Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsForensic Ballistics CARTRIDGE CASE
Forensic Ballistics CARTRIDGE CASE
Uploaded by
09055158584globeThe document discusses cartridge cases and their components. It examines the functions of parts like the rim, primer pocket, flash hole, body, neck, cannelure, crimp, base, shoulder, and extracting groove. It also evaluates classifications of cartridge cases based on case shape (straight, bottleneck, tapered) and head form (rimmed, semi-rimmed, rimless, rebated, belted). Finally, it describes the types of gunpowder - black powder and smokeless powder - that are contained in cartridge cases and responsible for propelling bullets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- T'au Codex 9th Ed (Full)Document62 pagesT'au Codex 9th Ed (Full)tdi0582% (11)
- Module 2 in Forensic BallisticsDocument9 pagesModule 2 in Forensic Ballisticscriminologyalliance100% (2)
- Edpm Assignment 2 PowerpointDocument15 pagesEdpm Assignment 2 PowerpointDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Ammunitions and Cartridges: Presented By: Alex P. Sarmiento MS CrimDocument114 pagesAmmunitions and Cartridges: Presented By: Alex P. Sarmiento MS CrimSundae Angenette100% (1)
- Anschutz 64Document18 pagesAnschutz 64JustinNo ratings yet
- SP 1075 PDFDocument17 pagesSP 1075 PDFHari Prakash GrandheyNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics Topic:: Bullet & Cartridge CaseDocument27 pagesForensic Ballistics Topic:: Bullet & Cartridge CasedenverboyboyNo ratings yet
- Galano, Gio S. Bs - Criminology Echo - 2 Pe Crim 4Document3 pagesGalano, Gio S. Bs - Criminology Echo - 2 Pe Crim 4JL HUFANONo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument94 pagesForensic BallisticsVergara BenjNo ratings yet
- MOdule For AmmunitionDocument30 pagesMOdule For AmmunitiongracelynNo ratings yet
- Firearm Ammunition and Cartridge CasesDocument5 pagesFirearm Ammunition and Cartridge CasesDomingo John-h Wyler CainoyNo ratings yet
- Forensic BasllisticDocument8 pagesForensic BasllisticKimmy Quiambao100% (1)
- Chapter 15 FirearmsDocument52 pagesChapter 15 FirearmsEngelbert MonteNo ratings yet
- For MidtermDocument30 pagesFor MidtermJaneth AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Ballistics PowerPointDocument42 pagesBallistics PowerPointSamira AbdoNo ratings yet
- Marksmanship 2nd ModuleDocument7 pagesMarksmanship 2nd Modulejenny sansanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiiDocument4 pagesChapter IiiCherry A. ArcioNo ratings yet
- Pe4 NotesDocument19 pagesPe4 NotesSIBAYAN, ZANEA AYNNo ratings yet
- Actuator: AvailableDocument17 pagesActuator: Availabledharmendra singhNo ratings yet
- Week5 AmmunitionDocument6 pagesWeek5 Ammunitionruui chizakuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter IvDocument5 pagesChapter IvCherry A. ArcioNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics Chapter 4Document16 pagesForensic Ballistics Chapter 4Ricci Earl Lauron100% (1)
- TerminologyDocument3 pagesTerminologyNotrobNo ratings yet
- Criminology Board Exam Reviewer: Forensic Ballistics Definition of TermsDocument14 pagesCriminology Board Exam Reviewer: Forensic Ballistics Definition of TermsEmmanuel BuanNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics 5Document8 pagesForensic Ballistics 5johnpaulacostaNo ratings yet
- Unit - III - Ammunition-1Document39 pagesUnit - III - Ammunition-1Nived K KNo ratings yet
- Cartridge Case and Bullets. EditedDocument54 pagesCartridge Case and Bullets. EditedAnjali yiascmNo ratings yet
- Notes in Forensic Ballistics Mapfiles: The AmmunitionDocument10 pagesNotes in Forensic Ballistics Mapfiles: The AmmunitionZenwel PaulaNo ratings yet
- Yllana Bay View College: Balangasan District Pagadian CityDocument9 pagesYllana Bay View College: Balangasan District Pagadian CityElla BanlasanNo ratings yet
- Ammunition: Forensic BallisticsDocument2 pagesAmmunition: Forensic BallisticsHaimelien De LimosNo ratings yet
- Firearms TerminologyDocument23 pagesFirearms Terminologyseversky100% (2)
- Ballistics PE4Document65 pagesBallistics PE4Dariel De VeneciaNo ratings yet
- Cartridge CaseDocument2 pagesCartridge CaseLOVELY TRAZONANo ratings yet
- Flintlock Mechanism DescriptionDocument6 pagesFlintlock Mechanism DescriptionMazhar Talaat100% (1)
- BS Criminology Program: Physically Distanced But Academically EngagedDocument10 pagesBS Criminology Program: Physically Distanced But Academically Engagedvworldpeace yanibNo ratings yet
- BulletDocument5 pagesBulletStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- CartridgeDocument26 pagesCartridgeMnavya SaiNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticDocument12 pagesForensic BallisticYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ballistic ModuleDocument6 pagesBallistic ModuleJoseNo ratings yet
- The Shotgun BibleDocument15 pagesThe Shotgun Biblesuasponte289% (9)
- WOUND BALLISTICS ExamDocument143 pagesWOUND BALLISTICS ExamGUILAY, KEVIN MARK F.No ratings yet
- News ZipgunsDocument2 pagesNews ZipgunsZarcano Farias100% (1)
- Forensic Ballistics Module 7Document12 pagesForensic Ballistics Module 720-0383.dizorNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics 2Document2 pagesForensic Ballistics 2john acostaNo ratings yet
- Shotgun Safety Overview V 9Document14 pagesShotgun Safety Overview V 9chí quyển trươngNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics (BIGWAS)Document19 pagesForensic Ballistics (BIGWAS)KARLVINNo ratings yet
- The M6 Aircrew Survival WeaponDocument9 pagesThe M6 Aircrew Survival Weaponblowmeasshole1911No ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument34 pagesForensic BallisticsNURUL A'TIKAHNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics 3Document2 pagesForensic Ballistics 3john acostaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Firearms and AmmunitionDocument20 pagesTopic 2 Firearms and AmmunitioncrmsncrseNo ratings yet
- How Shotguns WorkDocument6 pagesHow Shotguns WorkMurat SAVSA100% (4)
- Glossary of Firearms TerminologyDocument14 pagesGlossary of Firearms Terminologyaaraujo_117636No ratings yet
- Cartridge CaseDocument3 pagesCartridge Caseangyll agaledNo ratings yet
- Headspace GuideDocument7 pagesHeadspace Guideusn212100% (2)
- F - Topic 9 Firearms CharacteristicsDocument31 pagesF - Topic 9 Firearms CharacteristicsJent Denise DisepedaNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument8 pagesForensic BallisticsJoshua D None-NoneNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument9 pagesForensic BallisticsTim Sangalang100% (1)
- Chapter Iii Ammunitions/CartridgesDocument8 pagesChapter Iii Ammunitions/CartridgesEy GrailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document47 pagesChapter 1Angelie NapaliaNo ratings yet
- How To Drill A Rifle BarrelDocument6 pagesHow To Drill A Rifle BarrelMaria Donoghue50% (2)
- ReportDocument20 pagesReportjaylou taboriteNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument20 pagesForensic BallisticsKunfu kenny100% (1)
- Equipment Encyclopedia v2.0.5Document16 pagesEquipment Encyclopedia v2.0.5Asen0% (1)
- Mortar Ammunition Across The Globe: Anthony G Williams Editor, IHS Jane's Weapons: AmmunitionDocument20 pagesMortar Ammunition Across The Globe: Anthony G Williams Editor, IHS Jane's Weapons: AmmunitionEdgardo GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2 Reading Text 1Document2 pages2 Reading Text 1desy fitriNo ratings yet
- Marine Hsse Final Assignment Chop SawDocument11 pagesMarine Hsse Final Assignment Chop SawMuhammad Mirza RaziqNo ratings yet
- Winchester Model 1886 Takedown Lever Action RifleDocument0 pagesWinchester Model 1886 Takedown Lever Action Riflecarlosfanjul1No ratings yet
- 3.1 Hazards and Hazard Type What Is A Hazard?Document2 pages3.1 Hazards and Hazard Type What Is A Hazard?YURI ISHIDANo ratings yet
- Udmc Brochure Updated July2022Document28 pagesUdmc Brochure Updated July2022Konrad Neil IIINo ratings yet
- Fire Department: Residential Apartment Building Fire SafetyDocument4 pagesFire Department: Residential Apartment Building Fire SafetyMuhamad Salman AzmiNo ratings yet
- BSL 2Document30 pagesBSL 2Shafira Nurianti salimNo ratings yet
- BS Criminology Program: Physically Distanced But Academically EngagedDocument10 pagesBS Criminology Program: Physically Distanced But Academically Engagedvworldpeace yanibNo ratings yet
- Hirarc Level 1 (Contoh)Document5 pagesHirarc Level 1 (Contoh)Alvin MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 1 Some People Think That Lawbreakers Should Be Sent To PrisonDocument3 pages1 Some People Think That Lawbreakers Should Be Sent To PrisonRachit ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Section 304B of IPC Vs 498ADocument2 pagesSection 304B of IPC Vs 498AKushagr GautamNo ratings yet
- List of Naval Guns by CaliberDocument65 pagesList of Naval Guns by CaliberSoe Thu100% (1)
- Officer Involved Shooting 1.1.24 Final ReportDocument21 pagesOfficer Involved Shooting 1.1.24 Final ReportThe GazetteNo ratings yet
- Cstrike SpanishDocument66 pagesCstrike SpanishyowYouNo ratings yet
- BALLISTICSDocument21 pagesBALLISTICSVince Clint C. RiveraNo ratings yet
- Clockwork Dragons Expanded Armory 1 12Document13 pagesClockwork Dragons Expanded Armory 1 12Kaleb PrinceNo ratings yet
- Revolver ManufacturingDocument7 pagesRevolver ManufacturingTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Paombong - D3R - Mod 1 - Second Semester - First Quarter - Stem 11 Del Pilar - Stem 11 MalvarDocument23 pagesPaombong - D3R - Mod 1 - Second Semester - First Quarter - Stem 11 Del Pilar - Stem 11 MalvarRjei CinzelNo ratings yet
- Fire Service Rank StructureDocument4 pagesFire Service Rank StructurekieranfitzgeraldNo ratings yet
- Implan 2016 (Siniloan)Document4 pagesImplan 2016 (Siniloan)Bfp Siniloan FS LagunaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction Module 1 Basic Concept of Disaster and Disaster RiskDocument27 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction Module 1 Basic Concept of Disaster and Disaster Riskzkurt delmoNo ratings yet
- DRRR PresentationDocument9 pagesDRRR PresentationSofia Anne JoseNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistic For ReviewDocument227 pagesForensic Ballistic For ReviewJanice dela Cruz100% (3)
- Sort Set in Shine StandardizeDocument3 pagesSort Set in Shine StandardizeJan Bryan EslavaNo ratings yet
Forensic Ballistics CARTRIDGE CASE
Forensic Ballistics CARTRIDGE CASE
Uploaded by
09055158584globe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views18 pagesThe document discusses cartridge cases and their components. It examines the functions of parts like the rim, primer pocket, flash hole, body, neck, cannelure, crimp, base, shoulder, and extracting groove. It also evaluates classifications of cartridge cases based on case shape (straight, bottleneck, tapered) and head form (rimmed, semi-rimmed, rimless, rebated, belted). Finally, it describes the types of gunpowder - black powder and smokeless powder - that are contained in cartridge cases and responsible for propelling bullets.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses cartridge cases and their components. It examines the functions of parts like the rim, primer pocket, flash hole, body, neck, cannelure, crimp, base, shoulder, and extracting groove. It also evaluates classifications of cartridge cases based on case shape (straight, bottleneck, tapered) and head form (rimmed, semi-rimmed, rimless, rebated, belted). Finally, it describes the types of gunpowder - black powder and smokeless powder - that are contained in cartridge cases and responsible for propelling bullets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views18 pagesForensic Ballistics CARTRIDGE CASE
Forensic Ballistics CARTRIDGE CASE
Uploaded by
09055158584globeThe document discusses cartridge cases and their components. It examines the functions of parts like the rim, primer pocket, flash hole, body, neck, cannelure, crimp, base, shoulder, and extracting groove. It also evaluates classifications of cartridge cases based on case shape (straight, bottleneck, tapered) and head form (rimmed, semi-rimmed, rimless, rebated, belted). Finally, it describes the types of gunpowder - black powder and smokeless powder - that are contained in cartridge cases and responsible for propelling bullets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
CARTRIDGE CASE
Learning Objectives:
1. Examine the functions of the parts of the
cartridge case.
2. Evaluate the significance of studying the
classifications of the cartridge cases in
crime investigation.
Cartridge case/ Shell/ Casing
It is the part of the cartridge which houses the bullet,
gunpowder, and primer.
This part has a significant contribution to the identification
of firearms because it receives the individual
characteristics from the firearm where it was fired,
extracted, and ejected.
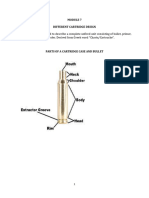
Parts of Cartridge Case
1. Rim – located on the base of the
cartridge case and is responsible
for limiting the forward movement
of the cartridge when loaded in the
chamber of a revolver or shotgun.
2. Primer Pocket – The hole at the
center of the base of the cartridge
is designed to house the primer.
3. Flash hole – The hole located at the
center of the primer pocket serves as
the canal of the ignition produced by
the primer towards the gunpowder.
4. Body – In order to develop sufficient
pressure, the heat should not be able
to escape during an explosion.
5. Neck – This part is occupied by the
bullet in a bottleneck cartridge case
and where the cannelure is located.
6. Cannelure – A serrated groove found at
the neck holds the bullet’s end part. It
prevents the bullet from being pushed back or
loosened.
7. Crimp – It is also a serrated groove located
inside the mouth of the cartridge case, which
aids the cannelure in holding the end portion
of the bullet.
8. Base – It is created when the cartridge
case is extracted out from the chamber and
pulled back towards the breech face.
9. Shoulder – This is a part of a
bottleneck cartridge case located
between the body and neck.
10. Extracting Groove – This refers
to the serrated groove located
between the cartridge case’s body
and case. It is created when the hand
of the extractor drags this part to
withdraw the cartridge case out from
the gun chamber.
Classification of Cartridge Case according to Case
Shape
• Straight cartridge case – it is straight from the rear portion of
the body towards the mouth. Designed to accommodate the
standard amount of gunpowder as well as the caliber of bullet
of the pistol and revolvers.
• Bottle neck cartridge case – The diameter of its body is
greater than the diameter of its neck and mouth.
• Tapered cartridge case – Its design is tapered towards the
mouth. It was used in a magnum jet cartridge case of caliber.
Classification of Cartridge Case
according to Head Form
• Rimmed Cartridge Case - The rim diameter is much
bigger than the body of the cartridge case. It is designed
so that the cartridge will not move forward after it is
loaded in the chamber of the said firearms.
• Semi-rimmed - This is appropriate for a semi-automatic
weapon. The diameter of its rim is a little bit bigger than
the body. Its rim does not serve to limit the forward
movement of the cartridge upon loading in the chamber.
• Rimless - It has a rim but its diameter is equal to the
body of the cartridge case.
• Rebated - The diameter of the rim is a little bit smaller
than its body.
• Belted - The rim is belted around the body of the
cartridge case.
Gunpowder
Is a compound contained in a cartridge that is
responsible for propelling the projectile.
This compound will undergo combustion when ignited by
the flash that came from the primer.
Two Types of Powder in Small Arms
• Black Powder
It is easily activated by heat and friction. Thus, it is the most
unsafe type of powder to keep. A large volume of smoke and
residue left in the barrel of the gun can be produced by this type of
powder.
The Standard Ingredients:
1. 75% of potassium nitrate
2. 10% of sulfur
3. 15% of charcoal
• Smokeless Powder
It is a propellant that does not give off a massive
cloud of white smoke like black powder when fired.
It is the most potent propellant in small arms.
Two main classes:
1. Single-base propellant (nitrocellulose) - It only
contains pure nitroglycerine gelatinized with
nitrocellulose. This type of propellant has a perfect shape
in grains like small squares, discs, flakes, strips, pellets,
or perforated cylindrical grains.
2. Double base propellant - has nitrocellulose and nitro-
glycerine as the significant ingredients mixed with minor
ingredients like vaseline phthalein esters and inorganic
salts.
End...
You might also like
- T'au Codex 9th Ed (Full)Document62 pagesT'au Codex 9th Ed (Full)tdi0582% (11)
- Module 2 in Forensic BallisticsDocument9 pagesModule 2 in Forensic Ballisticscriminologyalliance100% (2)
- Edpm Assignment 2 PowerpointDocument15 pagesEdpm Assignment 2 PowerpointDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Ammunitions and Cartridges: Presented By: Alex P. Sarmiento MS CrimDocument114 pagesAmmunitions and Cartridges: Presented By: Alex P. Sarmiento MS CrimSundae Angenette100% (1)
- Anschutz 64Document18 pagesAnschutz 64JustinNo ratings yet
- SP 1075 PDFDocument17 pagesSP 1075 PDFHari Prakash GrandheyNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics Topic:: Bullet & Cartridge CaseDocument27 pagesForensic Ballistics Topic:: Bullet & Cartridge CasedenverboyboyNo ratings yet
- Galano, Gio S. Bs - Criminology Echo - 2 Pe Crim 4Document3 pagesGalano, Gio S. Bs - Criminology Echo - 2 Pe Crim 4JL HUFANONo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument94 pagesForensic BallisticsVergara BenjNo ratings yet
- MOdule For AmmunitionDocument30 pagesMOdule For AmmunitiongracelynNo ratings yet
- Firearm Ammunition and Cartridge CasesDocument5 pagesFirearm Ammunition and Cartridge CasesDomingo John-h Wyler CainoyNo ratings yet
- Forensic BasllisticDocument8 pagesForensic BasllisticKimmy Quiambao100% (1)
- Chapter 15 FirearmsDocument52 pagesChapter 15 FirearmsEngelbert MonteNo ratings yet
- For MidtermDocument30 pagesFor MidtermJaneth AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Ballistics PowerPointDocument42 pagesBallistics PowerPointSamira AbdoNo ratings yet
- Marksmanship 2nd ModuleDocument7 pagesMarksmanship 2nd Modulejenny sansanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiiDocument4 pagesChapter IiiCherry A. ArcioNo ratings yet
- Pe4 NotesDocument19 pagesPe4 NotesSIBAYAN, ZANEA AYNNo ratings yet
- Actuator: AvailableDocument17 pagesActuator: Availabledharmendra singhNo ratings yet
- Week5 AmmunitionDocument6 pagesWeek5 Ammunitionruui chizakuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter IvDocument5 pagesChapter IvCherry A. ArcioNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics Chapter 4Document16 pagesForensic Ballistics Chapter 4Ricci Earl Lauron100% (1)
- TerminologyDocument3 pagesTerminologyNotrobNo ratings yet
- Criminology Board Exam Reviewer: Forensic Ballistics Definition of TermsDocument14 pagesCriminology Board Exam Reviewer: Forensic Ballistics Definition of TermsEmmanuel BuanNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics 5Document8 pagesForensic Ballistics 5johnpaulacostaNo ratings yet
- Unit - III - Ammunition-1Document39 pagesUnit - III - Ammunition-1Nived K KNo ratings yet
- Cartridge Case and Bullets. EditedDocument54 pagesCartridge Case and Bullets. EditedAnjali yiascmNo ratings yet
- Notes in Forensic Ballistics Mapfiles: The AmmunitionDocument10 pagesNotes in Forensic Ballistics Mapfiles: The AmmunitionZenwel PaulaNo ratings yet
- Yllana Bay View College: Balangasan District Pagadian CityDocument9 pagesYllana Bay View College: Balangasan District Pagadian CityElla BanlasanNo ratings yet
- Ammunition: Forensic BallisticsDocument2 pagesAmmunition: Forensic BallisticsHaimelien De LimosNo ratings yet
- Firearms TerminologyDocument23 pagesFirearms Terminologyseversky100% (2)
- Ballistics PE4Document65 pagesBallistics PE4Dariel De VeneciaNo ratings yet
- Cartridge CaseDocument2 pagesCartridge CaseLOVELY TRAZONANo ratings yet
- Flintlock Mechanism DescriptionDocument6 pagesFlintlock Mechanism DescriptionMazhar Talaat100% (1)
- BS Criminology Program: Physically Distanced But Academically EngagedDocument10 pagesBS Criminology Program: Physically Distanced But Academically Engagedvworldpeace yanibNo ratings yet
- BulletDocument5 pagesBulletStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- CartridgeDocument26 pagesCartridgeMnavya SaiNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticDocument12 pagesForensic BallisticYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ballistic ModuleDocument6 pagesBallistic ModuleJoseNo ratings yet
- The Shotgun BibleDocument15 pagesThe Shotgun Biblesuasponte289% (9)
- WOUND BALLISTICS ExamDocument143 pagesWOUND BALLISTICS ExamGUILAY, KEVIN MARK F.No ratings yet
- News ZipgunsDocument2 pagesNews ZipgunsZarcano Farias100% (1)
- Forensic Ballistics Module 7Document12 pagesForensic Ballistics Module 720-0383.dizorNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics 2Document2 pagesForensic Ballistics 2john acostaNo ratings yet
- Shotgun Safety Overview V 9Document14 pagesShotgun Safety Overview V 9chí quyển trươngNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics (BIGWAS)Document19 pagesForensic Ballistics (BIGWAS)KARLVINNo ratings yet
- The M6 Aircrew Survival WeaponDocument9 pagesThe M6 Aircrew Survival Weaponblowmeasshole1911No ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument34 pagesForensic BallisticsNURUL A'TIKAHNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics 3Document2 pagesForensic Ballistics 3john acostaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Firearms and AmmunitionDocument20 pagesTopic 2 Firearms and AmmunitioncrmsncrseNo ratings yet
- How Shotguns WorkDocument6 pagesHow Shotguns WorkMurat SAVSA100% (4)
- Glossary of Firearms TerminologyDocument14 pagesGlossary of Firearms Terminologyaaraujo_117636No ratings yet
- Cartridge CaseDocument3 pagesCartridge Caseangyll agaledNo ratings yet
- Headspace GuideDocument7 pagesHeadspace Guideusn212100% (2)
- F - Topic 9 Firearms CharacteristicsDocument31 pagesF - Topic 9 Firearms CharacteristicsJent Denise DisepedaNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument8 pagesForensic BallisticsJoshua D None-NoneNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument9 pagesForensic BallisticsTim Sangalang100% (1)
- Chapter Iii Ammunitions/CartridgesDocument8 pagesChapter Iii Ammunitions/CartridgesEy GrailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document47 pagesChapter 1Angelie NapaliaNo ratings yet
- How To Drill A Rifle BarrelDocument6 pagesHow To Drill A Rifle BarrelMaria Donoghue50% (2)
- ReportDocument20 pagesReportjaylou taboriteNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument20 pagesForensic BallisticsKunfu kenny100% (1)
- Equipment Encyclopedia v2.0.5Document16 pagesEquipment Encyclopedia v2.0.5Asen0% (1)
- Mortar Ammunition Across The Globe: Anthony G Williams Editor, IHS Jane's Weapons: AmmunitionDocument20 pagesMortar Ammunition Across The Globe: Anthony G Williams Editor, IHS Jane's Weapons: AmmunitionEdgardo GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2 Reading Text 1Document2 pages2 Reading Text 1desy fitriNo ratings yet
- Marine Hsse Final Assignment Chop SawDocument11 pagesMarine Hsse Final Assignment Chop SawMuhammad Mirza RaziqNo ratings yet
- Winchester Model 1886 Takedown Lever Action RifleDocument0 pagesWinchester Model 1886 Takedown Lever Action Riflecarlosfanjul1No ratings yet
- 3.1 Hazards and Hazard Type What Is A Hazard?Document2 pages3.1 Hazards and Hazard Type What Is A Hazard?YURI ISHIDANo ratings yet
- Udmc Brochure Updated July2022Document28 pagesUdmc Brochure Updated July2022Konrad Neil IIINo ratings yet
- Fire Department: Residential Apartment Building Fire SafetyDocument4 pagesFire Department: Residential Apartment Building Fire SafetyMuhamad Salman AzmiNo ratings yet
- BSL 2Document30 pagesBSL 2Shafira Nurianti salimNo ratings yet
- BS Criminology Program: Physically Distanced But Academically EngagedDocument10 pagesBS Criminology Program: Physically Distanced But Academically Engagedvworldpeace yanibNo ratings yet
- Hirarc Level 1 (Contoh)Document5 pagesHirarc Level 1 (Contoh)Alvin MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 1 Some People Think That Lawbreakers Should Be Sent To PrisonDocument3 pages1 Some People Think That Lawbreakers Should Be Sent To PrisonRachit ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Section 304B of IPC Vs 498ADocument2 pagesSection 304B of IPC Vs 498AKushagr GautamNo ratings yet
- List of Naval Guns by CaliberDocument65 pagesList of Naval Guns by CaliberSoe Thu100% (1)
- Officer Involved Shooting 1.1.24 Final ReportDocument21 pagesOfficer Involved Shooting 1.1.24 Final ReportThe GazetteNo ratings yet
- Cstrike SpanishDocument66 pagesCstrike SpanishyowYouNo ratings yet
- BALLISTICSDocument21 pagesBALLISTICSVince Clint C. RiveraNo ratings yet
- Clockwork Dragons Expanded Armory 1 12Document13 pagesClockwork Dragons Expanded Armory 1 12Kaleb PrinceNo ratings yet
- Revolver ManufacturingDocument7 pagesRevolver ManufacturingTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Paombong - D3R - Mod 1 - Second Semester - First Quarter - Stem 11 Del Pilar - Stem 11 MalvarDocument23 pagesPaombong - D3R - Mod 1 - Second Semester - First Quarter - Stem 11 Del Pilar - Stem 11 MalvarRjei CinzelNo ratings yet
- Fire Service Rank StructureDocument4 pagesFire Service Rank StructurekieranfitzgeraldNo ratings yet
- Implan 2016 (Siniloan)Document4 pagesImplan 2016 (Siniloan)Bfp Siniloan FS LagunaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction Module 1 Basic Concept of Disaster and Disaster RiskDocument27 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction Module 1 Basic Concept of Disaster and Disaster Riskzkurt delmoNo ratings yet
- DRRR PresentationDocument9 pagesDRRR PresentationSofia Anne JoseNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistic For ReviewDocument227 pagesForensic Ballistic For ReviewJanice dela Cruz100% (3)
- Sort Set in Shine StandardizeDocument3 pagesSort Set in Shine StandardizeJan Bryan EslavaNo ratings yet