Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 General Principles and Concepts
1 General Principles and Concepts
Uploaded by
Rommel Espinocilla Jr.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views19 pagesThis document provides an overview of taxation principles and concepts. It defines taxation as the power by which a government raises revenue through compulsory contributions from inhabitants. Taxation is an inherent power of sovereignty and is essential for funding government operations. The document outlines the different types of taxes administered in the Philippines according to the national tax code, including income tax, value-added tax, and estate and donor taxes. It also discusses the characteristics and purposes of taxation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of taxation principles and concepts. It defines taxation as the power by which a government raises revenue through compulsory contributions from inhabitants. Taxation is an inherent power of sovereignty and is essential for funding government operations. The document outlines the different types of taxes administered in the Philippines according to the national tax code, including income tax, value-added tax, and estate and donor taxes. It also discusses the characteristics and purposes of taxation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views19 pages1 General Principles and Concepts
1 General Principles and Concepts
Uploaded by
Rommel Espinocilla Jr.This document provides an overview of taxation principles and concepts. It defines taxation as the power by which a government raises revenue through compulsory contributions from inhabitants. Taxation is an inherent power of sovereignty and is essential for funding government operations. The document outlines the different types of taxes administered in the Philippines according to the national tax code, including income tax, value-added tax, and estate and donor taxes. It also discusses the characteristics and purposes of taxation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Topics
🞂 1. General Principles and Concepts of Taxation
🞂 2. Tax Administration
🞂 3. Concept of Income
🞂 4. Gross Income
🞂 5. Exclusion from Gross Income
🞂 6. Fringe Benefits
🞂 7. Dealings in Property
🞂 8. Deductions from Gross Income
🞂 9. Losses
🞂 10. Income Tax Patterns
🞂 11. Tax On Sole And Corporation
GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND
CONCEPTS OF TAXATION
Inherent Powers of the State
🞂 Police power - to protect citizens and provide for
safety and welfare of society
🞂 Eminent Domain Power – the power to take private
property (with just compensation) for public use.
🞂 Power of Taxation – to enforce contributions to support
the government, and other inherent powers of the state.
What is Taxation?
Ia power by which an independent state,
through its law-making body, raises and
accumulates revenue from its inhabitants to
pay the necessary expenses of the government.
…What is Taxation?
Iis a mode by which government make exactions for
revenue in order to support their existence and carry out
their legitimate objectives (Tax Law and Jurisprudence by
Justice Vitug, 2000).
It is the most pervasive and the strongest of all the powers
of the government. Taxes are the lifeblood of the
government, without which, it cannot subsist.
Nature of taxation power
🞂 Inherent power of sovereignty
🞂 Essentially a legislative functions
🞂 For public purposes
🞂 Territorial in operation
🞂 Tax exemptions of government
🞂 The strongest among the inherent powers of the
government
🞂 Subject constitutional inherent limitations
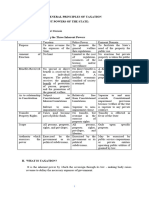
Distinction
Taxation Police power Eminent domain
Concept Enforce Make and To take private
contribution to implement laws property for public
raise govt funds for the general use with just
welfare compensation
Scope Plenary, General power to Take private
comprehensive make and property for public
and supreme implement laws use
Authority Exercise only by Exercise only by May be granted to
government or its government or its public service or
political political public utility
subdivision subdivision companies
Taxation Police power Eminent domain
As purpose Money is taken to Property is taken Private property is
support the or destroyed to taken for public
government promote general use
welfare
Necessity of Tax laws cant be Can be expressly Can be expressly
delegation delegated delegated delegated
Person affected Operates on Operates on Operates on
community or a community or a particular private
class of class of property of an
individuals individuals individual
Taxation Police power Eminent domain
Benefits Continuous Healthy economic Market value of
protection and standard of the property
organized society society expropriated
Amount of Generally no Cost of regulation, No imposition
imposition limits license, etc
Importance Inseparable for Protection, safety Common
the existence of a of society necessities of
nation community
transcend to
individual rights in
property
Taxation Police power Eminent domain
Relationship to Subject Free from Superior to and
constitution constitutional and constitutional may override
inherent limitations constitutional
limitations impairment
provision
Limitations Constraints by Limited by the Bounded by public
constitutional and demand for public purposes and just
inherent interest and due compensation
limitations process
Basis of taxation
🞂 Based on the principle of necessity
🞂 Based on reciprocal duties
Purpose of taxation
🞂 Revenue purpose - to raise revenue by collection
funds or property for the support of the government in
promoting the general welfare and protecting its
inhabitants
🞂 Regulatory purpose –(sumptuary) to regulate
inflation, achieve economic and social stability and to
serve as key instrument for social control
🞂 Compensatory purpose – an excise tax on gasoline
consumed is imposed on vehicle owners using roads.
Objects of taxation
🞂 Persons
◦ Natural person
◦ Juridical person
🞂 Properties
◦ Real
◦ Personal
◦ Tangible or intangible
🞂 Excise objects
◦ Transaction (sell or buy)
◦ Privilege (transfer such donation/estate)
◦ Right
◦ Interest
Doctrines in taxation
🞂 Prospectivity of tax laws
🞂 Imprescriptibility of taxes
🞂 Double taxation
🞂 Escape from taxation (evasion & avoidance)
🞂 Exemption from taxation
🞂 Equitable recoupment
🞂 Set-off taxes
🞂 Compromises
🞂 Power to destroy
General rules of tax situs
Nature of tax Citizenship Residency Within Phil Outside Phil
Income tax Filipino Resident yes Yes
Filipino Nonresident yes No
Alien Resident Yes No
Alien Nonresident yes No
Characteristics of taxes
🞂 Enforced contribution
🞂 Imposed by legislative body
🞂 Proportionate in character
🞂 Payable in the form of money
🞂 Imposed for the purpose of raising revenue
🞂 Used for a public purpose
🞂 Enforced on some persons, properties or rights
🞂 Commonly required to be paid at regular intervals
🞂 Imposed by the sovereign state within its jurisdiction
What is tax law?
🞂 Body of laws which codifies all national tax laws
including income, estate, gift, excise, stamp and other
taxes.
◦ RA 8424 – The comprehensive tax reform of the Philippines
also know as National Internal Revenue Code of 1997 or Tax
code
◦ RA 9337 – Vat reform law
◦ RA 10963 - TRAIN Law, effective Jan 1, 2018.
Taxes under the administration of BIR
🞂 Income tax
🞂 Transfer taxes (estate and donor’s tax)
🞂 Business taxes (VAT, Percentage and Excise)
🞂 Documentary stamps tax (DST)
🞂 Other taxes
Sources of Phil Tax Laws
🞂 Constitution
🞂 Statutes
🞂 Executive orders
🞂 Tax treaties and conventions
🞂 Revenue regulations (Dept of Finance)
🞂 BIR revenue memorandum circulars & memorandum
orders
🞂 BIR rulings
🞂 Judicial decisions
🞂 Local tax ordinances
You might also like
- HR Induction Powerpoint Presentation SlidesDocument53 pagesHR Induction Powerpoint Presentation SlidesVivek SubburamanNo ratings yet
- TEST I: MCQ - THEORY: (1 Point Each) : B. Resident Citizen D. C. Tax Laws Shall Prevail Over GAAPDocument1 pageTEST I: MCQ - THEORY: (1 Point Each) : B. Resident Citizen D. C. Tax Laws Shall Prevail Over GAAPJoe Mari100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To TaxationDocument70 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To TaxationPrincess Diane VicenteNo ratings yet
- Income Tax PrelimDocument19 pagesIncome Tax PrelimCrasher KimNo ratings yet
- TAXATION LAW 1 NOTES (In Progress) v1 PDFDocument73 pagesTAXATION LAW 1 NOTES (In Progress) v1 PDFLoren Bea TulalianNo ratings yet
- Taxation by WMGDocument16 pagesTaxation by WMGLimmuel LumbaNo ratings yet
- Taxation TheoriesDocument8 pagesTaxation TheoriesJean Fajardo BadilloNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation General PrinciplesDocument22 pagesIncome Taxation General PrinciplesashNo ratings yet
- Reo Notes - TaxDocument20 pagesReo Notes - TaxgeexellNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles and Concepts of TaxationDocument56 pagesFundamental Principles and Concepts of TaxationAnastasha GreyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 TaxationDocument27 pagesChapter 1 TaxationBEA CARMONANo ratings yet
- W2 Tax AdministrationDocument82 pagesW2 Tax AdministrationAce AlquinNo ratings yet
- Taxation: Basic Principles of TaxationDocument33 pagesTaxation: Basic Principles of TaxationErika Villanueva MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - TaxationDocument28 pagesChapter 1 - TaxationJoan AbieraNo ratings yet
- Module No 1 - INCOME TAXATION PART 1ADocument8 pagesModule No 1 - INCOME TAXATION PART 1APrinces S. RoqueNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Income TaxDocument9 pagesModule 1 Income TaxTina ValdezNo ratings yet
- TAX.3401 General Principles in Taxation PDFDocument19 pagesTAX.3401 General Principles in Taxation PDFDestiny Lim CalambaNo ratings yet
- Taxation: Basic Principles of TaxationDocument28 pagesTaxation: Basic Principles of TaxationJackielou Lumanog SumogatNo ratings yet
- Fundamental TaxDocument82 pagesFundamental Taxjessejames.supangNo ratings yet
- Basic TaxationDocument13 pagesBasic TaxationMarilyn Perez OlañoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of TaxationDocument7 pagesFundamental Principles of TaxationJoseph AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Overall Review For Prelim Topics: BY: Mrs. Rovelle Siazon, Mr. Aldrian Ventura and Mr. John LiquiganDocument77 pagesOverall Review For Prelim Topics: BY: Mrs. Rovelle Siazon, Mr. Aldrian Ventura and Mr. John LiquiganQueenie ValleNo ratings yet
- General Principles of TaxationDocument14 pagesGeneral Principles of TaxationJulie Ann RosalesNo ratings yet
- Principles of TaxationDocument42 pagesPrinciples of TaxationMarj Jules Lorain JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Module 01 - General Principles of TaxationDocument19 pagesModule 01 - General Principles of TaxationblueplaneskiesNo ratings yet
- Module 01 Fundamrental Principles of TaxationDocument21 pagesModule 01 Fundamrental Principles of TaxationRieXDNo ratings yet
- 01 - Fundamental Principles of Taxation PDFDocument5 pages01 - Fundamental Principles of Taxation PDFdaenielle reyesNo ratings yet
- Module 01 Fundamrental Principles of TaxationDocument21 pagesModule 01 Fundamrental Principles of TaxationDonna Mae FernandezNo ratings yet
- Taxation Law Pre Week 2019Document88 pagesTaxation Law Pre Week 2019harrygolunaNo ratings yet
- TAXATION General PrinciplesDocument26 pagesTAXATION General PrinciplesMarie Mendoza100% (1)
- HQ01 General Principles of TaxationDocument12 pagesHQ01 General Principles of TaxationRenzo RamosNo ratings yet
- As A Power As A Process: Fundamental Principles of TaxationDocument15 pagesAs A Power As A Process: Fundamental Principles of TaxationLeanne TolentinoNo ratings yet
- TAX01 Basic PrinciplesDocument10 pagesTAX01 Basic Principlesanon_812164091No ratings yet
- TaxationDocument129 pagesTaxationNaong-Carrollo Law OfficeNo ratings yet
- TX 101Document7 pagesTX 101Pau SantosNo ratings yet
- Taxation NotesDocument106 pagesTaxation NotesJonathan GiananNo ratings yet
- Tax.3201 1 General Principles in TaxationDocument7 pagesTax.3201 1 General Principles in TaxationAether SkywardNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of TaxationDocument21 pagesFundamentals of TaxationShanille Kate AlegreNo ratings yet
- Principles of TaxationDocument32 pagesPrinciples of TaxationJames GuiruelaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Taxation I. Three Inherent Powers of The StateDocument9 pagesGeneral Principles of Taxation I. Three Inherent Powers of The Statejumawaymichaeljeffrey65No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument7 pagesLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoAngelica DiuNo ratings yet
- Principles of Income TaxationDocument29 pagesPrinciples of Income TaxationAriane Grace Hiteroza MargajayNo ratings yet
- Boss Amo Master IdolDocument87 pagesBoss Amo Master IdolMaria Seleena HipolitoNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Taxation Power of Cir PDFDocument16 pagesGeneral Principles of Taxation Power of Cir PDFGayle LalloNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles OF Taxation: Mr. Mario M. Castro, Cpa, Mba Tax ConsultantDocument19 pagesFundamental Principles OF Taxation: Mr. Mario M. Castro, Cpa, Mba Tax ConsultantKristine Aubrey AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles: 1 Valisnotes Taxation Prof. Enrico Tabag LecturesDocument7 pagesFundamental Principles: 1 Valisnotes Taxation Prof. Enrico Tabag LecturesJaymie ValisnoNo ratings yet
- Module 01 Fundamrental Principles of Taxation RevisedDocument21 pagesModule 01 Fundamrental Principles of Taxation RevisedSly BlueNo ratings yet
- Taxation ReviewerDocument143 pagesTaxation ReviewerChristine Joy V. AlascoNo ratings yet
- Tax 1 - Unit 1. Chapter IDocument6 pagesTax 1 - Unit 1. Chapter IJamaica ManilaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Taxation HandoutsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Taxation HandoutsErika BNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Taxation HandoutsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Taxation HandoutsErika BNo ratings yet
- Basic Taxation and Commercial LawDocument7 pagesBasic Taxation and Commercial LawSarah Mae Sumawang CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of Taxation 2Document33 pagesFundamental Principles of Taxation 2Mila Casandra CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Taxation 2013Document268 pagesTaxation 2013Lenard TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Taxation-ReviewerDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Taxation-ReviewerNikki Coleen SantinNo ratings yet
- General Principles of TaxationDocument26 pagesGeneral Principles of TaxationGilner PomarNo ratings yet
- Income TaxationDocument5 pagesIncome TaxationRhea Mae CarantoNo ratings yet
- Tax Midterms Reviwer-CompressedDocument245 pagesTax Midterms Reviwer-Compressedalia fauniNo ratings yet
- Tax Notes Chapter 1-5Document34 pagesTax Notes Chapter 1-5Jane Antonette ArcalesNo ratings yet
- 2012 Bar Reviewer in TaxationDocument277 pages2012 Bar Reviewer in Taxationkent_009No ratings yet
- A Real Estate Agent's Guide to Pay Less Tax & Build More WealthFrom EverandA Real Estate Agent's Guide to Pay Less Tax & Build More WealthNo ratings yet
- The Economic Policies of Alexander Hamilton: Works & Speeches of the Founder of American Financial SystemFrom EverandThe Economic Policies of Alexander Hamilton: Works & Speeches of the Founder of American Financial SystemNo ratings yet
- PrayerDocument1 pagePrayerRommel Espinocilla Jr.No ratings yet
- Separating Components of Mixed Costs Seatwork No.1Document2 pagesSeparating Components of Mixed Costs Seatwork No.1Rommel Espinocilla Jr.No ratings yet
- 4 Sources of IncomeDocument16 pages4 Sources of IncomeRommel Espinocilla Jr.No ratings yet
- Scanned DocumentsDocument1 pageScanned DocumentsRommel Espinocilla Jr.No ratings yet
- Benguet Corp Vs CBAADocument11 pagesBenguet Corp Vs CBAAtink echivereNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Income Taxation (Individual)Document8 pagesLecture 2 - Income Taxation (Individual)Lovenia Magpatoc100% (1)
- Sitel Phils Corp vs. Commissioner of Internal Revenue 817 SCRA 193Document14 pagesSitel Phils Corp vs. Commissioner of Internal Revenue 817 SCRA 193Jay Telan IINo ratings yet
- Trusts and EstatesDocument140 pagesTrusts and EstatesSam Bam100% (1)
- Improperly Accumulated Earnings Tax Return: Mac Arthur Highway, Brgy. Dolores, City of San Fernando, PampangaDocument3 pagesImproperly Accumulated Earnings Tax Return: Mac Arthur Highway, Brgy. Dolores, City of San Fernando, PampangaTrisha Mae Mendoza MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Please Open An Account Via PRESTIA OnlineDocument2 pagesPlease Open An Account Via PRESTIA OnlineChris JonesNo ratings yet
- Revenue Memorandum Order No. 32-07: October 8, 2007 October 8, 2007Document14 pagesRevenue Memorandum Order No. 32-07: October 8, 2007 October 8, 2007nathalie velasquezNo ratings yet
- Progressive Development Corporation vs. Quezon City GR 36081, 24 April 1989Document1 pageProgressive Development Corporation vs. Quezon City GR 36081, 24 April 1989Gela Bea BarriosNo ratings yet
- Sa2 TaxDocument52 pagesSa2 TaxIsaiah John Domenic M. CantaneroNo ratings yet
- Hilado V Collector of Internal RevenueDocument2 pagesHilado V Collector of Internal RevenueErnest Levanza83% (6)
- General Principles 2017Document11 pagesGeneral Principles 2017Vertine Paul Fernandez BelerNo ratings yet
- ZknamcxDocument68 pagesZknamcxdominic100% (1)
- MARUBENI Vs CIR TAXDocument2 pagesMARUBENI Vs CIR TAXLemuel Angelo M. EleccionNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Deductions and Credits: Learning ObjectivesDocument22 pagesOrdinary Deductions and Credits: Learning ObjectivesS. M. MUNAWAR MAHTAB 1603061No ratings yet
- 03 Chap 03 05 Mamalateo 2019 Tax BookDocument151 pages03 Chap 03 05 Mamalateo 2019 Tax BookZachary Siayngco100% (1)
- CIR v. Central Luzon Drug CorpDocument2 pagesCIR v. Central Luzon Drug CorpSophia SyNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Taxation: Pakistan Tax Bar AssociationDocument6 pagesDiploma in Taxation: Pakistan Tax Bar AssociationAbdul wahabNo ratings yet
- CH 0372704327Document8 pagesCH 0372704327barjotNo ratings yet
- Gancayco vs. Collector - Case DigestDocument6 pagesGancayco vs. Collector - Case DigestYvon BaguioNo ratings yet
- CPAR Filing, Penalties, and Remedies (Batch 89) HandoutDocument25 pagesCPAR Filing, Penalties, and Remedies (Batch 89) HandoutlllllNo ratings yet
- Overview of Canadian Income TaxDocument8 pagesOverview of Canadian Income TaxSaf PopalNo ratings yet
- DTAA With USA PDFDocument23 pagesDTAA With USA PDFDehradun MootNo ratings yet
- Question 44 (65 Minutes) (Chapters 11, 12) : NotesDocument2 pagesQuestion 44 (65 Minutes) (Chapters 11, 12) : Notesromie2bNo ratings yet
- CIR vs. de La Salle University (G.R. No. 196596)Document18 pagesCIR vs. de La Salle University (G.R. No. 196596)Vincent RachNo ratings yet
- TaxDocument9 pagesTaxRossette AnaNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 206526 January 28, 2015 Winebrenner & Iñigo Insurance BROKERS, INC., Petitioner, Commissioner of Internal RevenueDocument8 pagesG.R. No. 206526 January 28, 2015 Winebrenner & Iñigo Insurance BROKERS, INC., Petitioner, Commissioner of Internal RevenueAnathema DeviceNo ratings yet
- HQ05 - Capital Gains TaxationDocument10 pagesHQ05 - Capital Gains TaxationClarisaJoy Sy100% (3)
- Dimaampao Tax NotesDocument63 pagesDimaampao Tax NotesMaruSalvatierra100% (1)