Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Occupational Hazards in Dental, Textile Industry and Mechanic
Occupational Hazards in Dental, Textile Industry and Mechanic
Uploaded by
imtahifOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Occupational Hazards in Dental, Textile Industry and Mechanic
Occupational Hazards in Dental, Textile Industry and Mechanic
Uploaded by
imtahifCopyright:
Available Formats
Occupational hazards in Dental
clinic, Textile industries, and
mechanical workers
Tahif. TY . Optometry
Introduction
Occupational hazards are risks associated with working
in specific occupations. The Occupational Safety and
Health Administration (OSHA) describes five
categories of occupational hazards: physical safety
hazards, chemical hazards, biological hazards, physical
hazards, and ergonomic risk factors.
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 2
Hazards in dental
clinic
Eye health is becoming an increasingly important subject both for the health
care system and the society . Since infections and injuries in the eyes may go
unnoticed, partial loss of vision or even blindness may occur . On the other
hand; there are some protective and preventive measures which could easily
provide good visibility while maintaining the integrity of eye health. The use
of eye protection gear, such as protective goggles and visors, reduces the risk
of eye damage or complete loss of vision while working with dangerous
floating materials or performing sportive activities.
dental clinic may be a source of eye-related injuries because of the
constant risk of mechanical trauma as well as the possibility of being
exposed to various chemicals and electromagnetic activity. Accidents
resulting in injuries related to face and eyes may occur at any time during
the treatment, and dentists, dental assistants as well as patients may be
involved
prevalence of ocular injuries and infections among dental personnel
which consists of dental assistants, dentists and technicians. The foreign
body related injury prevalence of dental personnel, the dentists and the
technicians was found to be 42.3%. The conjunctivitis prevalence of the
dentists was, respectively, 7.1% and 42.8%
Causes of eye-trauma and
contamination
The harmful effects and contamination concerning the eyes most commonly occur in two ways.
The first one is the development of contamination in the areas recently traumatized by infected solid
materials such as tooth corpuscles, calculus, bone particles, parts of steel, gold, and amalgam particles
which may fly off from dental tools or materials and hit the eyes with a speed up to 96 km per hour
The second cause is the presence of
micro-organisms in the blood and
saliva mixture, which may be
transferred into the conjunctiva by
the absorption of aerosol effect
created by high-speed turbine and
micro motors.
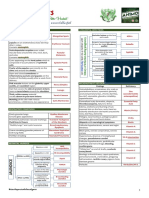
Table
Infective/Trauma Adverse Effect Cause Symptoms Treatment Outcome
Heals rapidly, Recurrent
Trauma Corneal abrasion Foreign Body Acutely Painful Self limiting corneal erosion, Secondary
infection
Haemorrhage into anterior Remove foreign body,
Penetrating foreign body Acute Pain Cataracts
chamber Suturing
Altered vision Altered Pupil distortion Detached
Torn iris
appearance retina Uveitis
Laceration, may involve lid
Lacerations Blunt / Sharp object Anatomical repair Scarring
margin
Copious irrigation Remove
Mild conjunctivitis
any particles pH with litmus Usually recovers Corneal
Epithelial erosions
Chemical Injury Acid / Alkali paper Topical antibiotics defects (opacities and
Superficial punctuate
Lubricants Topical steroids perforation)
keratopathy
Vitamin C
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 8
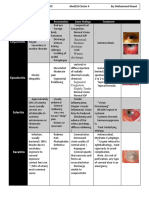
Infective/Trauma Adverse Effect Cause Symptoms Treatment Outcome
Table
Staphylococcus,
Infective Bacterial Conjunctivits Streptococcus, Redness, Discharge, Usually self limiting Heals
Pneumococcus Haemophilus
Ocular irritation
Staphylococcus epidermidis,
Staphylococcus aureus,
Bacterial keratitis Streptococcus pneumoniae, Pain, Purulent discharge, Topical antibiotics Heals
Coliforms, Pseudomonas,
Haemophilus
Ciliary injection,
Visual impairment, White
corneal opacity
Adenovirus, Coxsackie, Watery, Purulent discharge, Self limiting but highly
Viral conjunctivitis Heals
Picornavirus Chemosis, contagious
Excess lacrimation
Dendritic ulcers on the
Viral keratitis Herpes simplex cornea, May involve the Ulcers heal without scarring,
stoma
Risk of permanent scarring
and blindness
Possible chronic hepatitis,
Hepatitis B and C Hepatitis virus Systemic infection Interferon treatment cirrohosis, Risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma
HIV HIV Systemic infection Supportive drug therapy Poor long term prognosis
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 9
Injuries caused by trauma
Standard or high speed drills are widely used in nearly every dental treatment such as
removal of old fillings, cleaning of caries, polishing, orthodontic application s, prosthetic
preparations or bone removal. Tissue particles or excess materials flying off in every
direction during cavity preparation significantly increase the risk of eye injury for dental
professionals
When the injury occurs, foreign body is located in the conjunctival sac or cornea in most of
the cases. This causes acute pain, lacrimation and erythema in the eyeball. Deeper
penetrations may result in corneal perforation and lens injuries. Eye injuries constitute about
10% of all the injuries that occur during dental treatment and oral surgery. They are mostly
caused by aerosols and foreign bodies
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 10
Preventions of these hazards
Safety goggles
Wearing of Gloves
PPE's
Use of disposable masks
Washing hands after dental procedures( both patient and
clinician
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 11
Hazards in Textile industries
The textile industry has various divisions like spinning, dyeing, printing, etc. Many hazards and risks in
such industries affect the physical and mental health of professionals. Diseases arising from the textile
industry are noise-induced hearing loss, heart-related and vision-related diseases, neurotoxicity, and other
skin diseases. Recent studies have shown that the amount of dust and debris generated by picking cotton
from the field using machinery is more significant than that of picking cotton by hand. Workers are exposed
to dust from various materials such as cotton, wool, flax, hemp, sisal etc. When inhaled, these dust particles
enter the lungs through the respiratory tract leading to various respiratory disorders in the workers
0 2 /11 /20 2 4 SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 12
Disease caused are
Byssinosis => inhalation of cotton dust
Deafness due machine noise
Heat stress
Penetrating Foreign body in eye
0 2 /11 /20 2 4 SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 13
Most of Eye related injuries re seen in Dyeing, Printing ,and finishing unit
Dyeing:
Dyeing involves a chemical combination or a powerful physical affinity between the dye
and the fibre of the fabric. An extensive variety of dyes and processes is used, depending on
the type of fabric and the end-product desired.
Hazards in dyeing: Fire and explosion
The fire hazards found in a dye works are the flammable solvents used in the processes and
certain flammable dye material
0 2 /11 /20 2 4 SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 14
Dyes used alkaline in nature thus alkalies have strong tissue penetrating power and destroy
the eye completely and cutaneous
How it can happen ?
Splash of dye in eye
accidental touching the eye without washing hands
Fumes from chemicals can cause eye skin irritation
0 2 /11 /20 2 4 SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 15
Prevention
Many textile industrial hazards can be prevented by following proper protocols setup by
Central Industrial management
i.e.
1. Use of disposable face masks and Face shield \ safety goggles
2. Use of Disposable long elbow length Rubber Gloves
3. Rubber shoes and use of aprons
4. Washing of hands
0 2 /11 /20 2 4 SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 16
Hazards in Garage mechanics
What do mechanics do?
Mechanics work in many different industries including aviation, automotive,
commercial, industrial or residential settings. Some of their main duties are to:
Install, repair and maintain mechanical systems.
Prepare cost estimates and documentation for clients.
Use, clean and maintain various equipment and machines.
Supervise apprentices or other workers
0 2 /11 /20 2 4 SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 17
What are some health and safety issues for mechanics ?
Working with explosive items, such as air bags.
Mechanics work in a variety of settings and may be Bursting of tires while repairing or installing.
exposed to several hazards, including: Extreme temperatures.
Risk of pain or injury from awkward positions,
Exposure to chemicals, solvents, solder, and other repetitive manual tasks, or lifting heavy objects.
products.(skin and eye injuries ) Risk of falling objects (including the vehicle) when
working under vehicles, or with jacks, hoists, or
Exposure to gasoline or diesel exhaust. hydraulic lifts.
Risk of electrical shock or burns. Possibility of working at heights.
Risk of eye injury from flying particles.
Fire risk from fuels and other products. Risk of hand injuries.
Burns from battery acid, hot surfaces, exhaust, etc. Slips, trips and falls.
Working with various hand tools, power tools and
Potentially working in confined spaces.
equipment.
Welding hazards, including UV radiation. Stress.
Shift work or extended work days.
Working with compressed air.
Working alone.
Working near rotating parts (being caught in or between). Possible exposure to asbestos.
Exposure to noise.
Dealing with hostile customers
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 18
What are some preventive measures for mechanics?
Keep tools and equipment in good working order.
Work safely with chemicals and related products.
Use appropriate personal protective equipment for the task, including footwear.
Keep work areas clear of clutter and equipment.
Avoid awkward positions, and repetitive tasks, or take frequent breaks.
Learn safe lifting techniques.
Follow a recommended shift work pattern, and know the associated hazards.
Inspect work area before work starts to identify potential hazards and their controls.
Follow workplace policies and procedures relating to preventing workplace violence
and harassment
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 19
Thank you
Tahif
TY Optometry
GMC
T
SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 20
You might also like
- Pediatrics: Compilation of Tables From Topnotch Pedia HandoutDocument6 pagesPediatrics: Compilation of Tables From Topnotch Pedia HandoutCielo Lomibao0% (1)
- Aboriginal Hypertension Brochure Resource PDFDocument2 pagesAboriginal Hypertension Brochure Resource PDFRickNo ratings yet
- Humphrey Visual Field Interpretation - : Basic Glaucoma CourseDocument75 pagesHumphrey Visual Field Interpretation - : Basic Glaucoma CourseKetut AryawanNo ratings yet
- Basic Care & Comfort Nclex RN UwDocument10 pagesBasic Care & Comfort Nclex RN Uwgwen scribd100% (1)
- Micro - para FINALDocument53 pagesMicro - para FINALfilchibuff95% (19)
- Ocular Emergencies-Sept2013 PDFDocument22 pagesOcular Emergencies-Sept2013 PDFKaramsi Gopinath NaikNo ratings yet
- Red Eye TableDocument2 pagesRed Eye TableFatimah AlsultanNo ratings yet
- Materi Bimbingan Kepaniteraan Klinik Ilmu Penyakit Mata: No Pembimbing Topik Sub TopikDocument2 pagesMateri Bimbingan Kepaniteraan Klinik Ilmu Penyakit Mata: No Pembimbing Topik Sub TopikRizka ChairaniNo ratings yet
- Complication CL OsceDocument6 pagesComplication CL OsceAdam EdzelNo ratings yet
- Red EyeDocument54 pagesRed EyeT786 kharNo ratings yet
- Care For Patients With Alteration in Perception and CoordinationDocument12 pagesCare For Patients With Alteration in Perception and Coordinationevlujtrep9690100% (1)
- Kul Mata Merah PDFDocument56 pagesKul Mata Merah PDFMuhammad HasanNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis: Radang Konjungtiva Yang Menutupi Belakang Kelopak Dan Bola Mata, Dalam Bentuk Akut Maupun KronisDocument18 pagesConjunctivitis: Radang Konjungtiva Yang Menutupi Belakang Kelopak Dan Bola Mata, Dalam Bentuk Akut Maupun KronisnasikaceliaNo ratings yet
- Trauma OkuliDocument50 pagesTrauma Okuliaditya brahmantio sujakaNo ratings yet
- (Ophtha) Ocular Emergenices - Dr. VillalvaDocument6 pages(Ophtha) Ocular Emergenices - Dr. VillalvaPatricia ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Ophtha ReviewerDocument3 pagesOphtha ReviewerToni Sy EncinaresNo ratings yet
- Cataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification: Prepared By: Heinstein Marc C. AmparadoDocument1 pageCataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification: Prepared By: Heinstein Marc C. AmparadoNYENYENo ratings yet
- Care For Patients With Alteration in Perception and CoordinationDocument13 pagesCare For Patients With Alteration in Perception and Coordinationevlujtrep9690No ratings yet
- عملي السليداتDocument92 pagesعملي السليداتSandyDavidNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document15 pagesPart 1solimanmahmoudaNo ratings yet
- Ocular EmergencyDocument86 pagesOcular EmergencyMohammadNo ratings yet
- Endophthalmitis: Current Trends, Drugs and Protocols: Aditya Verma, Vinata Muralidharan and Eesh NigamDocument10 pagesEndophthalmitis: Current Trends, Drugs and Protocols: Aditya Verma, Vinata Muralidharan and Eesh NigamHerman Kurt Ludvik100% (1)
- Ocular EmergencyDocument29 pagesOcular EmergencyMohammad Farouq Omar100% (3)
- ConjungtivitisDocument86 pagesConjungtivitisIvo AfianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Injuries of Organ of Vision.Document47 pagesLecture Injuries of Organ of Vision.rajarajachozhan139No ratings yet
- Cornea and External DiseasesDocument18 pagesCornea and External DiseasesMiguel C. DolotNo ratings yet
- The Tearing Patient: Diagnosis and Management: Ophthalmic PearlsDocument3 pagesThe Tearing Patient: Diagnosis and Management: Ophthalmic PearlsAnonymous otk8ohj9No ratings yet
- Cataract Week 13Document9 pagesCataract Week 13Janselle H ArmaNo ratings yet
- Cornea: Dr. Izar Aziz, DR., SPM (K)Document30 pagesCornea: Dr. Izar Aziz, DR., SPM (K)Anonymous HgX3mN1oNo ratings yet
- Outline Notes of CS 27 - Ocular Orbital TraumaDocument8 pagesOutline Notes of CS 27 - Ocular Orbital TraumaTaif SalimNo ratings yet
- EGurukul - Uveitis and Uveal TractDocument10 pagesEGurukul - Uveitis and Uveal TractOscar Daniel MendezNo ratings yet
- CNMC Eye OSPE Problems With SolutionsDocument26 pagesCNMC Eye OSPE Problems With SolutionsShahbaz AAnsariNo ratings yet
- Corneal Ulcer DR - IZDocument30 pagesCorneal Ulcer DR - IZmohamadNo ratings yet
- Complicaciones en Trauma FacialDocument13 pagesComplicaciones en Trauma FacialcarlosNo ratings yet
- Red-Eye - Vanilla DrJAMDocument40 pagesRed-Eye - Vanilla DrJAMDr J A M “JAYGOUR”No ratings yet
- EktropionDocument31 pagesEktropionapriliaNo ratings yet
- Normal Body FloraDocument1 pageNormal Body FloraJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Hajera FinalDocument38 pagesDiabetic Foot Hajera FinalAfifah SelamatNo ratings yet
- Retinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentDocument3 pagesRetinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentJordz Placi100% (1)
- The Red EyeDocument42 pagesThe Red EyeDenise CarbonellNo ratings yet
- Selected Differential Diagnosis of Red Eye: Table 1Document3 pagesSelected Differential Diagnosis of Red Eye: Table 1Rian DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Corneal Ulcers in General Practice: Clinical IntelligenceDocument2 pagesCorneal Ulcers in General Practice: Clinical IntelligenceBenitaNo ratings yet
- ติว NL2 ปี 5 2022 outlineDocument49 pagesติว NL2 ปี 5 2022 outlineSugus PichayaNo ratings yet
- Referat Mata KeratititsDocument28 pagesReferat Mata KeratititsjantyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyNicole Rachelyn MartinNo ratings yet
- Delayed Wound Healing-3Document19 pagesDelayed Wound Healing-3heri setiawanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosticop Diferencial Ojos RojosDocument1 pageDiagnosticop Diferencial Ojos RojosluisNo ratings yet
- Otitis Externa:: BacterialDocument9 pagesOtitis Externa:: BacterialNashat SaadiNo ratings yet
- Cariology-The Susceptible Tooth 9Document106 pagesCariology-The Susceptible Tooth 9Free PsPlusNo ratings yet
- CH 068 Ophthalmia NeonatorumDocument7 pagesCH 068 Ophthalmia NeonatorumrehanaNo ratings yet
- Orbital and Ocular TumorsDocument13 pagesOrbital and Ocular TumorsstarlytexpressNo ratings yet
- Catatan Koass MataDocument6 pagesCatatan Koass MataYPramudiyaNo ratings yet
- Intervention For Clients With Eye and Vision Problems: Eyelid Disorders Blepharitis ChalazionDocument11 pagesIntervention For Clients With Eye and Vision Problems: Eyelid Disorders Blepharitis ChalazionDarius CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Infection DiseaseDocument1 pageOdontogenic Infection Diseasealvarez.sofiadennieceNo ratings yet
- L3 Conjunctival DiseaseDocument70 pagesL3 Conjunctival DiseaseAlhNo ratings yet
- Ceh 12 30 019 PDFDocument2 pagesCeh 12 30 019 PDFHerwandiNo ratings yet
- Bhavna, M Optom, FASCO. Faculty, Sankara College of Optometry, BangaloreDocument9 pagesBhavna, M Optom, FASCO. Faculty, Sankara College of Optometry, BangaloreBHUVANANo ratings yet
- ErythromycinDocument1 pageErythromycinJozarine ChelseaNo ratings yet
- SOPS For Blunt Trauma02Document2 pagesSOPS For Blunt Trauma02jawad awanNo ratings yet
- Causative Agent Characteristic Symptom 1 Management: Surgery Is The Most Important Modality For MalignantDocument2 pagesCausative Agent Characteristic Symptom 1 Management: Surgery Is The Most Important Modality For MalignantJp CasperNo ratings yet
- Skin AbnormalsDocument2 pagesSkin AbnormalsJp CasperNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Easy GuideDocument46 pagesOphthalmology Easy Guidesri sinaga0% (1)
- Ocular Chemical Burns From Accidental Exposure To.28Document2 pagesOcular Chemical Burns From Accidental Exposure To.28qalbiNo ratings yet
- Ablation Pédiatrique Alice MaltretDocument36 pagesAblation Pédiatrique Alice Maltretmihalcea alinNo ratings yet
- Covid - 19 - v4 2Document47 pagesCovid - 19 - v4 2dori aarlevNo ratings yet
- Ozempic Dispensing Quick Reference Guide 2023-06-07Document2 pagesOzempic Dispensing Quick Reference Guide 2023-06-07Graham Thomas GipsonNo ratings yet
- Blood Examination ReportDocument11 pagesBlood Examination Reportapi-3745021No ratings yet
- Vaksinasi Dewasa Sby 14Document51 pagesVaksinasi Dewasa Sby 14Ku Ha KuNo ratings yet
- Radiobiology 5 021023Document26 pagesRadiobiology 5 021023Nuha HamedNo ratings yet
- KatukiDocument21 pagesKatukiShantu ShirurmathNo ratings yet
- Rcs e v13 With Guidelines Score SheetDocument4 pagesRcs e v13 With Guidelines Score SheetgabrimarteNo ratings yet
- Acute Complications of Diabetes MellitusDocument43 pagesAcute Complications of Diabetes MellitusalphaphoenixNo ratings yet
- Cornelia de Lange SyndromeDocument10 pagesCornelia de Lange SyndromeKelvinNo ratings yet
- Aravind Eye Care SystemDocument3 pagesAravind Eye Care SystemShruti MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Activity-Sheets ParaydayDocument2 pagesActivity-Sheets ParaydayJohn Vincent ParaydayNo ratings yet
- PainDocument14 pagesPainAmer Abdulla SachitNo ratings yet
- PPHDocument108 pagesPPHsanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- FilariaDocument16 pagesFilariaJessa MayNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument13 pagesInfection ControlSheryl Reyes100% (1)
- IVMS ICM-Heart MurmursDocument22 pagesIVMS ICM-Heart MurmursMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Nbe Thesis ProtocolDocument8 pagesNbe Thesis Protocolsarahdavisjackson100% (2)
- Ranolazine and Hallucinations: Case ReportDocument3 pagesRanolazine and Hallucinations: Case ReportKenny KenNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Effect of Lonicera Ligustrina Wall in Alloxan Induced Diabetes in Wistar RatsDocument8 pagesAntidiabetic Effect of Lonicera Ligustrina Wall in Alloxan Induced Diabetes in Wistar RatssrirampharmNo ratings yet
- Doctor ListDocument5 pagesDoctor ListAbhijitNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: Aiims MedeasyDocument19 pagesGeneral Surgery: Aiims Medeasyvk100% (2)
- Neuroleptics & AnxiolyticsDocument65 pagesNeuroleptics & AnxiolyticsAntonPurpurovNo ratings yet
- Standar Asuhan Keperawatan Diabetes MellitusDocument39 pagesStandar Asuhan Keperawatan Diabetes MellitusSherly DensieNo ratings yet
- nsg-430cc Care Plan 2Document10 pagesnsg-430cc Care Plan 2api-509452165No ratings yet
- Introduction To Orthodontics: Jonathan Chapple Department of Orthodontics Newcastle Dental HospitalDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Orthodontics: Jonathan Chapple Department of Orthodontics Newcastle Dental HospitalMohammed RashwanNo ratings yet