Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Locomotive - Fuel Oil System
Locomotive - Fuel Oil System
Uploaded by
Arpan Maheshwari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesThe fuel oil system injects precisely metered fuel at high pressure into engine cylinders. It must provide the correct amount and timing of fuel injection for varying engine speeds and loads. Failures can occur due to issues like clogged filters, leaks, defective pumps or injectors, or insufficient fuel level. Maintenance includes regular filter changes, inspection and overhaul of pumps and injectors, and testing of fuel quality and injection parameters.
Original Description:
Original Title
2. Locomotive- Fuel Oil system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe fuel oil system injects precisely metered fuel at high pressure into engine cylinders. It must provide the correct amount and timing of fuel injection for varying engine speeds and loads. Failures can occur due to issues like clogged filters, leaks, defective pumps or injectors, or insufficient fuel level. Maintenance includes regular filter changes, inspection and overhaul of pumps and injectors, and testing of fuel quality and injection parameters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesLocomotive - Fuel Oil System
Locomotive - Fuel Oil System
Uploaded by
Arpan MaheshwariThe fuel oil system injects precisely metered fuel at high pressure into engine cylinders. It must provide the correct amount and timing of fuel injection for varying engine speeds and loads. Failures can occur due to issues like clogged filters, leaks, defective pumps or injectors, or insufficient fuel level. Maintenance includes regular filter changes, inspection and overhaul of pumps and injectors, and testing of fuel quality and injection parameters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
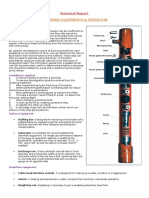
FUEL OIL SYSTEM
The fuel oil system is designed to inject correctly
metered amount of fuel oil at correct high pressure
into the engine cylinders at a stipulated time in a
highly atomized form. High pressure of fuel is
required for lifting the nozzle valve, penetration of
fuel into pressurized combustion chamber and
proper atomization. As the engine is a variable
speed and load engine with variable fuel
requirement within a particular range correct
metered quantity is essential. Timing of injection is
important to burn the fuel completely.
Fuel oil tank, Capacity- 5000 (WDM2), 6000 (WDG3A) lts
Fuel primary filter-(paper type filter)
Booster pump (fuel transfer pump)
Pump capacity- 14 lts/ minutes (at 1725 rpm)
Pessure-4-4.8 kg/cm2
Fuel relief valve set at 5.2 kg/cm2
Fuel secondary valve- (Paper type filter )
Fuel regulating valve adjusted at 3.8 to 4.0 kg/cm2.
Working of Fuel oil System
Fuel oil booster pump draws fuel from the tank and then distributes
it through out the system.
The suction side is between the tank and the booster pump. All oil
drawn from the tank must pass through primary filter used.
The pressure side is between the booster pump and the pressure-
regulating valve. As the oil flows through the system, it first passes
by a pressure relief valve set for 75 psi, the purpose of which is to
protect the booster pump, motor and system from overload.
Oil then passes through the primary and secondary filter into the
right bank fuel header, which feeds the fuel injection pumps on the
right side of the engine.
Fuel crosses over at the generator end into the left bank header,
which feeds the left back fuel injection pumps.
The 50 psi pressure regulating valve, located at the discharge end of
the left bank header, control the fuel oil pressure in both headers.
Near this valve is the line connecting to the fuel oil pressure gauge.
Failures in fuel oil system
FAILURE OF LOCOMOTIVE DUE TO FUEL OIL • Defective Fuel Booster Pump and Motor
SYSTEM (a) Rotor or idler gear damaged.
The locomotive generally fails due to fuel oil pressure not (b) Leakages from the cover gasket.
(c) Leakages from the pump seals.
building up, which may be due to following reasons:- (d) Breakage of spring
(e) Broken booster pump coupling.
• Fuel - Less than 700 Litres fuel in tank. (f) Breakage of carbon brush
(g) Commutator flashover.
(h) Improper wire connections securing of fuel pump
• Clogging of fuel filters motor.
(a) Quality of primary and secondary filters-If • Leakages
the elements are not as per the RDSO specifications. (a) Suction pipe leaking.
(b) Quality of HSD oil-When the fuel is contaminated with (b) Bursting of high pressure tubes.
water, rust, dirt, dust, fungi or any micro-organism. (c) Leakages from flexible and metallic pipes.
(d) Leakages from banjo pipes.
(c) Condition of HSD tank-The fuel in the tank is required
to be free from water, dirt, dust, rust and other • Defective Fuel Injection Pump and Injector Nozzle
contaminations. It is known that some sort of micro- (a) Excessive hot pump.
(b) Broken delivery valve spring.
biological growth takes place inside the HSD storage (c) Broken guide cup spring.
tanks, but the condition worsens due to prolonged (d) Working out or breakage of FIP foundation bolts
storage and the oil water inter phase becomes (e) Injection nozzle stuck open or closed.
(f) Injector nozzle cap cracked.
susceptible to infectious attack by micro-organisms.
Such an attack would lead to constant build-up of • Relief and Regulating valve
bacterial and fungal cells, which can ultimately cause (a) Sticking of relief and regulating valve
choking of filter pores. • Battery switch not closed
Fuel Oil Test and significances
• Water content (by Crackle test, 0.05% by vol.).
• Viscosity (Spray pattern affects).
• Carbon residue (10% by mass).
• Sulphur content (0.25% by mass, may cause corrosion in engine parts).
• Cetane number (indicate ignition quality, 45).
• Specific gravity (Co-relates with calorific value of fuel so tested at 15’C).
• Flash point(Temp.at which it gives sufficient vapour to form a mixture with air).
• Colour comparison (with potassium dichromate solution)
Maintenance of Fuel Injection System
SCHEDULE MAINTENANCE OF FUEL INJECTION
1. Trip Fuel Pump rack to be oiled and checked for free TESTING PROCEDURES OF INJECTOR ON THE
SYSTEM movement. TEST STAND:
1. Atomization The mist spray n a misty form and the
2. Fortnightly Fuel oil sample from the tank to be tested for injector must be sharp. If atomization is not
water contamination. good the valve must be re-lapped.
3. Monthly Fuel oil primary filter to renew, if it is paper
type. 2. Breaking The breaking pressure must be within
4. Quarterly Test Injector in the test stand and overhaul if Pressure limits. If not adjust the pressure by adding
necessary and keep a record of condition. The or removing shims.
injection pump timing to be checked and 3. Chattering sound Sound due to sharp closing of nozzle valve.
adjusted. Fuel oil secondary filter to be 4 Dribbling After injection wait and see if oil collects at
renewed. the tip in drops. This indicates dribbling.
5. Half yearly Fuel oil Booster pump to overhaul; also F.I.P. This must be overcome by correcting
6. Yearly Fuel injection pump to be overhauled and test in spring tension to standard value or
the test stand. Record the performances and standardizing the life or replacing the
watch during the intermediatory schedule valve.
examination
5. Leak off rate Set the breaking pressure 100 PSI less and
7. Vacuum 30 to 40 cm (Fuel Booster Pump Suction Vac)
allow the pressure to drop to 0. For new
pump delivery per minute: 10 to 14 lits.
nozzle the time will be more than 19 sec
Pressure during bleed by 9/16” hole=3.5 to 4.2
and the old nozzle above 6 secs.
Kg/Cm2 bleed delivery per minute: 8 to 10
litre/min 6. Spray pattern 9 spray holes will be seen on the Blotting
paper.
You might also like
- Lister Cs Manual PDFDocument16 pagesLister Cs Manual PDFMASSERONNo ratings yet
- APSA 80 EnglishDocument9 pagesAPSA 80 EnglishSrikanth G K Hegde100% (5)
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesFrom EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fuel Oil System by P.KDocument28 pagesFuel Oil System by P.Kkr_abhijeet72356587100% (1)
- Swabbing Equipments Mod 2Document5 pagesSwabbing Equipments Mod 2Anonymous Vb1Tsv106No ratings yet
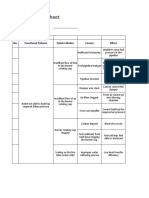
- FMECA Worksheet: No. Functional Failures Failure Modes Causes EffectDocument15 pagesFMECA Worksheet: No. Functional Failures Failure Modes Causes EffectBarathNo ratings yet
- 2016 Grand Cherokee - 3.0L TURBO DIESEL PDFDocument665 pages2016 Grand Cherokee - 3.0L TURBO DIESEL PDFprueba2No ratings yet
- Carter BBD Type Dual Throat Carburettor Servicing and MaintenanceDocument4 pagesCarter BBD Type Dual Throat Carburettor Servicing and MaintenancegabosakrNo ratings yet
- Management Engine - ML E C8Document5 pagesManagement Engine - ML E C8Jay Ron P. DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Compass 2008 2.0LDocument234 pagesCompass 2008 2.0LDavid Ulloa SalazarNo ratings yet
- Mep Aug 23 SolvedDocument22 pagesMep Aug 23 Solvedchandramohandass22No ratings yet
- Manual HSD PumpDocument5 pagesManual HSD PumpAhmad Tedjo RukmonoNo ratings yet
- Fuel InjectorDocument3 pagesFuel InjectorPar Nd Oo100% (3)
- LO2 Maintain Instrumentation and Control DevicesDocument4 pagesLO2 Maintain Instrumentation and Control Deviceslealem bishawNo ratings yet
- Patriot 2008 2.4LDocument260 pagesPatriot 2008 2.4LCynthia MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2.4l EngineDocument237 pages2.4l EngineRene SanchezNo ratings yet
- Servicing of Cooling System and Engine Trouble Shootings-1Document19 pagesServicing of Cooling System and Engine Trouble Shootings-1Hafiz Asfahan100% (1)
- Manual of Operation and Maintenance (QW)Document6 pagesManual of Operation and Maintenance (QW)Ronald AstriaNo ratings yet
- Wwmetc Set.3Document55 pagesWwmetc Set.3Thet Htet AungNo ratings yet
- Er 105 8Document4 pagesEr 105 8cesar coronadoNo ratings yet
- Management Engine ML E C7Document5 pagesManagement Engine ML E C7rogelio loganaNo ratings yet
- 4 Operate Main and Auxiliary Machinery and Associated Control SystemsDocument47 pages4 Operate Main and Auxiliary Machinery and Associated Control Systemsaldiyovan24No ratings yet
- (D) Viewing Procedure of Piston Assembly: Cleaning BasketDocument7 pages(D) Viewing Procedure of Piston Assembly: Cleaning BasketesakkimuthuNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Hydraulic System For Promotional SSE/ Track MachineDocument40 pagesAn Overview of Hydraulic System For Promotional SSE/ Track MachineRavi Shankar JoshiNo ratings yet
- Zander OWS EcoSep WT-5-10-20-30 ManualDocument9 pagesZander OWS EcoSep WT-5-10-20-30 ManualMistysPartsNo ratings yet
- (MAHINDRA) Manual de Taller Mahindra Pick Up 2.6 InglesDocument620 pages(MAHINDRA) Manual de Taller Mahindra Pick Up 2.6 InglesRodrigo Henriquez100% (1)
- Guidelines On FCC Fractionator Bottoms System Rev2Document5 pagesGuidelines On FCC Fractionator Bottoms System Rev2M Scott GreenNo ratings yet
- Exam Question AnswerDocument3 pagesExam Question AnswerSahariar Bin Shafique100% (1)
- Pra Ukp 1-1Document34 pagesPra Ukp 1-1Evantius TariganNo ratings yet
- Exam Question-1Document4 pagesExam Question-1Sahariar Bin ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Vincke Gear Pumps CatDocument48 pagesVincke Gear Pumps CatVelibor KaranovicNo ratings yet
- Presentation: Reliability of Hydrogen Area Diaphragm CompressorDocument43 pagesPresentation: Reliability of Hydrogen Area Diaphragm CompressorBiju_Pottayil100% (1)
- Pra Ukp 1Document35 pagesPra Ukp 1Fauzan FatihNo ratings yet
- Mep December 2022Document17 pagesMep December 2022sardar singhNo ratings yet
- Oil Flushing Procedures For Steam Turbine & Generator Sets 1Document8 pagesOil Flushing Procedures For Steam Turbine & Generator Sets 1atul singhNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Susuki Baleno Sy418Document395 pagesService Manual Susuki Baleno Sy418juanmahepa75% (4)
- Vacuum Pump Manual-2022-05VERSIONDocument8 pagesVacuum Pump Manual-2022-05VERSIONonline MNo ratings yet
- Grand Cherokee 2011 3.0TDDocument329 pagesGrand Cherokee 2011 3.0TDRoberto Ortega MicalizziNo ratings yet
- Trouble Shooting The Fuel SystemDocument24 pagesTrouble Shooting The Fuel SystemAhmed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Power Unit MaintenanceDocument11 pagesPower Unit MaintenanceAzlan RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Gmi 404470935806Document5 pagesGmi 404470935806b8505887No ratings yet
- Fuel Oil SysDocument58 pagesFuel Oil SysMAMADO2015No ratings yet
- Detect and Indentity The Cause of Machinery Ma-1Document64 pagesDetect and Indentity The Cause of Machinery Ma-1sukarlem marsiahNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual For Wp4g95e221 EngineDocument28 pagesOperation Manual For Wp4g95e221 EngineCarlos Astudillo VargasNo ratings yet
- ESN2013S PumpDocument4 pagesESN2013S PumpHeber LeyvaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Repair InstructionsDocument12 pagesMaintenance and Repair InstructionsDhananjay NilkuteNo ratings yet
- Joyride 125-4Document13 pagesJoyride 125-4شاكر عبد الهادي الاسديNo ratings yet
- Gen Set 2.5 KVA 1Document17 pagesGen Set 2.5 KVA 1Pankaj TiwariNo ratings yet
- Brahma Pumps MaintananceDocument19 pagesBrahma Pumps MaintanancePavel SokolovNo ratings yet
- CAV Pintaux Injection Nozzle RebuildDocument6 pagesCAV Pintaux Injection Nozzle RebuildDanny DanNo ratings yet
- Manual de Taller de Motor Completo Suzuki Gran Viatara 2.5Document93 pagesManual de Taller de Motor Completo Suzuki Gran Viatara 2.5Toni diestreNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Fowa - Fuel - 50305Document20 pagesMaintenance Fowa - Fuel - 50305darwin100% (1)
- Fluid Machinery - Eng - Pump - Part2 (Compatibility Mode)Document65 pagesFluid Machinery - Eng - Pump - Part2 (Compatibility Mode)ณัฐวัศ มั่นบุญสมNo ratings yet
- Mud PumpDocument35 pagesMud PumpAboZaidNo ratings yet
- Ram 1500-2013-3.6Document480 pagesRam 1500-2013-3.6luis67% (3)
- Maintenance and Repair of Fuel Suppply, Lubrication and Cooling System Fuel Pump TestingDocument12 pagesMaintenance and Repair of Fuel Suppply, Lubrication and Cooling System Fuel Pump TestingAdarsh AnilNo ratings yet
- 17-Oil Centrifuge PDFDocument89 pages17-Oil Centrifuge PDFUmangtarangNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Ear and Nose Drop Leaflet FinalDocument2 pagesEar and Nose Drop Leaflet Finalkim ceroNo ratings yet
- Water Nozzle SprayDocument4 pagesWater Nozzle SprayonurkirtogluNo ratings yet
- Safematic Greasing ManualDocument50 pagesSafematic Greasing ManualDenis VieiraNo ratings yet
- Pesticides Application Training CourseDocument27 pagesPesticides Application Training CourseMULYONONo ratings yet
- Eutalloy 1202Document2 pagesEutalloy 1202Siddharth DasNo ratings yet
- CB14B InglesDocument12 pagesCB14B InglesAlberi Dilamar BaumartNo ratings yet
- Tubine Bypass SystemDocument12 pagesTubine Bypass Systemkalyanm203515No ratings yet
- Optimizing Spray Performance With Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument8 pagesOptimizing Spray Performance With Computational Fluid DynamicsDavidNo ratings yet
- US5305721Rotary Wankel Type EngineDocument10 pagesUS5305721Rotary Wankel Type Engine임학진No ratings yet
- Tactical Missile Conceptual DesignDocument204 pagesTactical Missile Conceptual DesignAnibal VettorelNo ratings yet
- Seaforce ShieldDocument4 pagesSeaforce ShieldMuhammad Iqbal Al HaidarNo ratings yet
- BS en 00546-4-2006Document16 pagesBS en 00546-4-2006Karina CastroNo ratings yet
- TDS 49082 AF Max Guard Euk GBDocument4 pagesTDS 49082 AF Max Guard Euk GBtebongedeNo ratings yet
- Coating of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: (1922) Kremers and Urdang (1940) Anon, 1920Document14 pagesCoating of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: (1922) Kremers and Urdang (1940) Anon, 1920GERSON ARMANDO MORENO BERMUDEZNo ratings yet
- Actara (5 24 01) PDFDocument12 pagesActara (5 24 01) PDFBand Dvesto Plus CrepajaNo ratings yet
- Vooner Paper Industry Dewatering Solutions Brochure 2023Document12 pagesVooner Paper Industry Dewatering Solutions Brochure 2023Eduardo PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Hempadur Primer 1530yDocument4 pagesHempadur Primer 1530yRodrigo CondorettyNo ratings yet
- Astm C1516Document7 pagesAstm C1516adolfo camayoNo ratings yet
- SpiralJETssco Cat70 B PDFDocument52 pagesSpiralJETssco Cat70 B PDFjlvega18No ratings yet
- TDS OF H-77 Agriculture Organosilicone AdjuvantDocument3 pagesTDS OF H-77 Agriculture Organosilicone AdjuvantAda FuNo ratings yet
- MinimecDocument4 pagesMinimecHukiro ItachiNo ratings yet
- Karcher G 3050 OH Pressure WasherDocument42 pagesKarcher G 3050 OH Pressure WasherJon CottrillNo ratings yet
- SHF Breakup Model OpenFOAMDocument8 pagesSHF Breakup Model OpenFOAMSuryaKaundinyaOrugantiNo ratings yet
- CenpesDocument33 pagesCenpesOrlando PWRNo ratings yet
- Kiekens-DSH-brochure MNS VDSDocument2 pagesKiekens-DSH-brochure MNS VDSAnand AsangiNo ratings yet
- DR-60 Cleaner-Remover: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesDR-60 Cleaner-Remover: Technical Data Sheetrebeca cabelloNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Gaining Competitive Advantage 9th Edition Noe Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesHuman Resource Management Gaining Competitive Advantage 9th Edition Noe Solutions ManualKimberlyBennettcipym100% (36)
- Túnel VEITDocument27 pagesTúnel VEITgamusino2No ratings yet
- Quick Guide Manual: SoftwareDocument19 pagesQuick Guide Manual: SoftwareMessi EmetievNo ratings yet