Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wepik Formula One Unveiling The Thrills of Tracks Cars Engines and Pit Stops 20231113095112en9u
Wepik Formula One Unveiling The Thrills of Tracks Cars Engines and Pit Stops 20231113095112en9u
Uploaded by
pepeperete10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views9 pagesFormula 1 (F1) is the highest class of international single-seater auto racing sanctioned by the FIA. It has been one of the premier forms of motorsport in the world since its inaugural season in 1950. F1 cars are the pinnacle of racing technology, capable of over 200 mph. The document traces the history of F1 from its early years dominated by front-engined cars to the modern hybrid era. It also describes key aspects of F1 including the tracks, cars, engines, and the importance of pit stops.
Original Description:
Original Title
Wepik Formula One Unveiling the Thrills of Tracks Cars Engines and Pit Stops 20231113095112en9u
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFormula 1 (F1) is the highest class of international single-seater auto racing sanctioned by the FIA. It has been one of the premier forms of motorsport in the world since its inaugural season in 1950. F1 cars are the pinnacle of racing technology, capable of over 200 mph. The document traces the history of F1 from its early years dominated by front-engined cars to the modern hybrid era. It also describes key aspects of F1 including the tracks, cars, engines, and the importance of pit stops.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views9 pagesWepik Formula One Unveiling The Thrills of Tracks Cars Engines and Pit Stops 20231113095112en9u
Wepik Formula One Unveiling The Thrills of Tracks Cars Engines and Pit Stops 20231113095112en9u
Uploaded by
pepeperete1Formula 1 (F1) is the highest class of international single-seater auto racing sanctioned by the FIA. It has been one of the premier forms of motorsport in the world since its inaugural season in 1950. F1 cars are the pinnacle of racing technology, capable of over 200 mph. The document traces the history of F1 from its early years dominated by front-engined cars to the modern hybrid era. It also describes key aspects of F1 including the tracks, cars, engines, and the importance of pit stops.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Formula One
Maximiliano Penna y Fabrizio Miranda
6to
Introduction
The Formula 1 is not merely an
automotive competition; it is a
spectacle that merges science,
engineering, and human courage.
From its humble beginnings in the
1950s, Formula 1 has evolved into a
blend of sporting talent and cutting-
edge technological development.
What is F1?
Formula One, also known as F1, is the
highest class of international single-seater
auto racing, sanctioned by the Fédération
Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The
FIA Formula One World Championship
has been one of the premier forms of
racing around the world since its inaugural
season in 1950. The World Drivers'
Championship, which became the FIA
Formula One World Championship in
1981, has been one of the few elite events
that have taken place continuously since its
inception.
Whats the history?
The early years of F1 were marked by front-engined, open-
wheeled cars, dominated by Italian teams like Alfa Romeo
and Ferrari. Legendary drivers like Juan Manuel Fangio and
Stirling Moss captured the hearts of racing enthusiasts
with their daring maneuvers and fearless driving.
In the 1960s, a revolution occurred as rear-engined cars
gained prominence, spearheaded by teams like Lotus and
Colin Chapman. This shift brought about significant
aerodynamic advancements, allowing cars to hug corners
at incredible speeds.
The 1970s saw the introduction of turbocharged engines,
propelling F1 cars to new heights of power and
performance. Ground effect aerodynamics emerged,
generating massive downforce and enabling drivers to
push the limits of adhesion.
Whats the history?
The 1990s and early 2000s marked an era of technological refinement and safety enhancements. Electronic
driver aids were introduced, and safety regulations were tightened to minimize the risk of accidents. Teams
like McLaren, Ferrari, and Williams dominated this period, with drivers like Michael Schumacher and Mika
Häkkinen becoming household names.
In 2014, F1 entered the hybrid era, incorporating a combination of turbocharged internal combustion
engines and energy recovery systems. This shift aimed to improve fuel efficiency and open up new avenues
for technological innovation.
Today, Formula One remains one of the most popular and technologically advanced sports in the world,
captivating millions of fans worldwide. It continues to push the boundaries of automotive engineering and
innovation, showcasing the pinnacle of motorsport.
The Tracks
F1 tracks are designed for speed and challenge. From iconic circuits like Monaco to modern
marvels like Abu Dhabi's Yas Marina, each track presents a unique test for drivers and teams.
The Cars
Formula One (F1) cars are the pinnacle of
motorsport technology, designed to be the
fastest and most technologically advanced
racing cars in the world. They are single-seat,
open-wheeled racing cars with a high-powered
engine positioned behind the driver, and
substantial front and rear wings that generate
downforce to keep the car stuck to the track at
high speeds. F1 cars are capable of reaching
speeds of over 200 miles per hour (320
kilometers per hour), and they can accelerate
from 0 to 60 miles per hour (0 to 97 kilometers
per hour) in under 2 seconds. This is due to
their powerful engines, aerodynamic design,
and advanced technology..
The Engines
Formula 1 engines are the symphony of power,
precision, and relentless pursuit of performance.
At the heart of these racing machines beats an
engineering marvel that defines the very essence
of speed and competition.
The power unit in a Formula 1 car is a masterpiece
of combustion technology, seamlessly blending
traditional internal combustion engines with
cutting-edge hybrid systems. These power units
are meticulously crafted to extract maximum
power from every drop of fuel while harnessing
energy from braking and exhaust to boost
performance.
The Pit
A pit stop is S topselement of Formula One racing,
a crucial
where drivers enter their team’s pit lane to change
tires, refuel, or make necessary repairs. These quick
and precise stops can significantly impact a driver’s
race position and overall performance.The primary
purpose of pit stops is to change tires. F1 tires are
designed to provide maximum grip and performance,
but they have a limited lifespan. As the tires wear
down, their grip diminishes, affecting the car's handling
and lap times. Pit stops allow drivers to switch to fresh
tires, regaining optimal grip and maintaining their
pace.
You might also like
- Assetto Pirate ModlistDocument444 pagesAssetto Pirate ModlistjimmkampNo ratings yet
- Leaked Assetto Corsa ModsDocument10 pagesLeaked Assetto Corsa Modslufelipolufalufa50% (2)
- Total Competition: Lessons in Strategy from Formula OneFrom EverandTotal Competition: Lessons in Strategy from Formula OneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- Logistics Project Report On f1 (Formula 1)Document73 pagesLogistics Project Report On f1 (Formula 1)rajivagrawal1567% (3)
- ERP Software Systems and Formula One Title PageDocument13 pagesERP Software Systems and Formula One Title PageGregg TrudeNo ratings yet
- Formula 1Document7 pagesFormula 1api-27477209No ratings yet
- Ferrari Company ProfileDocument14 pagesFerrari Company Profilechauhanbrothers3423No ratings yet
- Formula 1-3Document24 pagesFormula 1-3Lucian RaduNo ratings yet
- F1Document1 pageF1rapikil324No ratings yet
- The World of Formula OneDocument2 pagesThe World of Formula OneNihar MadkaikerNo ratings yet
- Formula OneDocument2 pagesFormula Onesiddharthgurung.weempowernepalNo ratings yet
- Subject Seminar Understanding A Formula 1 CarDocument14 pagesSubject Seminar Understanding A Formula 1 CarAbhinand AshokanandaNo ratings yet
- F1 CarsDocument6 pagesF1 CarsmeghaNo ratings yet
- Formula 1Document3 pagesFormula 1MajaNo ratings yet
- The Development of Formula One Car Racing: Cronaca L'AquilaDocument1 pageThe Development of Formula One Car Racing: Cronaca L'AquilacronacapescaraNo ratings yet
- 17 F1 Engineering SaminAliHemmatiDocument13 pages17 F1 Engineering SaminAliHemmatidleodnjs2006No ratings yet
- Formula One: F1 (Disambiguation) Formula One (Disambiguation) List of FIA EventsDocument19 pagesFormula One: F1 (Disambiguation) Formula One (Disambiguation) List of FIA EventsCristian MateiNo ratings yet
- MasterCard F1 KeynoteDocument4 pagesMasterCard F1 KeynotebenNo ratings yet
- Formula One Grand Prix Motor Racing Fédération Internationale de L'automobile Formula One RegulationsDocument5 pagesFormula One Grand Prix Motor Racing Fédération Internationale de L'automobile Formula One RegulationsAmitkumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Formula 1 ScribbidDocument2 pagesFormula 1 ScribbidSonal MahajanNo ratings yet
- f1 Science SpeechDocument13 pagesf1 Science Speechteacherroger2020No ratings yet
- Motor SportDocument24 pagesMotor SportDaksh DhariwalNo ratings yet
- Muskan Get Into F1Document11 pagesMuskan Get Into F1Vanshika ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Sport RulesDocument121 pagesSport RulesParmesh ChopraNo ratings yet
- Ferrari - Speed and StyleDocument17 pagesFerrari - Speed and StyleSuhaani BhandarkarNo ratings yet
- The Business Of: Chase For Viewers Puts Sport at CrossroadsDocument4 pagesThe Business Of: Chase For Viewers Puts Sport at CrossroadsSaket KumarNo ratings yet
- Formula 1Document1 pageFormula 1xirafi5376No ratings yet
- Formula OneDocument1 pageFormula Onenanol17698No ratings yet
- Promoting F1 As A Lifestyle and Entertainment Sport.: 2. Appealing To Motorsport Fans (Technical Side)Document5 pagesPromoting F1 As A Lifestyle and Entertainment Sport.: 2. Appealing To Motorsport Fans (Technical Side)immacoolcatNo ratings yet
- Formula 1Document2 pagesFormula 1Justina TerruzziNo ratings yet
- Research Formula OneDocument10 pagesResearch Formula Onedano qrNo ratings yet
- Bhavna'sDocument10 pagesBhavna'sMadhavan MaheshwaramNo ratings yet
- Part Two - Black Boxes & BarriersDocument13 pagesPart Two - Black Boxes & BarriersyogeshkurheNo ratings yet
- Formula 1 - Unleashing The Greatest Racing Spectacle On The PlanetDocument9 pagesFormula 1 - Unleashing The Greatest Racing Spectacle On The PlanetcaseyNo ratings yet
- McLaren F1Document10 pagesMcLaren F1jacalynwicksNo ratings yet
- Formula 1Document21 pagesFormula 1AakashNo ratings yet
- Brochure 2012 Formula FordDocument29 pagesBrochure 2012 Formula Fordslitz ferrariNo ratings yet
- F1Document29 pagesF1yoyotoyoNo ratings yet
- Motorsports: Who Is in Charge?Document2 pagesMotorsports: Who Is in Charge?MatteoBiancheriNo ratings yet
- Document Sejarah F1Document11 pagesDocument Sejarah F1Sergio Saldano YudaNo ratings yet
- The Legacy and Evolution of McLarenDocument3 pagesThe Legacy and Evolution of McLarenwiddayudaubou-2882No ratings yet
- Wa0040.Document15 pagesWa0040.Raghul SundarNo ratings yet
- J-Dampers in Formula OneDocument3 pagesJ-Dampers in Formula Onertech01No ratings yet
- Big BusinessDocument2 pagesBig BusinessМилош ПезерNo ratings yet
- Formula OneDocument1 pageFormula OneМилош ПезерNo ratings yet
- Formula 1 PresentationDocument2 pagesFormula 1 Presentationdinis2006rochaNo ratings yet
- Few Lines About Racing Cars For PrithivDocument2 pagesFew Lines About Racing Cars For PrithivSan BrothersNo ratings yet
- F1-Cars SeminarsDocument25 pagesF1-Cars Seminarsphantaman100% (1)
- F1 Constructors Case ES13e pp584-592Document9 pagesF1 Constructors Case ES13e pp584-592venkateswari25799No ratings yet
- F1 Car TechnologyDocument20 pagesF1 Car TechnologyHimanshu Dhingra100% (1)
- The Formula 1 Challenge: Sustaining Performance in A Highly Competitive and Turbulent EnvironmentDocument2 pagesThe Formula 1 Challenge: Sustaining Performance in A Highly Competitive and Turbulent EnvironmentraheelNo ratings yet
- Renault Reveals 2014 Formula 1 Power Unit v6 55588Document17 pagesRenault Reveals 2014 Formula 1 Power Unit v6 55588Blaze123xNo ratings yet
- Expository ParagraphDocument3 pagesExpository ParagraphAna SilvaNo ratings yet
- Essayfirstdraftfixed 1111 BrandanburkhartDocument3 pagesEssayfirstdraftfixed 1111 Brandanburkhartapi-302846668No ratings yet
- Formula One Car DetailsDocument22 pagesFormula One Car DetailsBalaji AeroNo ratings yet
- Renault SportDocument32 pagesRenault SportUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- At The Heart of FerrariDocument2 pagesAt The Heart of FerrariZayd OnnNo ratings yet
- F1 EnginesDocument11 pagesF1 Enginessachin_sawant1985No ratings yet
- How Do Race Cars Work? Car Book for Kids | Children's Transportation BooksFrom EverandHow Do Race Cars Work? Car Book for Kids | Children's Transportation BooksNo ratings yet
- Order & Ranking Short Tricks & Questions With Solutions: WWW - Onlyjob.inDocument35 pagesOrder & Ranking Short Tricks & Questions With Solutions: WWW - Onlyjob.indivya chawlaNo ratings yet
- RESULTSDocument36 pagesRESULTSDRAGON BLADE 123No ratings yet
- Zenith AvailabilityDocument38 pagesZenith AvailabilityPolycom IncNo ratings yet
- 2210 Ayrton Senna BF FKBDocument20 pages2210 Ayrton Senna BF FKBaledotinoNo ratings yet
- Tires Pricelist 2022Document3 pagesTires Pricelist 2022Lastrella RueNo ratings yet
- Cardinal and Ordinal NumbersDocument2 pagesCardinal and Ordinal NumbersRaquel NoeliaNo ratings yet
- LMGC 2023-24 Racing RulesDocument9 pagesLMGC 2023-24 Racing RulesFarkasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Lesson 3 Super Sea Animals ReadingDocument21 pagesUnit 2 Lesson 3 Super Sea Animals Readingmylyn ortizNo ratings yet
- 2009 Formula One AerodynamicsDocument9 pages2009 Formula One AerodynamicsCRISTIAN LEVI ALBORNOZ REATEGUINo ratings yet
- The Worst Drivers in F1 HIstory - Number 13 - Dave Walker - The ParabolicaDocument6 pagesThe Worst Drivers in F1 HIstory - Number 13 - Dave Walker - The ParabolicaYuji IdeNo ratings yet
- F1 TakeoverDocument2 pagesF1 Takeovermick.pride81No ratings yet
- F1 Calendar - ESPNDocument2 pagesF1 Calendar - ESPNMark Erwin SalduaNo ratings yet
- MCPEDL at AshmingguDocument3 pagesMCPEDL at AshminggualbateranantonioNo ratings yet
- f1 2023 Predictions Draft FinalDocument9 pagesf1 2023 Predictions Draft Finalapi-644288740No ratings yet
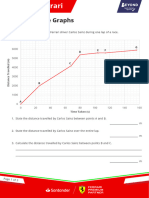
- Scuderia Ferrari Distance Time GraphsDocument3 pagesScuderia Ferrari Distance Time GraphsnowarabdullaaNo ratings yet
- 2by1 Digit1Document2 pages2by1 Digit1BimBel PolimNo ratings yet
- F1 Master 2009 - GP12Document11 pagesF1 Master 2009 - GP12api-3705307No ratings yet
- Racelogic Ebook c16Document7 pagesRacelogic Ebook c16Juan Ramón Pérez LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Writing Dates in English!!!: Always Use Capital Letter!!!Document2 pagesWriting Dates in English!!!: Always Use Capital Letter!!!Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lamborghini: Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. (Document12 pagesLamborghini: Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. (chethan jagadeeswaraNo ratings yet
- KT-ISMS-FR-15 Supplier, Vendor Re Evaluation FormDocument1 pageKT-ISMS-FR-15 Supplier, Vendor Re Evaluation FormAdil AbdulkhaderNo ratings yet
- 2018 19 Mex f1 q0 Timing Qualifyingsessionmaximumspeeds v01Document1 page2018 19 Mex f1 q0 Timing Qualifyingsessionmaximumspeeds v01adeney_nickNo ratings yet
- Sam Technical SeminarDocument14 pagesSam Technical SeminarRithwik RanjanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Record (Editable)Document15 pagesAssessment Record (Editable)ELLIE BAYNOSANo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking SystemDocument14 pagesRegenerative Braking Systemmonu patelNo ratings yet
- Astm / Api TablesDocument126 pagesAstm / Api TablesсвакNo ratings yet
- FOM Sales Brochure UpdatedDocument4 pagesFOM Sales Brochure UpdatedPrecision Performance BrakesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledAditya Anand 60No ratings yet