Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Noun & Pronoun
1 Noun & Pronoun
Uploaded by
Salam Zaheer Educational CenterCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chomsky DefinitionDocument7 pagesChomsky DefinitionNMK@KC90% (20)
- CLIL SkeletonDocument2 pagesCLIL SkeletonSaulet BexultanovaNo ratings yet
- 01 BLAZE 3 Test 1ADocument4 pages01 BLAZE 3 Test 1Acristina_georgianav100% (4)
- Workbook 9a-9bDocument3 pagesWorkbook 9a-9balinaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Kls 3Document15 pagesGrammar Kls 3Nur Najmi Laila 04No ratings yet
- Notes I. Personal Pronouns Pronouns Are Words We Use in The Place of A Full NounDocument9 pagesNotes I. Personal Pronouns Pronouns Are Words We Use in The Place of A Full Nounelin_zlinNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun Is The Pronoun Used To Stand For The NounDocument41 pagesPersonal Pronoun Is The Pronoun Used To Stand For The NounHaris HarahapNo ratings yet
- Pronoun and It's Types.: Presented byDocument11 pagesPronoun and It's Types.: Presented byAsim ImtiazNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument8 pagesPronounI D.P.B. Karan Putra WirekaNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal Toefl: Emphatic Pronoun Self Form Digunakan Untuk Menegaskan (To Emphasize) Arti KataDocument4 pagesBentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal Toefl: Emphatic Pronoun Self Form Digunakan Untuk Menegaskan (To Emphasize) Arti KataSAHRUL MUNIRNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument9 pagesPart of SpeechJennifer PittmanNo ratings yet
- Pronouns. Types of Pronouns.: Personal Pronoun As Subject Personal Pronoun As ObjectDocument7 pagesPronouns. Types of Pronouns.: Personal Pronoun As Subject Personal Pronoun As ObjectMohd FaisNo ratings yet
- Language Focus: She Is A Subject Pronoun Her Is An ObjectDocument5 pagesLanguage Focus: She Is A Subject Pronoun Her Is An ObjectRaihan RidhoNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument46 pagesBasicTNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris: Mata Kuliah Wajib UniversitasDocument27 pagesBahasa Inggris: Mata Kuliah Wajib UniversitasNovianti LalongNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: Pronoun Ialah Kata Yang Digunakan Atau Difungsikan Sebagai Pengganti Kata Benda (Noun)Document4 pagesPronoun: Pronoun Ialah Kata Yang Digunakan Atau Difungsikan Sebagai Pengganti Kata Benda (Noun)ryo apriansyahNo ratings yet
- 3 PronounDocument34 pages3 PronounAlouddin HaqdostNo ratings yet
- Meeting 7 Kelas 7: Materi + Lembar Kerja: Kegiatan Pembelajaran 3: PronounDocument3 pagesMeeting 7 Kelas 7: Materi + Lembar Kerja: Kegiatan Pembelajaran 3: PronounZaid AbduraufNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLDocument8 pagesBentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLEri TeriNo ratings yet
- Pronoun (Kata Ganti)Document11 pagesPronoun (Kata Ganti)Alifia RismaNo ratings yet
- English IDocument15 pagesEnglish ISomen SahaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris 1: Prodi D3 Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Ilmu Terapan Universitas TelkomDocument31 pagesBahasa Inggris 1: Prodi D3 Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Ilmu Terapan Universitas TelkomAnik DarwatiNo ratings yet
- Topic:2 Parts of SpeechDocument18 pagesTopic:2 Parts of SpeechVIMAL NAIR SURESHNo ratings yet
- Rules of Narration According To TensesDocument4 pagesRules of Narration According To TensesRizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Makalah KumpulanDocument70 pagesMakalah Kumpulanagam arunaNo ratings yet
- Abdullah Fuad (5115151822)Document16 pagesAbdullah Fuad (5115151822)Gabriellia Surya PutriNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4 Dan 5 Basic StructuredDocument48 pagesPertemuan 4 Dan 5 Basic StructuredNisa R DharmawanNo ratings yet
- English Language, Corrections - Copy-1Document56 pagesEnglish Language, Corrections - Copy-1Julien KhalilNo ratings yet
- A01 Act#1 IBALEDocument6 pagesA01 Act#1 IBALELester IbaleNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument11 pagesPronounsDevika BaburajNo ratings yet
- PronoonsDocument11 pagesPronoonsMuhammad Matloob Uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument18 pagesEnglishToram LoversNo ratings yet
- Reflexive PronounDocument5 pagesReflexive Pronounamanda salsaNo ratings yet
- Alfelor Sr. Memorial College Inc. Poblacion Zone II Del Gallego, Camarines Sur May 19, 2020 8:15 - 9:05 Detailed Lesson Plan in English IV 50 MinutesDocument6 pagesAlfelor Sr. Memorial College Inc. Poblacion Zone II Del Gallego, Camarines Sur May 19, 2020 8:15 - 9:05 Detailed Lesson Plan in English IV 50 Minuteschris orlanNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Nouns and Pronouns IiDocument22 pagesWeek 10 - Nouns and Pronouns IiIsa BellaNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLDocument20 pagesBentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLawab adiNo ratings yet
- Class 5 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Pronoun and Its KindsDocument8 pagesClass 5 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Pronoun and Its Kindsgphysics007No ratings yet
- Reflexive and Emphatic PronounsDocument6 pagesReflexive and Emphatic Pronounssifa100% (1)
- Parts of Speech Part 2Document8 pagesParts of Speech Part 2Ii nanda SafitriNo ratings yet
- The ABC of Grammar PDFDocument15 pagesThe ABC of Grammar PDFShihab Al QuraishNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNDocument16 pagesPRONOUNNadiyaNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument9 pagesPronounsMujeeb SamejoNo ratings yet
- English Grade 7 - Fourth QuarterDocument2 pagesEnglish Grade 7 - Fourth QuarterNanay GiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Infinitive?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Infinitive?Jesus David Dominguez RamirezNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Document9 pagesPRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Meriliana Candra DeviNo ratings yet
- G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 2Document6 pagesG5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 2Hadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Pronoun 52Document6 pagesPronoun 52Mayank SagarNo ratings yet
- Caes of Nouns and PronounsDocument8 pagesCaes of Nouns and PronounsJaizanie BacabacNo ratings yet
- What Is A PronounDocument23 pagesWhat Is A Pronounpamir.amiry2005No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 pagesParts of SpeechAsdf GhjkNo ratings yet
- College English Reviewer FinalsDocument17 pagesCollege English Reviewer FinalsJuan Miguel TevesNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.inggrisDocument34 pagesTugas B.inggrisAndrea SusantiNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLDocument19 pagesBentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLAnita SNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 1Document22 pagesEnglish Assignment 1katilabbuNo ratings yet
- Name: Buya Ahmad Bilal Nim:200502502015 Class: English Educatioan ADocument17 pagesName: Buya Ahmad Bilal Nim:200502502015 Class: English Educatioan ABilal BuyaNo ratings yet
- The Basics GrammarDocument78 pagesThe Basics GrammarChef M.husain100% (2)
- 6th MathDocument12 pages6th MathHaji SahibNo ratings yet
- Phrases & Sentence TypesDocument34 pagesPhrases & Sentence Typeseaonyinye13No ratings yet
- Basic English: Parts of SpeechDocument60 pagesBasic English: Parts of SpeechSifat ullah shah pakhtoonNo ratings yet
- Advance Structure - Passive Voice Edit TGL 13Document117 pagesAdvance Structure - Passive Voice Edit TGL 13estu kaniraNo ratings yet
- Finite and Infinite Verbs PDFDocument4 pagesFinite and Infinite Verbs PDFMirza Haider RezaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar 146-158Document13 pagesEnglish Grammar 146-158Оля АкимоваNo ratings yet
- THP Practice 2Document13 pagesTHP Practice 2Dewi Astuti Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- Definiteness Across Languages: An OverviewDocument18 pagesDefiniteness Across Languages: An Overviewali mohammedNo ratings yet
- MRP Executive SummaryDocument129 pagesMRP Executive SummaryVishakha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Future WillDocument4 pagesFuture WillJuliana Chancafe IncioNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem English Prepositional PhrasesDocument3 pages3rd Sem English Prepositional PhrasesG Ramesh babuNo ratings yet
- Maroon 5 para o 3ano PDFDocument2 pagesMaroon 5 para o 3ano PDFAnonymous 6baDBV6No ratings yet
- Together Starter 4A Two-StarDocument2 pagesTogether Starter 4A Two-StarCarla Morales MazzochiNo ratings yet
- The Roots of The Word DravidDocument4 pagesThe Roots of The Word DravidAsim MahatoNo ratings yet
- Collocations s3Document18 pagesCollocations s3Isferra RezanaNo ratings yet
- English Task MakalahDocument7 pagesEnglish Task MakalahndynvNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument9 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogJONALYN EVANGELISTANo ratings yet
- Extensive Reading (Er) Practices and The Development of Language FluencyDocument6 pagesExtensive Reading (Er) Practices and The Development of Language FluencyLina MardiyanaNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Deepfake V2Document24 pagesA Framework For Deepfake V2Abdullah fawaz altulahiNo ratings yet
- Korean AlphabetDocument4 pagesKorean AlphabetCipo Lletti100% (2)
- Tema 31 Text Context Types of Texts (N)Document10 pagesTema 31 Text Context Types of Texts (N)royalvillage2222-1No ratings yet
- Globetrotter Spanish in Your Pocket Phrase BookDocument10 pagesGlobetrotter Spanish in Your Pocket Phrase BookMapStudio100% (1)
- CELTA Language Awareness Task FINALDocument2 pagesCELTA Language Awareness Task FINALTeddy Broughton100% (1)
- (Extra) Questões - Present PerfectDocument5 pages(Extra) Questões - Present PerfectRafael GomesNo ratings yet
- MVDocument3 pagesMVAndreea RaduNo ratings yet
- The Latvian Language,: Languages in LatviaDocument18 pagesThe Latvian Language,: Languages in Latviaankara271828No ratings yet
- Summary English 2 With Exercises-3Document41 pagesSummary English 2 With Exercises-3Cindy paulaNo ratings yet
- Undergrad Programme in English Syllabus PDFDocument26 pagesUndergrad Programme in English Syllabus PDFahmad khanNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Verbos Irregulares en Orden AlfabéticoDocument4 pagesTabla de Verbos Irregulares en Orden AlfabéticoWallace Ludwing Lion100% (1)
- 1A Grammar Question Formation PDFDocument4 pages1A Grammar Question Formation PDFTijana CurcicNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap Between Second Language Acquisition Research and Memory Science: The Case of Foreign Language AttritionDocument8 pagesBridging The Gap Between Second Language Acquisition Research and Memory Science: The Case of Foreign Language AttritionCharlene OliverosNo ratings yet
- (Kiparsky) Phonological ChangeDocument27 pages(Kiparsky) Phonological ChangembujalanceNo ratings yet
1 Noun & Pronoun
1 Noun & Pronoun
Uploaded by
Salam Zaheer Educational CenterCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Noun & Pronoun
1 Noun & Pronoun
Uploaded by
Salam Zaheer Educational CenterCopyright:
Available Formats
Speech
• The act of delivering a formal spoken communication
to the audience is called speech.
• Speech is the language, dialect of a nation or region.
• The act of capacity of speaking in a language is called
speech.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
Parts of speech
• The basic words of a language are divided into different
kinds that are called parts of speech and they are ,8, in
numbers, but in some grammar books they are nine by
adding Articles.
1. Noun
2. Pronoun
3. Adjective
4. Adverb
5. Verb
6. Conjunction
7. Interjection
8. Preposition Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
Noun
Noun is a naming word.
(Naming here means giving name to a person, place, thing, idea, etc)
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
• Common Noun: A common noun is a name given in common or to every
person , place or thing of the same kind.
Example: man, teacher, student…etc
• Proper Noun: A word which indicates a particular person, thing or place
is called proper noun, or a word which denotes a specific person, thing or
place. Proper means one’s own). The first letter of the proper noun is
always capitalized. (Afghanistan, English
book, Ahmad)
Example: Karzai who is the president of Afghanistan is intelligent.
• Compound Noun: A noun made of two or more than two nouns.
Examples:
Handbook, handbag,
Bank teller, bus driver, college student
Father-in-law, mother-in-law, off-license
(shortcut. Magazine reading, driving school, a man from Afghanistan,
students’ class, Ali’s car.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
pronoun
• Pronoun is a word that functions as a substitute for a noun
and avoids a noun from its repetition.
E.g. Ali is a student; he is a very smart boy.
subject. Pro
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
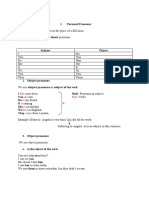
A. Subject pronouns:
(I, you, we, they, he, she, it)
Subject pronouns are used mainly as subject before verbs.
singular plural
I We
You You
He They
She
It
E.g. They reconstructed new building in Afghanistan.
sub. pro
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
Subject and predicate
Every sentence has two main parts namely subject and predicate.
Subject contains a noun or a pronoun and the predicate contains verb, so it
can be said that the naming part is the subject and the telling part is the
predicate. A sentence is divided into two parts:
1. Subject (the name of a person or the thing we speak about)
2. Predicate (what is said about the subject)
subject predicate
Ali is very intelligent.
Man is a social animal.
He went to Kabul yesterday.
The moon looks pretty.
E.g. He became a politician.
sub verb predicate E.g. write your name.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
B. Object pronoun
(me, you, us, them, him, her, it)
Object pronouns are used as object of a verb or a preposition.
Singular Plural
Me Us
You You
Him Them
Her
It
E.g. She sent me some flowers.
obj. pro
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
Kinds of object
A. Direct object
The name of a person or a thing directly receiving an action of
a verb is called direct object and direct objects are usually
identified by asking (who) or (what is affected by the subject)
E.g. I wrote a letter. E.g. We saw a snake.
B. Indirect object
The person to whom something is given or for whom
something is done is called indirect object.
E.g. I gave him a book.
E.g. I wrote her a letter.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
C. Demonstrative Pronoun
• They are used to point out the object or the noun to which they
refer.
(this, that, these, those)
Singular Plural
This These
That Those
E.g. This is Omar and these are his friends.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
D. Possessive Pronouns
• They are used to show possession or ownership in sentences and they
are used without following nouns.
(mine, yours, ours, theirs, his, hers, its)
Singular Plural
Mine Ours
Yours Yours
His Theirs
Hers
Its
E.g. Which car is yours?
E.g. That car is mine.
. Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
E. Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are
• Myself
• Yourself
• Himself
• himself
• Itself
• Oneself
• Ourselves
• Yourselves
• Themselves
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
Use
A common use of reflexive pronoun is to talk about actions where the
subject and object are the same person.
E.g. I cut myself shaving this morning. (Not I cut me.)
E.g. We got out of the water and dried ourselves.
E.g. I am going to Jalalabad to get myself a pair of shoes.
E.g. Talking to oneself is the first sign of madness.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
Use continued…….
A reflexive pronoun can refer to other things besides the subject of a
clause.
Examples:
E.g. His letters are all about himself.
E.g. I am going to tell him a few facts about himself.
E.g. I like you for yourself, not for your money.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
Use continued…….
We can use reflexives as subject or object emphasizers to mean that
person or thing and nobody or nothing else.
Examples:
E.g. The manager spoke to me himself.
E.g. The manager himself spoke to me.
E.g. The house is nice itself.
E.g. The house itself is nice.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
By + Reflexive pronouns
We use the above structure to mean either alone or without help.
Examples:
E.g. I often wash my car by myself.
E.g. A. Do you need help?
B. No, thanks.
I can do it by myself.
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
Exercise
Choose letter of the best answer
1. Khan plays cricket, he is a very good player.
a. subject pronoun b. object pronoun
c. demonstrative pronoun d. indefinite pronoun
2. She washed the dishes by herself.
a. Object pronoun b. interesting pronoun
c. reflexive pronoun d. none of them
3. Mom wants to prepare us dinner.
a. relative pronoun b. indefinite pronoun
c. object pronoun d. both a & b
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
4. Wow! Is it yours?
a. demonstrative pronoun b. surprising pronoun
c. letter ,a, is correct d. possessive pronoun
5. Hey Ali! That is my car.
a. indefinite pronoun b. relative pronoun
c. demonstrative pronoun d. reflexive pronoun
6. It is not a good way of learning English language.
a. reflexive pronoun b. subject pronoun
c interrogative pronoun d. none of them
Prepared by: Zabihullah 'Ibrahimi'
You might also like
- Chomsky DefinitionDocument7 pagesChomsky DefinitionNMK@KC90% (20)
- CLIL SkeletonDocument2 pagesCLIL SkeletonSaulet BexultanovaNo ratings yet
- 01 BLAZE 3 Test 1ADocument4 pages01 BLAZE 3 Test 1Acristina_georgianav100% (4)
- Workbook 9a-9bDocument3 pagesWorkbook 9a-9balinaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Kls 3Document15 pagesGrammar Kls 3Nur Najmi Laila 04No ratings yet
- Notes I. Personal Pronouns Pronouns Are Words We Use in The Place of A Full NounDocument9 pagesNotes I. Personal Pronouns Pronouns Are Words We Use in The Place of A Full Nounelin_zlinNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun Is The Pronoun Used To Stand For The NounDocument41 pagesPersonal Pronoun Is The Pronoun Used To Stand For The NounHaris HarahapNo ratings yet
- Pronoun and It's Types.: Presented byDocument11 pagesPronoun and It's Types.: Presented byAsim ImtiazNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument8 pagesPronounI D.P.B. Karan Putra WirekaNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal Toefl: Emphatic Pronoun Self Form Digunakan Untuk Menegaskan (To Emphasize) Arti KataDocument4 pagesBentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal Toefl: Emphatic Pronoun Self Form Digunakan Untuk Menegaskan (To Emphasize) Arti KataSAHRUL MUNIRNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument9 pagesPart of SpeechJennifer PittmanNo ratings yet
- Pronouns. Types of Pronouns.: Personal Pronoun As Subject Personal Pronoun As ObjectDocument7 pagesPronouns. Types of Pronouns.: Personal Pronoun As Subject Personal Pronoun As ObjectMohd FaisNo ratings yet
- Language Focus: She Is A Subject Pronoun Her Is An ObjectDocument5 pagesLanguage Focus: She Is A Subject Pronoun Her Is An ObjectRaihan RidhoNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument46 pagesBasicTNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris: Mata Kuliah Wajib UniversitasDocument27 pagesBahasa Inggris: Mata Kuliah Wajib UniversitasNovianti LalongNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: Pronoun Ialah Kata Yang Digunakan Atau Difungsikan Sebagai Pengganti Kata Benda (Noun)Document4 pagesPronoun: Pronoun Ialah Kata Yang Digunakan Atau Difungsikan Sebagai Pengganti Kata Benda (Noun)ryo apriansyahNo ratings yet
- 3 PronounDocument34 pages3 PronounAlouddin HaqdostNo ratings yet
- Meeting 7 Kelas 7: Materi + Lembar Kerja: Kegiatan Pembelajaran 3: PronounDocument3 pagesMeeting 7 Kelas 7: Materi + Lembar Kerja: Kegiatan Pembelajaran 3: PronounZaid AbduraufNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLDocument8 pagesBentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLEri TeriNo ratings yet
- Pronoun (Kata Ganti)Document11 pagesPronoun (Kata Ganti)Alifia RismaNo ratings yet
- English IDocument15 pagesEnglish ISomen SahaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris 1: Prodi D3 Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Ilmu Terapan Universitas TelkomDocument31 pagesBahasa Inggris 1: Prodi D3 Manajemen Informatika Fakultas Ilmu Terapan Universitas TelkomAnik DarwatiNo ratings yet
- Topic:2 Parts of SpeechDocument18 pagesTopic:2 Parts of SpeechVIMAL NAIR SURESHNo ratings yet
- Rules of Narration According To TensesDocument4 pagesRules of Narration According To TensesRizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Makalah KumpulanDocument70 pagesMakalah Kumpulanagam arunaNo ratings yet
- Abdullah Fuad (5115151822)Document16 pagesAbdullah Fuad (5115151822)Gabriellia Surya PutriNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4 Dan 5 Basic StructuredDocument48 pagesPertemuan 4 Dan 5 Basic StructuredNisa R DharmawanNo ratings yet
- English Language, Corrections - Copy-1Document56 pagesEnglish Language, Corrections - Copy-1Julien KhalilNo ratings yet
- A01 Act#1 IBALEDocument6 pagesA01 Act#1 IBALELester IbaleNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument11 pagesPronounsDevika BaburajNo ratings yet
- PronoonsDocument11 pagesPronoonsMuhammad Matloob Uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument18 pagesEnglishToram LoversNo ratings yet
- Reflexive PronounDocument5 pagesReflexive Pronounamanda salsaNo ratings yet
- Alfelor Sr. Memorial College Inc. Poblacion Zone II Del Gallego, Camarines Sur May 19, 2020 8:15 - 9:05 Detailed Lesson Plan in English IV 50 MinutesDocument6 pagesAlfelor Sr. Memorial College Inc. Poblacion Zone II Del Gallego, Camarines Sur May 19, 2020 8:15 - 9:05 Detailed Lesson Plan in English IV 50 Minuteschris orlanNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Nouns and Pronouns IiDocument22 pagesWeek 10 - Nouns and Pronouns IiIsa BellaNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLDocument20 pagesBentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLawab adiNo ratings yet
- Class 5 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Pronoun and Its KindsDocument8 pagesClass 5 English Grammar Ncert Solutions Pronoun and Its Kindsgphysics007No ratings yet
- Reflexive and Emphatic PronounsDocument6 pagesReflexive and Emphatic Pronounssifa100% (1)
- Parts of Speech Part 2Document8 pagesParts of Speech Part 2Ii nanda SafitriNo ratings yet
- The ABC of Grammar PDFDocument15 pagesThe ABC of Grammar PDFShihab Al QuraishNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNDocument16 pagesPRONOUNNadiyaNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument9 pagesPronounsMujeeb SamejoNo ratings yet
- English Grade 7 - Fourth QuarterDocument2 pagesEnglish Grade 7 - Fourth QuarterNanay GiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Infinitive?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Infinitive?Jesus David Dominguez RamirezNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Document9 pagesPRONOUNS - Kelompok 12Meriliana Candra DeviNo ratings yet
- G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 2Document6 pagesG5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 2Hadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Pronoun 52Document6 pagesPronoun 52Mayank SagarNo ratings yet
- Caes of Nouns and PronounsDocument8 pagesCaes of Nouns and PronounsJaizanie BacabacNo ratings yet
- What Is A PronounDocument23 pagesWhat Is A Pronounpamir.amiry2005No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 pagesParts of SpeechAsdf GhjkNo ratings yet
- College English Reviewer FinalsDocument17 pagesCollege English Reviewer FinalsJuan Miguel TevesNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.inggrisDocument34 pagesTugas B.inggrisAndrea SusantiNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLDocument19 pagesBentuk Pronoun Dalam Soal TOEFLAnita SNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 1Document22 pagesEnglish Assignment 1katilabbuNo ratings yet
- Name: Buya Ahmad Bilal Nim:200502502015 Class: English Educatioan ADocument17 pagesName: Buya Ahmad Bilal Nim:200502502015 Class: English Educatioan ABilal BuyaNo ratings yet
- The Basics GrammarDocument78 pagesThe Basics GrammarChef M.husain100% (2)
- 6th MathDocument12 pages6th MathHaji SahibNo ratings yet
- Phrases & Sentence TypesDocument34 pagesPhrases & Sentence Typeseaonyinye13No ratings yet
- Basic English: Parts of SpeechDocument60 pagesBasic English: Parts of SpeechSifat ullah shah pakhtoonNo ratings yet
- Advance Structure - Passive Voice Edit TGL 13Document117 pagesAdvance Structure - Passive Voice Edit TGL 13estu kaniraNo ratings yet
- Finite and Infinite Verbs PDFDocument4 pagesFinite and Infinite Verbs PDFMirza Haider RezaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar 146-158Document13 pagesEnglish Grammar 146-158Оля АкимоваNo ratings yet
- THP Practice 2Document13 pagesTHP Practice 2Dewi Astuti Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- Definiteness Across Languages: An OverviewDocument18 pagesDefiniteness Across Languages: An Overviewali mohammedNo ratings yet
- MRP Executive SummaryDocument129 pagesMRP Executive SummaryVishakha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Future WillDocument4 pagesFuture WillJuliana Chancafe IncioNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem English Prepositional PhrasesDocument3 pages3rd Sem English Prepositional PhrasesG Ramesh babuNo ratings yet
- Maroon 5 para o 3ano PDFDocument2 pagesMaroon 5 para o 3ano PDFAnonymous 6baDBV6No ratings yet
- Together Starter 4A Two-StarDocument2 pagesTogether Starter 4A Two-StarCarla Morales MazzochiNo ratings yet
- The Roots of The Word DravidDocument4 pagesThe Roots of The Word DravidAsim MahatoNo ratings yet
- Collocations s3Document18 pagesCollocations s3Isferra RezanaNo ratings yet
- English Task MakalahDocument7 pagesEnglish Task MakalahndynvNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument9 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogJONALYN EVANGELISTANo ratings yet
- Extensive Reading (Er) Practices and The Development of Language FluencyDocument6 pagesExtensive Reading (Er) Practices and The Development of Language FluencyLina MardiyanaNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Deepfake V2Document24 pagesA Framework For Deepfake V2Abdullah fawaz altulahiNo ratings yet
- Korean AlphabetDocument4 pagesKorean AlphabetCipo Lletti100% (2)
- Tema 31 Text Context Types of Texts (N)Document10 pagesTema 31 Text Context Types of Texts (N)royalvillage2222-1No ratings yet
- Globetrotter Spanish in Your Pocket Phrase BookDocument10 pagesGlobetrotter Spanish in Your Pocket Phrase BookMapStudio100% (1)
- CELTA Language Awareness Task FINALDocument2 pagesCELTA Language Awareness Task FINALTeddy Broughton100% (1)
- (Extra) Questões - Present PerfectDocument5 pages(Extra) Questões - Present PerfectRafael GomesNo ratings yet
- MVDocument3 pagesMVAndreea RaduNo ratings yet
- The Latvian Language,: Languages in LatviaDocument18 pagesThe Latvian Language,: Languages in Latviaankara271828No ratings yet
- Summary English 2 With Exercises-3Document41 pagesSummary English 2 With Exercises-3Cindy paulaNo ratings yet
- Undergrad Programme in English Syllabus PDFDocument26 pagesUndergrad Programme in English Syllabus PDFahmad khanNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Verbos Irregulares en Orden AlfabéticoDocument4 pagesTabla de Verbos Irregulares en Orden AlfabéticoWallace Ludwing Lion100% (1)
- 1A Grammar Question Formation PDFDocument4 pages1A Grammar Question Formation PDFTijana CurcicNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap Between Second Language Acquisition Research and Memory Science: The Case of Foreign Language AttritionDocument8 pagesBridging The Gap Between Second Language Acquisition Research and Memory Science: The Case of Foreign Language AttritionCharlene OliverosNo ratings yet
- (Kiparsky) Phonological ChangeDocument27 pages(Kiparsky) Phonological ChangembujalanceNo ratings yet