Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Viral Infection of The Eyes: Name: Jean Clark Phobe L. Razo Section: BSN 1-Silver
Viral Infection of The Eyes: Name: Jean Clark Phobe L. Razo Section: BSN 1-Silver
Uploaded by
Phobe RazoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Viral Infection of The Eyes: Name: Jean Clark Phobe L. Razo Section: BSN 1-Silver
Viral Infection of The Eyes: Name: Jean Clark Phobe L. Razo Section: BSN 1-Silver
Uploaded by
Phobe RazoCopyright:
Available Formats
Viral Infection of the Eyes
NAME: JEAN CLARK PHOBE L. RAZO
SECTION: BSN 1- SILVER
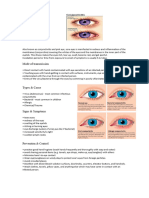
Hemorrhagic Conjunctivitis
Isa derivative of the highly contagious
conjunctivitis virus, also known as pink eye and is
characterized by sudden onset of painful, swollen,
red eyes, with conjunctival hemorrhaging and
excessive tearing
System Involved
It is involved to our sensory system
Pathogen:
usually caused by the picornaviruses,
especially enterovirus 70 and coxsackievirus
A24
Reservoir & Mode of Transmission:
Most viruses that cause conjunctivitis spread
through hand-to-eye contact by hands or objects
that are contaminated with the infectious virus.
Having contact with infectious tears, eye discharge,
fecal matter, or respiratory discharges can
contaminate hands.
Signs and Symptoms:
When infected with AHC, patients will experience:
• Painful
• Red eyes
• Swelling of the conjunctival tissue
• frequent mucus discharge from the eyes accompanied by excessive tearing and
subconjunctival hemorrhaging.
Laboratory Diagnosis
A rapidimmunodetection assay is often used to
confirm the diagnosis, and PCR can be used to
determine the serotype.
Patient Care/Nursing Considerations:
• Apply warm and cold water
• Avoid sharing of washcloths and towels.
• Cleaning of the eyelids with wet cloth will keep the
surrounding of the eyes clean and it can also
promote comfort.
Adenoviral Conjunctivitis
Adenoviral conjunctivitis (Ad-CS), also known as “pink
eye,” is one of the most common eye infections
worldwide. Ad-CS is highly symptomatic, causing
discomfort, tearing, lid swelling, photophobia, and
decreased vision.
System involved:
This is also involved the sensory system
Pathogen:
Viralconjunctivitis is a highly contagious acute
conjunctival infection usually caused by an
adenovirus
Reservoir & Mode of Transmission:
The virus can spread through contact with droplets
from the nose and throat of an infected person
(e.g., during coughing or sneezing) or by touching
hands, an object, or surface with the virus on it and
then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes before hand
washing
Signs & Symptoms:
When infected with Adenoviral Conjunctivitis, patients will experience:
• "Red eye" noted by the patient
• watery during the day and crusting noted in the mornings
• swollen lids
• patient noticed in one eye first, perhaps with later spread to the opposite eye
• in pharyngoconjunctival fever—sore throat, fever, and headache may be present
Laboratory Diagnosis:
Adenovirus infections can be identified using
antigen detection, polymerase chain reaction
(PCR), virus isolation, and serology.
Patient Care/Nursing Considerations:
• usually supportive
• cool compress and artificial tears for comfort several times a day
• prevent contagious spread (including washing sheets and pillowcases,
handwashing, and cleaning of instrumentation in the physician’s office).
Temporary leave of absence should be considered for patients who work with the
public who have active infection.
• NO antibiotic or antiviral drops are routinely used. In cases where bacterial co- or
super- infection is suspect, antibiotic drops may be indicated. There are no
antiviral drugs approved for adenoviral conjunctivitis
• in EKC only: pseudomembranes should be manually peeled every 2-3days.
Topical corticosteroids may be needed (i.e. prednisolone acetate, 0.125%, q.i.d.)
to prevent scarring
You might also like
- CASE STUDY - ConjunctivitisDocument9 pagesCASE STUDY - ConjunctivitisAngela CancinoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation On Corneal Ulcers Power PointDocument24 pagesClinical Presentation On Corneal Ulcers Power Pointgideon A. owusu88% (8)
- Sore Eyes (Conjunctivitis/Pink Eyes)Document21 pagesSore Eyes (Conjunctivitis/Pink Eyes)Diana MaeNo ratings yet
- CONJUNCTIVITISDocument67 pagesCONJUNCTIVITISNauli Panjaitan86% (7)
- 1st READING TEST PDFDocument171 pages1st READING TEST PDFNars Oet Materyales100% (2)
- Sore EyesDocument2 pagesSore EyescpborneoNo ratings yet
- Eye Pain and DischargeDocument53 pagesEye Pain and DischargeJitendra ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Viral Infection On HumansDocument29 pagesViral Infection On HumansMashimallowNo ratings yet
- ConjunctivitisDocument7 pagesConjunctivitisTabarak BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivits (Viral)Document5 pagesConjunctivits (Viral)lkdsjflsNo ratings yet
- Konjungtivitis Dan KeratitisDocument117 pagesKonjungtivitis Dan KeratitisResti Puteri ApriyuslimNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)Document15 pagesConjunctivitis (Pink Eye)MD TristanNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis - UpToDateDocument19 pagesConjunctivitis - UpToDateEddie Mondragon GomezNo ratings yet
- MICRO BIOLOGY ConjunctivitisDocument5 pagesMICRO BIOLOGY Conjunctivitisbabyko143444No ratings yet
- Bacterial and Viral ConjunctivitisDocument31 pagesBacterial and Viral ConjunctivitisSiddhant GautamNo ratings yet
- Viral Conjunctivitis: Daniel Solano Craig N. CzyzDocument6 pagesViral Conjunctivitis: Daniel Solano Craig N. CzyzJavier BarretoNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis On The Rise - Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and TreatmentDocument2 pagesConjunctivitis On The Rise - Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and TreatmentKamatNo ratings yet
- CONJUNCTIVITISDocument7 pagesCONJUNCTIVITISogwal andrewictynetNo ratings yet
- CONJUNCTIVITISDocument2 pagesCONJUNCTIVITIScpborneoNo ratings yet
- Viral ConjunctivitisDocument15 pagesViral ConjunctivitisMary Cathlane TeroNo ratings yet
- ConjunctivitisDocument15 pagesConjunctivitisPuviyarasiNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis (H10)Document3 pagesConjunctivitis (H10)unit cdc pkd raubNo ratings yet
- Viral Conjunctivitis AlgorithmDocument8 pagesViral Conjunctivitis AlgorithmRobert Selvin MNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis (Bacterial and Viral)Document2 pagesConjunctivitis (Bacterial and Viral)Abhay SagarNo ratings yet
- H3e8g OczbiDocument7 pagesH3e8g OczbiShumaila AzamNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis and Other Ocular Lesions Opthalmology ClassDocument43 pagesConjunctivitis and Other Ocular Lesions Opthalmology ClassJaikrit SinghNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis 1Document28 pagesConjunctivitis 1Nrs Sani Sule MashiNo ratings yet
- Red Eyes PresentationDocument34 pagesRed Eyes Presentationflokathy12No ratings yet
- Eye InfectionsDocument16 pagesEye InfectionsrodericpalanasNo ratings yet
- Author: Section Editor: Deputy EditorDocument20 pagesAuthor: Section Editor: Deputy EditorEvy Alvionita YurnaNo ratings yet
- Contact Lens-Associated Microbial KeratitisDocument39 pagesContact Lens-Associated Microbial Keratitisณัช เกษมNo ratings yet
- ABC of Red EyeDocument5 pagesABC of Red Eyeakmar887No ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis UpToDateDocument21 pagesConjunctivitis UpToDateRosejane MagauayNo ratings yet
- ConjungtivitisDocument9 pagesConjungtivitisDiana Fadly MatondangNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis: Justine S. VillanuevaDocument96 pagesConjunctivitis: Justine S. VillanuevaTee VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis - AAFPDocument23 pagesConjunctivitis - AAFP21613284No ratings yet
- ConjunctivitisDocument52 pagesConjunctivitisFiona H.D.100% (2)
- Overview Agent Penyebab Infeksi MataDocument31 pagesOverview Agent Penyebab Infeksi MataCharina SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis - 2015Document31 pagesBacterial Conjunctivitis - 2015Hamza RiazNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument11 pagesCase PresentationJOhn DiCeNo ratings yet
- Mata MerahDocument119 pagesMata MerahAzwanHamdiNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis 120201025034 Phpapp02Document34 pagesConjunctivitis 120201025034 Phpapp02Ilham RafisNo ratings yet
- Adenovirus Factsheet 508Document2 pagesAdenovirus Factsheet 508Suraj DuttaNo ratings yet
- KonjungtivitisDocument46 pagesKonjungtivitisBakri BayquniNo ratings yet
- BLEPHARITISDocument25 pagesBLEPHARITISSrijana MahatoNo ratings yet
- Eye Emergency: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedDocument63 pagesEye Emergency: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedYousef Al-AmeenNo ratings yet
- All About Gonococcal ConjunctivitisDocument2 pagesAll About Gonococcal Conjunctivitisdanna aflahNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis (Inflammation of The Eye)Document3 pagesConjunctivitis (Inflammation of The Eye)Jzia DadieNo ratings yet
- MS SensesDocument13 pagesMS SensesFrechel Ann Landingin PedrozoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ConjunctivitisDocument32 pagesBacterial ConjunctivitisYouhengNo ratings yet
- ConjunctivitisDocument19 pagesConjunctivitiskatrina_velasco_1No ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis 1Document8 pagesConjunctivitis 1Opubo BrownNo ratings yet
- Konjungtivitis ViralDocument6 pagesKonjungtivitis ViralNia FitriyaniNo ratings yet
- Bacteria PowerpointDocument21 pagesBacteria PowerpointOpubo BrownNo ratings yet
- Eye & Ear - Eye - Conjunctivitis - PharmaPedia - PharmaGatesDocument9 pagesEye & Ear - Eye - Conjunctivitis - PharmaPedia - PharmaGatesIslam FawzyNo ratings yet
- L2E Red EyeDocument39 pagesL2E Red EyeazraNo ratings yet
- Conjunctival Disorders OghreDocument59 pagesConjunctival Disorders Oghreteamtruth50No ratings yet
- 09conjunctival Infections 13-12-07Document55 pages09conjunctival Infections 13-12-07ari rujatiNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Red EyeDocument1 pagePrevention of Red EyeMaxcer AdNo ratings yet
- Health Care Services and Their Levels of CareDocument22 pagesHealth Care Services and Their Levels of CarePhobe RazoNo ratings yet
- TODDLERDocument12 pagesTODDLERPhobe RazoNo ratings yet
- VIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM SayenDocument12 pagesVIRAL INFECTIONS OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM SayenPhobe RazoNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Presentationml Presentationrendition1-4Document11 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Presentationml Presentationrendition1-4Phobe RazoNo ratings yet
- Preschool Parent Handbook 09-10Document20 pagesPreschool Parent Handbook 09-10Mawan ManyokNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics QuestionsDocument6 pagesPediatrics QuestionsJonathan A. SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Horizon Academic Research Journal Vol. 4 No. 2Document348 pagesHorizon Academic Research Journal Vol. 4 No. 2Horizon AcademicNo ratings yet
- Jovr 12 193Document12 pagesJovr 12 193supaidi97No ratings yet
- Eye DropDocument36 pagesEye DropArnold DanielNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis 1385 PILDocument2 pagesConjunctivitis 1385 PILMicius91No ratings yet
- 8 Most Common College DiseasesDocument13 pages8 Most Common College DiseasesgizleNo ratings yet
- Arnold Devries-Therapeutic Fasting (1963)Document48 pagesArnold Devries-Therapeutic Fasting (1963)Silambarasu KaruppiahNo ratings yet
- Vaka TustimeDocument887 pagesVaka TustimeMohamed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Diagnosa Non Spesialistik Di PCareDocument13 pagesDiagnosa Non Spesialistik Di PCarelooklistenfeelNo ratings yet
- Qs Ophthalmology Lecture NotesDocument23 pagesQs Ophthalmology Lecture NotesAmin Zeid0% (1)
- MCQ OpthalmologyDocument45 pagesMCQ OpthalmologyMuhdZaeed100% (1)
- Viral Infections of HumansDocument89 pagesViral Infections of HumansMark Vincent JanoyogNo ratings yet
- Selected Differential Diagnosis of Red Eye: Table 1Document3 pagesSelected Differential Diagnosis of Red Eye: Table 1Rian DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ophthalmology Made Easy®Document419 pagesClinical Ophthalmology Made Easy®Uzair Akhter100% (2)
- Chalazion and Hordeolum: Adult & Pediatric: BackgroundDocument6 pagesChalazion and Hordeolum: Adult & Pediatric: BackgroundHocie Trinanda SardiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Riot Control Agents - 441 - 484Document44 pagesChapter 13 - Riot Control Agents - 441 - 484Darko Zlatkovik100% (1)
- Ophthalmology Question BankDocument45 pagesOphthalmology Question BankVsmfhjn0% (1)
- Compile Soal Mata PreklinikDocument77 pagesCompile Soal Mata PreklinikFika RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Lucas v. TuanoDocument25 pagesLucas v. TuanojNo ratings yet
- Activity in Medical SurgicalDocument9 pagesActivity in Medical SurgicalAlbert LaporeNo ratings yet
- (+) Pain and (+) Discharge (-) Pain and (+) Discharge: Red EyeDocument1 page(+) Pain and (+) Discharge (-) Pain and (+) Discharge: Red EyeMariel TagazaNo ratings yet
- Simulado para Prova de Proficiência em Inglês Da FFLCHDocument8 pagesSimulado para Prova de Proficiência em Inglês Da FFLCHlilianoakNo ratings yet
- Homœopathic Materia MedicaDocument193 pagesHomœopathic Materia MedicaMohammad ShoebNo ratings yet
- 144 Diagnosa Non SpesialistikDocument27 pages144 Diagnosa Non SpesialistikFebriana AtmanegaraNo ratings yet
- Ocular SymptomatologyDocument7 pagesOcular SymptomatologySharon Danisha Vaswani100% (2)
- Health Education and Contagious Diseases Group 1Document32 pagesHealth Education and Contagious Diseases Group 1Jason CamaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 2Document235 pagesOphthalmology 2yididiyagirma30No ratings yet