Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Ahana SenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Ahana SenCopyright:
Available Formats
(a) Mitosis of a spermatogonial stem
cell involves a single cell division that
results in two identical, diploid
daughter cells (spermatogonia to
primary spermatocyte). Meiosis has
two rounds of cell division: primary
spermatocyte to secondary
spermatocyte, and then secondary
spermatocyte to spermatid. This
produces four haploid daughter cells
(spermatids). (b) In this electron
micrograph of a cross-section of a
seminiferous tubule from a rat, the
lumen is the light-shaded area in the
center of the image. The location of the
primary spermatocytes is near the
basement membrane, and the early
spermatids are approaching the lumen
(tissue source: rat). EM × 900.
(Micrograph provided by the Regents
of University of Michigan Medical
School © 2012)
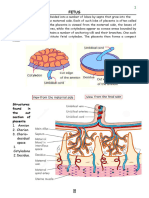
Some of the positions of the placenta are:
The placenta is a temporary organ that connects the baby to •Posterior placenta: The placenta grows on the back wall of
uterus during pregnancy. The placenta develops shortly after uterus.
implantation and attaches to the wall of the uterus. Baby is •Anterior placenta: The placenta grows on the front wall of
connected to the placenta by the umbilical cord. Together, the uterus
placenta and umbilical cord act as your baby's lifeline while in closest to abdomen.
the uterus. Functions of the placenta include: •Fundal placenta: The placenta grows at the top of uterus.
•Lateral placenta: The placenta grows on the right or left
wall of the uterus.
Human placental hormones
Human Placenta act as endocrine glands as its secret certain hormones like oestrogen, progesterone, human chorionic
gonadotropin (HCG) and human placental lactogen (HPL).
Functions of Placenta
1) help in nutrition of embryo as the nutrient like amino acids, mono Sugars, vitamins etc pass from the maternal
blood into fetal blood through placenta.
2) also helps in respiration of embryo as oxygen of the maternal blood and carbon dioxide of the fetal blood diffuse
through placenta in the into the foetal blood and maternal blood respectively.
3) human Placenta act as an endocrine glands it secret certain Harman like oestrogen, progesterone, human chorionic
gonadotropin and human placental lactogen.
4) antibodies (against diphtheria, smallpox, Scarlet fever, measles etc) pass from maternal blood to fetal blood through
Placenta and it provide passive immunity in foetus.
5) placenta store the glycogen till the formation of liver.
6) it also help in excretion of embryo as nitrogenous waste of fetal blood like urea pass into maternal blood through
placenta
7) through the Placenta act as an effective barrier for certain toxic chemical like histamine but certain germs like AIDS
virus, syphilis bacteria, virus of German measles, and intoxicant like nicotine of cigarette, smoke and addictive drugs
like Heroin and cocaine can pass through the Placenta and cause the developmental defect.
You might also like
- Doctors ListDocument212 pagesDoctors ListSaranya Chandrasekar33% (3)
- Bio PresentationDocument17 pagesBio PresentationkamiiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 HandsoutDocument10 pagesModule 2 HandsoutErin SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology GCSDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology GCSSherry Ann FayeNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument5 pagesPlacentaMutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- Embryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesDocument13 pagesEmbryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesAudrey100% (5)
- Developmental Biology 10 Placental Structure and ClassificationDocument6 pagesDevelopmental Biology 10 Placental Structure and ClassificationPijush PramanikNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument32 pagesPlacentaAbedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Growing Fetus FertilizationDocument6 pagesThe Growing Fetus FertilizationJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- The Growing FetusDocument68 pagesThe Growing Fetusjean thereseNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio (Case Pres)Document7 pagesAnaphysio (Case Pres)Ralph_John_Pac_8337No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Document37 pagesMaternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- X EZ12 RDX 2 O7 D P5 Ts Yf VTQ Thai 81 R4 I Oxl FYSh DGCDocument6 pagesX EZ12 RDX 2 O7 D P5 Ts Yf VTQ Thai 81 R4 I Oxl FYSh DGCoverfabz1No ratings yet
- 1-Prenatal & Fetal Development-93666Document45 pages1-Prenatal & Fetal Development-93666Izziddin YassineNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan Plasenta (Autosaved) .En - IdDocument18 pagesPerkembangan Plasenta (Autosaved) .En - IdFATIMAHNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesExploring The Female Reproductive Systemlegall_650582301No ratings yet
- Obstetrics V10 Common Obstetric Conditions Chapter Pathology of The Placenta 1663285373Document11 pagesObstetrics V10 Common Obstetric Conditions Chapter Pathology of The Placenta 1663285373Nurliana NingsihNo ratings yet
- External StructuresDocument7 pagesExternal StructuressittizhainabNo ratings yet
- Normal PregnancyDocument65 pagesNormal PregnancyRhesie Joyce AguilarNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument5 pagesNCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusKristine BartsNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument6 pagesFertilizationKristine Castillo100% (1)
- Written by AHMED ATEF K-719610990 AHMED KHALIL K-719610923: Anatomy Assignment 2Document15 pagesWritten by AHMED ATEF K-719610990 AHMED KHALIL K-719610923: Anatomy Assignment 2Dr. Mohammad JamaliNo ratings yet
- Note of The ChapterDocument19 pagesNote of The ChapterMotiourNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument30 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectSANDIPAN BISWAS80% (5)
- Embryology IDocument94 pagesEmbryology Imasemola koketsoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Part 2Document12 pagesReproduction Part 2Yuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument8 pagesChapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- CVM Pres - IIDocument152 pagesCVM Pres - IIseraphim8No ratings yet
- Pregnancy 1Document70 pagesPregnancy 1Annapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument4 pagesReproduction in HumansIsra OmerNo ratings yet
- Competency 1-The Family Before Birth: 1. Explain The Structure and Function of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesCompetency 1-The Family Before Birth: 1. Explain The Structure and Function of The Female Reproductive SystemEnorl FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Human ReproductionDocument8 pagesChapter-3 Human ReproductionbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormalities of The UterusDocument7 pagesCongenital Abnormalities of The Uterusمحمود الموسويNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Human NotesDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human NotesTasneem HamdyNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: 1-1. GENERALDocument5 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: 1-1. GENERALgladz25No ratings yet
- Normal PregnancyDocument86 pagesNormal PregnancygayleesinfuegoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityDocument62 pagesUnit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityN. Siva100% (1)
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDocument11 pagesProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableFrankie Macabada0% (2)
- Prenataldevelopment PDFDocument14 pagesPrenataldevelopment PDFAmber TajwerNo ratings yet
- Soft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofDocument6 pagesSoft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofKhristin Joy GamponiaNo ratings yet
- 7 Perkembangan EMbrio Manusia PDFDocument57 pages7 Perkembangan EMbrio Manusia PDFFadhilah SiregarNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cyst FinalDocument26 pagesOvarian Cyst FinalReicy Aquino SacularNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesStages of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentGrant KhangabNo ratings yet
- 10 Placenta DR - GosaiDocument29 pages10 Placenta DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDocument16 pagesThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMDocument127 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gNo ratings yet
- Makalah Fisiologi HewanDocument11 pagesMakalah Fisiologi HewanMethaNurIndahNo ratings yet
- Gastulation and PlacentationDocument3 pagesGastulation and PlacentationAnsuman priyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 2 Notes (Class 12)Document6 pagesHuman Reproduction 2 Notes (Class 12)Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive Systemsubi100% (1)
- Embryological Development of The Human BrainDocument17 pagesEmbryological Development of The Human BrainErika LmNo ratings yet
- 8 Bartholin's Glands: These Glands Are Located Next To The Vaginal Opening andDocument4 pages8 Bartholin's Glands: These Glands Are Located Next To The Vaginal Opening andalyssaaaaa1234885No ratings yet
- Reproductive System HandoutDocument21 pagesReproductive System HandoutJei SanNo ratings yet
- The Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 7Document75 pagesThe Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 795kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- OR Write-Up CSDocument13 pagesOR Write-Up CSalex_tan1981No ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumanDocument17 pagesReproduction in HumananonymousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document26 pagesChapter 12Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemNanen CaminceNo ratings yet
- 10 Kuliah PLACENTADocument33 pages10 Kuliah PLACENTAAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Placenta UpdatedDocument49 pagesPlacenta UpdatedSaad HasanNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument4 pagesMeconium Aspiration SyndromeGwEn LimNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology 14th Edition Fox Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesHuman Physiology 14th Edition Fox Solutions Manualoraliemaximusp474w3100% (31)
- Alteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesAlteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture Notes0912247251No ratings yet
- Respiratory System Exchange of Gases: Powerpoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Robert J. Sullivan, Marist CollegeDocument13 pagesRespiratory System Exchange of Gases: Powerpoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Robert J. Sullivan, Marist CollegeJoan Rescate Rigodon-AgustinNo ratings yet
- Somatic EmbryogenesisDocument2 pagesSomatic EmbryogenesisrifanirdNo ratings yet
- Swara Sastra - Key To Correct Breathing1 - TextDocument18 pagesSwara Sastra - Key To Correct Breathing1 - TextIgor Budzanivskiy100% (5)
- Factors That Affect Physical DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFactors That Affect Physical DevelopmentmomuNo ratings yet
- Uman Hysiology: Endocrine Control of Growth and MetabolismDocument24 pagesUman Hysiology: Endocrine Control of Growth and Metabolismpanairina03026273No ratings yet
- The Class MammaliaDocument5 pagesThe Class MammaliaMohammad Raza RizviNo ratings yet
- BIO202L Lab 16 Upload DocumentDocument9 pagesBIO202L Lab 16 Upload Documentzape limitedNo ratings yet
- Final CreamDocument22 pagesFinal CreamCyrus VizonNo ratings yet
- Biatrial Enlargement: An Unusual Cause of Massive CardiomegalyDocument2 pagesBiatrial Enlargement: An Unusual Cause of Massive CardiomegalynadiaNo ratings yet
- Amelia Pebrianti (2307240001) PhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 3Document5 pagesAmelia Pebrianti (2307240001) PhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 3Amalia SalfadilaNo ratings yet
- 3 Interview Transcripts From The Diy Detox SummitDocument34 pages3 Interview Transcripts From The Diy Detox SummitPaulina DeyanovaNo ratings yet
- NCP Close Complete FractureDocument3 pagesNCP Close Complete FractureArt Christian RamosNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Model SHODocument4 pagesCellular Respiration Model SHOCorey AnselmiNo ratings yet
- Resp System. ExamDocument145 pagesResp System. ExamIrina CornilovNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Classification of MossesDocument53 pagesMorphology and Classification of MossesIlham ArfiansyahNo ratings yet
- Efectos de La Realidad Virtual en La Plasticidad Neuronal en La Rehabilitacion de Ictus. Revision SistematicaDocument19 pagesEfectos de La Realidad Virtual en La Plasticidad Neuronal en La Rehabilitacion de Ictus. Revision SistematicaÁngel OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Some GI DisordersDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Some GI Disordersghee05No ratings yet
- Role of Oxidative Stress in Semen Quality of Infertile MenDocument9 pagesRole of Oxidative Stress in Semen Quality of Infertile MenAyadPalaniNo ratings yet
- Yagiela John A Et Al Pharmacology and Therapeutics For Denti1Document1 pageYagiela John A Et Al Pharmacology and Therapeutics For Denti1AntonPurpurovNo ratings yet
- Dietz-2012-Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology - The Official Journal of The International...Document9 pagesDietz-2012-Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology - The Official Journal of The International...Putri Utie DinarNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Surgery PresentationDocument191 pagesPediatric Surgery PresentationdanoonotNo ratings yet
- ESR Ebook For Undergraduate Education in Radiology - 15 Urogenital Radiology-Opt PDFDocument74 pagesESR Ebook For Undergraduate Education in Radiology - 15 Urogenital Radiology-Opt PDFANAS ALINo ratings yet
- Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV AIDS Patient: Case ReportDocument72 pagesCerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV AIDS Patient: Case Reportnovy rosalia chandra100% (1)
- Positions For ExaminationDocument7 pagesPositions For ExaminationKarisma NurhidayatNo ratings yet
- J Vet Emergen Crit Care - 2020 - Donati - Caudal Vena Cava Collapsibility Index As A Tool To Predict Fluid ResponsivenessDocument10 pagesJ Vet Emergen Crit Care - 2020 - Donati - Caudal Vena Cava Collapsibility Index As A Tool To Predict Fluid ResponsivenessJHON BAEZ SERRANONo ratings yet
- Microbial Enzymes and Biotechnology: 2Nd EditionDocument10 pagesMicrobial Enzymes and Biotechnology: 2Nd EditionKenan YılmazNo ratings yet