Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GPS Year 5 Autumn Block 3 PPT Recognising Modal Verbs
GPS Year 5 Autumn Block 3 PPT Recognising Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
Shabnam Fatima NathaniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- A Close Look at Student Learning Outcomes (SLO) : Group 1Document31 pagesA Close Look at Student Learning Outcomes (SLO) : Group 1Laarni Marie Cariño75% (16)
- JRR 13-2 RabanDocument11 pagesJRR 13-2 RabanDL GirolettiNo ratings yet
- CrucibleDocument395 pagesCrucibleКонстантин Иванов100% (2)
- GPS Year 4 Autumn Block 3 Step 1 PPT What Is An AdverbialDocument22 pagesGPS Year 4 Autumn Block 3 Step 1 PPT What Is An AdverbialfatheenafayazNo ratings yet
- Friday PPT Using Adverbs To Express TimeDocument18 pagesFriday PPT Using Adverbs To Express TimeSanjana GaneshNo ratings yet
- GPS Year 1 Autumn Block 1 Step 2 PPT Leaving Spaces Between WordsDocument22 pagesGPS Year 1 Autumn Block 1 Step 2 PPT Leaving Spaces Between WordsSamantha Hugh-SaintNo ratings yet
- SPAG Identify Adjectives and AdverbsDocument21 pagesSPAG Identify Adjectives and AdverbsSanjana GaneshNo ratings yet
- GPS PPT What Are AdjectivesDocument22 pagesGPS PPT What Are AdjectivesRouselle RaraNo ratings yet
- Gps Year 4 Spring Block 1 Step 4 PPT Using Apostrophes For Possession or ContractionDocument20 pagesGps Year 4 Spring Block 1 Step 4 PPT Using Apostrophes For Possession or ContractionCaro- linaNo ratings yet
- Noun Phrase Example Questions With AnswersDocument21 pagesNoun Phrase Example Questions With AnswersAlaa QuraanNo ratings yet
- GPS Year 5 Spring Block 3 Step 3 PPT Recognising Past Perfect FormDocument22 pagesGPS Year 5 Spring Block 3 Step 3 PPT Recognising Past Perfect Formdana.oh.parentNo ratings yet
- T2 E 2149 Year 6 Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Modal Verbs - Ver - 1Document11 pagesT2 E 2149 Year 6 Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Modal Verbs - Ver - 1Pham Hong AnhNo ratings yet
- 8vo Adverbs-to-Express-TimeDocument21 pages8vo Adverbs-to-Express-TimeJosseph DannyNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument6 pagesModal VerbsGINA MALAGUENANo ratings yet
- HMH Module 1 (Big Idea Words Essential Question Writing)Document21 pagesHMH Module 1 (Big Idea Words Essential Question Writing)KO GINNo ratings yet
- Effective Strategies To Learn Vocabulary: Abdulaziz SaifDocument13 pagesEffective Strategies To Learn Vocabulary: Abdulaziz SaifZaenati mghNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Fever Unit LessonDocument10 pagesChocolate Fever Unit LessonMichael ValloneNo ratings yet
- t2 e 2149 Year 6 Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Modal VerbsDocument11 pagest2 e 2149 Year 6 Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Modal Verbschayma melitiNo ratings yet
- RLT 05 CB File 6Document1 pageRLT 05 CB File 6efsunfreiNo ratings yet
- Mastering Workplace Skills Grammar FundamentalsDocument240 pagesMastering Workplace Skills Grammar FundamentalsKit ChanNo ratings yet
- Examples of Jargons Jargon Meaning Better EquivalentDocument6 pagesExamples of Jargons Jargon Meaning Better Equivalentaccounting probNo ratings yet
- MindTree Verbal Questions and Answers For Mindtree Verbal Ability SectionDocument10 pagesMindTree Verbal Questions and Answers For Mindtree Verbal Ability SectionROHIT KUMAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Grammar: Cleft SentencesDocument5 pagesGrammar: Cleft SentencesJudit KissNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Activity Sheets Quarter 1 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 9 Activity Sheets Quarter 1 Week 3LadyAn DegamoNo ratings yet
- Write and Evaluate Algebraic Expressions: IcanDocument10 pagesWrite and Evaluate Algebraic Expressions: Icanafnan a.muhammadNo ratings yet
- Sentence Correction - IDocument34 pagesSentence Correction - IvighneshmanojNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test of TimDocument11 pagesAchievement Test of Timrubelyn baquiranNo ratings yet
- Change The Sentence Types KS2 SPAG SATs Test Practice Interactive BeginnerDocument2 pagesChange The Sentence Types KS2 SPAG SATs Test Practice Interactive BeginnerRodaina MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Awkward Sentences: LessonDocument7 pagesAvoiding Awkward Sentences: LessonЮлія ІщенкоNo ratings yet
- PDF Quarter 2 Module 4 Argumentative Text Modal Verbs and Adverbs CompressDocument2 pagesPDF Quarter 2 Module 4 Argumentative Text Modal Verbs and Adverbs CompressAinel CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Welcome Students To Grade 8 !: Ms Leela RaniDocument27 pagesWelcome Students To Grade 8 !: Ms Leela RaniSuman JoyNo ratings yet
- Au t2 e 2149 Modal Verbs Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Powerpoint Australian Ver 1Document12 pagesAu t2 e 2149 Modal Verbs Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Powerpoint Australian Ver 1Thanh Huyen LeNo ratings yet
- The Filipino Value System and Its Influence On Business PracticesDocument8 pagesThe Filipino Value System and Its Influence On Business PracticesJoan Marie SalayogNo ratings yet
- Br2e Upper-Int Reading Notes 4Document1 pageBr2e Upper-Int Reading Notes 4Haydee GallardoNo ratings yet
- Types of SentencesDocument6 pagesTypes of SentencesJenieNo ratings yet
- Mastermind 1 Unit 10 Grammar 1Document10 pagesMastermind 1 Unit 10 Grammar 1Mauricio Martinez GambaNo ratings yet
- The Destrier Writing 1 (SPE W)Document35 pagesThe Destrier Writing 1 (SPE W)Renz Louie LedseyNo ratings yet
- Year 3 Summer Block 1 Step 1 PPT Equivalent Fractions 1Document20 pagesYear 3 Summer Block 1 Step 1 PPT Equivalent Fractions 1Sahar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Change The Sentence Types KS2 SPAG SATs Test Practice Interactive EasyDocument2 pagesChange The Sentence Types KS2 SPAG SATs Test Practice Interactive EasyRodaina MahmoudNo ratings yet
- 7 Cs of CommunicationDocument27 pages7 Cs of CommunicationHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Modal Auxiliary: This Paper Is Structured To Fulfill The English Task Lecturer: Nikmatul Khoiriah, S.PDDocument10 pagesModal Auxiliary: This Paper Is Structured To Fulfill The English Task Lecturer: Nikmatul Khoiriah, S.PDBona LasagnaNo ratings yet
- SLM Week 1 Q2 Oral Com FinalDocument5 pagesSLM Week 1 Q2 Oral Com FinalJean RomarNo ratings yet
- ParaphrasingDocument13 pagesParaphrasingapi-3697552100% (7)
- Slide Powerpoint - The Cooperative PrinciplesDocument40 pagesSlide Powerpoint - The Cooperative PrinciplesQuỳnh Ngân VõNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology Worksheet Module 17Document6 pagesChild Psychology Worksheet Module 17Şterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Paragraph Writing-1Document1 pageRubric For Paragraph Writing-1Kevin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Using Modal Verbs To Indicate Degrees of Possibility Mini TestDocument3 pagesUsing Modal Verbs To Indicate Degrees of Possibility Mini TestTilly KyriakidesNo ratings yet
- Group Work-Modal VerbsDocument9 pagesGroup Work-Modal Verbsmalonamige20No ratings yet
- Thank You: Stellar Teacher Co. LLC. All Rights ReservedDocument7 pagesThank You: Stellar Teacher Co. LLC. All Rights ReservedAleksandra NikolskaiaNo ratings yet
- Cute Little Notes SlidesManiaDocument23 pagesCute Little Notes SlidesManiaDilla FadillaNo ratings yet
- Gps Year 4 Spring Block 2 Step 3 PPT Direct or Indirect Speech PDFDocument21 pagesGps Year 4 Spring Block 2 Step 3 PPT Direct or Indirect Speech PDFVeloso Angela FaithNo ratings yet
- What Is An AdverbDocument3 pagesWhat Is An AdverbJonard JocoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Ladders - Grade 6 - Spending MoneyDocument6 pagesVocabulary Ladders - Grade 6 - Spending MoneyfairfurNo ratings yet
- Sharp Minds GMAT Prep - Grammar-Handbook - Part 5Document15 pagesSharp Minds GMAT Prep - Grammar-Handbook - Part 5Anonymous brpVlaVBNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 9Document8 pagesDLL Grade 9kaylleapiladaNo ratings yet
- MySide 007Document1 pageMySide 007api-26739370No ratings yet
- Bài Thuyết Trình Nhóm 6Document41 pagesBài Thuyết Trình Nhóm 6Quỳnh Ngân VõNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 - P4 - Unit 1 - Spell Zone - AKDocument35 pages2022-2023 - P4 - Unit 1 - Spell Zone - AKGuan Tang CheungNo ratings yet
- Day 3Document6 pagesDay 3LUCYNIL OBERESNo ratings yet
- Complete-Vocabulary-Preview 11 PlusDocument26 pagesComplete-Vocabulary-Preview 11 PlusHong DangNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Lesson 4 What Is An AdverbDocument3 pagesCH 5 Lesson 4 What Is An AdverbNoviani al husnul kenNo ratings yet
- IAL Mathematics Sample Assessment MaterialDocument460 pagesIAL Mathematics Sample Assessment MaterialMohamed Naaif100% (3)
- Cambridge Aice BrochureDocument2 pagesCambridge Aice Brochureapi-294488294No ratings yet
- Corrigendum/ Extension of Date of Submission Last Date of Submission of Application Form For Post of Professor/ AssociateDocument20 pagesCorrigendum/ Extension of Date of Submission Last Date of Submission of Application Form For Post of Professor/ AssociateguruNo ratings yet
- Industrial Motor Controls I: IDSY 1110Document5 pagesIndustrial Motor Controls I: IDSY 1110Ajay SolateNo ratings yet
- (Note: Discussions May Change Course (Deviate From The Original Plan) Depending On Students' Responses ToDocument2 pages(Note: Discussions May Change Course (Deviate From The Original Plan) Depending On Students' Responses ToRubenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3, Capt. AguillonDocument44 pagesChapter 1-3, Capt. AguillonJohn Ross RamosNo ratings yet
- Sarah Corba ResumeDocument3 pagesSarah Corba Resumeapi-505000786No ratings yet
- Mahouka Koukou No Rettousei Vol 12 - Double Seven ChapterDocument174 pagesMahouka Koukou No Rettousei Vol 12 - Double Seven ChapterStratogan0% (1)
- Shays Rebellion Lesson Plan 3Document4 pagesShays Rebellion Lesson Plan 3api-434731744No ratings yet
- Motivational BreakthroughDocument36 pagesMotivational Breakthroughapi-240997758No ratings yet
- Final Work Assignments Monitoring Tool June 2020Document70 pagesFinal Work Assignments Monitoring Tool June 2020Louise BenzNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Instructional Leadership For Filipino Teachers in Senior High School: A Case Study in The School Division of ManilaDocument6 pagesEnhancing Instructional Leadership For Filipino Teachers in Senior High School: A Case Study in The School Division of ManilaPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- For Admission Please Visit: Onlineadmission - Numl.edu - PK: Admissions Fall - 2020Document7 pagesFor Admission Please Visit: Onlineadmission - Numl.edu - PK: Admissions Fall - 2020ranaaliahmedNo ratings yet
- Ict Assignment 1 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesIct Assignment 1 Lesson Planapi-280946178No ratings yet
- KHDA - Al Sadiq Islamic English School 2016-2017Document26 pagesKHDA - Al Sadiq Islamic English School 2016-2017Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- Assessment Is a-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesAssessment Is a-WPS Officejsjjsjs ksksndNo ratings yet
- Gcu Performance Evaluation and Action Plan 1Document8 pagesGcu Performance Evaluation and Action Plan 1api-606287911No ratings yet
- Concordia UniversityDocument4 pagesConcordia Universitybuetce041662912No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan - Gherlyn, Sia, JasperDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan - Gherlyn, Sia, Jasperariannerose gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Resume Marsha LarsonDocument1 pageResume Marsha Larsonapi-445526818No ratings yet
- Holly TurnerDocument39 pagesHolly Turnerapi-324846334No ratings yet
- Grading System For TeachersDocument3 pagesGrading System For TeachersLaurenNo ratings yet
- A Report On Induction Programme - FinalDocument9 pagesA Report On Induction Programme - FinalDipakNo ratings yet
- Human CapitalDocument4 pagesHuman CapitalKumar DayanidhiNo ratings yet
- Borrower'S Slip: Pag-Asa National High SchoolDocument1 pageBorrower'S Slip: Pag-Asa National High SchoolCristian PortugalNo ratings yet
- M C M C M C: Super Minds Lesson 61Document2 pagesM C M C M C: Super Minds Lesson 61thinagaranNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeNaya KayalaNo ratings yet
GPS Year 5 Autumn Block 3 PPT Recognising Modal Verbs
GPS Year 5 Autumn Block 3 PPT Recognising Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
Shabnam Fatima NathaniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GPS Year 5 Autumn Block 3 PPT Recognising Modal Verbs
GPS Year 5 Autumn Block 3 PPT Recognising Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
Shabnam Fatima NathaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 5 – Autumn Block 3 – Modal Verbs – Recognising Modal Verbs
About This Resource:
This PowerPoint has been designed to support your teaching of this small step. It includes a starter activity and an example of
each question from the Varied Fluency and Application and Reasoning resources also provided in this pack. You can choose to
work through all examples provided or a selection of them depending on the needs of your class.
National Curriculum Objectives:
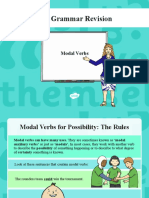
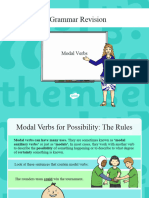
English Year 5: (5G4.1c) Indicating degrees of possibility using modal verbs [for example, might, should, will, must]
Terminology for pupils:
• (5G4.1c) modal verb
More resources from our Grammar, Punctuation and Spelling scheme of work.
Did you like this resource? Don’t forget to review it on our website.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Year 5 – Autumn Block 3 – Modal Verbs – Recognising Modal Verbs
Notes and Guidance
• In this step, children will learn to recognise modal verbs in sentences. The modal verbs are: can, could, may, might, shall,
should, must, will, would, ought to.
• Children need to know that modal verbs work with another verb to indicate the possibility of something. They tell you
how certain, how necessary or how able the other verb is, e.g. ‘It will rain today.’ indicates that it is certain, whereas ‘It
may rain today.’ indicates that there is also a possibility that it won’t rain.
• Children should also know that modal verbs are always in the same form such as may, can or should. Modal verbs do not
have any other forms, i.e. mayed or maying.
• Children should also be taught that most modal verbs are followed by the base form of the verb with exceptions being the
semi-modal verbs, for example, ought and used which are followed by the infinitive e.g. ought to be, used to be.
Focused Questions
• What does a modal verb tell you?
• How certain/necessary/able is the verb in this sentence?
• What word is the modal verb in this sentence?
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Year 5 – Autumn Block 3 – Modal Verbs
Step 1: Recognising Modal
Verbs
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Introduction
Sort the verbs into the correct place in the table.
Modal Verb Not a Modal Verb
can think may could did will
achieve try might finish do should
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Introduction
Sort the verbs into the correct place in the table.
Modal Verb Not a Modal Verb
can think
may did
could achieve
will try
might finish
should do
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Varied Fluency 1
Circle the modal verb below.
setting wish
might carrying
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Varied Fluency 1
Circle the modal verb below.
setting wish
might carrying
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Varied Fluency 2
Underline the modal verb in the sentence below.
Maria would like to go to basketball club, but it is on Thursdays.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Varied Fluency 2
Underline the modal verb in the sentence below.
Maria would like to go to basketball club, but it is on Thursdays.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Varied Fluency 3
Which sentence tells you it would be a good idea for Charlie to join the relay
team?
A. Charlie ought to join the relay team if he runs that fast every
time.
B. Charlie can join the relay team if he runs that fast every
time.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Varied Fluency 3
Which sentence tells you it would be a good idea for Charlie to join the relay
team?
A. Charlie ought to join the relay team if he runs that fast every
time.
B. Charlie can join the relay team if he runs that fast every
time.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Varied Fluency 4
Fill the gap with the modal verb which shows that the 7pm meeting is certain
to happen.
Whatever happens, I _________ meet you back here at 7pm.
shall could used
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Varied Fluency 4
Fill the gap with the modal verb which shows that the 7pm meeting is certain
to happen.
Whatever happens, I _________
shallmeet you back here at 7pm.
shall could used
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Reasoning 1
Dexter wants his sentence to show that winning is something he has to do at
all costs.
Whatever happens in the
match, I could beat the other
team.
Has Dexter chosen the correct modal verb to convey this?
Explain your answer.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Reasoning 1
Dexter wants his sentence to show that winning is something he has to do at
all costs.
Whatever happens in the
match, I could beat the other
team.
Has Dexter chosen the correct modal verb to convey this?
Explain your answer.
No. The modal verb ‘could’…
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Reasoning 1
Dexter wants his sentence to show that winning is something he has to do at
all costs.
Whatever happens in the
match, I could beat the other
team.
Has Dexter chosen the correct modal verb to convey this?
Explain your answer.
No. The modal verb ‘could’ is not certain. ‘Must’ would be a better choice.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Application 1
Rewrite the sentence below so that the modal verb ‘may’ is in the correct
position in the sentence.
It rain may tomorrow so you should take an umbrella.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Application 1
Rewrite the sentence below so that the modal verb ‘may’ is in the correct
position in the sentence.
It rain may tomorrow so you should take an umbrella.
It may rain tomorrow so you should take an umbrella.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Reasoning 2
Order the sentences below based on the necessity (least to most) that the
modal verb implies. Explain your order.
A. I must order the cake for the party before tomorrow.
B. I could order the cake for the party before tomorrow.
C. I ought to order the cake for the party before tomorrow.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Reasoning 2
Order the sentences below based on the necessity (least to most) that the
modal verb implies. Explain your order.
B. I could order the cake for the party before tomorrow.
C. I ought to order the cake for the party before tomorrow.
A. I must order the cake for the party before tomorrow
The order would be B, C, A because …
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
Reasoning 2
Order the sentences below based on the necessity (least to most) that the
modal verb implies. Explain your order.
B. I could order the cake for the party before tomorrow.
C. I ought to order the cake for the party before tomorrow.
A. I must order the cake for the party before tomorrow
The order would be B, C, A because ‘could’ suggests a
possibility, ‘ought to’ suggests a possibility with a level of
compulsion, ‘must’ suggests compulsion.
© Classroom Secrets Limited 2018
You might also like
- A Close Look at Student Learning Outcomes (SLO) : Group 1Document31 pagesA Close Look at Student Learning Outcomes (SLO) : Group 1Laarni Marie Cariño75% (16)
- JRR 13-2 RabanDocument11 pagesJRR 13-2 RabanDL GirolettiNo ratings yet
- CrucibleDocument395 pagesCrucibleКонстантин Иванов100% (2)
- GPS Year 4 Autumn Block 3 Step 1 PPT What Is An AdverbialDocument22 pagesGPS Year 4 Autumn Block 3 Step 1 PPT What Is An AdverbialfatheenafayazNo ratings yet
- Friday PPT Using Adverbs To Express TimeDocument18 pagesFriday PPT Using Adverbs To Express TimeSanjana GaneshNo ratings yet
- GPS Year 1 Autumn Block 1 Step 2 PPT Leaving Spaces Between WordsDocument22 pagesGPS Year 1 Autumn Block 1 Step 2 PPT Leaving Spaces Between WordsSamantha Hugh-SaintNo ratings yet
- SPAG Identify Adjectives and AdverbsDocument21 pagesSPAG Identify Adjectives and AdverbsSanjana GaneshNo ratings yet
- GPS PPT What Are AdjectivesDocument22 pagesGPS PPT What Are AdjectivesRouselle RaraNo ratings yet
- Gps Year 4 Spring Block 1 Step 4 PPT Using Apostrophes For Possession or ContractionDocument20 pagesGps Year 4 Spring Block 1 Step 4 PPT Using Apostrophes For Possession or ContractionCaro- linaNo ratings yet
- Noun Phrase Example Questions With AnswersDocument21 pagesNoun Phrase Example Questions With AnswersAlaa QuraanNo ratings yet
- GPS Year 5 Spring Block 3 Step 3 PPT Recognising Past Perfect FormDocument22 pagesGPS Year 5 Spring Block 3 Step 3 PPT Recognising Past Perfect Formdana.oh.parentNo ratings yet
- T2 E 2149 Year 6 Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Modal Verbs - Ver - 1Document11 pagesT2 E 2149 Year 6 Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Modal Verbs - Ver - 1Pham Hong AnhNo ratings yet
- 8vo Adverbs-to-Express-TimeDocument21 pages8vo Adverbs-to-Express-TimeJosseph DannyNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument6 pagesModal VerbsGINA MALAGUENANo ratings yet
- HMH Module 1 (Big Idea Words Essential Question Writing)Document21 pagesHMH Module 1 (Big Idea Words Essential Question Writing)KO GINNo ratings yet
- Effective Strategies To Learn Vocabulary: Abdulaziz SaifDocument13 pagesEffective Strategies To Learn Vocabulary: Abdulaziz SaifZaenati mghNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Fever Unit LessonDocument10 pagesChocolate Fever Unit LessonMichael ValloneNo ratings yet
- t2 e 2149 Year 6 Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Modal VerbsDocument11 pagest2 e 2149 Year 6 Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Modal Verbschayma melitiNo ratings yet
- RLT 05 CB File 6Document1 pageRLT 05 CB File 6efsunfreiNo ratings yet
- Mastering Workplace Skills Grammar FundamentalsDocument240 pagesMastering Workplace Skills Grammar FundamentalsKit ChanNo ratings yet
- Examples of Jargons Jargon Meaning Better EquivalentDocument6 pagesExamples of Jargons Jargon Meaning Better Equivalentaccounting probNo ratings yet
- MindTree Verbal Questions and Answers For Mindtree Verbal Ability SectionDocument10 pagesMindTree Verbal Questions and Answers For Mindtree Verbal Ability SectionROHIT KUMAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Grammar: Cleft SentencesDocument5 pagesGrammar: Cleft SentencesJudit KissNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Activity Sheets Quarter 1 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 9 Activity Sheets Quarter 1 Week 3LadyAn DegamoNo ratings yet
- Write and Evaluate Algebraic Expressions: IcanDocument10 pagesWrite and Evaluate Algebraic Expressions: Icanafnan a.muhammadNo ratings yet
- Sentence Correction - IDocument34 pagesSentence Correction - IvighneshmanojNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test of TimDocument11 pagesAchievement Test of Timrubelyn baquiranNo ratings yet
- Change The Sentence Types KS2 SPAG SATs Test Practice Interactive BeginnerDocument2 pagesChange The Sentence Types KS2 SPAG SATs Test Practice Interactive BeginnerRodaina MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Awkward Sentences: LessonDocument7 pagesAvoiding Awkward Sentences: LessonЮлія ІщенкоNo ratings yet
- PDF Quarter 2 Module 4 Argumentative Text Modal Verbs and Adverbs CompressDocument2 pagesPDF Quarter 2 Module 4 Argumentative Text Modal Verbs and Adverbs CompressAinel CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Welcome Students To Grade 8 !: Ms Leela RaniDocument27 pagesWelcome Students To Grade 8 !: Ms Leela RaniSuman JoyNo ratings yet
- Au t2 e 2149 Modal Verbs Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Powerpoint Australian Ver 1Document12 pagesAu t2 e 2149 Modal Verbs Grammar Revision Guide and Quick Quiz Powerpoint Australian Ver 1Thanh Huyen LeNo ratings yet
- The Filipino Value System and Its Influence On Business PracticesDocument8 pagesThe Filipino Value System and Its Influence On Business PracticesJoan Marie SalayogNo ratings yet
- Br2e Upper-Int Reading Notes 4Document1 pageBr2e Upper-Int Reading Notes 4Haydee GallardoNo ratings yet
- Types of SentencesDocument6 pagesTypes of SentencesJenieNo ratings yet
- Mastermind 1 Unit 10 Grammar 1Document10 pagesMastermind 1 Unit 10 Grammar 1Mauricio Martinez GambaNo ratings yet
- The Destrier Writing 1 (SPE W)Document35 pagesThe Destrier Writing 1 (SPE W)Renz Louie LedseyNo ratings yet
- Year 3 Summer Block 1 Step 1 PPT Equivalent Fractions 1Document20 pagesYear 3 Summer Block 1 Step 1 PPT Equivalent Fractions 1Sahar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Change The Sentence Types KS2 SPAG SATs Test Practice Interactive EasyDocument2 pagesChange The Sentence Types KS2 SPAG SATs Test Practice Interactive EasyRodaina MahmoudNo ratings yet
- 7 Cs of CommunicationDocument27 pages7 Cs of CommunicationHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Modal Auxiliary: This Paper Is Structured To Fulfill The English Task Lecturer: Nikmatul Khoiriah, S.PDDocument10 pagesModal Auxiliary: This Paper Is Structured To Fulfill The English Task Lecturer: Nikmatul Khoiriah, S.PDBona LasagnaNo ratings yet
- SLM Week 1 Q2 Oral Com FinalDocument5 pagesSLM Week 1 Q2 Oral Com FinalJean RomarNo ratings yet
- ParaphrasingDocument13 pagesParaphrasingapi-3697552100% (7)
- Slide Powerpoint - The Cooperative PrinciplesDocument40 pagesSlide Powerpoint - The Cooperative PrinciplesQuỳnh Ngân VõNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology Worksheet Module 17Document6 pagesChild Psychology Worksheet Module 17Şterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Paragraph Writing-1Document1 pageRubric For Paragraph Writing-1Kevin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Using Modal Verbs To Indicate Degrees of Possibility Mini TestDocument3 pagesUsing Modal Verbs To Indicate Degrees of Possibility Mini TestTilly KyriakidesNo ratings yet
- Group Work-Modal VerbsDocument9 pagesGroup Work-Modal Verbsmalonamige20No ratings yet
- Thank You: Stellar Teacher Co. LLC. All Rights ReservedDocument7 pagesThank You: Stellar Teacher Co. LLC. All Rights ReservedAleksandra NikolskaiaNo ratings yet
- Cute Little Notes SlidesManiaDocument23 pagesCute Little Notes SlidesManiaDilla FadillaNo ratings yet
- Gps Year 4 Spring Block 2 Step 3 PPT Direct or Indirect Speech PDFDocument21 pagesGps Year 4 Spring Block 2 Step 3 PPT Direct or Indirect Speech PDFVeloso Angela FaithNo ratings yet
- What Is An AdverbDocument3 pagesWhat Is An AdverbJonard JocoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Ladders - Grade 6 - Spending MoneyDocument6 pagesVocabulary Ladders - Grade 6 - Spending MoneyfairfurNo ratings yet
- Sharp Minds GMAT Prep - Grammar-Handbook - Part 5Document15 pagesSharp Minds GMAT Prep - Grammar-Handbook - Part 5Anonymous brpVlaVBNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 9Document8 pagesDLL Grade 9kaylleapiladaNo ratings yet
- MySide 007Document1 pageMySide 007api-26739370No ratings yet
- Bài Thuyết Trình Nhóm 6Document41 pagesBài Thuyết Trình Nhóm 6Quỳnh Ngân VõNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 - P4 - Unit 1 - Spell Zone - AKDocument35 pages2022-2023 - P4 - Unit 1 - Spell Zone - AKGuan Tang CheungNo ratings yet
- Day 3Document6 pagesDay 3LUCYNIL OBERESNo ratings yet
- Complete-Vocabulary-Preview 11 PlusDocument26 pagesComplete-Vocabulary-Preview 11 PlusHong DangNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Lesson 4 What Is An AdverbDocument3 pagesCH 5 Lesson 4 What Is An AdverbNoviani al husnul kenNo ratings yet
- IAL Mathematics Sample Assessment MaterialDocument460 pagesIAL Mathematics Sample Assessment MaterialMohamed Naaif100% (3)
- Cambridge Aice BrochureDocument2 pagesCambridge Aice Brochureapi-294488294No ratings yet
- Corrigendum/ Extension of Date of Submission Last Date of Submission of Application Form For Post of Professor/ AssociateDocument20 pagesCorrigendum/ Extension of Date of Submission Last Date of Submission of Application Form For Post of Professor/ AssociateguruNo ratings yet
- Industrial Motor Controls I: IDSY 1110Document5 pagesIndustrial Motor Controls I: IDSY 1110Ajay SolateNo ratings yet
- (Note: Discussions May Change Course (Deviate From The Original Plan) Depending On Students' Responses ToDocument2 pages(Note: Discussions May Change Course (Deviate From The Original Plan) Depending On Students' Responses ToRubenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3, Capt. AguillonDocument44 pagesChapter 1-3, Capt. AguillonJohn Ross RamosNo ratings yet
- Sarah Corba ResumeDocument3 pagesSarah Corba Resumeapi-505000786No ratings yet
- Mahouka Koukou No Rettousei Vol 12 - Double Seven ChapterDocument174 pagesMahouka Koukou No Rettousei Vol 12 - Double Seven ChapterStratogan0% (1)
- Shays Rebellion Lesson Plan 3Document4 pagesShays Rebellion Lesson Plan 3api-434731744No ratings yet
- Motivational BreakthroughDocument36 pagesMotivational Breakthroughapi-240997758No ratings yet
- Final Work Assignments Monitoring Tool June 2020Document70 pagesFinal Work Assignments Monitoring Tool June 2020Louise BenzNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Instructional Leadership For Filipino Teachers in Senior High School: A Case Study in The School Division of ManilaDocument6 pagesEnhancing Instructional Leadership For Filipino Teachers in Senior High School: A Case Study in The School Division of ManilaPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- For Admission Please Visit: Onlineadmission - Numl.edu - PK: Admissions Fall - 2020Document7 pagesFor Admission Please Visit: Onlineadmission - Numl.edu - PK: Admissions Fall - 2020ranaaliahmedNo ratings yet
- Ict Assignment 1 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesIct Assignment 1 Lesson Planapi-280946178No ratings yet
- KHDA - Al Sadiq Islamic English School 2016-2017Document26 pagesKHDA - Al Sadiq Islamic English School 2016-2017Edarabia.comNo ratings yet
- Assessment Is a-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesAssessment Is a-WPS Officejsjjsjs ksksndNo ratings yet
- Gcu Performance Evaluation and Action Plan 1Document8 pagesGcu Performance Evaluation and Action Plan 1api-606287911No ratings yet
- Concordia UniversityDocument4 pagesConcordia Universitybuetce041662912No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan - Gherlyn, Sia, JasperDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan - Gherlyn, Sia, Jasperariannerose gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Resume Marsha LarsonDocument1 pageResume Marsha Larsonapi-445526818No ratings yet
- Holly TurnerDocument39 pagesHolly Turnerapi-324846334No ratings yet
- Grading System For TeachersDocument3 pagesGrading System For TeachersLaurenNo ratings yet
- A Report On Induction Programme - FinalDocument9 pagesA Report On Induction Programme - FinalDipakNo ratings yet
- Human CapitalDocument4 pagesHuman CapitalKumar DayanidhiNo ratings yet
- Borrower'S Slip: Pag-Asa National High SchoolDocument1 pageBorrower'S Slip: Pag-Asa National High SchoolCristian PortugalNo ratings yet
- M C M C M C: Super Minds Lesson 61Document2 pagesM C M C M C: Super Minds Lesson 61thinagaranNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeNaya KayalaNo ratings yet