Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsMatters at Hon'ble High Court
Matters at Hon'ble High Court
Uploaded by
ayesha30062004The Calcutta High Court is the oldest high court in India, established in 1862. It has jurisdiction over West Bengal and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The high court has both original and appellate jurisdiction over civil and criminal cases. It can issue writs for enforcing fundamental rights or other purposes under Article 226 of the Constitution. The high court also has powers of judicial superintendence over lower courts under Article 227. Common types of cases dealt with include writ petitions, petitions challenging orders of the Labour Relations Tribunal, and cases filed under the supervisory jurisdiction of Article 227.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Law Notes (LL.B Notes) - Constitutional Law-2Document41 pagesLaw Notes (LL.B Notes) - Constitutional Law-2balaji100% (2)
- Here Is The Voter Fraud EvidenceDocument81 pagesHere Is The Voter Fraud EvidenceJoshua Sanchez100% (4)
- Indian High CourtsDocument9 pagesIndian High CourtsManmohan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- The High CourtDocument17 pagesThe High CourtAditya JhaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - The Indian High Court Act 1861Document9 pages1.3 - The Indian High Court Act 1861Syed Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- Indian JudiciaryDocument9 pagesIndian JudiciaryAhana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- The Indian High Courts Act of 1861Document2 pagesThe Indian High Courts Act of 1861shriya rao0% (1)
- High Courts Upsc Notes 92Document6 pagesHigh Courts Upsc Notes 92rajhp54321No ratings yet
- The Supreme Court and High Court JurisdictionDocument4 pagesThe Supreme Court and High Court JurisdictionAisha singhNo ratings yet
- Writ JurisdictionDocument20 pagesWrit JurisdictionMuskan SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian JudiciaryDocument51 pagesIndian JudiciaryPavan BangaloreNo ratings yet
- Article 8. Sec 5Document34 pagesArticle 8. Sec 5Ann GuillemNo ratings yet
- Writ JurisdictionDocument60 pagesWrit Jurisdictionaayush lathiNo ratings yet
- Writs 2Document5 pagesWrits 2SarvikaNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of The Supreme CourtDocument17 pagesJurisdiction of The Supreme CourtraghavNo ratings yet
- CPC - Jurisdiction of The CourtsDocument23 pagesCPC - Jurisdiction of The Courtsgaurav singhNo ratings yet
- Civics Chapter 4 - The Supreme Court 2023Document16 pagesCivics Chapter 4 - The Supreme Court 2023Thangsian KhaiNo ratings yet
- The High CourtSDocument17 pagesThe High CourtSUPSC AspirantNo ratings yet
- Judiciary 29062022 045250pmDocument18 pagesJudiciary 29062022 045250pmJehanzaib AminNo ratings yet
- Powers and Functions of High Court in IndiaDocument17 pagesPowers and Functions of High Court in Indiasai kiran gudisevaNo ratings yet
- Hirarchy of Courts 33Document27 pagesHirarchy of Courts 33drishyasck123No ratings yet
- Cons Law Main ProjectDocument11 pagesCons Law Main ProjectBhawna Jha 036No ratings yet
- Discuss The Jurisdiction and Powers of High CourtsDocument4 pagesDiscuss The Jurisdiction and Powers of High CourtsMrinmoy BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Right To Constitutional Remedies: Article-32Document22 pagesRight To Constitutional Remedies: Article-32Dolphin100% (1)
- Jurisdiction of SCDocument5 pagesJurisdiction of SCraghavNo ratings yet
- JUDICIAL SYSTEM IN KENYA - Lesson 5Document9 pagesJUDICIAL SYSTEM IN KENYA - Lesson 5arnoldochieng125No ratings yet
- JurisdictionDocument64 pagesJurisdictionPragya Gupta100% (2)
- Anushka Constitution ProjectDocument16 pagesAnushka Constitution ProjectSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Powers and Functions of High Court in IndiaDocument11 pagesPowers and Functions of High Court in Indiasai kiran gudisevaNo ratings yet
- Article VIII Judiciary Branch ConstiDocument29 pagesArticle VIII Judiciary Branch ConstiDeanne Mitzi Somollo100% (1)
- Supreme Court and The Constitutional ProcessDocument34 pagesSupreme Court and The Constitutional ProcessKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- High Court VisitDocument8 pagesHigh Court Visitminturaha.blg92No ratings yet
- GOVT S K S J T Institute of Engineering KR Circle, Bengalore-560001Document10 pagesGOVT S K S J T Institute of Engineering KR Circle, Bengalore-560001Jeevan ShettyNo ratings yet
- Module 26Document11 pagesModule 26Siddhant ChandakNo ratings yet
- The Indian Judiciary - Supreme Court, High Court & Subordinate CourtsDocument6 pagesThe Indian Judiciary - Supreme Court, High Court & Subordinate CourtsCOW GUPTANo ratings yet
- GSTAT & HC CA. Vyankatesh AgarwalDocument47 pagesGSTAT & HC CA. Vyankatesh Agarwalpramodmurkya13No ratings yet
- 12 Solved Paper - I-2018-Practice and ProcedureDocument20 pages12 Solved Paper - I-2018-Practice and Proceduredumbthings1729No ratings yet
- Union Judiciary Part IIDocument23 pagesUnion Judiciary Part IIDevendraNo ratings yet
- High CourtDocument4 pagesHigh CourtSaketh JainNo ratings yet
- Courts and ProcedureDocument6 pagesCourts and ProcedureJohn MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of IndiaDocument7 pagesSupreme Court of Indiaanuradha KNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy and Jurisdiction of CourtsDocument56 pagesHierarchy and Jurisdiction of Courtsaayush lathiNo ratings yet
- Enc Encoded 4 M Wes 8 P4 A 8 RVL VZHYz NY4 Uu 2 ZD KM 7 X QBT4 Aqlol EYGsj KTNRDNG WJADocument5 pagesEnc Encoded 4 M Wes 8 P4 A 8 RVL VZHYz NY4 Uu 2 ZD KM 7 X QBT4 Aqlol EYGsj KTNRDNG WJASaketh JainNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of Courts in BangladeshDocument21 pagesJurisdiction of Courts in BangladeshAyesha Kanta100% (1)
- High Court (1) - WatermarkDocument60 pagesHigh Court (1) - WatermarkVijayNo ratings yet
- Legal Methods (Ultimate Version)Document45 pagesLegal Methods (Ultimate Version)oshin agrawalNo ratings yet
- By: Atty. Jose Aguila GrapilonDocument31 pagesBy: Atty. Jose Aguila GrapilonDiaz Ragu100% (1)
- Powers and Functions of High Court in IndiaDocument9 pagesPowers and Functions of High Court in Indiasai kiran gudiseva100% (1)
- Polity SelfDocument30 pagesPolity Selfsupriya debbarmaNo ratings yet
- Law Notes (LL.B Notes) - Constitutional Law-2Document34 pagesLaw Notes (LL.B Notes) - Constitutional Law-2Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of IndiaDocument20 pagesSupreme Court of IndiaMAYANK GUPTANo ratings yet
- High Court and Its JurisdictionDocument7 pagesHigh Court and Its JurisdictionHari GovindNo ratings yet
- Powers and Functions of High Court in IndiaDocument15 pagesPowers and Functions of High Court in Indiasai kiran gudisevaNo ratings yet
- The High Courts of IndiaDocument8 pagesThe High Courts of IndiaNidhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Consti Mohit KumarDocument3 pagesConsti Mohit KumarTushar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Indian Legal System An IntroductionDocument32 pagesIndian Legal System An Introductionptiypiya100% (1)
- Judicial System of India - Hierarchy of CourtsDocument10 pagesJudicial System of India - Hierarchy of CourtsAndroid app developerNo ratings yet
- Constitution Law 2 This Notes For 1st Year LLB 2nd SemesterDocument45 pagesConstitution Law 2 This Notes For 1st Year LLB 2nd SemesterPrisha BauskarNo ratings yet
- Types of Writs:: Writs Under The Constitution OfindiaDocument4 pagesTypes of Writs:: Writs Under The Constitution OfindiaSmiti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Courts and Procedure in England and in New JerseyFrom EverandCourts and Procedure in England and in New JerseyNo ratings yet
- Sip LakeDocument215 pagesSip Lakeayesha30062004No ratings yet
- MANU MH 3022 2018 BomDocument53 pagesMANU MH 3022 2018 Bomayesha30062004No ratings yet
- Memorial National Moot Court Competition 070223 1 461021Document33 pagesMemorial National Moot Court Competition 070223 1 461021ayesha30062004No ratings yet
- Narayanan V State of Keralawatermark 1553168Document19 pagesNarayanan V State of Keralawatermark 1553168ayesha30062004No ratings yet
- PYQsDocument10 pagesPYQsayesha30062004No ratings yet
- L.G.R. Enterprises v. P. AnbazhagDocument7 pagesL.G.R. Enterprises v. P. AnbazhagRakshit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Masereka V Muhindo (Divorce Appeal No 8 of 2017) 2023 UGHCFD 3 (6 February 2023)Document6 pagesMasereka V Muhindo (Divorce Appeal No 8 of 2017) 2023 UGHCFD 3 (6 February 2023)Derrick HartNo ratings yet
- X DacanayDocument2 pagesX DacanayTynny Roo BelduaNo ratings yet
- Ahenkora Ii v. OfeDocument7 pagesAhenkora Ii v. OfeZACHARIAH MANKIRNo ratings yet
- The Legal Framework Order FINALLDocument7 pagesThe Legal Framework Order FINALLazharmazhar074100% (1)
- Summary of The Petitions - Anti Terrorism LawDocument9 pagesSummary of The Petitions - Anti Terrorism LawHoneylyn Jiza WaycoNo ratings yet
- Lajeromeny Brown Sentencing OrderDocument2 pagesLajeromeny Brown Sentencing OrderFOX54 News HuntsvilleNo ratings yet
- Notice of Motion 1display - PDFDocument3 pagesNotice of Motion 1display - PDFVarsha MangtaniNo ratings yet
- Durevs. JoDocument7 pagesDurevs. JoCharlene LaurinoNo ratings yet
- P L D 2016 Supreme Court 347Document8 pagesP L D 2016 Supreme Court 347Yahia MustafaNo ratings yet
- (Anil Choudhary) Member (Judicial) : (Order Dictated in The Open Court)Document2 pages(Anil Choudhary) Member (Judicial) : (Order Dictated in The Open Court)Akash chandoraNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Rti Act 2005Document11 pagesMCQ - Rti Act 2005Mini DipiNo ratings yet
- Consti Sem 4Document12 pagesConsti Sem 4Prashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Iowa BEV PAC 6098 - 6098 - B - ExpendituresDocument7 pagesIowa BEV PAC 6098 - 6098 - B - ExpendituresZach EdwardsNo ratings yet
- S.M.C. 1 2023Document5 pagesS.M.C. 1 2023Khawaja BurhanNo ratings yet
- LLS - Administrative Dutch LawDocument9 pagesLLS - Administrative Dutch Lawotis flowerNo ratings yet
- Colbert v. State Farm Mutual Automobile Insurance Company - DocketDocument2 pagesColbert v. State Farm Mutual Automobile Insurance Company - DocketShagun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Vijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors vs. Union of India & OrsDocument206 pagesVijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors vs. Union of India & OrsSanskar BarekarNo ratings yet
- Separation of Power in UK AssignmentDocument2 pagesSeparation of Power in UK Assignmentsapuni NayananayakeNo ratings yet
- Taule vs. Santos - Full TextDocument14 pagesTaule vs. Santos - Full TextLouvanne Jessa Orzales BesingaNo ratings yet
- UK Public LawDocument88 pagesUK Public Lawjmn.elmNo ratings yet
- People v. Baay y FalcoDocument9 pagesPeople v. Baay y FalcoAlex FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Mayelane V Ngwenyama 2013 SummaryDocument2 pagesMayelane V Ngwenyama 2013 SummarymunyanganerichmondNo ratings yet
- ConstitutiondayDocument2 pagesConstitutiondayapi-597200800No ratings yet
- Evolution of Philippine ConstitutionDocument19 pagesEvolution of Philippine ConstitutionKhen KhenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument41 pagesUntitledCherry Grace Lapnite NumeronNo ratings yet
- 2023 BAR SYLLABUS TRACKER - XLSX - Remedial LawDocument5 pages2023 BAR SYLLABUS TRACKER - XLSX - Remedial LawAiza CabenianNo ratings yet
- Case Digest 7Document3 pagesCase Digest 7Princess PanNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines v. MuletaDocument2 pagesPeople of The Philippines v. Muletarafael.louise.roca2244No ratings yet
Matters at Hon'ble High Court
Matters at Hon'ble High Court
Uploaded by
ayesha300620040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views46 pagesThe Calcutta High Court is the oldest high court in India, established in 1862. It has jurisdiction over West Bengal and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The high court has both original and appellate jurisdiction over civil and criminal cases. It can issue writs for enforcing fundamental rights or other purposes under Article 226 of the Constitution. The high court also has powers of judicial superintendence over lower courts under Article 227. Common types of cases dealt with include writ petitions, petitions challenging orders of the Labour Relations Tribunal, and cases filed under the supervisory jurisdiction of Article 227.
Original Description:
Original Title
Matters at Hon’ble High Court
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Calcutta High Court is the oldest high court in India, established in 1862. It has jurisdiction over West Bengal and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The high court has both original and appellate jurisdiction over civil and criminal cases. It can issue writs for enforcing fundamental rights or other purposes under Article 226 of the Constitution. The high court also has powers of judicial superintendence over lower courts under Article 227. Common types of cases dealt with include writ petitions, petitions challenging orders of the Labour Relations Tribunal, and cases filed under the supervisory jurisdiction of Article 227.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views46 pagesMatters at Hon'ble High Court
Matters at Hon'ble High Court
Uploaded by
ayesha30062004The Calcutta High Court is the oldest high court in India, established in 1862. It has jurisdiction over West Bengal and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The high court has both original and appellate jurisdiction over civil and criminal cases. It can issue writs for enforcing fundamental rights or other purposes under Article 226 of the Constitution. The high court also has powers of judicial superintendence over lower courts under Article 227. Common types of cases dealt with include writ petitions, petitions challenging orders of the Labour Relations Tribunal, and cases filed under the supervisory jurisdiction of Article 227.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 46
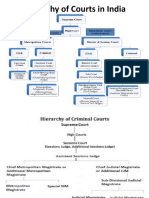
Matters at Hon’ble High Court:
Establishment of Hon’ble High Court:
Calcutta High Court is the oldest High
Court in India. It was established on
1st July, 1862 under the High Court’s
Act,1861. It has jurisdiction over the
State of West Bengal & the Union
Territory of Andaman & Nicobar
Islands. Sanctioned Judge strength is
72. Ashis Kumar Gupta
Jurisdiction of the High Court’s:
• The jurisdiction of each high court depends on the letters
Patent issued by her Majesty. She could give them power to
exercise all civil, criminal, intestate, testamentary, admiralty
and matrimonial jurisdiction. She could also confer on them
original and appellate jurisdiction and all such powers and
authority with respect to the administration of justice in
the presidency, as she thought fit. Thus High Courts were
given the following original and appellate jurisdiction.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• 1. Original jurisdiction: The
court had original jurisdiction
in the following matters:
• (a) Civil Jurisdiction and
• (b) Criminal Jurisdiction
• (a) Civil Jurisdiction: The
Original Civil Jurisdiction of
the court was of two types:-
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Ordinary Civil Jurisdiction: The
Ordinary Civil Jurisdiction extended to
the town of Calcutta and such local
limit as from time to time could be
prescribed by law of a competent
legislature in British India. All suits of
the value of Rs. 100 or more and
which were not cognizable by the
small court at Calcutta were
cognizable under High Courts.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Further, the ordinary civil jurisdiction
could be invoked only if:
• Ø The movable property was situated
within the town of Calcutta;
• Ø The cause of action wholly or partly
arose in Calcutta;
• Ø The defendant was carrying on
business or working for gain in Calcutta.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Extra Ordinary Civil Jurisdiction: Extra
Ordinary Civil Jurisdiction provides
that the High Court could call a case
pending in any lower court subject to
its superintendence and could decide
that case itself. This jurisdiction could
be exercised in a case where the
parties agreed to such exercise or the
High Court thought it proper to impart
justice. Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Criminal Jurisdiction: It is of two types also:-
• Ordinary Original Criminal Jurisdiction: In
exercise of its Ordinary Original Criminal
Jurisdiction the High Court was empowered to
try all persons brought before it in due course of
law. This jurisdiction was made available over
the native criminals and crimes committed with
the local limits of the presidency towns and
beyond this limit over the Britishers and
Europeans as the Supreme Court used to enjoy
the jurisdiction over them before the
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• ii. Extra Ordinary Original Criminal
Jurisdiction: The High Courts were to have
extra Ordinary Original Criminal Jurisdiction
which was not enjoyed by the High Court.
Under this jurisdiction the High Court hear any
criminal case against any person within the
cognizance of any court which was subject to
the superintendence of the High Court. If such
case was referred to the high court by the
advocate general or by any magistrate or any
other officer specially empowered for that
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Revenue Jurisdiction: The High Court
was given jurisdiction to here revenue
cases also which were precluded from
the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
by the Act of Settlement, 1781.
• Admiralty Jurisdiction: The admiralty
and vice-admiralty jurisdiction was also
given to the high court.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Testamentary and miscellaneous
jurisdiction: The High Courts were
given similar testamentary, intestate
and probate jurisdiction as was
enjoyed by the Supreme Court. It
also worked as the court of words for
the administration of the estate and
persons (lunatics, idiots and minors).
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Appellate Jurisdiction: The appellate
jurisdiction of the High Court was of two
types:-
• (a) Civil Jurisdiction: The High Court could
hear appeals in all cases authorised by any
law or regulation.
• (b) Criminal Jurisdiction: The High Court had
criminal jurisdiction in all cases decided by the
subordinate courts to it. It could also
entertain revisions against the decision of the
lower court and reference from them.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• At the Hon’ble High Court writ
Petitions may be filed before the
Appellate Side or Original Side
depending on whether the Address of
the Petitioners/defendants fall within
the Appellate Jurisdiction or Original
Jurisdiction of Calcutta high Court
respectively or whether extra-ordinary
original jurisdiction is being invoked.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Some relevant terms relating to
Rules of Original Side/Appellate
Side:
• i)Application (Original Side): Shall
have the same meaning as “Petition”
and would mean the main application
or petition to initiate any proceeding
in the original jurisdiction of High
Court. Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Application(Appellate Side):Means the main
Application to initiate proceeding for Civil
Order or Criminal Misc.Cases or Civil or
Criminal Revisional Jurisdiction of the High
Court and would include contempt
applications.
• ii) Memo Of Appeal :Means Memo of Appeal
either for Civil or Constitutional Writ
Jurisdiction of the Original Side or A memo of
appeal for Civil, Criminal or Mandamus
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• iii)Petition-Means the main petition to initiate
or invoke the Constitutional Jurisdiction of the
High Court as well as Contempt Proceedings
and is defined in Appellate side Rules.
• iv)Interlocutory Application-Applies to
Appellate/Original Side Rules and means any
application other than as mentioned
above/before.
• v)Plaint-Includes any pleading initiating a
proceeding under the provisions of law as in
force and as applies to Original Side Rules.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
Absolute Necessary Articles of
Constitution of India relating to
powers of Hon’ble High Court:
• Article 226 : Vide this Article, High Court
has the power to issue to any person/
authority/ Government, direction, order,
writs for enforcement of rights
conferred in Part III(Fundamental Rights)
of the Constitution of India or for any
other purpose.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
Types of Writs:
i)Habeas Corpus: The writ is issued to
produce a person who has been
detained,either in prison or in private
custody, before the Court and release him
if the detention is illegal
i)Mandamus: Command from High Court to
Lower Courts, Tribunal, Public Authority to
perform statutory duty.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• ii) Certiorari: The Writ is issued quashing
the order passed by inferior Court, Tribunal,
Quasi-Judicial Authority
• iv)Prohibition: Issued prohibiting any
inferior Court/Quasi-Judicial Authority from
continuing the proceeding of a particular
case where it has no jurisdiction.
• v)Quo Warranto:The writ is issued to
restrain a person from holding public office
to which he is not entitled.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Article 227: Confers the power of
Superintendence over all Courts by the
High Court; it can be invoked to correct
errors of jurisdiction but not to upset
findings of the fact. Under this Article the
High Court may call for returns from
lower Courts. High Court may make and
issue Rules and prescribe forms regarding
the practice and proceedings of lower
Courts. Ashis Kumar Gupta
• However, the Article does not confer the power of
superintendence over any Court/Tribunal
constituted under law relating to Armed Forces.
• The primary concern of the of the State
Respondent/Petitioners in respect of dealing with
Original/Appellate Side issues is in the procedure of
engagement of State Advocate. In case of petition
filed before the Original Jurisdiction, the
engagement of State Advocate is dealt with by the
office of Ld. AOR, W.B while for petitions filed
before the Appellate Side, the engagement of State
Advocate is dealt with by the office of Ld. Legal
Remembrancer, W.B. Ashis Kumar Gupta
Of the various types of cases, the most
frequent types that are needed to be
dealt with are:
• W.P(Writ Petition): These may be filed
before the Ld. Single Bench in respect of
matters relating to MM(D&R) Act and/or
in respect of other Act(s) also if the
Petitioners seek relief in the form of
issuance of Writs (Certiorari, Prohibition,
Mandamus ,etc.) Ashis Kumar Gupta
• WPLRT: These are Writ Petitions
filed before the Hon’ble Division
Bench of High Court by the
Petitioners who are aggrieved with
the judgment of LRTT as passed in
OA/TA, etc.; there is no time limit
for filing these Writs.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• COLRT: The supervisory jurisdiction
conferred on the High Courts under
Article 227 of the Constitution is
limited to seeing that an inferior
Court or Tribunal functions within
the limits of its authority, and not
to correct an error apparent on the
face of the record, or anything that
is much less than an error of law.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• These are Writ Petitions filed before
the Hon’ble Division Bench of High
Court under Article 227 of the
Constitution by the Petitioners who are
aggrieved with the judgment of the
Hon’ble WBLRTT passed in OA/TA, etc.
as while passing the judgment the
Hon’ble Tribunal has surpassed its
jurisdiction; there is no time limit for
filing these Writs.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
However, the power of supervisory
jurisdiction does not vest the High
Court with any unlimited prerogative to
correct all species of hardship or wrong
decisions made within the limits of the
jurisdiction of the Court or Tribunal and
therefore, it must be restricted to grave
derelictions of duty and flagrant abuse
of fundamental principle of law or
justice. Ashis Kumar Gupta
• WPST: These are Writ Petitions filed
before the Hon’ble Division Bench of
High Court by the Petitioners who are
aggrieved with the judgment of
WBAT as passed in OA, MA, etc.; here
also there is no time limit.
• SA: Second Appeal; these arise out of
judgment of Ld. Addl. District Judge in
Title Appeals. Ashis Kumar Gupta
• CAN: These are normally Civil
Applications filed in connection with
any already filed W.P/ FMAT, etc
• CPAN- (i) Contempt Application
(Appellate Side)
(ii) CC-Contempt of Court
Cases (Original side)
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• RVW-Review Petitions, these are
filed seeking review/recalling of
any order as passed by Hon’ble
High Court.
• CRR- Criminal Revision
• CR- Civil Revision
• WP.CRC-Civil Rule (Contempt)
• Ashis Kumar Gupta
• APO-Appeal from Order (Original
side)
• CP-Company Petition (Original Side)
• CA- (Company Applications (Original
Side)
• CO-Civil Misc.Case (Civil Order)
(Appellate Side) (Special
mentionable- CO.LRT)
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• FMAT: Admission of Civil
Appeal from Order
• MAT: Tender of Mandamus
Appeal
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• As per WBLR Manual’91, the Law-Cell
of DLLRO is a body constituted and
such law-cell is entrusted with duties of
engagement of State Advocate, filing of
appeals, etc; but ROs at Block as also
BLLROs are required to maintain close
liaison with the district law-cell who in
turn need to keep close liaison with the
law-cell at Directorate.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
Introduction to some terms as are acquainted
with functioning at Law-Cell:
• Brief-history: Since meeting the Ld.
State Advocate appearing for State
Respondents in a particular case, we
need to prepare a brief history of the
matter as represented via
Application/ Petition.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Statement Of facts: Based on the
depiction of events as enumerated
para-wise in the Petition/
Application/ Memo of Appeal, etc, we
need to prepare and present to the
Ld. State Advocate a statement of
facts para-wise itself based on office
records and provisions of law.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• List of Dates: An attempt to
chronologically set out the
various events as are incidental
to the filing of the Petition and
its adjudication.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Grounds of Appeal: If we are
aggrieved with the order of a
particular Court and are considering
preferring appeal at higher forum,
we need to prepare grounds of
appeal based on law points as are
apparently overlooked/
misinterpreted by the trial Court.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Affidavit-in-Opposition: If directed by
Hon’ble High Court, we may need to file
an affidavit opposing the contentions of
the Petition and based on such Written
Affidavit affirmed before the
Commissioner of Oaths at High Court as
also based on oral pleadings by the
Ld.Advocate appearing, Hon’ble High
Court moves to dispose the Petition,etc.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Affidavit-in-Reply: If we are the
Petitioner, then Hon’ble Court
may permit Opposition to be
filed by the Respondents and we
may get the chance to file Reply
to such Opposition.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Special Caution is needed while filing
these Affidavits for the disposal of the
Case depends on facts and statements
as in Affidavit and High Court being a
Court of Records vide Art.215 of
Constitution of India its acts/
proceedings are enrolled for perpetual
memory and testimony.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
Contempt of Court
• Contempt of court is behavior that oppose
s or defies the authority, justice and
dignity of the court.
Contempt charges may be brought against
parties to proceedings; lawyers or other
court officers or personnel; jurors;
witnesses; or people who insert
themselves in a case, such as protesters
outside a courtroom.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Courts have great leeway in making co
ntempt charges, and thus confusion so
metimes exists about the distinctions
between types of contempt. Generally,
however, contempt proceedings are
categorized as civil or criminal, and dir
ect or indirect. Acquaintance with the
Contempt of Courts Act, 1971 is
required.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
Business of Court
• Of all the Courts as function at High
Court some are Single Bench being
managed by a single Hon’ble Justice but
there are also Division Benches
comprising of at least 2 judges.
• The daily as well as monthly schedule of
the Courts at High Court are published in
the form of Daily List/ Monthly List.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• In respect of all various types of appeals that are
filed at various levels, officers should keep
themselves acquainted with the provision of
Sec.5 of Limitation Act,1963 and/or Sec.10 of
WBLRTT Act,1997, etc., because the period(s) of
limitation in respect of filing of various
appeals/review, etc. are detailed in such
sections. We may need to contest the prayers for
condonation of delay to appeal, if appeal is
preferred by individual petitioner or may also
need to describe the reasons for delay, if delay is
caused in preferring appeal on our part.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• Besides, all these issues at various
Courts, there may be occasions to go
to Hon’ble Supreme Court also in
connection with Appeals as arise
from the order(s) of Division Bench of
Hon’ble High Court and then
procurement of Certified Copy of the
order is a primary duty.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
For Obtaining Certified Copy of Judgments
Pronounced By The Hon’ble High Court
• Application is to be made to the
Ld. Legal Remembrancer,
Government of West Bengal, 2 & 3
Kiran Shankar Roy Road, 5th Floor,
Kolkata- 700001.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
• To mention-
(i) Case Number
(ii) Cause Title
(iii) Bench
(iv)Order date
• A copy of the application may be
forwarded to the Directorate.
Ashis Kumar Gupta
Thank You
Ashis Kumar Gupta
You might also like
- Law Notes (LL.B Notes) - Constitutional Law-2Document41 pagesLaw Notes (LL.B Notes) - Constitutional Law-2balaji100% (2)
- Here Is The Voter Fraud EvidenceDocument81 pagesHere Is The Voter Fraud EvidenceJoshua Sanchez100% (4)
- Indian High CourtsDocument9 pagesIndian High CourtsManmohan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- The High CourtDocument17 pagesThe High CourtAditya JhaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - The Indian High Court Act 1861Document9 pages1.3 - The Indian High Court Act 1861Syed Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- Indian JudiciaryDocument9 pagesIndian JudiciaryAhana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- The Indian High Courts Act of 1861Document2 pagesThe Indian High Courts Act of 1861shriya rao0% (1)
- High Courts Upsc Notes 92Document6 pagesHigh Courts Upsc Notes 92rajhp54321No ratings yet
- The Supreme Court and High Court JurisdictionDocument4 pagesThe Supreme Court and High Court JurisdictionAisha singhNo ratings yet
- Writ JurisdictionDocument20 pagesWrit JurisdictionMuskan SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian JudiciaryDocument51 pagesIndian JudiciaryPavan BangaloreNo ratings yet
- Article 8. Sec 5Document34 pagesArticle 8. Sec 5Ann GuillemNo ratings yet
- Writ JurisdictionDocument60 pagesWrit Jurisdictionaayush lathiNo ratings yet
- Writs 2Document5 pagesWrits 2SarvikaNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of The Supreme CourtDocument17 pagesJurisdiction of The Supreme CourtraghavNo ratings yet
- CPC - Jurisdiction of The CourtsDocument23 pagesCPC - Jurisdiction of The Courtsgaurav singhNo ratings yet
- Civics Chapter 4 - The Supreme Court 2023Document16 pagesCivics Chapter 4 - The Supreme Court 2023Thangsian KhaiNo ratings yet
- The High CourtSDocument17 pagesThe High CourtSUPSC AspirantNo ratings yet
- Judiciary 29062022 045250pmDocument18 pagesJudiciary 29062022 045250pmJehanzaib AminNo ratings yet
- Powers and Functions of High Court in IndiaDocument17 pagesPowers and Functions of High Court in Indiasai kiran gudisevaNo ratings yet
- Hirarchy of Courts 33Document27 pagesHirarchy of Courts 33drishyasck123No ratings yet
- Cons Law Main ProjectDocument11 pagesCons Law Main ProjectBhawna Jha 036No ratings yet
- Discuss The Jurisdiction and Powers of High CourtsDocument4 pagesDiscuss The Jurisdiction and Powers of High CourtsMrinmoy BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Right To Constitutional Remedies: Article-32Document22 pagesRight To Constitutional Remedies: Article-32Dolphin100% (1)
- Jurisdiction of SCDocument5 pagesJurisdiction of SCraghavNo ratings yet
- JUDICIAL SYSTEM IN KENYA - Lesson 5Document9 pagesJUDICIAL SYSTEM IN KENYA - Lesson 5arnoldochieng125No ratings yet
- JurisdictionDocument64 pagesJurisdictionPragya Gupta100% (2)
- Anushka Constitution ProjectDocument16 pagesAnushka Constitution ProjectSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Powers and Functions of High Court in IndiaDocument11 pagesPowers and Functions of High Court in Indiasai kiran gudisevaNo ratings yet
- Article VIII Judiciary Branch ConstiDocument29 pagesArticle VIII Judiciary Branch ConstiDeanne Mitzi Somollo100% (1)
- Supreme Court and The Constitutional ProcessDocument34 pagesSupreme Court and The Constitutional ProcessKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- High Court VisitDocument8 pagesHigh Court Visitminturaha.blg92No ratings yet
- GOVT S K S J T Institute of Engineering KR Circle, Bengalore-560001Document10 pagesGOVT S K S J T Institute of Engineering KR Circle, Bengalore-560001Jeevan ShettyNo ratings yet
- Module 26Document11 pagesModule 26Siddhant ChandakNo ratings yet
- The Indian Judiciary - Supreme Court, High Court & Subordinate CourtsDocument6 pagesThe Indian Judiciary - Supreme Court, High Court & Subordinate CourtsCOW GUPTANo ratings yet
- GSTAT & HC CA. Vyankatesh AgarwalDocument47 pagesGSTAT & HC CA. Vyankatesh Agarwalpramodmurkya13No ratings yet
- 12 Solved Paper - I-2018-Practice and ProcedureDocument20 pages12 Solved Paper - I-2018-Practice and Proceduredumbthings1729No ratings yet
- Union Judiciary Part IIDocument23 pagesUnion Judiciary Part IIDevendraNo ratings yet
- High CourtDocument4 pagesHigh CourtSaketh JainNo ratings yet
- Courts and ProcedureDocument6 pagesCourts and ProcedureJohn MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of IndiaDocument7 pagesSupreme Court of Indiaanuradha KNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy and Jurisdiction of CourtsDocument56 pagesHierarchy and Jurisdiction of Courtsaayush lathiNo ratings yet
- Enc Encoded 4 M Wes 8 P4 A 8 RVL VZHYz NY4 Uu 2 ZD KM 7 X QBT4 Aqlol EYGsj KTNRDNG WJADocument5 pagesEnc Encoded 4 M Wes 8 P4 A 8 RVL VZHYz NY4 Uu 2 ZD KM 7 X QBT4 Aqlol EYGsj KTNRDNG WJASaketh JainNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of Courts in BangladeshDocument21 pagesJurisdiction of Courts in BangladeshAyesha Kanta100% (1)
- High Court (1) - WatermarkDocument60 pagesHigh Court (1) - WatermarkVijayNo ratings yet
- Legal Methods (Ultimate Version)Document45 pagesLegal Methods (Ultimate Version)oshin agrawalNo ratings yet
- By: Atty. Jose Aguila GrapilonDocument31 pagesBy: Atty. Jose Aguila GrapilonDiaz Ragu100% (1)
- Powers and Functions of High Court in IndiaDocument9 pagesPowers and Functions of High Court in Indiasai kiran gudiseva100% (1)
- Polity SelfDocument30 pagesPolity Selfsupriya debbarmaNo ratings yet
- Law Notes (LL.B Notes) - Constitutional Law-2Document34 pagesLaw Notes (LL.B Notes) - Constitutional Law-2Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of IndiaDocument20 pagesSupreme Court of IndiaMAYANK GUPTANo ratings yet
- High Court and Its JurisdictionDocument7 pagesHigh Court and Its JurisdictionHari GovindNo ratings yet
- Powers and Functions of High Court in IndiaDocument15 pagesPowers and Functions of High Court in Indiasai kiran gudisevaNo ratings yet
- The High Courts of IndiaDocument8 pagesThe High Courts of IndiaNidhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Consti Mohit KumarDocument3 pagesConsti Mohit KumarTushar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Indian Legal System An IntroductionDocument32 pagesIndian Legal System An Introductionptiypiya100% (1)
- Judicial System of India - Hierarchy of CourtsDocument10 pagesJudicial System of India - Hierarchy of CourtsAndroid app developerNo ratings yet
- Constitution Law 2 This Notes For 1st Year LLB 2nd SemesterDocument45 pagesConstitution Law 2 This Notes For 1st Year LLB 2nd SemesterPrisha BauskarNo ratings yet
- Types of Writs:: Writs Under The Constitution OfindiaDocument4 pagesTypes of Writs:: Writs Under The Constitution OfindiaSmiti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Courts and Procedure in England and in New JerseyFrom EverandCourts and Procedure in England and in New JerseyNo ratings yet
- Sip LakeDocument215 pagesSip Lakeayesha30062004No ratings yet
- MANU MH 3022 2018 BomDocument53 pagesMANU MH 3022 2018 Bomayesha30062004No ratings yet
- Memorial National Moot Court Competition 070223 1 461021Document33 pagesMemorial National Moot Court Competition 070223 1 461021ayesha30062004No ratings yet
- Narayanan V State of Keralawatermark 1553168Document19 pagesNarayanan V State of Keralawatermark 1553168ayesha30062004No ratings yet
- PYQsDocument10 pagesPYQsayesha30062004No ratings yet
- L.G.R. Enterprises v. P. AnbazhagDocument7 pagesL.G.R. Enterprises v. P. AnbazhagRakshit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Masereka V Muhindo (Divorce Appeal No 8 of 2017) 2023 UGHCFD 3 (6 February 2023)Document6 pagesMasereka V Muhindo (Divorce Appeal No 8 of 2017) 2023 UGHCFD 3 (6 February 2023)Derrick HartNo ratings yet
- X DacanayDocument2 pagesX DacanayTynny Roo BelduaNo ratings yet
- Ahenkora Ii v. OfeDocument7 pagesAhenkora Ii v. OfeZACHARIAH MANKIRNo ratings yet
- The Legal Framework Order FINALLDocument7 pagesThe Legal Framework Order FINALLazharmazhar074100% (1)
- Summary of The Petitions - Anti Terrorism LawDocument9 pagesSummary of The Petitions - Anti Terrorism LawHoneylyn Jiza WaycoNo ratings yet
- Lajeromeny Brown Sentencing OrderDocument2 pagesLajeromeny Brown Sentencing OrderFOX54 News HuntsvilleNo ratings yet
- Notice of Motion 1display - PDFDocument3 pagesNotice of Motion 1display - PDFVarsha MangtaniNo ratings yet
- Durevs. JoDocument7 pagesDurevs. JoCharlene LaurinoNo ratings yet
- P L D 2016 Supreme Court 347Document8 pagesP L D 2016 Supreme Court 347Yahia MustafaNo ratings yet
- (Anil Choudhary) Member (Judicial) : (Order Dictated in The Open Court)Document2 pages(Anil Choudhary) Member (Judicial) : (Order Dictated in The Open Court)Akash chandoraNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Rti Act 2005Document11 pagesMCQ - Rti Act 2005Mini DipiNo ratings yet
- Consti Sem 4Document12 pagesConsti Sem 4Prashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Iowa BEV PAC 6098 - 6098 - B - ExpendituresDocument7 pagesIowa BEV PAC 6098 - 6098 - B - ExpendituresZach EdwardsNo ratings yet
- S.M.C. 1 2023Document5 pagesS.M.C. 1 2023Khawaja BurhanNo ratings yet
- LLS - Administrative Dutch LawDocument9 pagesLLS - Administrative Dutch Lawotis flowerNo ratings yet
- Colbert v. State Farm Mutual Automobile Insurance Company - DocketDocument2 pagesColbert v. State Farm Mutual Automobile Insurance Company - DocketShagun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Vijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors vs. Union of India & OrsDocument206 pagesVijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors vs. Union of India & OrsSanskar BarekarNo ratings yet
- Separation of Power in UK AssignmentDocument2 pagesSeparation of Power in UK Assignmentsapuni NayananayakeNo ratings yet
- Taule vs. Santos - Full TextDocument14 pagesTaule vs. Santos - Full TextLouvanne Jessa Orzales BesingaNo ratings yet
- UK Public LawDocument88 pagesUK Public Lawjmn.elmNo ratings yet
- People v. Baay y FalcoDocument9 pagesPeople v. Baay y FalcoAlex FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Mayelane V Ngwenyama 2013 SummaryDocument2 pagesMayelane V Ngwenyama 2013 SummarymunyanganerichmondNo ratings yet
- ConstitutiondayDocument2 pagesConstitutiondayapi-597200800No ratings yet
- Evolution of Philippine ConstitutionDocument19 pagesEvolution of Philippine ConstitutionKhen KhenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument41 pagesUntitledCherry Grace Lapnite NumeronNo ratings yet
- 2023 BAR SYLLABUS TRACKER - XLSX - Remedial LawDocument5 pages2023 BAR SYLLABUS TRACKER - XLSX - Remedial LawAiza CabenianNo ratings yet
- Case Digest 7Document3 pagesCase Digest 7Princess PanNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines v. MuletaDocument2 pagesPeople of The Philippines v. Muletarafael.louise.roca2244No ratings yet