Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsGeralyn&christine (Not Reported)
Geralyn&christine (Not Reported)
Uploaded by
Rofelda Santiago VianaMagnesium is the lightest structural metal and was first isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy through electrolysis. It has many important uses including in aluminium alloys to make lightweight materials, as a nutrient for humans and plants, and in industrial processes. Magnesium plays a key role in photosynthesis as part of the chlorophyll molecule and is thus essential for all life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Astm d2035Document4 pagesAstm d2035sussy74No ratings yet
- Magnesium (MG) OrigionDocument7 pagesMagnesium (MG) OrigionharoonNo ratings yet
- تقريرDocument5 pagesتقريرjmalahmed853No ratings yet
- Elements Info. GoodDocument59 pagesElements Info. GoodSaid Alauddeen FaiszNo ratings yet
- Alloys MGDocument16 pagesAlloys MGJuan Diego Ospina FlorezNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionImdad JalaliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project MGDocument4 pagesChemistry Project MGPirvu ValentinaNo ratings yet
- Magnesium: 1 CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesMagnesium: 1 Characteristicsdroy21No ratings yet
- Material Engineering: Magnesium (MG)Document10 pagesMaterial Engineering: Magnesium (MG)Yb LangkawiNo ratings yet
- MagCemHistory PDFDocument3 pagesMagCemHistory PDFTaraknath PalNo ratings yet
- Mia G Assignment For FridayDocument8 pagesMia G Assignment For FridayHamim ImamNo ratings yet
- Science PTDocument11 pagesScience PTmarsha enriquezNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument9 pagesAlkaline Earth Metalssamuelstu01No ratings yet
- Magnesium Oxide: Low Sin Wang Am080141 881215-05-5379Document7 pagesMagnesium Oxide: Low Sin Wang Am080141 881215-05-5379idioit2001No ratings yet
- A Flash of Magnesium - Updated VersionDocument1 pageA Flash of Magnesium - Updated Versionelyanacn6No ratings yet
- About MagnesiumDocument2 pagesAbout MagnesiumNUR FAIQAH SYIFANo ratings yet
- De Castro, Jeremy DC (BSFT 1-2) Chem 1223-Long Quiz MidtermDocument4 pagesDe Castro, Jeremy DC (BSFT 1-2) Chem 1223-Long Quiz MidtermJeremy De CastroNo ratings yet
- Extractive Metallurgy of Rare EarthsDocument11 pagesExtractive Metallurgy of Rare EarthsWilliam Jesus Cabrera Meza100% (1)
- Magnesium: Elements Are Building Blocks of Matter. Magnesium Is One of Sixty Three ElementsDocument6 pagesMagnesium: Elements Are Building Blocks of Matter. Magnesium Is One of Sixty Three Elementsanon_593383259No ratings yet
- Form A To PosterDocument6 pagesForm A To PosterEric Manuel Mercedes AbreuNo ratings yet
- Definition of A Heavy Metal: Where FoundDocument2 pagesDefinition of A Heavy Metal: Where FoundarifNo ratings yet
- Element in A PeriodDocument10 pagesElement in A PeriodLavenderPonnuNo ratings yet
- Group 2 The Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument12 pagesGroup 2 The Alkaline Earth MetalsDarya SeredNo ratings yet
- Elling Sen 2015Document22 pagesElling Sen 2015vasoalebizouNo ratings yet
- Copper: Handbook On The Toxicology of Metals 4EDocument22 pagesCopper: Handbook On The Toxicology of Metals 4EChanWingSanNo ratings yet
- Refratechnik Bricks Wear RreasonsDocument8 pagesRefratechnik Bricks Wear Rreasonsengr kazamNo ratings yet
- Magnesium AlloysDocument14 pagesMagnesium AlloysTamerNo ratings yet
- Antimony in SerbiaDocument5 pagesAntimony in SerbiaJovan MilićevićNo ratings yet
- Metal Chemistry Group WorkDocument12 pagesMetal Chemistry Group WorkParis GreenNo ratings yet
- ZincDocument2 pagesZincRajini KumarNo ratings yet
- Magnesiu 1Document2 pagesMagnesiu 1Elkay Rebel-Ikons MillerNo ratings yet
- 204 Aguilarrochelle Fossil Fuels Extraction of MetalsDocument38 pages204 Aguilarrochelle Fossil Fuels Extraction of MetalsJodie CabreraNo ratings yet
- TungstenDocument15 pagesTungstenJon Be GoodNo ratings yet
- Antimony - Special StoneDocument5 pagesAntimony - Special StoneTri UtomoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Crossword 1Document2 pagesChemical Elements Crossword 1David LockartNo ratings yet
- MetallurgyDocument10 pagesMetallurgy呂布No ratings yet
- Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University Lucknow: Assignment On Topic Minerology and Crystallography Submitted ToDocument4 pagesBabasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University Lucknow: Assignment On Topic Minerology and Crystallography Submitted ToKumar ankitNo ratings yet
- Iron Ore, Steel and Coal: by Group 4Document26 pagesIron Ore, Steel and Coal: by Group 4Harshavardhan GuntupalliNo ratings yet
- Lanthanides - Real-Life ApplicationsDocument5 pagesLanthanides - Real-Life ApplicationsSERAPHINENo ratings yet
- Metallurgy: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesMetallurgy: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBobNo ratings yet
- Where Does Chromium Come From?Chromite, An Oxide of Iron, Magnesium, Aluminum, andDocument4 pagesWhere Does Chromium Come From?Chromite, An Oxide of Iron, Magnesium, Aluminum, andJumil PadilloNo ratings yet
- Science Wanted PosterDocument1 pageScience Wanted PosterMayra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of Manganese Health Effects of Manganese Environmental Effects of ManganeseDocument5 pagesChemical Properties of Manganese Health Effects of Manganese Environmental Effects of ManganeseRaj ManiNo ratings yet
- SMK Puteri Seremban: Chemistry ProjectDocument28 pagesSMK Puteri Seremban: Chemistry ProjectHaemaavadhaanaNo ratings yet
- History of Silicon DiodeDocument7 pagesHistory of Silicon DiodeAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- The FTIR Spectra of Raw Magnesite and Sintered MagnesiteDocument5 pagesThe FTIR Spectra of Raw Magnesite and Sintered MagnesiteEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Extracting Metals From Their OresDocument7 pagesExtracting Metals From Their OresChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- Ferromanganese 4Document1 pageFerromanganese 4eximNo ratings yet
- Ammonia: A Very Important Molecule For Biological Organisms To Make Proteins or Nucleic AcidsDocument14 pagesAmmonia: A Very Important Molecule For Biological Organisms To Make Proteins or Nucleic AcidsAnonymous s2DiXhNo ratings yet
- Valeri Consulenza IndustrialeDocument4 pagesValeri Consulenza IndustrialeGualtiero A.N.ValeriNo ratings yet
- Mineral AccountingDocument9 pagesMineral AccountingJudith LlemitNo ratings yet
- Production of Magnesium From Great Salt Lake Utah USADocument8 pagesProduction of Magnesium From Great Salt Lake Utah USAraminNo ratings yet
- Lanthanides: - LanthanumDocument6 pagesLanthanides: - LanthanumlolNo ratings yet
- Raw Materials-IronDocument22 pagesRaw Materials-IronAilson Silva AlvesNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Waqar Me172031 TALHA ALI ME172056 .Document15 pagesMuhammad Waqar Me172031 TALHA ALI ME172056 .vj kumarNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument13 pagesChemistrySu Lae Wah ShweNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy: SmeltingDocument42 pagesMetallurgy: SmeltingNaniNo ratings yet
- 19 5 865 PDFDocument11 pages19 5 865 PDFwakasensei99No ratings yet
- Chapter 58 - Tungsten - 2015 - Handbook On The Toxicology of MetalsDocument10 pagesChapter 58 - Tungsten - 2015 - Handbook On The Toxicology of MetalsChanWingSanNo ratings yet
- Magnesium-A ResearchDocument21 pagesMagnesium-A ResearchDhanvini BasavaNo ratings yet
- The World of Mineral Deposits: A Beginner's Guide to Economic GeologyFrom EverandThe World of Mineral Deposits: A Beginner's Guide to Economic GeologyNo ratings yet
- Encoded Physics and ChemDocument5 pagesEncoded Physics and ChemPrince Lancelot100% (1)
- Sweet Potatao As SuperfoodDocument6 pagesSweet Potatao As SuperfoodLyka MahrNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Chemistry HWDocument2 pagesQuantitative Chemistry HWSaira LakhwaniNo ratings yet
- Careram: Tablets 25 MGDocument6 pagesCareram: Tablets 25 MGPriya Ranjan100% (1)
- Total Fluorine Chlorine Sulfur Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument1 pageTotal Fluorine Chlorine Sulfur Aromatic HydrocarbonsAmol AdsulNo ratings yet
- Arabian Journal For Science and Engineering, 2022, 47, 5587-5599Document13 pagesArabian Journal For Science and Engineering, 2022, 47, 5587-5599DanCosminNo ratings yet
- Growing Raspberries & Blackberries in The Home GardenDocument54 pagesGrowing Raspberries & Blackberries in The Home Gardenormonds100% (2)
- Safety Data Sheet Black Magic SFT: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet Black Magic SFT: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The Company123456ccNo ratings yet
- Las Diatomitas en El Peerú PDFDocument10 pagesLas Diatomitas en El Peerú PDFAlex Condori SallucaNo ratings yet
- ACANA PJDocument1 pageACANA PJGabriel CirciogNo ratings yet
- Water QualityDocument5 pagesWater QualityupgradeNo ratings yet
- Assignment General Chemistry 1Document2 pagesAssignment General Chemistry 1john gabriel zapantaNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Manual On Standard Operating Procedures (Document25 pagesA Laboratory Manual On Standard Operating Procedures (shimaa khaterNo ratings yet
- CopperBicinchoninate DOC316.53.01039Document8 pagesCopperBicinchoninate DOC316.53.01039Edan ManzanNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document19 pagesChem 1obaj obajNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Characterization and Mechanical Properties of A356.1 Aluminium Alloy Matrix Composite Reinforced With Mgo Nano ParticlesDocument7 pagesSynthesis, Characterization and Mechanical Properties of A356.1 Aluminium Alloy Matrix Composite Reinforced With Mgo Nano ParticlesinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Alkalinity Management in Shrimp PondDocument3 pagesAlkalinity Management in Shrimp Pondly minh quanNo ratings yet
- 9 - Oils and FatsDocument9 pages9 - Oils and FatsUvvj RajuNo ratings yet
- Asthma Management - AdultsDocument1 pageAsthma Management - AdultsItharshan IndreswaranNo ratings yet
- MSDS CalciteDocument8 pagesMSDS CalcitethemsfxNo ratings yet
- 2 ChemistryDocument10 pages2 ChemistryFatima GhanemNo ratings yet
- Coconut BrixDocument4 pagesCoconut BrixShanaka KulasuriyaNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Laboratory ManualDocument153 pagesA Comprehensive Laboratory ManualVIHIKA ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Atomic AnswersDocument10 pagesAtomic AnswersKelumNo ratings yet
- Supplement Catalogue 2013Document135 pagesSupplement Catalogue 2013Faiz El MakkyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Water Treatment)Document59 pagesLecture 3 (Water Treatment)NomanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 5Document61 pagesChapter 1 5jurilla.johncarlmce1965No ratings yet
- C4 Acid - and - Redox - Ox - NumbersDocument24 pagesC4 Acid - and - Redox - Ox - Numbersdosibo2378No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab ReportDocument6 pagesChemistry Lab ReportNajihah IsmailNo ratings yet
Geralyn&christine (Not Reported)
Geralyn&christine (Not Reported)
Uploaded by
Rofelda Santiago Viana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views15 pagesMagnesium is the lightest structural metal and was first isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy through electrolysis. It has many important uses including in aluminium alloys to make lightweight materials, as a nutrient for humans and plants, and in industrial processes. Magnesium plays a key role in photosynthesis as part of the chlorophyll molecule and is thus essential for all life.
Original Description:
Original Title
geralyn&Christine(not reported)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMagnesium is the lightest structural metal and was first isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy through electrolysis. It has many important uses including in aluminium alloys to make lightweight materials, as a nutrient for humans and plants, and in industrial processes. Magnesium plays a key role in photosynthesis as part of the chlorophyll molecule and is thus essential for all life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views15 pagesGeralyn&christine (Not Reported)
Geralyn&christine (Not Reported)
Uploaded by
Rofelda Santiago VianaMagnesium is the lightest structural metal and was first isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy through electrolysis. It has many important uses including in aluminium alloys to make lightweight materials, as a nutrient for humans and plants, and in industrial processes. Magnesium plays a key role in photosynthesis as part of the chlorophyll molecule and is thus essential for all life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
MAGNESIUM
HISTORY AND DISCOVERY OF
MAGNESIUM ELEMENT
Magnesium (Mg), chemical element, one of the
alkaline-earth metals of Group 2 (Iia) of the
periodic table, and the lightest structural
metal.
Its compounds are widely used in construction
and medicine, and magnesium is one of the
elements essential to all cellular life.
The name magnesium comes from Magnesia, a
district of Thessaly (Greece) where the mineral
magnesia alba was first found.
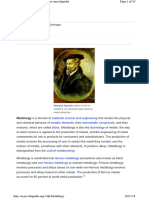
It was first isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy,
who evaporated the mercury from a magnesium
amalgam made by electrolyzing a mixture of moist
magnesia and mercuric oxide.
Magnesium was first isolated by Sir Humphry
Davy, an English chemist, through the
electrolysis of a mixture of magnesium oxide
(MgO) and mercuric oxide (HgO) in 1808.
The first person to recognise that magnesium
was an element was Joseph Black at Edinburgh
in 1755. He distinguished magnesia
(magnesium oxide, MgO) from lime (calcium
oxide, CaO) although both were produced by
heating similar kinds of carbonate rocks,
magnesite and limestone respectively.
Another magnesium mineral called meerschaum
(magnesium silicate) was reported by Thomas
Henry in 1789, who said that it was much used in
Turkey to make pipes for smoking tobacco.
Impure form of metallic magnesium was first
produced in 1792 by Anton Rupprecht who
heated magnesia with charcoal. A pure, but
tiny, amount of the metal was isolated in 1808
by Humphry Davy by the electrolysis of
magnesium oxide.
However, it was the French scientist, Antoine-
Alexandre-Brutus Bussy who made a sizeable
amount of the metal in 1831 by reacting
magnesium chloride with potassium, and he
then studied its properties.
USES OF MAGNESIUM ELEMENT
Magnesium is one-third less dense than aluminium. It improves the
mechanical, fabrication and welding characteristics of aluminium when
used as an alloying agent. These alloys are useful in aeroplane and car
construction.
Magnesium is used in products that benefit from being lightweight, such
as car seats, luggage, laptops, cameras and power tools.
It is also added to molten iron and steel to remove
sulfur.
• As magnesium ignites easily in air and burns with
a bright light, it’s used in flares, fireworks and
sparklers.
Magnesium sulfate is sometimes used as a
mordant for dyes. Magnesium hydroxide is
added to plastics to make them fire retardant.
Magnesium oxide is used to make heat-resistant
bricks for fireplaces and furnaces. It is also
added to cattle feed and fertilisers. Magnesium
hydroxide (milk of magnesia), sulfate (Epsom
salts), chloride and citrate are all used in
medicine.
Grignard reagents are organic magnesium
compounds that are important for the
chemical industry.Magnesium is a nutrient that
the body needs to stay healthy.
Magnesium is important for many processes in
the body, including regulating muscle and
nerve function, blood sugar levels, and blood
pressure and making protein, bone, and DNA.
Magnesium is an essential element in both
plant and animal life. Chlorophyll is the
chemical that allows plants to capture
sunlight, and photosynthesis to take place.
Chlorophyll is a magnesium-centred porphyrin
complex. Without magnesium photosynthesis
could not take place, and life as we know it
would not exist.
Magnesium is the central core of the
chlorophyll molecule in plant tissue. Thus, if
Mg is deficient, the shortage of chlorophyll
results in poor and stunted plant growth.
Magnesium also helps to activate specific
enzyme systems.
You might also like
- Astm d2035Document4 pagesAstm d2035sussy74No ratings yet
- Magnesium (MG) OrigionDocument7 pagesMagnesium (MG) OrigionharoonNo ratings yet
- تقريرDocument5 pagesتقريرjmalahmed853No ratings yet
- Elements Info. GoodDocument59 pagesElements Info. GoodSaid Alauddeen FaiszNo ratings yet
- Alloys MGDocument16 pagesAlloys MGJuan Diego Ospina FlorezNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionImdad JalaliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project MGDocument4 pagesChemistry Project MGPirvu ValentinaNo ratings yet
- Magnesium: 1 CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesMagnesium: 1 Characteristicsdroy21No ratings yet
- Material Engineering: Magnesium (MG)Document10 pagesMaterial Engineering: Magnesium (MG)Yb LangkawiNo ratings yet
- MagCemHistory PDFDocument3 pagesMagCemHistory PDFTaraknath PalNo ratings yet
- Mia G Assignment For FridayDocument8 pagesMia G Assignment For FridayHamim ImamNo ratings yet
- Science PTDocument11 pagesScience PTmarsha enriquezNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument9 pagesAlkaline Earth Metalssamuelstu01No ratings yet
- Magnesium Oxide: Low Sin Wang Am080141 881215-05-5379Document7 pagesMagnesium Oxide: Low Sin Wang Am080141 881215-05-5379idioit2001No ratings yet
- A Flash of Magnesium - Updated VersionDocument1 pageA Flash of Magnesium - Updated Versionelyanacn6No ratings yet
- About MagnesiumDocument2 pagesAbout MagnesiumNUR FAIQAH SYIFANo ratings yet
- De Castro, Jeremy DC (BSFT 1-2) Chem 1223-Long Quiz MidtermDocument4 pagesDe Castro, Jeremy DC (BSFT 1-2) Chem 1223-Long Quiz MidtermJeremy De CastroNo ratings yet
- Extractive Metallurgy of Rare EarthsDocument11 pagesExtractive Metallurgy of Rare EarthsWilliam Jesus Cabrera Meza100% (1)
- Magnesium: Elements Are Building Blocks of Matter. Magnesium Is One of Sixty Three ElementsDocument6 pagesMagnesium: Elements Are Building Blocks of Matter. Magnesium Is One of Sixty Three Elementsanon_593383259No ratings yet
- Form A To PosterDocument6 pagesForm A To PosterEric Manuel Mercedes AbreuNo ratings yet
- Definition of A Heavy Metal: Where FoundDocument2 pagesDefinition of A Heavy Metal: Where FoundarifNo ratings yet
- Element in A PeriodDocument10 pagesElement in A PeriodLavenderPonnuNo ratings yet
- Group 2 The Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument12 pagesGroup 2 The Alkaline Earth MetalsDarya SeredNo ratings yet
- Elling Sen 2015Document22 pagesElling Sen 2015vasoalebizouNo ratings yet
- Copper: Handbook On The Toxicology of Metals 4EDocument22 pagesCopper: Handbook On The Toxicology of Metals 4EChanWingSanNo ratings yet
- Refratechnik Bricks Wear RreasonsDocument8 pagesRefratechnik Bricks Wear Rreasonsengr kazamNo ratings yet
- Magnesium AlloysDocument14 pagesMagnesium AlloysTamerNo ratings yet
- Antimony in SerbiaDocument5 pagesAntimony in SerbiaJovan MilićevićNo ratings yet
- Metal Chemistry Group WorkDocument12 pagesMetal Chemistry Group WorkParis GreenNo ratings yet
- ZincDocument2 pagesZincRajini KumarNo ratings yet
- Magnesiu 1Document2 pagesMagnesiu 1Elkay Rebel-Ikons MillerNo ratings yet
- 204 Aguilarrochelle Fossil Fuels Extraction of MetalsDocument38 pages204 Aguilarrochelle Fossil Fuels Extraction of MetalsJodie CabreraNo ratings yet
- TungstenDocument15 pagesTungstenJon Be GoodNo ratings yet
- Antimony - Special StoneDocument5 pagesAntimony - Special StoneTri UtomoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Crossword 1Document2 pagesChemical Elements Crossword 1David LockartNo ratings yet
- MetallurgyDocument10 pagesMetallurgy呂布No ratings yet
- Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University Lucknow: Assignment On Topic Minerology and Crystallography Submitted ToDocument4 pagesBabasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University Lucknow: Assignment On Topic Minerology and Crystallography Submitted ToKumar ankitNo ratings yet
- Iron Ore, Steel and Coal: by Group 4Document26 pagesIron Ore, Steel and Coal: by Group 4Harshavardhan GuntupalliNo ratings yet
- Lanthanides - Real-Life ApplicationsDocument5 pagesLanthanides - Real-Life ApplicationsSERAPHINENo ratings yet
- Metallurgy: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesMetallurgy: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBobNo ratings yet
- Where Does Chromium Come From?Chromite, An Oxide of Iron, Magnesium, Aluminum, andDocument4 pagesWhere Does Chromium Come From?Chromite, An Oxide of Iron, Magnesium, Aluminum, andJumil PadilloNo ratings yet
- Science Wanted PosterDocument1 pageScience Wanted PosterMayra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of Manganese Health Effects of Manganese Environmental Effects of ManganeseDocument5 pagesChemical Properties of Manganese Health Effects of Manganese Environmental Effects of ManganeseRaj ManiNo ratings yet
- SMK Puteri Seremban: Chemistry ProjectDocument28 pagesSMK Puteri Seremban: Chemistry ProjectHaemaavadhaanaNo ratings yet
- History of Silicon DiodeDocument7 pagesHistory of Silicon DiodeAndreo Miguel H. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- The FTIR Spectra of Raw Magnesite and Sintered MagnesiteDocument5 pagesThe FTIR Spectra of Raw Magnesite and Sintered MagnesiteEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Extracting Metals From Their OresDocument7 pagesExtracting Metals From Their OresChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- Ferromanganese 4Document1 pageFerromanganese 4eximNo ratings yet
- Ammonia: A Very Important Molecule For Biological Organisms To Make Proteins or Nucleic AcidsDocument14 pagesAmmonia: A Very Important Molecule For Biological Organisms To Make Proteins or Nucleic AcidsAnonymous s2DiXhNo ratings yet
- Valeri Consulenza IndustrialeDocument4 pagesValeri Consulenza IndustrialeGualtiero A.N.ValeriNo ratings yet
- Mineral AccountingDocument9 pagesMineral AccountingJudith LlemitNo ratings yet
- Production of Magnesium From Great Salt Lake Utah USADocument8 pagesProduction of Magnesium From Great Salt Lake Utah USAraminNo ratings yet
- Lanthanides: - LanthanumDocument6 pagesLanthanides: - LanthanumlolNo ratings yet
- Raw Materials-IronDocument22 pagesRaw Materials-IronAilson Silva AlvesNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Waqar Me172031 TALHA ALI ME172056 .Document15 pagesMuhammad Waqar Me172031 TALHA ALI ME172056 .vj kumarNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument13 pagesChemistrySu Lae Wah ShweNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy: SmeltingDocument42 pagesMetallurgy: SmeltingNaniNo ratings yet
- 19 5 865 PDFDocument11 pages19 5 865 PDFwakasensei99No ratings yet
- Chapter 58 - Tungsten - 2015 - Handbook On The Toxicology of MetalsDocument10 pagesChapter 58 - Tungsten - 2015 - Handbook On The Toxicology of MetalsChanWingSanNo ratings yet
- Magnesium-A ResearchDocument21 pagesMagnesium-A ResearchDhanvini BasavaNo ratings yet
- The World of Mineral Deposits: A Beginner's Guide to Economic GeologyFrom EverandThe World of Mineral Deposits: A Beginner's Guide to Economic GeologyNo ratings yet
- Encoded Physics and ChemDocument5 pagesEncoded Physics and ChemPrince Lancelot100% (1)
- Sweet Potatao As SuperfoodDocument6 pagesSweet Potatao As SuperfoodLyka MahrNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Chemistry HWDocument2 pagesQuantitative Chemistry HWSaira LakhwaniNo ratings yet
- Careram: Tablets 25 MGDocument6 pagesCareram: Tablets 25 MGPriya Ranjan100% (1)
- Total Fluorine Chlorine Sulfur Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument1 pageTotal Fluorine Chlorine Sulfur Aromatic HydrocarbonsAmol AdsulNo ratings yet
- Arabian Journal For Science and Engineering, 2022, 47, 5587-5599Document13 pagesArabian Journal For Science and Engineering, 2022, 47, 5587-5599DanCosminNo ratings yet
- Growing Raspberries & Blackberries in The Home GardenDocument54 pagesGrowing Raspberries & Blackberries in The Home Gardenormonds100% (2)
- Safety Data Sheet Black Magic SFT: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet Black Magic SFT: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The Company123456ccNo ratings yet
- Las Diatomitas en El Peerú PDFDocument10 pagesLas Diatomitas en El Peerú PDFAlex Condori SallucaNo ratings yet
- ACANA PJDocument1 pageACANA PJGabriel CirciogNo ratings yet
- Water QualityDocument5 pagesWater QualityupgradeNo ratings yet
- Assignment General Chemistry 1Document2 pagesAssignment General Chemistry 1john gabriel zapantaNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Manual On Standard Operating Procedures (Document25 pagesA Laboratory Manual On Standard Operating Procedures (shimaa khaterNo ratings yet
- CopperBicinchoninate DOC316.53.01039Document8 pagesCopperBicinchoninate DOC316.53.01039Edan ManzanNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document19 pagesChem 1obaj obajNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Characterization and Mechanical Properties of A356.1 Aluminium Alloy Matrix Composite Reinforced With Mgo Nano ParticlesDocument7 pagesSynthesis, Characterization and Mechanical Properties of A356.1 Aluminium Alloy Matrix Composite Reinforced With Mgo Nano ParticlesinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Alkalinity Management in Shrimp PondDocument3 pagesAlkalinity Management in Shrimp Pondly minh quanNo ratings yet
- 9 - Oils and FatsDocument9 pages9 - Oils and FatsUvvj RajuNo ratings yet
- Asthma Management - AdultsDocument1 pageAsthma Management - AdultsItharshan IndreswaranNo ratings yet
- MSDS CalciteDocument8 pagesMSDS CalcitethemsfxNo ratings yet
- 2 ChemistryDocument10 pages2 ChemistryFatima GhanemNo ratings yet
- Coconut BrixDocument4 pagesCoconut BrixShanaka KulasuriyaNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Laboratory ManualDocument153 pagesA Comprehensive Laboratory ManualVIHIKA ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Atomic AnswersDocument10 pagesAtomic AnswersKelumNo ratings yet
- Supplement Catalogue 2013Document135 pagesSupplement Catalogue 2013Faiz El MakkyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Water Treatment)Document59 pagesLecture 3 (Water Treatment)NomanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 5Document61 pagesChapter 1 5jurilla.johncarlmce1965No ratings yet
- C4 Acid - and - Redox - Ox - NumbersDocument24 pagesC4 Acid - and - Redox - Ox - Numbersdosibo2378No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab ReportDocument6 pagesChemistry Lab ReportNajihah IsmailNo ratings yet