA BhavyaNo ratings yet
- The Future ContinuousDocument6 pagesThe Future ContinuousAndre AndrianNo ratings yet
- Active N Passive NewDocument6 pagesActive N Passive Newsangay.dekiNo ratings yet
- English Tenses TableDocument2 pagesEnglish Tenses TablevashsauNo ratings yet
- Tiempos VerbalesDocument6 pagesTiempos VerbalesTeresa MiNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument64 pagesTensesJumani AcademyNo ratings yet
- Escola de Línguas: RefrescamentoDocument41 pagesEscola de Línguas: RefrescamentocristtianoNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument36 pagesTensesyadavraj55607No ratings yet
- Unit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Document14 pagesUnit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Johana CamposNo ratings yet
- Exceptions in Spelling: Affirmative NegativeDocument6 pagesExceptions in Spelling: Affirmative NegativeEnGiNo ratings yet
- Novita TobingDocument15 pagesNovita TobingJesen ANo ratings yet
- Day5 Present Continuous TenseDocument30 pagesDay5 Present Continuous TenseM.Nawaz SharifNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument25 pagesTensesFAN OF RGVNo ratings yet
- ¿Cuándo Usar La Voz Activa?Document8 pages¿Cuándo Usar La Voz Activa?Paloma LasavickasNo ratings yet
- 4 - Verb TensesDocument24 pages4 - Verb TensesJemie CortilloNo ratings yet
- Materi B InggrisDocument4 pagesMateri B InggrisariNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument18 pagesVerb TensesRayyanNo ratings yet
- Abilities and Present Cont. LessonDocument11 pagesAbilities and Present Cont. LessonSilviaJerez96No ratings yet
- TensesDocument25 pagesTensesAfzan Kahloon100% (1)
- Review of English TensesDocument8 pagesReview of English TensesSyifaa' NajibNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VioceDocument27 pagesActive and Passive VioceRida RidaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3 StudentsDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3 StudentsDIEGO ALEJANDRO HERNANDEZ LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous and Past ContinuousDocument15 pagesPresent Continuous and Past ContinuousMiss KikiNo ratings yet
- Inglês 10ºanoDocument5 pagesInglês 10ºanoDANIELA TEIXEIRANo ratings yet
- Wepik The Psychology of Superstitions Exploring The Science Behind Beliefs 20240522132814qXRvDocument14 pagesWepik The Psychology of Superstitions Exploring The Science Behind Beliefs 20240522132814qXRvNnoorNo ratings yet
- Expository WritingDocument48 pagesExpository WritingNnoorNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Object Oriented Programming - Fall 23 - 14 LabsDocument139 pagesLab Manual - Object Oriented Programming - Fall 23 - 14 LabsNnoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7-Week7 - Single Public and Private Inheritance-Constructor ChainingDocument32 pagesLecture 7-Week7 - Single Public and Private Inheritance-Constructor ChainingNnoorNo ratings yet
- CHAP 4 LearningDocument52 pagesCHAP 4 LearningNnoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Decision MakingDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Decision MakingNnoorNo ratings yet
- PersonalityDocument20 pagesPersonalityNnoorNo ratings yet
- PersonalityDocument11 pagesPersonalityNnoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Week3 - Access Specifier, Constructor, DestructorDocument27 pagesLecture 3-Week3 - Access Specifier, Constructor, DestructorNnoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 0-Week1Document16 pagesLecture 0-Week1NnoorNo ratings yet
- Intro To Psychology - CH #2Document15 pagesIntro To Psychology - CH #2NnoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Week2 - OOP, Data Member, Function, ConstDocument38 pagesLecture 2-Week2 - OOP, Data Member, Function, ConstNnoorNo ratings yet
- CH # 3 Sensation - PerceptionDocument21 pagesCH # 3 Sensation - PerceptionNnoorNo ratings yet
- Reading Strategies of Good ReadersDocument37 pagesReading Strategies of Good ReadersNnoorNo ratings yet
- Assigment Calculus LaibaDocument1 pageAssigment Calculus LaibaNnoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 15 Applied VersionDocument32 pagesLecture No 15 Applied VersionNnoorNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Identification ExercisesDocument1 pageParts of Speech Identification ExercisesNnoorNo ratings yet
- Error Spotting R Ules - PDF: LethedoitDocument9 pagesError Spotting R Ules - PDF: LethedoitUmanNo ratings yet
- Irregular Simple Past and Past Participle Verb Forms From MyEnglishTeacherDocument4 pagesIrregular Simple Past and Past Participle Verb Forms From MyEnglishTeacherJose Luis ValladaresNo ratings yet
- (Studies in Natural Language and Linguistic Theory) William D. Davies, Stanley Dubinsky - New Horizons in The Analysis of Control and Raising - Springer (2007) PDFDocument347 pages(Studies in Natural Language and Linguistic Theory) William D. Davies, Stanley Dubinsky - New Horizons in The Analysis of Control and Raising - Springer (2007) PDFHammouddou ElhoucineNo ratings yet
- Kisi Kisi Bahasa Inggris Wajib Kelas 11Document4 pagesKisi Kisi Bahasa Inggris Wajib Kelas 11Shofia NafisahNo ratings yet
- PRACTISE WITH KEYS - Present Continuous Tense: Eat Play Have Paint Sleep WaitDocument4 pagesPRACTISE WITH KEYS - Present Continuous Tense: Eat Play Have Paint Sleep WaitBulti CostantiniNo ratings yet
- NANDADEEP VIDYALAY1 1st 50Document7 pagesNANDADEEP VIDYALAY1 1st 50saniyaNo ratings yet
- Declinaciones GriegoDocument197 pagesDeclinaciones GriegoISAIASCASTRONo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5Huỳnh Trọng KimNo ratings yet
- Syntactical ElementsDocument21 pagesSyntactical ElementsAngeline Limbaga TrayfalgarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 9 Quarter 4 Active and Passive VOiceDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in English 9 Quarter 4 Active and Passive VOiceChristel Ann EscalaNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument17 pagesPurposive CommunicationPauloNo ratings yet
- Finite and Non FiniteDocument7 pagesFinite and Non FiniteAsha SyamnafshifaNo ratings yet
- The Renaissance, 1500-1650 (Article 177-183)Document3 pagesThe Renaissance, 1500-1650 (Article 177-183)abdullahsiddiqui686No ratings yet
- 3a. Context Free GrammarDocument18 pages3a. Context Free GrammarRhymeNo ratings yet
- Relationships Ups and DownsDocument2 pagesRelationships Ups and DownsYarenNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan of Possessive and Reflexive PronounsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan of Possessive and Reflexive PronounsNarcisa DeveraNo ratings yet
- Morphology: Marvin D. NacionalesDocument57 pagesMorphology: Marvin D. NacionalesCicero Ferreira100% (1)
- Quantifiers For Countable NounsDocument3 pagesQuantifiers For Countable NounsCharity VenusNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense (Daily Activity) : by Yessi, S.PD SMKN 2 Arga MakmurDocument12 pagesSimple Present Tense (Daily Activity) : by Yessi, S.PD SMKN 2 Arga MakmurSupriyanto Slamet100% (1)
- Action Verbs WDWZMDocument4 pagesAction Verbs WDWZMZaki FikriNo ratings yet
- All Modal VerbsDocument8 pagesAll Modal VerbsIonut TomaNo ratings yet
- Arabic SrSec 2023-24Document4 pagesArabic SrSec 2023-24Reema ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- ELA Syllabus Grade 2Document19 pagesELA Syllabus Grade 2Farzam GarshasbiNo ratings yet
- Sample Script NursingDocument28 pagesSample Script NursinghusnainjumiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Legal WritingDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Legal WritingAlyssa Mari Reyes67% (3)
- Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in EnglishAdonis CusipagNo ratings yet