Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio
Bio
Uploaded by
marcneil7730 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesCellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose to release energy. It occurs through aerobic respiration, which uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, or anaerobic respiration, which breaks down glucose without oxygen. Both produce energy through glycolysis but aerobic respiration produces more energy through the electron transport chain in mitochondria, while anaerobic respiration uses different molecules and occurs in the cytoplasm.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose to release energy. It occurs through aerobic respiration, which uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, or anaerobic respiration, which breaks down glucose without oxygen. Both produce energy through glycolysis but aerobic respiration produces more energy through the electron transport chain in mitochondria, while anaerobic respiration uses different molecules and occurs in the cytoplasm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesBio
Bio
Uploaded by
marcneil773Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose to release energy. It occurs through aerobic respiration, which uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, or anaerobic respiration, which breaks down glucose without oxygen. Both produce energy through glycolysis but aerobic respiration produces more energy through the electron transport chain in mitochondria, while anaerobic respiration uses different molecules and occurs in the cytoplasm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
Cellular Respiration
a process that takes place inside the cells
where energy is released by the breakdown
of glucose molecules. It is crucial to a cell’s
survival because if it cannot liberate energy
from fuels, it will not have enough energy to
drive its normal functions.
Type
s
The process can be
conveniently divided into two
categories based on the
usage of oxygen, namely
aerobic and anaerobic
respiration.
Aerobic
Respiration
is the process of cellular respiration that uses oxygen to
produce energy from food. This type of respiration is
common in most of the plants and animals, including humans,
birds and other mammals. While breathing, we inhale air that
contains oxygen and we exhale air rich in carbon dioxide.
As we breathe in, the oxygen-rich air is transported to all the
parts of our body and ultimately to each cell
Aerobic
Respiration
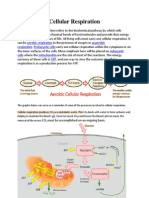
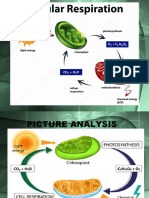
Inside the cell, the food, which contains glucose, is broken down
into carbon dioxide and water with the help of oxygen
through the different stages namely, glycolysis, Krebs
cycle, and electron transport chain. The process of breaking
down the food particles releases energy, which is then utilized
by our body. The process can be simply explained with the help
of the given equation:
Aerobic
Respiration
Anaerobic Respiration
Sometimes there is not enough oxygen around for some
organisms to respire, but they still need the energy to survive.
Due to lack of oxygen, they carry out respiration in the absence
of oxygen to produce the energy they require. Anaerobic
respiration usually occurs in some bacteria and archaea which
thrives in low oxygen environments.
Anaerobic Respiration
This method still incorporates the respiratory electron
transport chain, but without using oxygen as the terminal
electron acceptor. Instead, molecules such as sulfate through
sulfate reduction, and nitrate through denitrification are used
as electron acceptors. These molecules have a lower reduction
potential than oxygen; thus, less energy is formed per molecule
of glucose in anaerobic versus aerobic conditions.
Fermentation
is another way of harvesting chemical energy
without using either oxygen or any electron
transport chain. It can be classified as alcoholic
fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
Alcoholic
Fermentation
the process which produces ethanol and NAD+. The NAD+
allows glycolysis to continue making ATP. This type of
fermentation also explains why bread dough rises. Yeasts in
bread dough use alcoholic fermentation and produce carbon
dioxide gas. The gas forms bubbles in the dough, which
cause the dough to expand. The bubbles also leave small holes
in the bread after it bakes, making the bread light and fluffy.
Alcoholic
Fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation
is the process of splitting glucose into two molecules of lactic
acid to produce two ATP. It is used by multi-cellular organisms,
like us, as a temporary response to oxygen-less conditions.
During heavy or intensive exercise such as running,
sprinting, cycling or weightlifting, our body demands high
energy. As the supply of oxygen is limited, the muscle cells
inside our body resort to anaerobic respiration to fulfil the
energy demand.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Similarities Between Both aerobic and anaerobic
Aerobic And Anaerobic respiration are methods of
harvesting energy from a food
Respiration source, such as fats or sugars.
Both processes begin with the
splitting of a six-carbon sugar
molecule into 2 three-carbon
pyruvate molecules in a process
called glycolysis. This process
consumes two ATP molecules and
creates four ATP, for a net gain
of two ATP per sugar molecule
that is split
Bacteria and archaea can only
Similarities Between
perform anaerobic respiration Aerobic And Anaerobic
while other organisms can
perform either aerobic or Respiration
anaerobic respiration,
depending on whether oxygen
is present. Humans and other
animals rely on aerobic
respiration to stay alive but
can extend their cells’ lives
or performance in the absence
of oxygen through anaerobic
respiration.
Differences Between
During aerobic respiration,
Aerobic And the electron transport chain,
Anaerobic and most of the chemical
reactions of respiration,
Respiration occur in the mitochondria.
The mitochondria’s system of
membranes makes the process
much more efficient by
concentrating the chemical
reactants of respiration
together in one small space.
In contrast, anaerobic Differences Between
respiration typically takes
place in the cytoplasm. This Aerobic And
is because most cells that Anaerobic
exclusively carry out
anaerobic respiration do not
Respiration
have specialized organelles.
The series of reactions is
typically shorter in anaerobic
respiration and uses a final
electron acceptor such as
sulfate, nitrate, sulfur, or
fumarate instead of oxygen.
Differences Between
Aerobic And
Anaerobic
Respiration
Anaerobic respiration also produces less ATP for each
sugar molecule digested than aerobic respiration,
making it a less efficient method of generating
cellular energy. In addition, it produces different
waste products – including, in some cases, alcohol
You might also like
- Cellular Respiration: An Overview: Lesson SummaryDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: An Overview: Lesson Summaryandrea plalu33% (6)
- CRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualDocument6 pagesCRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualVanesha AnesNo ratings yet
- 8-C1.2 Cell RespirationDocument47 pages8-C1.2 Cell Respirationmakaya02No ratings yet
- Q2 W1 W2 W3 General Biology 1Document8 pagesQ2 W1 W2 W3 General Biology 1Samantha ManibogNo ratings yet
- Jinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDocument13 pagesJinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDEVIL GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- The Role of Oxygen in RespirationDocument11 pagesThe Role of Oxygen in RespirationLouie Joice MartinezNo ratings yet
- Q2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesQ2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationRaph tsuNo ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 5Document14 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 5Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Document18 pagesCellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Clarisse De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- GB 1 NotesDocument10 pagesGB 1 Notesrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- General MicrobiologyDocument16 pagesGeneral MicrobiologyNecromancer Gtr75 GtNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Biology 2nd QRTR Exam - OutlineDocument5 pagesBiology 2nd QRTR Exam - OutlineLouie Joice MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 Energy of LifeDocument29 pagesLec 9 Energy of LifeFahim AbidNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDocument3 pagesRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration in Animals.Document4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals.studyklieNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodDocument28 pagesCellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration Genbio g3Document13 pagesAnaerobic Respiration Genbio g3leeyaonde123No ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- 3 7 Cell RespirationDocument3 pages3 7 Cell Respirationapi-296446683No ratings yet
- 5Document2 pages5Mohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Downloadfile 15Document23 pagesDownloadfile 15Loren TejonesNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument34 pagesAnaerobic RespirationArmero, Mariah Sophia V.No ratings yet
- Student Module 3 Genbio1Document7 pagesStudent Module 3 Genbio1Lezel LaracasNo ratings yet
- There Are Two Types of Respiration:: What Is Aerobic Respiration?Document5 pagesThere Are Two Types of Respiration:: What Is Aerobic Respiration?Kyle JuntillaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio W3-5Document9 pagesGen Bio W3-5Alyson EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 1Document21 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 1LP May JaymeNo ratings yet
- Biology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaDocument3 pagesBiology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaAmirul HakimNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Energy SystemDocument27 pagesAerobic Energy SystemKavya KavyasujathaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio. 2ND Quarter RespirationDocument3 pagesGen Bio. 2ND Quarter RespirationChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- General Biology Q2W3Document2 pagesGeneral Biology Q2W3Geronimo, Jonamae S.No ratings yet
- Inbound 9168743087088869744Document9 pagesInbound 9168743087088869744MarkNo ratings yet
- CS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsDocument80 pagesCS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsJanrick CabuñasNo ratings yet
- Pearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationDocument77 pagesPearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationMetaknight360 LiveNo ratings yet
- Respiration PowerpointDocument14 pagesRespiration Powerpointmmpanjwani4No ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesLesson 14 Cellular RespirationGinalyn QuimsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonDocument6 pagesLesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonMarielle RamosNo ratings yet
- Bio1610 Discussion q2Document1 pageBio1610 Discussion q2api-241205310No ratings yet
- Jinky Oraiz@deped Gov PHDocument11 pagesJinky Oraiz@deped Gov PHAnnejhel Mae Poralan100% (1)
- Unit Vi Respirtion Magfirah Ramadhani Rusdi / 1714440008: Keywords: Respiration, Oxygen, Aerobic, AnaerobicDocument8 pagesUnit Vi Respirtion Magfirah Ramadhani Rusdi / 1714440008: Keywords: Respiration, Oxygen, Aerobic, AnaerobicCokroNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Study Guide 2015Document7 pagesCH 9 Study Guide 2015dickbeater73No ratings yet
- Teaching Science in Elementary GradesDocument2 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary GradesJenniferChantengcoCatacutan50% (2)
- Celluar Resp 2009Document58 pagesCelluar Resp 2009Kurt IgotNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Riparian Systems As Affected by Hydrological Extremes A Mini-ReviewDocument14 pagesGreenhouse Gas Emissions From Riparian Systems As Affected by Hydrological Extremes A Mini-Reviewraj cyberboyNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument4 pagesMolecular Orbital TheoryYuexun ZhangNo ratings yet
- Boiler Feed Water and Steam ChemistryDocument4 pagesBoiler Feed Water and Steam ChemistryVajid MadathilNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals - Library ContentDocument103 pagesPharmaceuticals - Library ContentCH M RehanNo ratings yet
- Desiccant Masterbatch PDFDocument1 pageDesiccant Masterbatch PDFNguyen Xuan GiangNo ratings yet
- Charaterization of Liquid Solid ReactionDocument8 pagesCharaterization of Liquid Solid ReactionYuni_Arifwati_5495No ratings yet
- 21 Cephalosp 2015 Mandell Douglas and Bennett S Principles and PracticeDocument20 pages21 Cephalosp 2015 Mandell Douglas and Bennett S Principles and PracticeHelen DyNo ratings yet
- Blo!'/Out Preventer: Kooi/) Ey Coi'ItrolDocument46 pagesBlo!'/Out Preventer: Kooi/) Ey Coi'ItrolHamid Reza Babaei100% (1)
- Certificate IPT 135Document3 pagesCertificate IPT 135JGGNo ratings yet
- T.Y.B.Sc. 4.1.3 DTA Analysis PPT TYDocument32 pagesT.Y.B.Sc. 4.1.3 DTA Analysis PPT TYmohamed arifNo ratings yet
- Ra22 ArmourZinc 120 PrimerDocument2 pagesRa22 ArmourZinc 120 PrimerDenis MNo ratings yet
- Valve Material Chemical Compatibility Lookup - Flowstar (UK) Limited PDFDocument5 pagesValve Material Chemical Compatibility Lookup - Flowstar (UK) Limited PDFHARSHANo ratings yet
- Vegetable-Oil Based Metalworking FluidsDocument11 pagesVegetable-Oil Based Metalworking FluidsRizal FahrezaNo ratings yet
- Acs-Climacs General CatalogueDocument86 pagesAcs-Climacs General CatalogueSaber EntzNo ratings yet
- Manual Contrangulo Ti Max X SG20LDocument154 pagesManual Contrangulo Ti Max X SG20LANDRES RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Bayhydur XP 2655 MSDS PDFDocument10 pagesBayhydur XP 2655 MSDS PDFrogerkid17No ratings yet
- 2013 H2 Chemistry Prelim Paper 2 AnswersDocument5 pages2013 H2 Chemistry Prelim Paper 2 AnswersMelinda BowmanNo ratings yet
- O-Ring Reference GuideDocument63 pagesO-Ring Reference GuideVenu Gopal100% (1)
- Spo Dializer BocorDocument3 pagesSpo Dializer BocorupikNo ratings yet
- KSB MIL Control Valves Specification V0998-SPECDocument36 pagesKSB MIL Control Valves Specification V0998-SPECNutan PowerNo ratings yet
- Pressure Nutsche FilterDocument1 pagePressure Nutsche FilterAhlada Group of Companies100% (1)
- Effi Cacy of Potassium Permanganate Impregnated Into Alumina Beads To Reduce Atmospheric EthyleneDocument6 pagesEffi Cacy of Potassium Permanganate Impregnated Into Alumina Beads To Reduce Atmospheric EthyleneARIF SETYAWAN YUSUF YUSUFNo ratings yet
- 7 Deterioration Concrete PDFDocument14 pages7 Deterioration Concrete PDFD113 Rahmadan PujiatmokoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Crossword Puzzle: Name: - DateDocument1 pageChemistry Crossword Puzzle: Name: - DateNtando Nkunzimanikina XimbaNo ratings yet
- Flojet Beer Pump Manual g56Document2 pagesFlojet Beer Pump Manual g56Max WeiheNo ratings yet
- AC428 Final Resolution PDFDocument8 pagesAC428 Final Resolution PDFSaeed MoradiNo ratings yet
- ASTM F1980 Thermoalterung Von VerpackungenDocument6 pagesASTM F1980 Thermoalterung Von VerpackungenRicha RohillaNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Maple SyrupDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Maple Syrupchumak.alyona.uaNo ratings yet
- Aqa 8464C1F QP Jun18 PDFDocument24 pagesAqa 8464C1F QP Jun18 PDFMustafa NabeihNo ratings yet
- TDS MD en 2131 Roswan QD HBDocument2 pagesTDS MD en 2131 Roswan QD HBcelescopitoNo ratings yet