Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsThe Cenozoic Era.2013
The Cenozoic Era.2013
Uploaded by
Andria EspejoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Birched by The Krampus - Siggy ShadeDocument101 pagesBirched by The Krampus - Siggy Shadelilfernweh100% (1)
- A To Z Alphabet Spelling Free PDF - Compressed PDFDocument26 pagesA To Z Alphabet Spelling Free PDF - Compressed PDFstarpearl14100% (2)
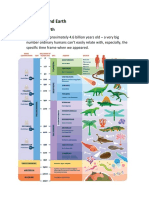
- Life Sciences Gr.10 PPT History of Life On EarthDocument39 pagesLife Sciences Gr.10 PPT History of Life On Earthdeveloping habit and lifestyle of praise and worshNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay:Dogs Vs CatsDocument2 pagesArgumentative Essay:Dogs Vs CatsBest FriendsNo ratings yet
- The Mesozoic EraDocument18 pagesThe Mesozoic EraQueen Justine100% (1)
- Draconomicon 2 Metallic DragonsDocument225 pagesDraconomicon 2 Metallic DragonsRodrigo Souza Justo100% (15)
- Earth HistoryDocument38 pagesEarth HistoryShiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNo ratings yet
- Cenozoic Era: Presented By: Group 6Document30 pagesCenozoic Era: Presented By: Group 6Ralf PayongaNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument41 pagesThe Geological Time Scalekaren milloNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument34 pagesThe Geological Time Scaleapi-239849703100% (1)
- Geologic Time Scale. FinaleDocument36 pagesGeologic Time Scale. FinalelaguillesneicolejazmineNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument4 pagesThe Geological Time ScalehahatdogNo ratings yet
- Geologic TimeDocument29 pagesGeologic TimePratiksha TNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale: - Pre Cambrian - Paleozoic - Mesozoic - CenozoicDocument38 pagesGeologic Time Scale: - Pre Cambrian - Paleozoic - Mesozoic - CenozoicRushikesh pawarNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument20 pagesGeologic Time ScaleSimone ApostolNo ratings yet
- Classification and Evolution of Living Things 2Document100 pagesClassification and Evolution of Living Things 2axelle89017No ratings yet
- Chapter 22-The Pre Cam Brian EarthDocument38 pagesChapter 22-The Pre Cam Brian Earthncl12142No ratings yet
- Geologic HistoryDocument13 pagesGeologic HistoryelixuudNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument47 pagesThe Geological Time Scaleapi-250946583100% (2)
- Era Cenozoico: Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina Facultad de Ciencias - DfymDocument63 pagesEra Cenozoico: Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina Facultad de Ciencias - DfymSergio Andres Mitma SalazarNo ratings yet
- Glaciers Part 2 NarrativesDocument10 pagesGlaciers Part 2 NarrativesKandraNo ratings yet
- ANTH - 18 - Prehistoric CulturesDocument139 pagesANTH - 18 - Prehistoric CulturesMahtaab HassanNo ratings yet
- History of EarthDocument22 pagesHistory of EarthHashi100% (1)
- 1 Geologic History of EarthDocument30 pages1 Geologic History of EarthIvan Bazilije BuhovacNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument85 pagesThe Geological Time ScaleRynamae SolerNo ratings yet
- Geologic TimeDocument18 pagesGeologic TimeReynald AntasoNo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 2 History of Life On EarthDocument42 pagesQ3 Lesson 2 History of Life On EarthJiane ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Canada's Geological HistoryDocument8 pagesChapter 11 - Canada's Geological HistoryRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- The Precambrian. PrecambrianDocument4 pagesThe Precambrian. PrecambrianNics RosalesNo ratings yet
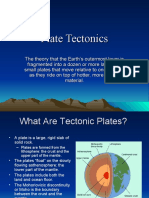
- Plate Tectonics Power PointDocument22 pagesPlate Tectonics Power PointGuia GoopioNo ratings yet
- Earth Time PeriodsDocument4 pagesEarth Time PeriodsSantosh KaurNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument66 pagesGeologic Time ScaleQuercusNo ratings yet
- Earth Processes: Plate Tectonics: Lecture 7 and 8Document23 pagesEarth Processes: Plate Tectonics: Lecture 7 and 8Mangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument105 pagesGeologic Time ScaleJay Jay Caguing100% (1)
- Maddin Lecture 12A KT and CenozoicDocument73 pagesMaddin Lecture 12A KT and CenozoicSamuel AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document82 pagesSession 3Shimaa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Phanerozoic EON: Consist of 3 Eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and CenozoicDocument17 pagesPhanerozoic EON: Consist of 3 Eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and CenozoicSamantha BaldovinoNo ratings yet
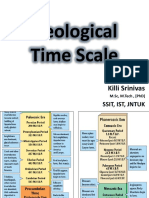
- 1a-Geological Time ScaleDocument84 pages1a-Geological Time ScaleKilli SrinivasNo ratings yet
- San Diego Natural History Museum Fossil Mysteries Geologic TimelineeeDocument5 pagesSan Diego Natural History Museum Fossil Mysteries Geologic Timelineeelasmandarinas deyoongiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 History of Life On EarthDocument5 pagesWeek 2 History of Life On EarthMy Brightest Star Park JisungNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Boundaries and HotspotsDocument34 pagesPlate Tectonics: Boundaries and HotspotsEzzadin BabanNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument39 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKrysfer Secusana100% (2)
- Module 4 ScienceDocument2 pagesModule 4 ScienceSunoo KimNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument30 pagesEarth ScienceElss ToonNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument17 pagesPlate TectonicsDharel Joy AbongNo ratings yet
- Geography Note - Geological Time Scale - For - U.P.S.C - W.B.C.S - General Combined - Ugcnet - ExamDocument3 pagesGeography Note - Geological Time Scale - For - U.P.S.C - W.B.C.S - General Combined - Ugcnet - ExamNabarun JanaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic and Ocean BathymetryDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonic and Ocean Bathymetrymuhammad affanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic and Ocean BathymetryDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonic and Ocean Bathymetrymuhammad affanNo ratings yet
- 13.earths HistoryDocument29 pages13.earths HistoryTEE TIONG SENG MoeNo ratings yet
- History of Life and EarthDocument6 pagesHistory of Life and EarthTobias Domenite P.No ratings yet
- MesozoicDocument11 pagesMesozoicGelo LibeloNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument33 pagesGeologic Time Scalejackie mae torresNo ratings yet
- History of LifeDocument53 pagesHistory of LifeDhanush BmNo ratings yet
- The Mesozoic and Cenozoic EraDocument28 pagesThe Mesozoic and Cenozoic EraLuca LK100% (1)
- 13.earths - History (1) ReadDocument30 pages13.earths - History (1) ReadRey VicencioNo ratings yet
- ENV: 1203 Fundamentals of Earth ScienceDocument49 pagesENV: 1203 Fundamentals of Earth ScienceJawad Rahman 1921324030No ratings yet
- 02-2300-Sea FloorDocument48 pages02-2300-Sea Floorsimranmahil02No ratings yet
- 13.earths - History Earth ScienceDocument30 pages13.earths - History Earth ScienceAlma PalomoNo ratings yet
- Tectonofisik 8Document78 pagesTectonofisik 8Harlen MuntheNo ratings yet
- Prentice Hall: Earth ScienceDocument30 pagesPrentice Hall: Earth ScienceAngela Danielle TanNo ratings yet
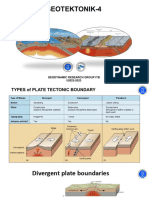
- Geotectonic-4Document58 pagesGeotectonic-4Arieq ClasherNo ratings yet
- The Dawn of Canadian History : A Chronicle of Aboriginal CanadaFrom EverandThe Dawn of Canadian History : A Chronicle of Aboriginal CanadaNo ratings yet
- UID Group 5Document11 pagesUID Group 5Castillo, Justine TristanNo ratings yet
- Essential Emergency KitDocument1 pageEssential Emergency KitCastillo, Justine TristanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NSTPDocument10 pagesChapter 1 NSTPCastillo, Justine TristanNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDula Mhiles Thrixie O PDFDocument1 pageReflection PaperDula Mhiles Thrixie O PDFCastillo, Justine TristanNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument6 pagesActivityandreskalikasansaraNo ratings yet
- VetresumeDocument1 pageVetresumeapi-248067332No ratings yet
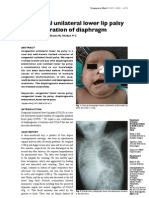
- IDweek Poster No397 Final CorrectedDocument1 pageIDweek Poster No397 Final CorrectedanaluvcNo ratings yet
- Diana Rocio Serrano Gonzalez CC 1106332927Document4 pagesDiana Rocio Serrano Gonzalez CC 1106332927Diana SerranoNo ratings yet
- CullpDocument3 pagesCullpGulherme NodaNo ratings yet
- Bears Everywhere - Songs Poems and Fingerplays PDFDocument30 pagesBears Everywhere - Songs Poems and Fingerplays PDFLourdes Gimenez NaveaNo ratings yet
- Havoc To The Medieval Times Affecting Virtually Every Aspect of LifeDocument4 pagesHavoc To The Medieval Times Affecting Virtually Every Aspect of LifeMungaiNo ratings yet
- Guía de Rinocerontes BlancosDocument82 pagesGuía de Rinocerontes BlancosLeila BritoNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Common Neonatal Presentations (Ashraf AboTaleb) 2017 PDFDocument293 pagesAtlas of Common Neonatal Presentations (Ashraf AboTaleb) 2017 PDFStancu Carmen100% (1)
- Tooth TroubleDocument35 pagesTooth TroubleReegen TeeNo ratings yet
- Cassowary: Casuarius, Is A Ratite ( Ightless BirdDocument62 pagesCassowary: Casuarius, Is A Ratite ( Ightless BirdHarish BhatNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room InstrumentsDocument2 pagesEmergency Room InstrumentsEduardo AnerdezNo ratings yet
- TG Animal Production PDFDocument144 pagesTG Animal Production PDFJoshua BoncodinNo ratings yet
- Aligns With Common Core State Standards For Grade 4Document12 pagesAligns With Common Core State Standards For Grade 4黃郁雯100% (2)
- Verbal Ability: Report This QuestionDocument42 pagesVerbal Ability: Report This QuestionRANJAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- IMPORTATN FROM SLIDE 10 - Think Like A Writer - Sentence Variety 2Document13 pagesIMPORTATN FROM SLIDE 10 - Think Like A Writer - Sentence Variety 2Mahad ArifNo ratings yet
- Standard 12 - Basic Life SupportDocument15 pagesStandard 12 - Basic Life SupportLuiza UngureanuNo ratings yet
- Human Dentition NotesDocument7 pagesHuman Dentition NotesARATHY M NAIR 2147718No ratings yet
- Pacific Ocean: Muir Woods Trail MapDocument2 pagesPacific Ocean: Muir Woods Trail MapGranicus CivicIdeasNo ratings yet
- Poppelbaum, Hermann - Man and Animal - Their Essential Differences (1960, Anthroposophical Publishing Co .) - Libgen - LiDocument185 pagesPoppelbaum, Hermann - Man and Animal - Their Essential Differences (1960, Anthroposophical Publishing Co .) - Libgen - LiJuan100% (1)
- March 2016 MailerDocument2 pagesMarch 2016 Mailerapi-208882322No ratings yet
- Romanian Fish Market 2015Document37 pagesRomanian Fish Market 2015Spînu Adriana Iuliana100% (1)
- Descriptive Text and OnDocument3 pagesDescriptive Text and OnKandean PoerbaNo ratings yet
- Zoobic SafariDocument1 pageZoobic SafariJhieDolienteCastilloNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Landmarks of The Maxilla and MandibleDocument34 pagesAnatomic Landmarks of The Maxilla and Mandiblespu123No ratings yet
- Somiya Mehta CorporateDocument2 pagesSomiya Mehta Corporateapi-345724380No ratings yet
The Cenozoic Era.2013
The Cenozoic Era.2013
Uploaded by
Andria Espejo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views18 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views18 pagesThe Cenozoic Era.2013
The Cenozoic Era.2013
Uploaded by
Andria EspejoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
THE CENOZOIC ERA
The Shaping of the Modern World
Themes of the Cenozoic
• Changes in Life
• Age of Mammals
• Make Way birds
• The Ascent of Humans
• Mountain Building in Western America continues
• Formation of the San Andreas Fault
• A Return to the Ice
• Several major glacial events
• Major Volcanic Eruptions
Early Cenozoic
• North America grows larger
• Formed due to a series of collisions between the North American
plate and small terranes in the Pacific
• The Interior Western Seaway retreats
and most of North America is above
sea level (very important event)
• The Appalachians are eroded
Early Cenozoic (65- 23 mya)
Early Cenozoic
• India begins its collision with Asia,
causing the Himalayas to be lifted
• “Ring of Fire” forms
• Australia separates from Antarctica
Early Cenozoic Era
• The demise of the dinosaurs allows
not only mammals, but birds to
diversify and flourish
• Birds got very large (to 10 feet tall) and were predatory
• Songbirds also develop in this time period
• First flowering plants develop -
angiosperms
Giant Birds
Early Cenozoic
• The climate of the Paleogene was notably
drier than previous periods
• Also much warmer than it is currently
• Lead to more land being above sea level
• Allowed for the evolution of first grasses and
therefore, grazing mammals (like horses) evolve
• Mammals diversify and grow very large
• Mammals are an extremely varied group!
• All major mammal groups are in place by the middle
of the Cenozoic
Mammals of the Paleogene
Marine Animals
• The marine mammals evolve at this
time
• Whales, dolphins, etc
• Relative of camels!!!
• Lose their visible limbs over time
• Sharks take over as the dominant predator in the
sea, filling the niche left by extinct mosasaurs and
pleisosaurs
Marine Animals
The Neogene: Middle of the Cenozoic to
Present (23 mya – Present)
• During the Neogene, the continents take
their modern shapes
• North and South America join
• Iceland emerges from the sea
• Polar Ice Caps form
• In North America, the San Andreas Fault
forms
(23 mya – Present)
The Pliestocene (1.6 mya –
10,000)
• The Pleistocene is often referred to as the
“Ice Age”
• about 4 major ice advances and 3 retreats
• Leads to sea level retreats and advances
• Great Lakes form
• Other major event includes the eruption of
the Yellowstone caldera and (even worse!)
the eruption of the Toba caldera
• Toba nearly wipes out humans
The Ice Ages
The Calderas of the Pleistocene
Pleistocene Megafauna
• Megafauna refers to the extreme large
mammals that dominated this time period
• Include the Mammoth, Mastodon, Saber-cat,
Giant Sloth and Giant Beaver (among others)
Pleistocene Extinction
• At the end of the last Ice Age (about
18,000 - 12,000 ya) most of the large
mammals went extinct
• This extinction event only affected large mammals
• Probable causes include climate changes affecting
the web chain and overkill by early humans
• Still plenty of room for doubt
• One question – is this extinction event a thing of the
past, or is it continuing today?????
You might also like
- Birched by The Krampus - Siggy ShadeDocument101 pagesBirched by The Krampus - Siggy Shadelilfernweh100% (1)
- A To Z Alphabet Spelling Free PDF - Compressed PDFDocument26 pagesA To Z Alphabet Spelling Free PDF - Compressed PDFstarpearl14100% (2)
- Life Sciences Gr.10 PPT History of Life On EarthDocument39 pagesLife Sciences Gr.10 PPT History of Life On Earthdeveloping habit and lifestyle of praise and worshNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay:Dogs Vs CatsDocument2 pagesArgumentative Essay:Dogs Vs CatsBest FriendsNo ratings yet
- The Mesozoic EraDocument18 pagesThe Mesozoic EraQueen Justine100% (1)
- Draconomicon 2 Metallic DragonsDocument225 pagesDraconomicon 2 Metallic DragonsRodrigo Souza Justo100% (15)
- Earth HistoryDocument38 pagesEarth HistoryShiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNo ratings yet
- Cenozoic Era: Presented By: Group 6Document30 pagesCenozoic Era: Presented By: Group 6Ralf PayongaNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument41 pagesThe Geological Time Scalekaren milloNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument34 pagesThe Geological Time Scaleapi-239849703100% (1)
- Geologic Time Scale. FinaleDocument36 pagesGeologic Time Scale. FinalelaguillesneicolejazmineNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument4 pagesThe Geological Time ScalehahatdogNo ratings yet
- Geologic TimeDocument29 pagesGeologic TimePratiksha TNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale: - Pre Cambrian - Paleozoic - Mesozoic - CenozoicDocument38 pagesGeologic Time Scale: - Pre Cambrian - Paleozoic - Mesozoic - CenozoicRushikesh pawarNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument20 pagesGeologic Time ScaleSimone ApostolNo ratings yet
- Classification and Evolution of Living Things 2Document100 pagesClassification and Evolution of Living Things 2axelle89017No ratings yet
- Chapter 22-The Pre Cam Brian EarthDocument38 pagesChapter 22-The Pre Cam Brian Earthncl12142No ratings yet
- Geologic HistoryDocument13 pagesGeologic HistoryelixuudNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument47 pagesThe Geological Time Scaleapi-250946583100% (2)
- Era Cenozoico: Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina Facultad de Ciencias - DfymDocument63 pagesEra Cenozoico: Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina Facultad de Ciencias - DfymSergio Andres Mitma SalazarNo ratings yet
- Glaciers Part 2 NarrativesDocument10 pagesGlaciers Part 2 NarrativesKandraNo ratings yet
- ANTH - 18 - Prehistoric CulturesDocument139 pagesANTH - 18 - Prehistoric CulturesMahtaab HassanNo ratings yet
- History of EarthDocument22 pagesHistory of EarthHashi100% (1)
- 1 Geologic History of EarthDocument30 pages1 Geologic History of EarthIvan Bazilije BuhovacNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time ScaleDocument85 pagesThe Geological Time ScaleRynamae SolerNo ratings yet
- Geologic TimeDocument18 pagesGeologic TimeReynald AntasoNo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 2 History of Life On EarthDocument42 pagesQ3 Lesson 2 History of Life On EarthJiane ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Canada's Geological HistoryDocument8 pagesChapter 11 - Canada's Geological HistoryRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- The Precambrian. PrecambrianDocument4 pagesThe Precambrian. PrecambrianNics RosalesNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Power PointDocument22 pagesPlate Tectonics Power PointGuia GoopioNo ratings yet
- Earth Time PeriodsDocument4 pagesEarth Time PeriodsSantosh KaurNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument66 pagesGeologic Time ScaleQuercusNo ratings yet
- Earth Processes: Plate Tectonics: Lecture 7 and 8Document23 pagesEarth Processes: Plate Tectonics: Lecture 7 and 8Mangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument105 pagesGeologic Time ScaleJay Jay Caguing100% (1)
- Maddin Lecture 12A KT and CenozoicDocument73 pagesMaddin Lecture 12A KT and CenozoicSamuel AdewumiNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document82 pagesSession 3Shimaa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Phanerozoic EON: Consist of 3 Eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and CenozoicDocument17 pagesPhanerozoic EON: Consist of 3 Eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and CenozoicSamantha BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- 1a-Geological Time ScaleDocument84 pages1a-Geological Time ScaleKilli SrinivasNo ratings yet
- San Diego Natural History Museum Fossil Mysteries Geologic TimelineeeDocument5 pagesSan Diego Natural History Museum Fossil Mysteries Geologic Timelineeelasmandarinas deyoongiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 History of Life On EarthDocument5 pagesWeek 2 History of Life On EarthMy Brightest Star Park JisungNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Boundaries and HotspotsDocument34 pagesPlate Tectonics: Boundaries and HotspotsEzzadin BabanNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument39 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKrysfer Secusana100% (2)
- Module 4 ScienceDocument2 pagesModule 4 ScienceSunoo KimNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument30 pagesEarth ScienceElss ToonNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument17 pagesPlate TectonicsDharel Joy AbongNo ratings yet
- Geography Note - Geological Time Scale - For - U.P.S.C - W.B.C.S - General Combined - Ugcnet - ExamDocument3 pagesGeography Note - Geological Time Scale - For - U.P.S.C - W.B.C.S - General Combined - Ugcnet - ExamNabarun JanaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic and Ocean BathymetryDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonic and Ocean Bathymetrymuhammad affanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic and Ocean BathymetryDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonic and Ocean Bathymetrymuhammad affanNo ratings yet
- 13.earths HistoryDocument29 pages13.earths HistoryTEE TIONG SENG MoeNo ratings yet
- History of Life and EarthDocument6 pagesHistory of Life and EarthTobias Domenite P.No ratings yet
- MesozoicDocument11 pagesMesozoicGelo LibeloNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument33 pagesGeologic Time Scalejackie mae torresNo ratings yet
- History of LifeDocument53 pagesHistory of LifeDhanush BmNo ratings yet
- The Mesozoic and Cenozoic EraDocument28 pagesThe Mesozoic and Cenozoic EraLuca LK100% (1)
- 13.earths - History (1) ReadDocument30 pages13.earths - History (1) ReadRey VicencioNo ratings yet
- ENV: 1203 Fundamentals of Earth ScienceDocument49 pagesENV: 1203 Fundamentals of Earth ScienceJawad Rahman 1921324030No ratings yet
- 02-2300-Sea FloorDocument48 pages02-2300-Sea Floorsimranmahil02No ratings yet
- 13.earths - History Earth ScienceDocument30 pages13.earths - History Earth ScienceAlma PalomoNo ratings yet
- Tectonofisik 8Document78 pagesTectonofisik 8Harlen MuntheNo ratings yet
- Prentice Hall: Earth ScienceDocument30 pagesPrentice Hall: Earth ScienceAngela Danielle TanNo ratings yet
- Geotectonic-4Document58 pagesGeotectonic-4Arieq ClasherNo ratings yet
- The Dawn of Canadian History : A Chronicle of Aboriginal CanadaFrom EverandThe Dawn of Canadian History : A Chronicle of Aboriginal CanadaNo ratings yet
- UID Group 5Document11 pagesUID Group 5Castillo, Justine TristanNo ratings yet
- Essential Emergency KitDocument1 pageEssential Emergency KitCastillo, Justine TristanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NSTPDocument10 pagesChapter 1 NSTPCastillo, Justine TristanNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDula Mhiles Thrixie O PDFDocument1 pageReflection PaperDula Mhiles Thrixie O PDFCastillo, Justine TristanNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument6 pagesActivityandreskalikasansaraNo ratings yet
- VetresumeDocument1 pageVetresumeapi-248067332No ratings yet
- IDweek Poster No397 Final CorrectedDocument1 pageIDweek Poster No397 Final CorrectedanaluvcNo ratings yet
- Diana Rocio Serrano Gonzalez CC 1106332927Document4 pagesDiana Rocio Serrano Gonzalez CC 1106332927Diana SerranoNo ratings yet
- CullpDocument3 pagesCullpGulherme NodaNo ratings yet
- Bears Everywhere - Songs Poems and Fingerplays PDFDocument30 pagesBears Everywhere - Songs Poems and Fingerplays PDFLourdes Gimenez NaveaNo ratings yet
- Havoc To The Medieval Times Affecting Virtually Every Aspect of LifeDocument4 pagesHavoc To The Medieval Times Affecting Virtually Every Aspect of LifeMungaiNo ratings yet
- Guía de Rinocerontes BlancosDocument82 pagesGuía de Rinocerontes BlancosLeila BritoNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Common Neonatal Presentations (Ashraf AboTaleb) 2017 PDFDocument293 pagesAtlas of Common Neonatal Presentations (Ashraf AboTaleb) 2017 PDFStancu Carmen100% (1)
- Tooth TroubleDocument35 pagesTooth TroubleReegen TeeNo ratings yet
- Cassowary: Casuarius, Is A Ratite ( Ightless BirdDocument62 pagesCassowary: Casuarius, Is A Ratite ( Ightless BirdHarish BhatNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room InstrumentsDocument2 pagesEmergency Room InstrumentsEduardo AnerdezNo ratings yet
- TG Animal Production PDFDocument144 pagesTG Animal Production PDFJoshua BoncodinNo ratings yet
- Aligns With Common Core State Standards For Grade 4Document12 pagesAligns With Common Core State Standards For Grade 4黃郁雯100% (2)
- Verbal Ability: Report This QuestionDocument42 pagesVerbal Ability: Report This QuestionRANJAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- IMPORTATN FROM SLIDE 10 - Think Like A Writer - Sentence Variety 2Document13 pagesIMPORTATN FROM SLIDE 10 - Think Like A Writer - Sentence Variety 2Mahad ArifNo ratings yet
- Standard 12 - Basic Life SupportDocument15 pagesStandard 12 - Basic Life SupportLuiza UngureanuNo ratings yet
- Human Dentition NotesDocument7 pagesHuman Dentition NotesARATHY M NAIR 2147718No ratings yet
- Pacific Ocean: Muir Woods Trail MapDocument2 pagesPacific Ocean: Muir Woods Trail MapGranicus CivicIdeasNo ratings yet
- Poppelbaum, Hermann - Man and Animal - Their Essential Differences (1960, Anthroposophical Publishing Co .) - Libgen - LiDocument185 pagesPoppelbaum, Hermann - Man and Animal - Their Essential Differences (1960, Anthroposophical Publishing Co .) - Libgen - LiJuan100% (1)
- March 2016 MailerDocument2 pagesMarch 2016 Mailerapi-208882322No ratings yet
- Romanian Fish Market 2015Document37 pagesRomanian Fish Market 2015Spînu Adriana Iuliana100% (1)
- Descriptive Text and OnDocument3 pagesDescriptive Text and OnKandean PoerbaNo ratings yet
- Zoobic SafariDocument1 pageZoobic SafariJhieDolienteCastilloNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Landmarks of The Maxilla and MandibleDocument34 pagesAnatomic Landmarks of The Maxilla and Mandiblespu123No ratings yet
- Somiya Mehta CorporateDocument2 pagesSomiya Mehta Corporateapi-345724380No ratings yet