Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6.
Chapter 6.
Uploaded by
Taimori Fadhili0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesPropane is a colorless hydrocarbon that exists as a gas at room temperature but condenses to a liquid when pressurized. It is produced from petroleum refining and natural gas processing, transported in liquid form, then distributed to bulk storage facilities. Propane has many uses including for heating homes and buildings, cooking, agricultural equipment, transportation, industrial processes, and portable fuel. Though a cleaner burning fossil fuel, propane does produce carbon dioxide and other emissions when combusted.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPropane is a colorless hydrocarbon that exists as a gas at room temperature but condenses to a liquid when pressurized. It is produced from petroleum refining and natural gas processing, transported in liquid form, then distributed to bulk storage facilities. Propane has many uses including for heating homes and buildings, cooking, agricultural equipment, transportation, industrial processes, and portable fuel. Though a cleaner burning fossil fuel, propane does produce carbon dioxide and other emissions when combusted.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesChapter 6.
Chapter 6.
Uploaded by
Taimori FadhiliPropane is a colorless hydrocarbon that exists as a gas at room temperature but condenses to a liquid when pressurized. It is produced from petroleum refining and natural gas processing, transported in liquid form, then distributed to bulk storage facilities. Propane has many uses including for heating homes and buildings, cooking, agricultural equipment, transportation, industrial processes, and portable fuel. Though a cleaner burning fossil fuel, propane does produce carbon dioxide and other emissions when combusted.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
Chapter 6
Propane
Fundamentals of Gas Technology
Introduction
Propane, also known as “bottled gas,” is a
colorless hydrocarbon with the chemical formula
C3H8.
Propane can exist in both gaseous and liquid form.
At room temperature and atmospheric pressure
(14.7 psi) it is a gas.
When tanks or containers are filled with propane,
they are pressurized to 100-200 psi, and the
increase in pressure causes propane to condense
and form a liquid.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 2
Introduction Cont…
The liquid form is often called liquefied petroleum
gas (LPG or LP for short). Although it is odorless,
a foul-smelling scent is added to propane so that
leaks can be easily detected.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 3
Production, Processing, and
Transportation of Propane
Petroleum refineries produce propane by heating
and distilling crude oil. Natural gas processing
plants also make propane.
After production, propane is transported in liquid
form by pipelines to a central distribution plant,
where it is stored in large steel cylinders and
tanks.
From there it is transported by trains, trucks,
barges, or ships to “bulk plants.” One gallon of
propane in LPG form contains 84,250 Btu of
energy.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 4
Production, Processing, and
Transportation of Propane
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 5
Production, Processing, and
Transportation of Propane
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 6
Uses of Propane
Propane is a versatile fuel, with a wide variety of
uses in industry, in agriculture, in homes, for
transportation fuel, and for recreational purposes.
Globally, the top five consumers of LPG in 2014
were the United States, China, Saudi Arabia,
Japan, and India (Wisconsin, 2020).
In 2012, Wisconsin used 245 million gallons of
LPG. Of this amount, over 87% was used for
residential purposes (Wisconsin, 2020).
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 7
Uses of Propane Cont…
Industrial Use
Nearly half of the propane consumed by industry
is used to make plastic.
Industries also use propane to run machinery, cut
metal, and for process heat.
Propane is also used to produce materials such as
aerosol propellants, solvents, and synthetic
vulcanized rubber.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 8
Uses of Propane Cont…
Agricultural Use
On farms, propane is used to operate various types
of farm equipment.
Farmers use propane to dry crops, warm chicken
coops, sterilize milk equipment, and more.
As of 2017, nearly 830,000 farms in the U.S. use
propane (Wisconsin, 2020).
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 9
Uses of Propane Cont…
Household Use
Many rural homeowners who do not have access
to natural gas pipelines rely on propane for space
heating, water heating, and clothes drying.
Roughly 8% of the homes in the Midwest are
heated with propane fuel, and nationally about 7
million households use propane for space heat
(Wisconsin, 2020).
Household use of LPG in 2014 accounted for 44%
of global propane consumption (Wisconsin, 2020).
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 10
Uses of Propane Cont…
Cooking Use
In the United States, 47 million households use
propane to fuel an outdoor gas grill (Wisconsin,
2020).
Restaurants and caterers use propane for cooking
and warming food, and also to fuel patio heaters
for outdoor seating areas in cold climates.
People often use propane for outdoor cooking, and
because of its portability, it is especially popular
with campers and mobile homeowners.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 11
Uses of Propane Cont…
Transportation Use
Propane is the energy source for more low
emission vehicles than any other fuel (including
ethanol, electricity, fuel cells, and solar cells).
Because propane is a very clean burning fuel with
very low emissions, it is especially ideal for
equipment such as forklifts and lift trucks that
operate in warehouses or construction sites where
indoor air quality is important.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 12
Uses of Propane Cont…
Transportation Use
It is also suitable for operating equipment in
underground mines and other enclosed spaces.
Propane is used as a fuel for vehicle fleets with
access to centralized LPG fueling stations (such as
buses or taxis), especially in urban areas that are
seeking to reduce tailpipe exhaust emissions.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 13
Uses of Propane Cont…
Electrical Production Use
Some utilities use propane to fuel backup
electrical generators when the demand for
electricity is very high, or if there is a disruption in
the supply of other energy sources.
However, most electric power plants do not use
much propane fuel, because it costs less to
produce electricity from other energy sources such
as solar, wind, hydropower, natural gas, coal or
uranium.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 14
Effects of Propane
Propane has helped many rural residents by
providing them with a relatively clean-burning
and reliable fuel.
Propane distribution and sales of propane-related
equipment have helped support rural economies.
Like natural gas, propane is one of the cleanest
burning fossil fuel products, releasing negligible
amounts of emissions. When burned, it leaves no
ash and produces practically no sulfur oxides,
particulate matter, or mercury emissions.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 15
Effects of Propane
On the other hand, burning propane produces
carbon dioxide, a cause of global climate change,
and it also emits nitrogen oxides which are key
ingredients in the formation of urban smog and
ozone.
02/06/2024 11:21 PM Propane 16
You might also like
- 50 Hydrogen Companies To Watch in 2024 1701946705Document9 pages50 Hydrogen Companies To Watch in 2024 1701946705MT HazrieNo ratings yet
- Capstone Design Project For Plant Design Steam Methane Reforming PlantDocument251 pagesCapstone Design Project For Plant Design Steam Methane Reforming PlantArman Jade LazarteNo ratings yet
- 93, 94Document282 pages93, 94Sulfa MubarikaNo ratings yet
- Astm D1067 PDFDocument8 pagesAstm D1067 PDFDaniela GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Facts About PropaneDocument10 pagesFacts About PropaneAbdulkadir Ali BageNo ratings yet
- PropaneDocument2 pagesPropaneapi-581666302No ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry Chemistry For Engineering students-CHEMI143 A Mini Research Paper On Propane Compound Course Instructor: Dr. Jack MustaklemDocument3 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Chemistry For Engineering students-CHEMI143 A Mini Research Paper On Propane Compound Course Instructor: Dr. Jack MustaklemSerina MohammedNo ratings yet
- Merits and Demerits of Alternative FuelsDocument11 pagesMerits and Demerits of Alternative FuelsShanky BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Process Propane DehydrogenationDocument4 pagesProcess Propane DehydrogenationRodrigo MazzarellaNo ratings yet
- Propane Workshop PPTDocument71 pagesPropane Workshop PPTch.kashifpervez100% (1)
- Propane LPGDocument9 pagesPropane LPGYeabsraNo ratings yet
- Abb LummusDocument2 pagesAbb LummusHonnoré christian souleyNo ratings yet
- Sarnia Lambton Propylene Investment Opportunity Final Report EDocument38 pagesSarnia Lambton Propylene Investment Opportunity Final Report EPranav Bhat100% (1)
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Applications and Uses:: 2-Metals IndustryDocument15 pagesCarbon Dioxide (CO2) Applications and Uses:: 2-Metals Industryahmed atwaNo ratings yet
- Green FertilizersDocument5 pagesGreen FertilizersAn NguyenNo ratings yet
- Iffco ReportDocument22 pagesIffco ReportNitin PatelNo ratings yet
- Training Report at NFL PanipatDocument22 pagesTraining Report at NFL PanipatKapil AroraNo ratings yet
- ENSYN RTP Description (2011)Document25 pagesENSYN RTP Description (2011)iboukis100% (1)
- Energy Sector (Natural Gas) - Long Term BuyDocument10 pagesEnergy Sector (Natural Gas) - Long Term BuychaakreeNo ratings yet
- Eb440b96 Ammonia Co Firing Analysis - EngDocument13 pagesEb440b96 Ammonia Co Firing Analysis - EngThuan Huynh MinhNo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument24 pagesHydrogenmeet003No ratings yet
- NictDocument10 pagesNictAKSHAT TIWARINo ratings yet
- Waste To Energy: Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)Document3 pagesWaste To Energy: Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)vijaykumarbitlaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument22 pagesUntitledsinghalmayank950No ratings yet
- Final Report Che231Document10 pagesFinal Report Che231nilamaziniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Topic - 2.1.6Document14 pagesLecture Topic - 2.1.6Amit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio Oil PriceDocument85 pagesBio Oil Pricerussell_mahmoodNo ratings yet
- AFV Quiz QuestionsDocument5 pagesAFV Quiz QuestionsSuryadev Sinh SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- Pru ReportDocument70 pagesPru ReportAravind MenonNo ratings yet
- FUELSDocument35 pagesFUELSJayson DayaoNo ratings yet
- LPG As Fuel PDFDocument8 pagesLPG As Fuel PDFNatesha SundharanNo ratings yet
- Our Company OrpicDocument6 pagesOur Company OrpicErik AlfiandyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 2Document7 pagesChemistry Module 2angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- A Perspective On The Use of Ammonia As A Clean FuelDocument8 pagesA Perspective On The Use of Ammonia As A Clean Fuel백종엽No ratings yet
- A Perspective On The Use of Ammonia As A Clean Fuel: Challenges and SolutionsDocument16 pagesA Perspective On The Use of Ammonia As A Clean Fuel: Challenges and Solutions1988anuNo ratings yet
- 12 PDH - Process Vora UOP PDFDocument12 pages12 PDH - Process Vora UOP PDFstxordNo ratings yet
- Preface: Plant, S.G.P, Nitric Acid Plant. It Also Contains An Overview of The NFL. The InformationDocument20 pagesPreface: Plant, S.G.P, Nitric Acid Plant. It Also Contains An Overview of The NFL. The InformationBhavesh BansalNo ratings yet
- Sweden BromDocument4 pagesSweden Bromseno_arjun5023No ratings yet
- Session: NH Fuel Use: Facilitator: Bill DavidDocument24 pagesSession: NH Fuel Use: Facilitator: Bill Davidkwayneolson6081No ratings yet
- Prospects of Green Ammonia For Fertilizer Production: Dr. S. NandDocument2 pagesProspects of Green Ammonia For Fertilizer Production: Dr. S. NandMinhquang NgoNo ratings yet
- Uses Rural HeatingDocument4 pagesUses Rural HeatingAhmed Amiir OmerNo ratings yet
- Total Essentiel 2014 GBDocument13 pagesTotal Essentiel 2014 GBAhmad NavidNo ratings yet
- Styrene Butadiene Rubber Production PlantDocument6 pagesStyrene Butadiene Rubber Production PlantHarold AldayNo ratings yet
- BF National Hydrogen Roadmap 2020Document48 pagesBF National Hydrogen Roadmap 2020Mahjoub AmriNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Users of LPG GasDocument12 pagesTop Ten Users of LPG GasHtoi San RoiNo ratings yet
- The Sdgs and Sustainable Fertilizer ProductionDocument6 pagesThe Sdgs and Sustainable Fertilizer ProductionAnonymous vWSYmPNo ratings yet
- Senza TitoloDocument28 pagesSenza TitoloGMSNo ratings yet
- Plastic To Oil: Dipak Kumar Shaw, Pranav SahniDocument3 pagesPlastic To Oil: Dipak Kumar Shaw, Pranav Sahniurfi ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- PropaneDocument6 pagesPropaneFERNANDO JOSE NOVAESNo ratings yet
- Gesalan, Jisille Abenoja (Final Term Paper)Document3 pagesGesalan, Jisille Abenoja (Final Term Paper)KristyneNo ratings yet
- Replacement of LPG To Propane Gas in Bicycle Manufacturing IndustriesDocument3 pagesReplacement of LPG To Propane Gas in Bicycle Manufacturing Industriesherdi sutanto adigunaNo ratings yet
- Individual AssignmentDocument8 pagesIndividual AssignmentEdwardLimNo ratings yet
- PropanepDocument3 pagesPropanepapi-581666302No ratings yet
- LPG RefrigeratorDocument29 pagesLPG RefrigeratorSodum MaheswarreddyNo ratings yet
- Propy-LENE Supply! Go Green! On-Purpose Technologies For The FutureDocument10 pagesPropy-LENE Supply! Go Green! On-Purpose Technologies For The FutureBeroe Inc.No ratings yet
- What Is A Refrigerant? Old and Modern Refrigerants Conclusion Discussion ForumDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Refrigerant? Old and Modern Refrigerants Conclusion Discussion ForumSharifur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Please Upload A Seminar or Project Report/Code/Material/Presentation HereDocument8 pagesPlease Upload A Seminar or Project Report/Code/Material/Presentation Hererushibmr19785604No ratings yet
- LNG RegasificationDocument22 pagesLNG RegasificationVu Duc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas InformationDocument13 pagesNatural Gas InformationSami Uddin Saifi100% (1)
- Polypropylne Expand On Consumer NeedsDocument53 pagesPolypropylne Expand On Consumer NeedsTato Flores100% (1)
- High Performance Solid Propellants For In-Space Propulsion: ReportingDocument16 pagesHigh Performance Solid Propellants For In-Space Propulsion: ReportingKundanNo ratings yet
- EntropyDocument39 pagesEntropyRohit Singh LatherNo ratings yet
- Algol Oy Mail - FWD - Carbon Black India - PCBL GroupDocument2 pagesAlgol Oy Mail - FWD - Carbon Black India - PCBL GroupAnshu SahniNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Materials: Presentation On Molten Salt Reactor Technology By: David Holcomb, PH.DDocument27 pagesModule 5: Materials: Presentation On Molten Salt Reactor Technology By: David Holcomb, PH.Dfarshid KarpasandNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument16 pagesLab ReportDaniel Razak0% (1)
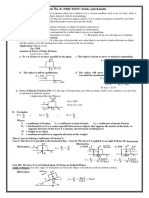
- Contents:: Physics 121 Practice Problem Solutions 09 Magnetic FieldsDocument12 pagesContents:: Physics 121 Practice Problem Solutions 09 Magnetic FieldsEdem Koffi MissihounNo ratings yet
- Material Engineering NotesDocument117 pagesMaterial Engineering NotesSudhir KumarNo ratings yet
- SILMACO - Lithium Silicates - Technical Brochure - EN - v5Document3 pagesSILMACO - Lithium Silicates - Technical Brochure - EN - v5Bose CatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/21Document20 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/21Fahad A. MalikNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) : According To GHSDocument7 pagesSafety Data Sheet (SDS) : According To GHSzejackalNo ratings yet
- Model of Sea-Floor SpreadingDocument10 pagesModel of Sea-Floor Spreadingmaan1988No ratings yet
- Personal - ATARNotes+ - ATAR Notes VCE Chemistry 3&4 Notes (2024-2025)Document122 pagesPersonal - ATARNotes+ - ATAR Notes VCE Chemistry 3&4 Notes (2024-2025)playstationus465No ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: Steve Kabore, Ryusei Ito, Naoyuki FunamizuDocument8 pagesJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering: Steve Kabore, Ryusei Ito, Naoyuki FunamizusaraNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan Simple MachineDocument4 pagesSoal Latihan Simple Machinegracelynfelicia46No ratings yet
- 4TTR3 - Product DataDocument16 pages4TTR3 - Product DataAreli MirandaNo ratings yet
- 10 Gravitation 01 Ans PDFDocument5 pages10 Gravitation 01 Ans PDFShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Correction Factors For Variable Area Flow MetersDocument5 pagesCalculation of Correction Factors For Variable Area Flow MetersgeorgehvaNo ratings yet
- A New Empirical Formula For The Calculation of MS Temperatures in Pure Iron and Super-Low Carbon Alloy SteelsDocument8 pagesA New Empirical Formula For The Calculation of MS Temperatures in Pure Iron and Super-Low Carbon Alloy SteelsMichaelKubaNo ratings yet
- Practical Demonstration of Pottali Kalpana (Gandhaka Druta), by VD - Ramakrishna.VDocument15 pagesPractical Demonstration of Pottali Kalpana (Gandhaka Druta), by VD - Ramakrishna.Vdr_saketram6146100% (2)
- 1ST SA BIOCHEMISTRY - AlmendrasDocument5 pages1ST SA BIOCHEMISTRY - AlmendrasCherry DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document50 pagesModule 3Venkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- Boq PCWDocument1 pageBoq PCWNARMADA ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Physics SL Paper 2 TZ2Document24 pagesPhysics SL Paper 2 TZ2믯차No ratings yet
- Lesson No.6.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Friction.may2023-1Document1 pageLesson No.6.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Friction.may2023-1Lloyd Christian PorlajeNo ratings yet
- Us20060145019a1 PDFDocument11 pagesUs20060145019a1 PDFJohnConnerNo ratings yet
- B951.927 - MG Alloy Naming and CompsDocument7 pagesB951.927 - MG Alloy Naming and Compswanghongxuan66No ratings yet
- Physics Binder 1Document2,790 pagesPhysics Binder 1tbs0sisirakumaraNo ratings yet
- Bogor Workshop Drying ProblemsDocument13 pagesBogor Workshop Drying ProblemsMeggy AraoNo ratings yet
- Federal Board Ssc-1 Chemistry Test # 1 Section - A: The Mark AcademyDocument2 pagesFederal Board Ssc-1 Chemistry Test # 1 Section - A: The Mark AcademySohail HameedNo ratings yet