Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsImmunopathology - Lecture 6. Tolerance Autoimmunity Pathogenesis of AI Diseases
Immunopathology - Lecture 6. Tolerance Autoimmunity Pathogenesis of AI Diseases
Uploaded by
pmm21d229This document provides an overview of immunological tolerance, autoimmunity, and autoimmune diseases. It discusses how tolerance develops through the destruction, inactivation, or change of self-aggressive lymphocyte clones. Loss of self-tolerance can lead to autoimmune diseases, which are classified based on the localization of autoantigens and can have different pathways of tissue damage. Genetic and environmental factors like infections can increase risk of autoimmune diseases by impacting tolerance. Autoantibodies also play a role in diseases' pathogenesis and diagnostic importance. Therapies aim to treat infections, normalize immune overactivity, and reduce chronic inflammation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Kuby Immunology 7e TBDocument134 pagesKuby Immunology 7e TBStarrx71494% (18)
- CPG Hypertension PDFDocument77 pagesCPG Hypertension PDFvetina86% (7)
- Autoimmunity PDFDocument73 pagesAutoimmunity PDFErum JanNo ratings yet
- University College London: Module Code: Assessment: Pattern Module NameDocument6 pagesUniversity College London: Module Code: Assessment: Pattern Module NameASDNo ratings yet
- Test QuestionsDocument14 pagesTest QuestionsMohammad Usman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Amity Institute of BiotechnologyDocument44 pagesAmity Institute of BiotechnologyMilind SagarNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument70 pagesAutoimmune DiseasesAdebisi OluwatomiwaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune-Disorders PDF Divya Mam PracticalDocument44 pagesAutoimmune-Disorders PDF Divya Mam Practicaltariqahmeda34No ratings yet
- Autoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersDocument39 pagesAutoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersSireeshasenapathi Sireesha SenapathiNo ratings yet
- AutoimmunityDocument40 pagesAutoimmunityKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- Immunity, Autoimmunity - QsDocument5 pagesImmunity, Autoimmunity - QsMaedehNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of A Client With Immunological Disorders: M.N Priyadarshanie BSC in NursingDocument47 pagesNursing Management of A Client With Immunological Disorders: M.N Priyadarshanie BSC in NursingClarissa Cabudoc OronosNo ratings yet
- AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE NURSING CARE-19.05.2022-Prof. Nurs - 1Document58 pagesAUTOIMMUNE DISEASE NURSING CARE-19.05.2022-Prof. Nurs - 1Nanik AndianiNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity HMLS IV 2022Document42 pagesAutoimmunity HMLS IV 2022Blessed RazimosNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders - AgungDocument40 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - AgungalgutNo ratings yet
- Копия Autoimmunity-and-Autoimmune-disordersDocument38 pagesКопия Autoimmunity-and-Autoimmune-disordersManav VyasNo ratings yet
- 1-How Immune System Works1 08 08Document63 pages1-How Immune System Works1 08 08all4one1983100% (1)
- Immunologic Tolerance & AutoimmunityDocument42 pagesImmunologic Tolerance & AutoimmunityTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Immuno Lec 1&2&3Document33 pagesImmuno Lec 1&2&3Ali AlhamdaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of AutoimmunityDocument29 pagesMechanism of AutoimmunityMalliga SundareshanNo ratings yet
- AutoimmunityDocument29 pagesAutoimmunitywissam salimNo ratings yet
- Understanding Autoimmune Disease PDFDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Autoimmune Disease PDFLiz TaylorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27: Hypersensitivity Reactions: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLesson 27: Hypersensitivity Reactions: Learning Objectives99manu99No ratings yet
- What Is An Autoimmune DiseaseDocument7 pagesWhat Is An Autoimmune DiseaseBISHOP MBILINo ratings yet
- Lect.12 - Immunologic and Endocrine Alterations in ChildrenDocument61 pagesLect.12 - Immunologic and Endocrine Alterations in ChildrenlouradelNo ratings yet
- Immunopathology Lec 4Document11 pagesImmunopathology Lec 4zaharNo ratings yet
- Notes On Auto ImmunityDocument6 pagesNotes On Auto ImmunitydeansAMVNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity 2022Document22 pagesAutoimmunity 2022Raphael AnajeNo ratings yet
- Autoimun MekanismeDocument22 pagesAutoimun MekanismeMeity ElvinaNo ratings yet
- Auto ImmunityDocument38 pagesAuto ImmunityMau studioNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of AutoimmunityDocument22 pagesMechanisms of Autoimmunitybudi darmantaNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument29 pagesImmunologyMaryam KhanNo ratings yet
- Paper Topics For ImmunologyDocument4 pagesPaper Topics For ImmunologyLouise Veronica JoseNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease - : Immune DeficienciesDocument34 pagesAutoimmune Disease - : Immune Deficienciesahana roy100% (1)
- Auto ImmunityDocument23 pagesAuto Immunitymuneera salimNo ratings yet
- Antigen AntibodiesDocument65 pagesAntigen AntibodiespradeepbawaneNo ratings yet
- AutoinmunidadDocument21 pagesAutoinmunidadRobert Caballero BardalesNo ratings yet
- From Relatively Benign Disease To Rapidly Progressive and EvenDocument2 pagesFrom Relatively Benign Disease To Rapidly Progressive and Evendiaa skamNo ratings yet
- antigensDocument36 pagesantigensManali PatelNo ratings yet
- Auto ImmunityDocument44 pagesAuto ImmunityA. PathakNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument19 pagesImmunityKailash Nagar100% (1)
- Autoimmunity: Jamie SturgillDocument43 pagesAutoimmunity: Jamie SturgillSeptiyani Monalisa AndriNo ratings yet
- Immunology in Infectious Disease: Titin Andri Wihastuti Psik FkubDocument29 pagesImmunology in Infectious Disease: Titin Andri Wihastuti Psik Fkubminnie_ranger4763No ratings yet
- Immunological Factors in Disease-) - AutoimmunityDocument49 pagesImmunological Factors in Disease-) - AutoimmunityDr anas AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 1lec. 02 ReactivityDocument65 pages1lec. 02 ReactivityFrt TrfNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument4 pagesAutoimmune Diseasesnizam syedNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease MechanismsDocument6 pagesAutoimmune Disease MechanismsHaliunaa BattulgaNo ratings yet
- L24 AutoimmDocument35 pagesL24 AutoimmFadli FadelNo ratings yet
- Suzy Maria: PositionDocument36 pagesSuzy Maria: PositionBintang FortunaNo ratings yet
- Immune DisordersDocument8 pagesImmune Disordersattiarph23No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemTurinawe Bin ByensiNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseaseDocument38 pagesAutoimmune DiseaseGustiandari FidhyaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Immune Function: Nurs 304: Adult Nursing LECTURER: Ms. MackeyDocument103 pagesAssessment of Immune Function: Nurs 304: Adult Nursing LECTURER: Ms. MackeyEstherThompsonNo ratings yet
- Zee's Autoimmunity, Basic Concept and ExamplesDocument2 pagesZee's Autoimmunity, Basic Concept and ExamplesjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersDocument46 pagesAutoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersJennifer EvansNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease: Duhok Polytechnic University Duhok Technical Institute Department of PharmacyDocument17 pagesAutoimmune Disease: Duhok Polytechnic University Duhok Technical Institute Department of PharmacyRasheed AliNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders - MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - MicrobiologyAll in oneNo ratings yet
- Discipline: B. Tech (Biotech) Module: BT 501 IV Semester: VDocument6 pagesDiscipline: B. Tech (Biotech) Module: BT 501 IV Semester: VsauravsarkarNo ratings yet
- Auto Immune Disorder 2016Document38 pagesAuto Immune Disorder 2016vistaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument21 pagesAutoimmune Diseases85robertNo ratings yet
- Document 22Document3 pagesDocument 22nicolasdanica018No ratings yet
- Activity 14 Understanding Immune SystemDocument20 pagesActivity 14 Understanding Immune SystemKendrix Aguiluz FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Healing, Transform Your Health, Reduce Inflammation, Heal The Immune System and Start Living HealthyFrom EverandAutoimmune Healing, Transform Your Health, Reduce Inflammation, Heal The Immune System and Start Living HealthyNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Gastrointestinal Allergic DisordersDocument13 pagesMechanisms of Gastrointestinal Allergic DisordersjordanbertoneNo ratings yet
- Food Allergies and Food IntolerancesDocument17 pagesFood Allergies and Food IntolerancesFy DaisyNo ratings yet
- Tolerance and Autoimmunity-NEJMDocument10 pagesTolerance and Autoimmunity-NEJMAsep HrNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12: Leukocyte Development Kinetics, and FunctionsDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 12: Leukocyte Development Kinetics, and FunctionsPrimo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Toxicology of Fishes 2Nd Edition Kristine L Willett Neelakanteswar Aluru Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesToxicology of Fishes 2Nd Edition Kristine L Willett Neelakanteswar Aluru Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFdernicelow433100% (6)
- VMC 221 Coursematerials PDFDocument61 pagesVMC 221 Coursematerials PDFavenger 2100% (1)
- Patho Immune System PathologyDocument7 pagesPatho Immune System PathologyCoy Nuñez100% (1)
- KMU 04 Blood and Immunology-II ModuleDocument23 pagesKMU 04 Blood and Immunology-II ModuleNau MaanNo ratings yet
- ASH Understaning On AlloimmunizationDocument6 pagesASH Understaning On AlloimmunizationM Asif NaveedNo ratings yet
- The Role of Genetic Risk Factors in PathogenesisDocument22 pagesThe Role of Genetic Risk Factors in PathogenesisVasincu AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Disease: NephrologyDocument16 pagesPathogenesis of Autoimmune Disease: NephrologyHector PonsNo ratings yet
- JEM Immunity-and-Cancer Special Issue PDFDocument74 pagesJEM Immunity-and-Cancer Special Issue PDFCici21No ratings yet
- Probiotics in Primary Prevention of Atopic Disease: A Randomised Placebo-Controlled TrialDocument4 pagesProbiotics in Primary Prevention of Atopic Disease: A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trialarguskao100% (1)
- Zbook Kuby Immunology 8th Edition by 632c9fDocument55 pagesZbook Kuby Immunology 8th Edition by 632c9fpaulabhijeet2000No ratings yet
- Tolerance: Chapter 20 - Regulation of Adaptive ImmunityDocument4 pagesTolerance: Chapter 20 - Regulation of Adaptive ImmunityZoe Alea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Immunological ToleranceDocument33 pagesChapter Immunological TolerancemkmicroduNo ratings yet
- Immunology For Medical StudentsDocument12 pagesImmunology For Medical StudentsZorce AleksovskaNo ratings yet
- Lymphocyte DevelopmentDocument48 pagesLymphocyte DevelopmentAgourram Taieb100% (2)
- MBBS Assignment PDFDocument9 pagesMBBS Assignment PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Physiology ImmunityDocument75 pagesPhysiology Immunitymohani maiyaNo ratings yet
- Mucosal Adjuvants: Charles O. Elson Mark T. DertzbaughDocument1 pageMucosal Adjuvants: Charles O. Elson Mark T. DertzbaughPortobello CadısıNo ratings yet
- Cellular and Molecular Immunology 10Th Edition Abul K Abbas Full ChapterDocument67 pagesCellular and Molecular Immunology 10Th Edition Abul K Abbas Full Chaptermarlene.harder13583% (6)
- Edible VaccinesDocument10 pagesEdible VaccinesOscar N.No ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseaseDocument38 pagesAutoimmune DiseaseGustiandari FidhyaNo ratings yet
- Kuby5 20 AutoImmunity PDFDocument19 pagesKuby5 20 AutoImmunity PDFASDASDDD2No ratings yet
- My Gut ImmunityDocument11 pagesMy Gut ImmunityGabriela LusiNo ratings yet
Immunopathology - Lecture 6. Tolerance Autoimmunity Pathogenesis of AI Diseases
Immunopathology - Lecture 6. Tolerance Autoimmunity Pathogenesis of AI Diseases
Uploaded by
pmm21d2290 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views45 pagesThis document provides an overview of immunological tolerance, autoimmunity, and autoimmune diseases. It discusses how tolerance develops through the destruction, inactivation, or change of self-aggressive lymphocyte clones. Loss of self-tolerance can lead to autoimmune diseases, which are classified based on the localization of autoantigens and can have different pathways of tissue damage. Genetic and environmental factors like infections can increase risk of autoimmune diseases by impacting tolerance. Autoantibodies also play a role in diseases' pathogenesis and diagnostic importance. Therapies aim to treat infections, normalize immune overactivity, and reduce chronic inflammation.
Original Description:
Original Title
Immunopathology_Lecture-6.-Tolerance-autoimmunity-Pathogenesis-of-AI-diseases
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of immunological tolerance, autoimmunity, and autoimmune diseases. It discusses how tolerance develops through the destruction, inactivation, or change of self-aggressive lymphocyte clones. Loss of self-tolerance can lead to autoimmune diseases, which are classified based on the localization of autoantigens and can have different pathways of tissue damage. Genetic and environmental factors like infections can increase risk of autoimmune diseases by impacting tolerance. Autoantibodies also play a role in diseases' pathogenesis and diagnostic importance. Therapies aim to treat infections, normalize immune overactivity, and reduce chronic inflammation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views45 pagesImmunopathology - Lecture 6. Tolerance Autoimmunity Pathogenesis of AI Diseases
Immunopathology - Lecture 6. Tolerance Autoimmunity Pathogenesis of AI Diseases
Uploaded by
pmm21d229This document provides an overview of immunological tolerance, autoimmunity, and autoimmune diseases. It discusses how tolerance develops through the destruction, inactivation, or change of self-aggressive lymphocyte clones. Loss of self-tolerance can lead to autoimmune diseases, which are classified based on the localization of autoantigens and can have different pathways of tissue damage. Genetic and environmental factors like infections can increase risk of autoimmune diseases by impacting tolerance. Autoantibodies also play a role in diseases' pathogenesis and diagnostic importance. Therapies aim to treat infections, normalize immune overactivity, and reduce chronic inflammation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 45
School of Biomedicine
Department of Immunology
Immunopathology: Immunological tolerance
and autoimmunity, autoimmune diseases
professor Tsogtsaikhan Sandag
Content
• Introduction to immunological tolerance
• Introduction to autoimmunity and autoimmune
diseases
• Autoantibody
Introduction to immunological tolerance
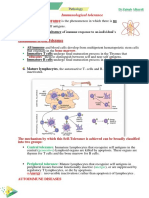
Immunological tolerance is an active state of
unresponsiveness the immune system to an antigen against
which a response has previously developed
• The development of this condition is due to the event that the
lymphocytes responsible for the immune response against this
antigen either lost the ability to activate, or were removed from
the body
• Antigens cause the tolerance called “tolerogens” or
“tolerogenic antigens”
• Tolerance to the self-antigens is the principle property of the
immune system.
• Loss of self-tolerance is the cause of autoimmune diseases
Introduction to immunological tolerance
• Self-tolerance is associated with specific lymphocytes
and:
– Immunological tolerance will develop when self-aggressive
lymphocyte clones 1/ destroyed; 2/ inactivated; 3/changed their
specificity
– Immunological tolerance is antigen-specific state, or tolerance is
specific only for given antigen
– Immunological tolerance may be developed in central (central
tolerance) or in peripheral (peripheral tolerance) organs of the
immune system
Development
of the
self-tolerance
Central tolerance
Central tolerance
Peripheral tolerance
Peripheral
tolerance
Peripheral tolerance
B cell central tolerance
B cell peripheral tolerance
Introduction to autoimmune diseases
• Autoimmune disease classified by the
localization/spread of autoantigens and divided into:
– Systemic /organ non-specific/
– Organ-specific diseases
• AI diseases have a different pathways for the tissue
damage
• AI have a chronic, progressive and self supporting
(epitope
spread) course
Conditions for
development
of AI diseases
(postulates)
Conditions for
development of AI
diseases
(genetic susceptibility,
HLA phenotype)
Conditions for development of AI diseases (HLA
phenotype & gender)
Conditions for development of AI diseases (gender)
Conditions for development of AI diseases (genetic susceptibility,
family predisposition)
Conditions for development of AI diseases
(genetic susceptibility)
Conditions for
development of AI
diseases
(genetic
susceptibility, non-
HLA genes)
Conditions for development of AI diseases (infection)
Conditions for development of AI diseases (infection)
AI diseases (epitope spread)
Pathogenesis of AI diseases
(signal stimulating or blocking autoantibodies)
AI diseases (autoantibodies transfer across the placenta)
AI diseases (Autoimmune thyroiditis, stimulating
autoantibodies)
AI diseases
(Autoimmune thyroiditis, stimulating autoantibodies)
AI diseases
(Autoimmune thyroiditis, stimulating autoantibodies)
AI diseases
(Myasthenia gravis, blocking autoantibodies)
AI diseases
(Goodpasture syndrome,
cross-reacting autoantibodies)
AI diseases
(Uveitis posterior, cross-reacting autoantibodies)
AI diseases
(Uveitis posterior, cross-reacting autoantibodies)
AI diseases (glomerulonephritis)
AI diseases
(gluten-sensitive enteropathy)
AI diseases (autoimmune hepatitis)
AI diseases (primary biliary cirrhosis)
AI diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus - SLE)
AI diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus - SLE)
AI diseases (Type I diabetes)
AI diseases (Type I diabetes)
AI diseases (multiple sclerosis, model of experimental
autoimmune encephalitis-EAE)
AI diseases
(multiple
sclerosis, model
of experimental
autoimmune
encephalitis-EAE)
AI diseases
(diagnostic
importance of
serum
autoantibodies)
Principles of autoimmune diseases therapy
1. First attack of many autoimmune diseases is associated with
infections, especially viral infection. Involvement of infectious agents
in development of autoimmune diseases have a evidence in many
cases, however it is hypothetic for some diseases. Anyway treatment
of infection and eradication of persistent infection foci is important.
2. Disorder of immune function is principle factor for development
and exacerbation of disease. Intervention directed to normalize over
activity of immune effectory function is rational part of the therapy
3. Important pathogenesis component of AI diseases determining a
clinical course of the disease is chronic inflammation. Anti-
inflammatory therapy is also rational part of the therapy.
Thank you
You might also like
- Kuby Immunology 7e TBDocument134 pagesKuby Immunology 7e TBStarrx71494% (18)
- CPG Hypertension PDFDocument77 pagesCPG Hypertension PDFvetina86% (7)
- Autoimmunity PDFDocument73 pagesAutoimmunity PDFErum JanNo ratings yet
- University College London: Module Code: Assessment: Pattern Module NameDocument6 pagesUniversity College London: Module Code: Assessment: Pattern Module NameASDNo ratings yet
- Test QuestionsDocument14 pagesTest QuestionsMohammad Usman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Amity Institute of BiotechnologyDocument44 pagesAmity Institute of BiotechnologyMilind SagarNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument70 pagesAutoimmune DiseasesAdebisi OluwatomiwaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune-Disorders PDF Divya Mam PracticalDocument44 pagesAutoimmune-Disorders PDF Divya Mam Practicaltariqahmeda34No ratings yet
- Autoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersDocument39 pagesAutoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersSireeshasenapathi Sireesha SenapathiNo ratings yet
- AutoimmunityDocument40 pagesAutoimmunityKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- Immunity, Autoimmunity - QsDocument5 pagesImmunity, Autoimmunity - QsMaedehNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of A Client With Immunological Disorders: M.N Priyadarshanie BSC in NursingDocument47 pagesNursing Management of A Client With Immunological Disorders: M.N Priyadarshanie BSC in NursingClarissa Cabudoc OronosNo ratings yet
- AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE NURSING CARE-19.05.2022-Prof. Nurs - 1Document58 pagesAUTOIMMUNE DISEASE NURSING CARE-19.05.2022-Prof. Nurs - 1Nanik AndianiNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity HMLS IV 2022Document42 pagesAutoimmunity HMLS IV 2022Blessed RazimosNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders - AgungDocument40 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - AgungalgutNo ratings yet
- Копия Autoimmunity-and-Autoimmune-disordersDocument38 pagesКопия Autoimmunity-and-Autoimmune-disordersManav VyasNo ratings yet
- 1-How Immune System Works1 08 08Document63 pages1-How Immune System Works1 08 08all4one1983100% (1)
- Immunologic Tolerance & AutoimmunityDocument42 pagesImmunologic Tolerance & AutoimmunityTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Immuno Lec 1&2&3Document33 pagesImmuno Lec 1&2&3Ali AlhamdaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of AutoimmunityDocument29 pagesMechanism of AutoimmunityMalliga SundareshanNo ratings yet
- AutoimmunityDocument29 pagesAutoimmunitywissam salimNo ratings yet
- Understanding Autoimmune Disease PDFDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Autoimmune Disease PDFLiz TaylorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27: Hypersensitivity Reactions: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLesson 27: Hypersensitivity Reactions: Learning Objectives99manu99No ratings yet
- What Is An Autoimmune DiseaseDocument7 pagesWhat Is An Autoimmune DiseaseBISHOP MBILINo ratings yet
- Lect.12 - Immunologic and Endocrine Alterations in ChildrenDocument61 pagesLect.12 - Immunologic and Endocrine Alterations in ChildrenlouradelNo ratings yet
- Immunopathology Lec 4Document11 pagesImmunopathology Lec 4zaharNo ratings yet
- Notes On Auto ImmunityDocument6 pagesNotes On Auto ImmunitydeansAMVNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity 2022Document22 pagesAutoimmunity 2022Raphael AnajeNo ratings yet
- Autoimun MekanismeDocument22 pagesAutoimun MekanismeMeity ElvinaNo ratings yet
- Auto ImmunityDocument38 pagesAuto ImmunityMau studioNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of AutoimmunityDocument22 pagesMechanisms of Autoimmunitybudi darmantaNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument29 pagesImmunologyMaryam KhanNo ratings yet
- Paper Topics For ImmunologyDocument4 pagesPaper Topics For ImmunologyLouise Veronica JoseNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease - : Immune DeficienciesDocument34 pagesAutoimmune Disease - : Immune Deficienciesahana roy100% (1)
- Auto ImmunityDocument23 pagesAuto Immunitymuneera salimNo ratings yet
- Antigen AntibodiesDocument65 pagesAntigen AntibodiespradeepbawaneNo ratings yet
- AutoinmunidadDocument21 pagesAutoinmunidadRobert Caballero BardalesNo ratings yet
- From Relatively Benign Disease To Rapidly Progressive and EvenDocument2 pagesFrom Relatively Benign Disease To Rapidly Progressive and Evendiaa skamNo ratings yet
- antigensDocument36 pagesantigensManali PatelNo ratings yet
- Auto ImmunityDocument44 pagesAuto ImmunityA. PathakNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument19 pagesImmunityKailash Nagar100% (1)
- Autoimmunity: Jamie SturgillDocument43 pagesAutoimmunity: Jamie SturgillSeptiyani Monalisa AndriNo ratings yet
- Immunology in Infectious Disease: Titin Andri Wihastuti Psik FkubDocument29 pagesImmunology in Infectious Disease: Titin Andri Wihastuti Psik Fkubminnie_ranger4763No ratings yet
- Immunological Factors in Disease-) - AutoimmunityDocument49 pagesImmunological Factors in Disease-) - AutoimmunityDr anas AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 1lec. 02 ReactivityDocument65 pages1lec. 02 ReactivityFrt TrfNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument4 pagesAutoimmune Diseasesnizam syedNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease MechanismsDocument6 pagesAutoimmune Disease MechanismsHaliunaa BattulgaNo ratings yet
- L24 AutoimmDocument35 pagesL24 AutoimmFadli FadelNo ratings yet
- Suzy Maria: PositionDocument36 pagesSuzy Maria: PositionBintang FortunaNo ratings yet
- Immune DisordersDocument8 pagesImmune Disordersattiarph23No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemTurinawe Bin ByensiNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseaseDocument38 pagesAutoimmune DiseaseGustiandari FidhyaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Immune Function: Nurs 304: Adult Nursing LECTURER: Ms. MackeyDocument103 pagesAssessment of Immune Function: Nurs 304: Adult Nursing LECTURER: Ms. MackeyEstherThompsonNo ratings yet
- Zee's Autoimmunity, Basic Concept and ExamplesDocument2 pagesZee's Autoimmunity, Basic Concept and ExamplesjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersDocument46 pagesAutoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersJennifer EvansNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease: Duhok Polytechnic University Duhok Technical Institute Department of PharmacyDocument17 pagesAutoimmune Disease: Duhok Polytechnic University Duhok Technical Institute Department of PharmacyRasheed AliNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders - MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - MicrobiologyAll in oneNo ratings yet
- Discipline: B. Tech (Biotech) Module: BT 501 IV Semester: VDocument6 pagesDiscipline: B. Tech (Biotech) Module: BT 501 IV Semester: VsauravsarkarNo ratings yet
- Auto Immune Disorder 2016Document38 pagesAuto Immune Disorder 2016vistaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument21 pagesAutoimmune Diseases85robertNo ratings yet
- Document 22Document3 pagesDocument 22nicolasdanica018No ratings yet
- Activity 14 Understanding Immune SystemDocument20 pagesActivity 14 Understanding Immune SystemKendrix Aguiluz FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Healing, Transform Your Health, Reduce Inflammation, Heal The Immune System and Start Living HealthyFrom EverandAutoimmune Healing, Transform Your Health, Reduce Inflammation, Heal The Immune System and Start Living HealthyNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Gastrointestinal Allergic DisordersDocument13 pagesMechanisms of Gastrointestinal Allergic DisordersjordanbertoneNo ratings yet
- Food Allergies and Food IntolerancesDocument17 pagesFood Allergies and Food IntolerancesFy DaisyNo ratings yet
- Tolerance and Autoimmunity-NEJMDocument10 pagesTolerance and Autoimmunity-NEJMAsep HrNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 12: Leukocyte Development Kinetics, and FunctionsDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 12: Leukocyte Development Kinetics, and FunctionsPrimo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Toxicology of Fishes 2Nd Edition Kristine L Willett Neelakanteswar Aluru Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesToxicology of Fishes 2Nd Edition Kristine L Willett Neelakanteswar Aluru Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFdernicelow433100% (6)
- VMC 221 Coursematerials PDFDocument61 pagesVMC 221 Coursematerials PDFavenger 2100% (1)
- Patho Immune System PathologyDocument7 pagesPatho Immune System PathologyCoy Nuñez100% (1)
- KMU 04 Blood and Immunology-II ModuleDocument23 pagesKMU 04 Blood and Immunology-II ModuleNau MaanNo ratings yet
- ASH Understaning On AlloimmunizationDocument6 pagesASH Understaning On AlloimmunizationM Asif NaveedNo ratings yet
- The Role of Genetic Risk Factors in PathogenesisDocument22 pagesThe Role of Genetic Risk Factors in PathogenesisVasincu AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Disease: NephrologyDocument16 pagesPathogenesis of Autoimmune Disease: NephrologyHector PonsNo ratings yet
- JEM Immunity-and-Cancer Special Issue PDFDocument74 pagesJEM Immunity-and-Cancer Special Issue PDFCici21No ratings yet
- Probiotics in Primary Prevention of Atopic Disease: A Randomised Placebo-Controlled TrialDocument4 pagesProbiotics in Primary Prevention of Atopic Disease: A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trialarguskao100% (1)
- Zbook Kuby Immunology 8th Edition by 632c9fDocument55 pagesZbook Kuby Immunology 8th Edition by 632c9fpaulabhijeet2000No ratings yet
- Tolerance: Chapter 20 - Regulation of Adaptive ImmunityDocument4 pagesTolerance: Chapter 20 - Regulation of Adaptive ImmunityZoe Alea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Immunological ToleranceDocument33 pagesChapter Immunological TolerancemkmicroduNo ratings yet
- Immunology For Medical StudentsDocument12 pagesImmunology For Medical StudentsZorce AleksovskaNo ratings yet
- Lymphocyte DevelopmentDocument48 pagesLymphocyte DevelopmentAgourram Taieb100% (2)
- MBBS Assignment PDFDocument9 pagesMBBS Assignment PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Physiology ImmunityDocument75 pagesPhysiology Immunitymohani maiyaNo ratings yet
- Mucosal Adjuvants: Charles O. Elson Mark T. DertzbaughDocument1 pageMucosal Adjuvants: Charles O. Elson Mark T. DertzbaughPortobello CadısıNo ratings yet
- Cellular and Molecular Immunology 10Th Edition Abul K Abbas Full ChapterDocument67 pagesCellular and Molecular Immunology 10Th Edition Abul K Abbas Full Chaptermarlene.harder13583% (6)
- Edible VaccinesDocument10 pagesEdible VaccinesOscar N.No ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseaseDocument38 pagesAutoimmune DiseaseGustiandari FidhyaNo ratings yet
- Kuby5 20 AutoImmunity PDFDocument19 pagesKuby5 20 AutoImmunity PDFASDASDDD2No ratings yet
- My Gut ImmunityDocument11 pagesMy Gut ImmunityGabriela LusiNo ratings yet