Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsPresentation On Shapes
Presentation On Shapes
Uploaded by
harshangpatel174This presentation summarizes the key properties of several basic shapes:
Ovals have a continuous curved shape without straight sides or sharp corners. Right triangles have one 90-degree angle and the hypotenuse is the longest side. Diamonds have polished facets that reflect light and four sides of equal length. Pentagons have five sides and five interior angles that sum to 540 degrees. Cylinders have two congruent circular bases connected by a curved lateral surface, with no vertices or edges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- WK 14Document20 pagesWK 14mariusreeNo ratings yet
- Properties of 2D 3D ShapesDocument24 pagesProperties of 2D 3D ShapesKumud Baliyan100% (1)
- Group 3: Ericha Febriyani Margareta Syahla Khairunnisa M.Faris Ramzi Asad Syamsul.ADocument21 pagesGroup 3: Ericha Febriyani Margareta Syahla Khairunnisa M.Faris Ramzi Asad Syamsul.ABagas AriqNo ratings yet
- 50-Important-Math-Concepts-1 by DaaDocument9 pages50-Important-Math-Concepts-1 by Daadaanish muftiNo ratings yet
- WK 11 12 Geometric Designs and 2dDocument61 pagesWK 11 12 Geometric Designs and 2dHoneybunch beforeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Geo. Const. Part IIIDocument20 pagesLecture 9 Geo. Const. Part IIIIriama RobertNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Geo. Const. Part IIIDocument20 pagesLecture 9 Geo. Const. Part IIIIriama RobertNo ratings yet
- 3D Shapes 151_152Document12 pages3D Shapes 151_152Nitya M VNo ratings yet
- Geometry Power PointDocument70 pagesGeometry Power PointDavid Hernandez100% (1)
- ADVGEOM Lecture5 Nov20Document26 pagesADVGEOM Lecture5 Nov20Ellaine LimpangogNo ratings yet
- UNIT:-2: Introduction To Lines and Geometric ShapesDocument23 pagesUNIT:-2: Introduction To Lines and Geometric ShapesBikash ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity No:01: Computer Aided Engineering DesignDocument11 pagesLab Activity No:01: Computer Aided Engineering DesignArshad AliNo ratings yet
- CAD Solids Surfaces Keletondaafav THDocument8 pagesCAD Solids Surfaces Keletondaafav THyash pradhanNo ratings yet
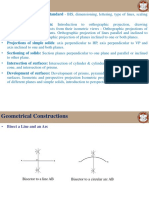
- 4 Geometrical ConstructionDocument23 pages4 Geometrical ConstructionTAE. J.SNo ratings yet
- Solid FiguresDocument22 pagesSolid FiguresSir Roby James DazaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4, Conics ConstructionsDocument31 pagesLecture - 4, Conics ConstructionsAmit GhadeNo ratings yet
- Geometry ReviewDocument3 pagesGeometry ReviewJose Luis PiñaNo ratings yet
- ShapesDocument11 pagesShapesanissafeniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 MATH13Document52 pagesLesson 1 MATH13Randel Boris de Ocampo100% (4)
- 3D Shape Properties Presentation in Colourful Fun Style - 20240513 - 194645 - 0000Document36 pages3D Shape Properties Presentation in Colourful Fun Style - 20240513 - 194645 - 0000ajmanaloto3016No ratings yet
- Basic Geometric Construction-TermsDocument21 pagesBasic Geometric Construction-TermsCarinaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Geometrical Shapes OsamaDocument17 pagesProperties of Geometrical Shapes OsamaIsam Al HassanNo ratings yet
- PL AN E SH AP ES: By: Adekeye Bisola Busayomi Oyinloye Eni KelechiDocument18 pagesPL AN E SH AP ES: By: Adekeye Bisola Busayomi Oyinloye Eni KelechiAbNo ratings yet
- CSEL 301 Lecture 2Document55 pagesCSEL 301 Lecture 2ianpatrickmesiasNo ratings yet
- Quads and PolysDocument71 pagesQuads and PolysKinsley David AdaigbeNo ratings yet
- WK Folder Cover PageDocument6 pagesWK Folder Cover PageAryan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 3Document24 pagesMathematics Form 3Amal Sufiah82% (33)
- PDF Document 35Document20 pagesPDF Document 35Adams BakerNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Mathematics 7Document2 pagesReviewer in Mathematics 7Khristian RuedaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Geometry II: Jan 15/ 2022 Muhammed ADocument41 pagesDescriptive Geometry II: Jan 15/ 2022 Muhammed AHULE ADDIS ENTERTAINMENTNo ratings yet
- Akshara ChhabraDocument8 pagesAkshara Chhabrameenuchhabra487No ratings yet
- Circular FunctionsDocument49 pagesCircular FunctionsJames Vhon ReyesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry-01 ENITV12D ELEP06Document50 pagesTrigonometry-01 ENITV12D ELEP06Frederick ExibiaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Core Math Fifth Edition NotesDocument92 pagesIGCSE Core Math Fifth Edition NotesShepherd HomeschoolNo ratings yet
- TLE GRADE 10 Performing Mensuration and CalculationDocument35 pagesTLE GRADE 10 Performing Mensuration and CalculationLeoben Galima50% (2)
- Grade 3 Geometry NotesDocument5 pagesGrade 3 Geometry NotesSimna BijuNo ratings yet
- Las Tech Drafting 3Q WK1Document17 pagesLas Tech Drafting 3Q WK1Clemenda TuscanoNo ratings yet
- Solid Geometry Lesson 1Document40 pagesSolid Geometry Lesson 1KEN XINGNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Solid Mensuration Part 2Document41 pagesModule 2 Solid Mensuration Part 2Shaena VillaluzNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Ext Mathematics (0580) FlashcardsDocument45 pagesIGCSE Ext Mathematics (0580) FlashcardsSamson YauNo ratings yet
- Numbers: Prepared By: Z.K. TeeDocument39 pagesNumbers: Prepared By: Z.K. TeeteezkangNo ratings yet
- 2D and 3D ShapesDocument3 pages2D and 3D ShapesvirusNo ratings yet
- Circles Review For Test 1 1Document4 pagesCircles Review For Test 1 1api-256105506No ratings yet
- MTC 121Document7 pagesMTC 121Rica AlhambraNo ratings yet
- DrawingDocument22 pagesDrawingCHRISTIAN PAUL ERANo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument43 pagesEngineering DrawingAnonymous QBOs17HT0No ratings yet
- GeometryDocument10 pagesGeometryapi-276852671No ratings yet
- QR Lec 10Document12 pagesQR Lec 10zi782004No ratings yet
- QR Lec 10Document12 pagesQR Lec 10fahmidaismaelNo ratings yet
- Maths Jss1 3rd Term MainDocument3 pagesMaths Jss1 3rd Term MainJiveNo ratings yet
- Class 5Document9 pagesClass 5amrithakhubaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Mom 1iDocument32 pagesChapter 2.2 Mom 1iKarell Faye BatulanNo ratings yet
- geom17Document2 pagesgeom17KrustyNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Explorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4From EverandExplorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4No ratings yet
Presentation On Shapes
Presentation On Shapes
Uploaded by
harshangpatel1740 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesThis presentation summarizes the key properties of several basic shapes:
Ovals have a continuous curved shape without straight sides or sharp corners. Right triangles have one 90-degree angle and the hypotenuse is the longest side. Diamonds have polished facets that reflect light and four sides of equal length. Pentagons have five sides and five interior angles that sum to 540 degrees. Cylinders have two congruent circular bases connected by a curved lateral surface, with no vertices or edges.
Original Description:
Original Title
Presentation on Shapes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis presentation summarizes the key properties of several basic shapes:
Ovals have a continuous curved shape without straight sides or sharp corners. Right triangles have one 90-degree angle and the hypotenuse is the longest side. Diamonds have polished facets that reflect light and four sides of equal length. Pentagons have five sides and five interior angles that sum to 540 degrees. Cylinders have two congruent circular bases connected by a curved lateral surface, with no vertices or edges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesPresentation On Shapes
Presentation On Shapes
Uploaded by
harshangpatel174This presentation summarizes the key properties of several basic shapes:
Ovals have a continuous curved shape without straight sides or sharp corners. Right triangles have one 90-degree angle and the hypotenuse is the longest side. Diamonds have polished facets that reflect light and four sides of equal length. Pentagons have five sides and five interior angles that sum to 540 degrees. Cylinders have two congruent circular bases connected by a curved lateral surface, with no vertices or edges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Presentation on shapes
Made by:- Aakansha Chauhan
Oval shape
• Closed Curve: It's a continuous, unbroken
loop without any points where the curve
intersects itself.
• No Straight Sides: Ovals consist solely of
smooth, curved lines with no straight
segments.
• No Vertices: They lack sharp corners or points
like those found in triangles or squares.
• Flat Face: Most ovals have one curved face
that doesn't fold back on itself.
Right Triangle
• Shape general rule:- • Calculations:-
1. One Right Angle: One of the 1. Area = (base * height) / 2
three interior angles always 2. Perimeter = sum of all sides
measures exactly 90 degrees.
2. Hypotenuse: The side opposite
the right angle is called the
hypotenuse and is always the
longest side.
Diamond shape
• General Rule:- • Calculation:-
1.Facets: All diamonds have 1. Area = ½ × d1 × d2.
facets, polished surfaces that help
reflect light and create brilliance and 2. Perimeter = 4 × a
fire. The number and arrangement of
facets vary according to the shape and
desired optical effects.
2.Proportions: Each shape has ideal
proportions for symmetry and light
performance. Deviating from these
proportions can negatively impact
brilliance and beauty.
Pentagon shape
• General rule:- • Calculations:-
1. Five sides: This is the defining 1. Area = (5 * s² * sqrt(5 + 2 *
characteristic of any pentagon. sqrt(5)) ) / 4
2. Five interior angles: The sum 2. Perimeter = 5*a
of these angles is always 540
degrees, regardless of the
pentagon's type.
3. Diagonals: A pentagon can
have 5 diagonals joining non-
consecutive vertices.
Cylinder shape
• General rule:- • Calculations:-
1. Two circular bases: Both bases are parallel
and congruent (same size and shape). 1. Area = π * r²
2. One curved lateral surface: This surface 2. Perimeter = 2 * π * r
connects the two bases and is formed by
rolling a rectangle.
3. No vertices or edges: Unlike shapes like
cubes, cylinders have no sharp corners or
points.
4. Height: Distance between the centers of
the two bases.
5. Axis: Line segment passing through the
centers of both bases.
THANK YOU
You might also like
- WK 14Document20 pagesWK 14mariusreeNo ratings yet
- Properties of 2D 3D ShapesDocument24 pagesProperties of 2D 3D ShapesKumud Baliyan100% (1)
- Group 3: Ericha Febriyani Margareta Syahla Khairunnisa M.Faris Ramzi Asad Syamsul.ADocument21 pagesGroup 3: Ericha Febriyani Margareta Syahla Khairunnisa M.Faris Ramzi Asad Syamsul.ABagas AriqNo ratings yet
- 50-Important-Math-Concepts-1 by DaaDocument9 pages50-Important-Math-Concepts-1 by Daadaanish muftiNo ratings yet
- WK 11 12 Geometric Designs and 2dDocument61 pagesWK 11 12 Geometric Designs and 2dHoneybunch beforeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Geo. Const. Part IIIDocument20 pagesLecture 9 Geo. Const. Part IIIIriama RobertNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Geo. Const. Part IIIDocument20 pagesLecture 9 Geo. Const. Part IIIIriama RobertNo ratings yet
- 3D Shapes 151_152Document12 pages3D Shapes 151_152Nitya M VNo ratings yet
- Geometry Power PointDocument70 pagesGeometry Power PointDavid Hernandez100% (1)
- ADVGEOM Lecture5 Nov20Document26 pagesADVGEOM Lecture5 Nov20Ellaine LimpangogNo ratings yet
- UNIT:-2: Introduction To Lines and Geometric ShapesDocument23 pagesUNIT:-2: Introduction To Lines and Geometric ShapesBikash ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity No:01: Computer Aided Engineering DesignDocument11 pagesLab Activity No:01: Computer Aided Engineering DesignArshad AliNo ratings yet
- CAD Solids Surfaces Keletondaafav THDocument8 pagesCAD Solids Surfaces Keletondaafav THyash pradhanNo ratings yet
- 4 Geometrical ConstructionDocument23 pages4 Geometrical ConstructionTAE. J.SNo ratings yet
- Solid FiguresDocument22 pagesSolid FiguresSir Roby James DazaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4, Conics ConstructionsDocument31 pagesLecture - 4, Conics ConstructionsAmit GhadeNo ratings yet
- Geometry ReviewDocument3 pagesGeometry ReviewJose Luis PiñaNo ratings yet
- ShapesDocument11 pagesShapesanissafeniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 MATH13Document52 pagesLesson 1 MATH13Randel Boris de Ocampo100% (4)
- 3D Shape Properties Presentation in Colourful Fun Style - 20240513 - 194645 - 0000Document36 pages3D Shape Properties Presentation in Colourful Fun Style - 20240513 - 194645 - 0000ajmanaloto3016No ratings yet
- Basic Geometric Construction-TermsDocument21 pagesBasic Geometric Construction-TermsCarinaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Geometrical Shapes OsamaDocument17 pagesProperties of Geometrical Shapes OsamaIsam Al HassanNo ratings yet
- PL AN E SH AP ES: By: Adekeye Bisola Busayomi Oyinloye Eni KelechiDocument18 pagesPL AN E SH AP ES: By: Adekeye Bisola Busayomi Oyinloye Eni KelechiAbNo ratings yet
- CSEL 301 Lecture 2Document55 pagesCSEL 301 Lecture 2ianpatrickmesiasNo ratings yet
- Quads and PolysDocument71 pagesQuads and PolysKinsley David AdaigbeNo ratings yet
- WK Folder Cover PageDocument6 pagesWK Folder Cover PageAryan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 3Document24 pagesMathematics Form 3Amal Sufiah82% (33)
- PDF Document 35Document20 pagesPDF Document 35Adams BakerNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Mathematics 7Document2 pagesReviewer in Mathematics 7Khristian RuedaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Geometry II: Jan 15/ 2022 Muhammed ADocument41 pagesDescriptive Geometry II: Jan 15/ 2022 Muhammed AHULE ADDIS ENTERTAINMENTNo ratings yet
- Akshara ChhabraDocument8 pagesAkshara Chhabrameenuchhabra487No ratings yet
- Circular FunctionsDocument49 pagesCircular FunctionsJames Vhon ReyesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry-01 ENITV12D ELEP06Document50 pagesTrigonometry-01 ENITV12D ELEP06Frederick ExibiaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Core Math Fifth Edition NotesDocument92 pagesIGCSE Core Math Fifth Edition NotesShepherd HomeschoolNo ratings yet
- TLE GRADE 10 Performing Mensuration and CalculationDocument35 pagesTLE GRADE 10 Performing Mensuration and CalculationLeoben Galima50% (2)
- Grade 3 Geometry NotesDocument5 pagesGrade 3 Geometry NotesSimna BijuNo ratings yet
- Las Tech Drafting 3Q WK1Document17 pagesLas Tech Drafting 3Q WK1Clemenda TuscanoNo ratings yet
- Solid Geometry Lesson 1Document40 pagesSolid Geometry Lesson 1KEN XINGNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Solid Mensuration Part 2Document41 pagesModule 2 Solid Mensuration Part 2Shaena VillaluzNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Ext Mathematics (0580) FlashcardsDocument45 pagesIGCSE Ext Mathematics (0580) FlashcardsSamson YauNo ratings yet
- Numbers: Prepared By: Z.K. TeeDocument39 pagesNumbers: Prepared By: Z.K. TeeteezkangNo ratings yet
- 2D and 3D ShapesDocument3 pages2D and 3D ShapesvirusNo ratings yet
- Circles Review For Test 1 1Document4 pagesCircles Review For Test 1 1api-256105506No ratings yet
- MTC 121Document7 pagesMTC 121Rica AlhambraNo ratings yet
- DrawingDocument22 pagesDrawingCHRISTIAN PAUL ERANo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument43 pagesEngineering DrawingAnonymous QBOs17HT0No ratings yet
- GeometryDocument10 pagesGeometryapi-276852671No ratings yet
- QR Lec 10Document12 pagesQR Lec 10zi782004No ratings yet
- QR Lec 10Document12 pagesQR Lec 10fahmidaismaelNo ratings yet
- Maths Jss1 3rd Term MainDocument3 pagesMaths Jss1 3rd Term MainJiveNo ratings yet
- Class 5Document9 pagesClass 5amrithakhubaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Mom 1iDocument32 pagesChapter 2.2 Mom 1iKarell Faye BatulanNo ratings yet
- geom17Document2 pagesgeom17KrustyNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Explorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4From EverandExplorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4No ratings yet