Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Investigational Drugs
Investigational Drugs
Uploaded by
IVORY DIANE AMANCIO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views34 pagesAn investigational new drug application (IND) must be filed with and approved by the FDA prior to administering an experimental drug to humans. An IND includes preclinical data, clinical trial protocols, and manufacturing information. The FDA has 30 days to review an IND and determine if clinical trials can proceed. Clinical trials involve 4 phases - Phase I evaluates safety, Phase II evaluates efficacy, Phase III involves large-scale trials to confirm efficacy and monitor safety, and Phase IV occurs after approval to further monitor long-term safety and efficacy. The goal of clinical trials is to generate sufficient data for a new drug application to the FDA to obtain marketing approval.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn investigational new drug application (IND) must be filed with and approved by the FDA prior to administering an experimental drug to humans. An IND includes preclinical data, clinical trial protocols, and manufacturing information. The FDA has 30 days to review an IND and determine if clinical trials can proceed. Clinical trials involve 4 phases - Phase I evaluates safety, Phase II evaluates efficacy, Phase III involves large-scale trials to confirm efficacy and monitor safety, and Phase IV occurs after approval to further monitor long-term safety and efficacy. The goal of clinical trials is to generate sufficient data for a new drug application to the FDA to obtain marketing approval.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views34 pagesInvestigational Drugs
Investigational Drugs
Uploaded by
IVORY DIANE AMANCIOAn investigational new drug application (IND) must be filed with and approved by the FDA prior to administering an experimental drug to humans. An IND includes preclinical data, clinical trial protocols, and manufacturing information. The FDA has 30 days to review an IND and determine if clinical trials can proceed. Clinical trials involve 4 phases - Phase I evaluates safety, Phase II evaluates efficacy, Phase III involves large-scale trials to confirm efficacy and monitor safety, and Phase IV occurs after approval to further monitor long-term safety and efficacy. The goal of clinical trials is to generate sufficient data for a new drug application to the FDA to obtain marketing approval.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 34
Investigational Drug
Presented by: Ivory Diane C. Amancio, RPh CPh
Investigational Drug
Investigational New Drug Application
- filed with FDA
- approved prior to administering new drug
products to humans
Components:
*Name of the inactive component
*Name and chemical description of the active
component
Investigational Drug
Components:
* name of the manufacturer
* method of preparation
* dosage form
* all preclinical data
* name and location of the investigators
Investigational Drug
Components:
* data from clinical trials conducted in other
countries
Within 30 days from receipt of IND, the FDA decides
if the proposed clinical trial should proceed.
The trial may proceed if the investigator is not
contacted within 30 days.
Investigational Drug
Reviews at the FDA may place a clinical hold
on the clinical trial at any time.
Reasons for placing an IND under clinical hold:
1.) Unreasonable or significant risk of illness or
injury to trial subjects.
2.) Insufficient information to assess patient risk
Investigational Drug
Reasons for placing an IND under clinical hold:
3. Inadequate qualification of the clinical
investigator
4. Misleading, erroneous or incomplete
investigator’s brochure (a document that contains
all relevant information about the drug.
Investigational Drug
No experimental agents may be
administered to patients for research in
the US without an IND.
It should be noted that not all clinical
trials require an IND.
Investigational Drug
A sponsor proposing a trial with a commercially
available, FDA-approved drug product is
exempted from IND requirements if:
1. It is not intended to be submitted to the FDA to
support labeling changes or a new indication.
2. It is not intended to support a major change in
advertising.
Investigational Drug
A sponsor proposing a trial with a commercially
available, FDA-approved drug product is
exempted from IND requirements if:
3. does not involve a route of administration,
dose, or patient population that significantly
increases the risk of the drug.
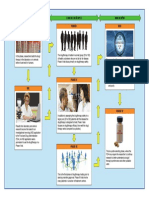
Clinical Investigation
The clinical investigation involves the
administration of a drug to humans.
4 phases of clinical trial:
PHASE I Clinical Trial
- is the assessment of the compound’s safety
- small # of generally healthy volunteers
(approximately 20-80 people)
Clinical Investigation
PHASE I Clinical Trial
For the investigation of drugs to treat life-
threatening diseases, such as cancer or AIDS,
patients afflicted with the disease may be
enrolled.
The starting dose is generally low, often 1/10 of
the highest no-effect dose in the animal models.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE I Clinical Trial
After the initial treatment is completed, additional
subjects may be recruited and administered
higher doses to determine the maximum dose
tolerated without significant side effects.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE I Clinical Trial
- preliminary ADME data of the parent drug and
all metabolites should be evaluated.
- data regarding pharmacokinetic and
pharmacologic effects are also obtained to be
used in designing future II trials.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE Il Clinical Trial
- - is the assessment of the compound’s efficacy
- a large # of people are enrolled
( 100-300 patients)
- participants suffer from the target illness
- side effects of the new drug are investigated
- failure during the trial is common
(as the human body is more complex than the test tube)
Clinical Investigation
PHASE Il Clinical Trial
At the end of phase II trials:
*The sponsors meet with the FDA to review the
acceptability of the past trials
*The FDA carefully review preclinical and clinical
data in evaluating proposed III protocols
Clinical Investigation
PHASE Il Clinical Trial
At the end of phase II trials:
*The FDA scrutinizes the proposed phase III trials
eg., dosing regimen
duration of treatment
blinding of the drug product
Clinical Investigation
PHASE Il Clinical Trial
At the end of phase II trials:
The overall goal of the meeting between the
sponsor and the FDA:
* Agreement regarding data required for
submission of a New Drug Application ( NDA )
-it is a document of hundreds of thousands of pages containing
highly detailed information
Clinical Investigation
PHASE Il Clinical Trial
At the end of phase II trials:
Before phase III trials, the final market
formulation for the drug product should be
optimized.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IlI Clinical Trial
The safety and efficacy of the new compound is monitored
Involves a large # of patients (1000-3000) who are afflicted
with the target illness
The longest and most comprehensive trial
Patients are recruited, tested, and monitored by several
major hospitals and clinics throughout the country
May be conducted internationally
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IlI Clinical Trial
the drug product may be compared to an existing
therapeutic regimen or a placebo
Compounds that complete Phase III testing have
a 95% chance of being approved by the FDA.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IlI Clinical Trial
Before the completion of the Phase III testing
and NDA submission, sponsors and FDA meet
again; to establish the appropriate format of the
submission so that the review proceeds smoothly
To determine if an additional animal or human
trials are necessary
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IlI Clinical Trial
Once the Phase III trials have been completed,
all preclinical and clinical data are compiled and
submitted to the FDA for review.
FDA reviews the proposed product
labeling and package insert.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IlI Clinical Trial
NDA review has been reduced from a median
of 22 months in 1992 to approximately 15
months in 2000.
The FDA may approve or disapprove the
drug product for market.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IlI Clinical Trial
Reasons for the disapproval by the FDA of the drug
product for the market:
lack of demonstrated safety and efficacy
issues with the manufacturing /processing
procedures
false/misleading labels
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IlI Clinical Trial
If NDA is not approved, a letter is sent to the
sponsor detailing deficiencies in the application.
If the NDA is approved, an approval letter
along with a draft of the product labeling is sent
to the sponsor.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IlI Clinical Trial
Before NDA approval, the FDA inspects the sponsor’s facilities
to ensure compliance with the cGMP.
If deficiencies are noted during the inspection, a letter is sent
to the sponsor delineating the problems.
Once the deficiencies are resolved, the company must provide
written certification and the FDA will clear the application
within 45 days.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IV Clinical Trial
post-approval clinical trial
Since the duration of exposure is often limited
during phase III testing, phase IV trials may be
required to assess long-term safety of the drug.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IV Clinical Trial
the FDA may mandate a phase IV trial in a specific
patient population to further assess efficacy and
side effects
- Companies may also choose to conduct
additional clinical tests to more fully understand
how their product compares to another
commercially available therapeutic regimen.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IV Clinical Trial
Post-approval activities:
after NDA has been granted, and marketing is
initiated, drug safety is still monitored
sponsors must submit reports of AEs
AEs reports are filed quarterly for the first three
years and then annually
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IV Clinical Trial
Post-approval activities:
For serious and unexpected AEs, ( eg., fatal, life-
threatening, permanent disabling, or requiring
prolonged hospitalization), the sponsor must
provide a written report to the FDA within 15
days of receipt of the information.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IV Clinical Trial
Post-approval activities:
Serious AEs may require minor labeling changes or
the addition of warning or precaution statements.
If serious safety concerns arise, the FDA may
withdraw approval of the NDA.
An FDA Advisory Committee reviews the NDA
before an official NDA withdrawal.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IV Clinical Trial
Post-approval activities:
The FDA MedWatch program encourages health-care
providers to directly report serious ADRs to the FDA.
( www.fda.gov/medwatch ).
The MedWatch program also provides to practitioners
regarding the actions and recommendations of the FDA.
Clinical Investigation
PHASE IV Clinical Trial
Post-approval activities:
In some instances, manufacturers have withdrawn drug
products before FDA action.
Periodic random inspections of drug production facilities
are conducted by the FDA to ensure conformance with
the cGMP.
Thank you
You might also like
- NSG 436 Analysis of A UDocument6 pagesNSG 436 Analysis of A Uapi-521018364No ratings yet
- REGULATORYDocument19 pagesREGULATORYsrishty100% (1)
- Pharmacoepidemiology, Pharmacoeconomics,PharmacovigilanceFrom EverandPharmacoepidemiology, Pharmacoeconomics,PharmacovigilanceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- An Overview of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)Document22 pagesAn Overview of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)Urlam Kumar71% (7)
- History of RH Law in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesHistory of RH Law in The PhilippinesAnonymous nYvtSgoQNo ratings yet
- Misha Regulatory AffairsDocument26 pagesMisha Regulatory AffairsGULSHAN MADHURNo ratings yet
- A Pre-Marketing ActivitiesDocument30 pagesA Pre-Marketing ActivitiesKaye DepabloNo ratings yet
- Schedule YDocument11 pagesSchedule YRamling Patrakar100% (1)
- IndndaandandaDocument46 pagesIndndaandandaPavani SriramNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Clinical TrialsDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To Clinical TrialsIrfan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Schedule YDocument55 pagesSchedule YshilpapillaiNo ratings yet
- Schedule y PPT EDITTED ONEDocument38 pagesSchedule y PPT EDITTED ONEKesetha100% (2)
- Drug Development: Development of A New Therapeutic Drug Is A and Process Costs Nearly and An Average ofDocument37 pagesDrug Development: Development of A New Therapeutic Drug Is A and Process Costs Nearly and An Average ofNim DCNo ratings yet
- Investigational New Drug Application (IND)Document48 pagesInvestigational New Drug Application (IND)Divya100% (1)
- Clinical TrialsDocument21 pagesClinical TrialsvishakhaNo ratings yet
- Schedule yDocument11 pagesSchedule ySiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- CRCP Lecture Reg Approvals Oct 2020Document65 pagesCRCP Lecture Reg Approvals Oct 2020EsEnGauharNo ratings yet
- Drug Development Process: Preclinical StageDocument4 pagesDrug Development Process: Preclinical Stagepeter mwangiNo ratings yet
- BT Sec Final Paper Answer Sem4Document3 pagesBT Sec Final Paper Answer Sem4Ankit AthreyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 8 Dr. Laiq (6.10.19) PDFDocument50 pagesLecture # 8 Dr. Laiq (6.10.19) PDFAbbas HassanNo ratings yet
- Ra Unit - 3Document25 pagesRa Unit - 304 Arunkumar.GNo ratings yet
- New Drug Application HardDocument37 pagesNew Drug Application HardGANESH KUMAR JELLA100% (1)
- Expanded Access Clinical TrialDocument134 pagesExpanded Access Clinical TrialsiddharthkamerkarNo ratings yet
- Single-double-phaseIV-drug ApprovalDocument3 pagesSingle-double-phaseIV-drug ApprovalRoma Ann ManahanNo ratings yet
- Investigational New Drug Application (IND)Document27 pagesInvestigational New Drug Application (IND)kavya nainitaNo ratings yet
- Investigational New Drug Application (INDA)Document25 pagesInvestigational New Drug Application (INDA)Mallikarjun MangapuramNo ratings yet
- Drug DevelopmentDocument33 pagesDrug Developmentapi-3750955No ratings yet
- INVESTIGATIONALNEWDRUGAPPLICATION INDAaaDocument32 pagesINVESTIGATIONALNEWDRUGAPPLICATION INDAaaHan XuNo ratings yet
- Bty459 CaDocument9 pagesBty459 Cavivekanand879355443612No ratings yet
- New Drug Application: Presented By: Amey DeshpandeDocument14 pagesNew Drug Application: Presented By: Amey Deshpandeamey_dpd100% (1)
- MPHR - 129 (Clinical Trial Managment)Document42 pagesMPHR - 129 (Clinical Trial Managment)Dr-Harikesh MauryaNo ratings yet
- The Drug Development ProcessDocument7 pagesThe Drug Development ProcessSACHIN BHASKAR NARKHEDE100% (1)
- WWW - Clinicaltrials.gov: Clinical Phase I-IIDocument2 pagesWWW - Clinicaltrials.gov: Clinical Phase I-IIhelmanadyaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PEDocument28 pagesModule 5 PEGauri GhuleNo ratings yet
- Unit2 Clinical-TrialsDocument12 pagesUnit2 Clinical-TrialsDevangNo ratings yet
- Clinical TrialDocument9 pagesClinical TrialAyanNo ratings yet
- Global Regulations in Clinical Trials by N.srinivas ICRIDocument62 pagesGlobal Regulations in Clinical Trials by N.srinivas ICRIravi9247No ratings yet
- Schedule YDocument54 pagesSchedule Yparminder.nain29No ratings yet
- Question: The Process of Approval and Stages in IndiaDocument3 pagesQuestion: The Process of Approval and Stages in Indiaamandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Drug DevelopmentDocument5 pagesDrug DevelopmentJessica GlitterNo ratings yet
- Topic 13 - Post Marketing SurveillanceDocument46 pagesTopic 13 - Post Marketing SurveillanceTerepe CrimsonNo ratings yet
- Drug DVLPMT StgsDocument18 pagesDrug DVLPMT Stgsvinay0717No ratings yet
- Drug Development Process Cleveland, 6.23.06Document65 pagesDrug Development Process Cleveland, 6.23.06Srinivasa Chary SriramadasuNo ratings yet
- Global Submission On IndDocument16 pagesGlobal Submission On IndRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Clinical Trails Phases - Clinical Research - Pharma DostDocument9 pages2.2 Clinical Trails Phases - Clinical Research - Pharma DostjhancyNo ratings yet
- Preclinical Research Clinical Research Nda Review Phase I NDA Basic Science ResearchDocument1 pagePreclinical Research Clinical Research Nda Review Phase I NDA Basic Science Researchgopi_dey8649No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument27 pagesProduct Life Cycle ManagementDeepanshu ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Investigational New Drug Application (IND)Document27 pagesInvestigational New Drug Application (IND)Pharmacology MnemonicsNo ratings yet
- Product Development and Technology Transfer Rushvi PatelDocument246 pagesProduct Development and Technology Transfer Rushvi Patelvidusha9727No ratings yet
- Latest Amendment in Schedule YDocument30 pagesLatest Amendment in Schedule Yapi-384271179% (19)
- Schedule YDocument30 pagesSchedule Yapi-3810976100% (13)
- GCP - Investigational New DrugsDocument14 pagesGCP - Investigational New DrugsRadio MiercolesNo ratings yet
- Schedule Y: Submitted BY Mr. Akshay A. Joshi Icbio BangaloreDocument32 pagesSchedule Y: Submitted BY Mr. Akshay A. Joshi Icbio BangaloreAkshay JoshiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Trials: FDA ApprovalDocument3 pagesClinical Trials: FDA Approvalthamizh555No ratings yet
- 04 - The Drug Development Process - Step 3 - Clinical ResearchDocument5 pages04 - The Drug Development Process - Step 3 - Clinical ResearchArunendu MajiNo ratings yet
- New Drug Application - WikipediaDocument26 pagesNew Drug Application - Wikipediakabirsahu0019No ratings yet
- Trajeshkumarppt1 220811164020 3776f822Document18 pagesTrajeshkumarppt1 220811164020 3776f822عبدالرحمن غنامNo ratings yet
- Fda Drug Approval Process: Discovery / ScreeningDocument1 pageFda Drug Approval Process: Discovery / ScreeningJamie Angelo PerezNo ratings yet
- 06 - The Drug Development Process - Step 5 - FDA Post-Market Drug Safety MonitoringDocument4 pages06 - The Drug Development Process - Step 5 - FDA Post-Market Drug Safety MonitoringArunendu MajiNo ratings yet
- R&D Group 8 Regulatory Roll No 3,6,11,15,17,40Document49 pagesR&D Group 8 Regulatory Roll No 3,6,11,15,17,40darpan30No ratings yet
- Clinical Trials: Phase I, II, IIIDocument16 pagesClinical Trials: Phase I, II, IIIJulie Hope CorveraNo ratings yet
- Pre MarketDocument12 pagesPre MarketNita Rezkiana AnwarNo ratings yet
- IRR Pharmacy LawDocument34 pagesIRR Pharmacy LawIVORY DIANE AMANCIONo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument31 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseIVORY DIANE AMANCIO100% (1)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument40 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseIVORY DIANE AMANCIONo ratings yet
- COPD AlgorithmNov2020 1Document1 pageCOPD AlgorithmNov2020 1IVORY DIANE AMANCIONo ratings yet
- Powders and GranulesDocument21 pagesPowders and GranulesIVORY DIANE AMANCIONo ratings yet
- Design of Dosage FormDocument23 pagesDesign of Dosage FormIVORY DIANE AMANCIONo ratings yet
- Solid Dosage Forms: CapsulesDocument18 pagesSolid Dosage Forms: CapsulesIVORY DIANE AMANCIONo ratings yet
- Trends of Mortality Indicators and Life Expectancy During The Last One DecadesDocument26 pagesTrends of Mortality Indicators and Life Expectancy During The Last One DecadesshireenNo ratings yet
- List of HMOs 2009 PDFDocument3 pagesList of HMOs 2009 PDFJaime AntunezNo ratings yet
- The Historical Aspect of Healthcare DeliveryDocument7 pagesThe Historical Aspect of Healthcare DeliveryafshanNo ratings yet
- Acceptance CertificateDocument1 pageAcceptance CertificateRebeca S.OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Halal Dan Haram VaksinDocument9 pagesHalal Dan Haram VaksinNunung NurazizahNo ratings yet
- Pencegahan Tuberkulosis Paru Dalam Keluarga: Kajian Literatur Sri Ayu Rahayu S. PaneoDocument5 pagesPencegahan Tuberkulosis Paru Dalam Keluarga: Kajian Literatur Sri Ayu Rahayu S. PaneoimronNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Contribution-PhilhealthDocument1 pageCertificate of Contribution-PhilhealthTrabaho PilipinasNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar EpidemiologiDocument22 pagesKonsep Dasar Epidemiologiari purwandiniNo ratings yet
- Daftar BukuDocument30 pagesDaftar BukuRezeki AdnaveNo ratings yet
- NDA ProcessDocument3 pagesNDA Processdustymarie100% (2)
- Timor Leste TB Profile 2021Document2 pagesTimor Leste TB Profile 2021noipiedade07No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument4 pagesIntroductionAddielou Fidelfio AbadNo ratings yet
- Jan. 13 Grand Forks Howell Vaccine ResponseDocument3 pagesJan. 13 Grand Forks Howell Vaccine ResponseJoe BowenNo ratings yet
- Clade X Model PDFDocument5 pagesClade X Model PDFAlexandre Rocha Lima e MarcondesNo ratings yet
- Assignment I On Basic Measurements of Disease Occurrence in EpidemiologyDocument2 pagesAssignment I On Basic Measurements of Disease Occurrence in EpidemiologyNathnael GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Essential VDocument4 pagesEssential Vapi-385640092No ratings yet
- Vital Health Stat Mabuhay 2023Document4 pagesVital Health Stat Mabuhay 2023Julie Suarez DaparNo ratings yet
- Innocenti Declaration 1990Document2 pagesInnocenti Declaration 1990ANDREASNo ratings yet
- Phrma Seniority List 01Document38 pagesPhrma Seniority List 01vasan980100% (1)
- Artikel OTAWA CARTER WIRATMAJADocument7 pagesArtikel OTAWA CARTER WIRATMAJADewa WiratmajaNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Karakteristik Ibu Inpartu Terhadap Kejadian Perdarahan Postpartum Di Rsu Budi Kemuliaan Periode Tahun 2019Document10 pagesHubungan Karakteristik Ibu Inpartu Terhadap Kejadian Perdarahan Postpartum Di Rsu Budi Kemuliaan Periode Tahun 2019MiMa Muach LadyzNo ratings yet
- Automatska Identifikacija I Optimizacija - Doktorska Disertacija VELIBOR JOVANOVICDocument216 pagesAutomatska Identifikacija I Optimizacija - Doktorska Disertacija VELIBOR JOVANOVICHokusyNo ratings yet
- CDC 1st Quar. REPORT 2015Document67 pagesCDC 1st Quar. REPORT 2015abdi qanoNo ratings yet
- Answers2ed OddDocument246 pagesAnswers2ed OddGaurav KamathNo ratings yet
- Health Care SystemsDocument15 pagesHealth Care Systems7hrqd6zxjkNo ratings yet
- Tugas PKBB Artikel PicotDocument9 pagesTugas PKBB Artikel PicotEsri DewiNo ratings yet
- List of Member States PICSDocument3 pagesList of Member States PICSShiinen GantumurNo ratings yet