Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Falls Assessment Cheat Sheet
Falls Assessment Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Rebecca Teng Siew YanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Falls Assessment Cheat Sheet
Falls Assessment Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Rebecca Teng Siew YanCopyright:
Available Formats
Big BMW COE
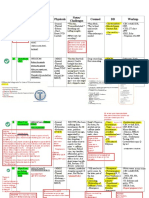
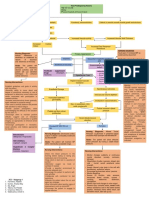
Mnemonic Details History Taking Physical Examination Investigations Tools Management
Big Balance • Giddiness Falls a/w low light settings Visual acuity (Snellens chart), HbA1c, Vit B12, Folate, KIV VDRL 6-minute walk test, 5x sit to stand test EYE/ENT review
• Vestibular dysfunction Giddiness Cataracts, Visual fields (Glaucoma vs MRI Brain contrasted/stroke Timed Up and Go Test, xqFunctional reach PT: Balance training eg Taichi, elastic band
• Cerebellar dysfunction AMD) protocol, MRI IAM assessment Vestibular PT
• Visual impairment Otoscopy Retinal photography Berg Balance Scale, Balance Evaluation Systems Test Low vision OT
• Proprioceptive/sensory loss (Peripheral neuropathy) HINTS test, Dix-Hallpike, Rhomberg’s Audiogram (BESTest) Mobility aid prescription
• Postural instability: PD and Parkinson plus syndromes test Performance-Oriented Mobility Assessment KIV Antidepressants (fear of falling) –Trial of low dose
esp PSP) Full neuro + PD + Gait exam Short Physical Performance Battery Escitalopram 2.5mg ON x 2-6 weeks, stop when better
• Cervical myelopathy Foot exam (injuries, ulcers, Falls Efficacy Scale – International (Fear of falling) –
• Fear of falling deformities) Validated for Chinese + Malay, Cut off 14 or more
B BP • Postural Hypotension Falls a/w postural changes, Postural BP assessment + BP FBC, RP Postural BP management:
• Hypovolemia including BGIT post meal measurement 1h after meal TFT, 8am cortisol, short synacthen • Non pharm: Hydration (2 glasses before getting out
• Dysautonomia (DM, PD, MSA, GBS) Pre syncopal symptoms of Fluid status test of bed), TED stockings/abdo binders, recovery
• Endocrine (Adrenal insuff, hypothyroid) lightheadedness, clamminess, Pallor ECG, Holter, TTE maneuvers, lying upright to sleep
• Situational dizziness, chest discomfort, CVM exam: Murmur, irregular pulse, Anemia panel • Pharm:Midodrine/Fludrocort
• Post-prandial, Post-micturition palpitations pulses parvus et tardus Implantable loop recorders Post micturition: Sit down to pee
• Carotid sinus hypersensitivity (when Endocrine screen Abdo exam: Succussion splash, DRE CTPA Post prandial: Low carb diet, small meals, lie down after
hanging clothes, shaving, neck massage) Full neuro + PD + Gait exam Electrophysiological tests meals, adjust BP meds
• Exertional -> LV outlet obstruction (eg AS) Tilt table test Heart failure management (AHA/ACC/HFSA 2022 GDMT)
• Acute Hypotension Ambulatory BP monitoring KIV CVM/GAS mx for acute life-threatening causes
• AMI, PE, Arrhythmias, Valve rupture,
Myxoma
• BGIT
M Medication • Sedatives, Antipsychotics Medication history BP monitoring with Drug levels if indicated e.g. digoxin, AGS Beers Criteria (2023) Med recon: SIRE (Symptoms, Indications, Risks, EOL)
• Less so: Antihypertensives Alcohol/Intoxicant history antihypertensives withheld valproate (over/underdosing) STOPP-START, STOPP- Frail, STOPP Fall Avoid sedatives if possible (non-pharm mx of insomnia,
• Medications with anticholinergic side effects CAGE questionnaire Medication Appropriateness Index alternative analgesia)
• Polypharmacy AEC, ACB Alcohol cessation counselling
• Alcohol/illicit drug use Potentially Inappropriate Medications
W Weakness • Acute: Stroke, Seizure Onset and progression of Full neuro + PD + Gait exam CT Brain/MRI Brain w MRC scale Acute stroke management
• Subacute: Infection (abscess/meningo-encephalitis), weakness Carotid bruit + pulse + CVM exam contrast/stroke protocol Mini nutritional assessment Optimise seizure control
GBS, MS flare, MG flare Video of seizure if present Spinal: structural deformity eg XR spine KIV MRI spine EWGSOP/ AWGS Sarcopenia definition and severity Rehabilitation: acute vs subacute vs
• Chronic: Associated numbness/ cortical kyphoscoliosis, step deformity, NCS/EMG assessment outpatient/community (Focused on resistance exercises)
• Degenerative spinal disease signs tenderness DEXA/CT limbs for muscle mass Mobility aid prescription
• Peripheral neuropathy Back pain/radicular pain Calf circumference Nutrition: Supplements if needed, High protein intake
• Sarcopenia Nutritional history Hand grip strength (1.5g/kg/day)
• Foot drop Physical activity at baseline KIV POD review
C Cognition • Poor safety awareness Cognitive history Full neuro + PD +Gait exam CT Brain/ MRI Brain dementia MMSE/MoCA Sleep, exercise, diet, cognitive stimulating activities
• Poor understanding of physical limitations Presence of carer supervision protocol GDS Cognitive enhancers, antidepressants
• Depression and carer stress Neuropsychiatric Assessment FAB Caregiver education and training
O Others • Pain CVM, Respi, Abdo, Skin, ENT exam Capillary blood glucose Analgesia
• Bone: Fracture, Foot deformities (Key points: Palpable bladder, sacral Inflammatory markers Optimise DM control
• Joint: Arthritis wounds/ other pressure injuries, RP, Ca/Mg/PO Replace electrolytes
• Muscle: Myositis, contusion atrophic vaginitis) XR of relevant joints Treat underlying infection
• Hypoglycemia, electrolyte imbalances PVRU CK (if muscle tenderness/ rapid Urge/stress incont +/- BPH mx, KIV URO
• Infections GALS examination muscular weakness with wasting) PT review
• Urinary problems: Urgency, incontinence from BPH/GUSM POD review
E Environment • Lighting Social history including home Saving Inventory-Revised (SIR) Preferred footwear: Thin mid sole (to feel the ground),
• Flooring environment and footwear Hoarding Rating Scale (HRS) good heel grip, closed cap
• Steps/stairs Screen for hoarding OT Home assessment
• Footwear tendencies Home care services, Hoarding clearance
PSY for hoarding disorder mx
HDB EASE programme
Bone health screening: Complications:
Vit D, RP (for CrCl) CT Brain if head injury
BMD XR of affected joint/bones
FRAX score CK for long lie, RP for rhabdo
Dental clearance
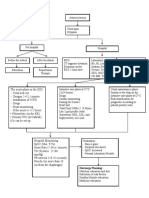
Definitions History Taking
• Fall: A sudden, unintentional change in position causing an individual to land at • Purpose
a lower level (either on an object or on the floor) other than as a consequence • Elicit contributing factors: Precipitating vs Predisposing, Intrinsic vs Extrinsic
of overwhelming external force • Assess for complications
• Recurrent falls: 2 or more falls in a year • SPLATT Mnemonic
• HPB definition: 2 falls in 6 months • Symptoms experienced
• Long lie: Inability to get up from a fallen position, usually on the floor or • Should include pre-fall, during fall, and post fall
ground, for more than an hour. • Previous falls, and resultant complications including fear of falling
• Location of the fall
• Activity at the time of the fall (eg relationship to posture, cough, micturition, meals,
Examination medications)
• Time of day the fall occurred
• Trauma associated with the fall: Physical and psychological
• PMHx
• Neurological: Stroke disease, Parkinson's disease, Seizures, Cognitive impairment
• Heart disease: Heart failure, arrhythmias, valvular diseases, outflow obstruction
• Osteoporosis
• Endocrinological: Adrenal insufficiency, TCM use, hypothyroidism
• Depression
• Premorbid
• Function: Ambulatory status, need for walking aids, activities of daily living (bADLs,
iADLs)
• Social history: Family support, presence of identified carer, home environment,
smoking/alcohol
• Premorbid personality: Values independence, resistant of aids
Complications
• Fractures
• Head injury: Cephalohaematoma, SDH, SAH
• Skin lacerations, facial injuries
• Complications of long lie e.g. rhabdomyolysis
• Fear of falling
You might also like
- Surgery PDFDocument163 pagesSurgery PDFjoedeegan_100% (1)
- Shelf IM Video SlidesDocument69 pagesShelf IM Video SlidesRuth SanmooganNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- 12 NeoDocument1 page12 Neogocelij948No ratings yet
- Society For Obesity and Bariatric Anaesthesia: OS-MRS Calculator Tools - Farmacologiaclinica.infoDocument1 pageSociety For Obesity and Bariatric Anaesthesia: OS-MRS Calculator Tools - Farmacologiaclinica.infoHizami Norddin100% (2)
- Pre and Post Op ManagementDocument2 pagesPre and Post Op Managementprincesszahra6498No ratings yet
- Concept Map (SMA)Document2 pagesConcept Map (SMA)Houda HayekNo ratings yet
- PGY Duty Round整合版pdf 2020 v2Document134 pagesPGY Duty Round整合版pdf 2020 v2Jacky 許智凱No ratings yet
- 26) Approach To Pediatric ArrhythmiasDocument44 pages26) Approach To Pediatric ArrhythmiasJude AlyousefNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Neuropathy DMDocument49 pagesAutonomic Neuropathy DMJaskaran SinghNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument10 pagesSepsisJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version PDFDocument20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version PDFSurgery CSC1No ratings yet
- Turkey Recipe 2Document43 pagesTurkey Recipe 2Laith الكويس Omar ANo ratings yet
- Things To Look For During Morning RoundDocument3 pagesThings To Look For During Morning RoundTom YipNo ratings yet
- OSCE ChecklistDocument3 pagesOSCE Checklistbumblebee9323No ratings yet
- Delirium: Lindsay Trantum ACNP-BC VUMC Neuroscience ICUDocument22 pagesDelirium: Lindsay Trantum ACNP-BC VUMC Neuroscience ICUarunNo ratings yet
- Nursing Holistic + Care Plan + Meds + LabsDocument20 pagesNursing Holistic + Care Plan + Meds + LabsMags100% (2)
- Chest Pain System - DisorderDocument1 pageChest Pain System - DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- CC History Mnemonics Physicals Notes/ Challenges Counsel DD WorkupDocument41 pagesCC History Mnemonics Physicals Notes/ Challenges Counsel DD WorkupAhmed AbdelgelilNo ratings yet
- Gubra DIO Mouse Data FlyerDocument2 pagesGubra DIO Mouse Data FlyerGabrielaMirelaAlexeNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument7 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromePuskesmas Pinang JayaNo ratings yet
- Takikardia Acls SayaDocument16 pagesTakikardia Acls Sayaolga adhityaNo ratings yet
- How To Diagnose VertigoDocument41 pagesHow To Diagnose VertigoHasbi Ash ShiddiqieNo ratings yet
- Inpatient Pocket Card SetDocument9 pagesInpatient Pocket Card SetJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Newborn AssessmentDocument3 pagesNewborn AssessmentMimie CaliNo ratings yet
- 12-Adult Post Resuscitation Care Algorithm 2021Document1 page12-Adult Post Resuscitation Care Algorithm 2021khaledNo ratings yet
- AAN Neuromuscular and SCI TalkDocument36 pagesAAN Neuromuscular and SCI TalkEvelina ȘabanovNo ratings yet
- Chapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney DisordersDocument40 pagesChapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney Disordersjericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- Femur FractureDocument19 pagesFemur FractureMadx VNo ratings yet
- Inpatient Pocket Card SetDocument10 pagesInpatient Pocket Card SetMuhammad Ahmad bin makruf syammakuNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Hipertensi BPJS 20518Document109 pagesPresentasi Hipertensi BPJS 20518Dody TamaraNo ratings yet
- Overnight Events Interdisciplinary Notes Vital Signs I/O and WeightsDocument8 pagesOvernight Events Interdisciplinary Notes Vital Signs I/O and WeightsGood MaishaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MafDocument3 pagesDrug Study MafSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Abbreviations Terms and The Do Not Use List Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesNursing Abbreviations Terms and The Do Not Use List Cheat SheetrachelleNo ratings yet
- Acute Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (Aub) : AlgorithmDocument8 pagesAcute Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (Aub) : AlgorithmPhiyaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Yes NoDocument1 pagePediatric Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Yes NoRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesAtherosclerosis Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- ElectrodiagnosticsDocument4 pagesElectrodiagnosticsAndy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cardiology 2023 FinalDocument208 pagesCardiology 2023 FinalBelinda ELISHA100% (1)
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2Document20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version-2zoozsuhai2No ratings yet
- Medications: B (Breakfast), L (Lunch), D (Dinner) Lab Values/Diagnostic Test ResultsDocument3 pagesMedications: B (Breakfast), L (Lunch), D (Dinner) Lab Values/Diagnostic Test Resultsapi-547510423No ratings yet
- Bites PecartDocument48 pagesBites PecartFaizan KhanNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pagers Vent WeaningDocument1 pageICU One Pagers Vent WeaningHossameldin GamalNo ratings yet
- Multi-System AlterationsDocument33 pagesMulti-System Alterationsficap51232No ratings yet
- Senior Project ProductDocument7 pagesSenior Project Productapi-732018343No ratings yet
- Cronic Heart FailureDocument37 pagesCronic Heart FailureHanif RobbanizerNo ratings yet
- MIB 3 AnnotatedDocument78 pagesMIB 3 AnnotatedShekhar NandalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Generalized Edema and Protein Losing-NephropathiesDocument39 pagesPathophysiology of Generalized Edema and Protein Losing-NephropathiesVARITPOL CHAROENYINGPAISALNo ratings yet
- J1 (Program Rehabilitasi Post Rupture)Document1 pageJ1 (Program Rehabilitasi Post Rupture)Okky SaidNo ratings yet
- Curs 2-Managementul Pacientului Cu TCCDocument46 pagesCurs 2-Managementul Pacientului Cu TCCMarina ApostolNo ratings yet
- Pcol-Tables V2Document25 pagesPcol-Tables V2Donna Kate QuintoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocument10 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- L8 9 Cardiac Fluids Disorders in ChildrenDocument17 pagesL8 9 Cardiac Fluids Disorders in ChildrenRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- 3C3 Subgroup1 M11 PT1Document1 page3C3 Subgroup1 M11 PT1ENKELI VALDECANTOSNo ratings yet
- ENT 讀書報告Chapter74 C2 吳丞皓Document20 pagesENT 讀書報告Chapter74 C2 吳丞皓陳永杰No ratings yet
- AMI CP EnglishDocument1 pageAMI CP EnglishNovema AsharNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Angel Nieto PengsonNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Technician Skills - Mastered - KimtierneyDocument1 pageVeterinary Technician Skills - Mastered - Kimtierneyapi-207993624No ratings yet
- Drug Study CRF PDFDocument21 pagesDrug Study CRF PDFshiplusNo ratings yet
- Labs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeFrom EverandLabs & Imaging for Primary Eye Care: Optometry In Full ScopeNo ratings yet
- Ward Rounds - Geriatric SyndromeDocument19 pagesWard Rounds - Geriatric SyndromeRebecca Teng Siew YanNo ratings yet
- NDT Oct 2023 FinalDocument175 pagesNDT Oct 2023 FinalRebecca Teng Siew YanNo ratings yet
- PACEs ECPS Template 2017Document15 pagesPACEs ECPS Template 2017Rebecca Teng Siew YanNo ratings yet
- ABIM SyllabusDocument28 pagesABIM SyllabusRebecca Teng Siew YanNo ratings yet
- #150 - People vs. BalubarDocument1 page#150 - People vs. BalubarGenerousdeGuzmanNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument287 pagesNeuro Anatomynikithagb.notesNo ratings yet
- Edited By: Tenth EditionDocument4 pagesEdited By: Tenth EditionOctavian BrinzaNo ratings yet
- Jacked Vegan Planche Wrist ConditioningDocument17 pagesJacked Vegan Planche Wrist Conditioningaltclips0No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Installation of Exhaust FansDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment - Installation of Exhaust FansehteshamNo ratings yet
- Fisher - Paykel DD60SCW9 DishDrawer User ManualDocument56 pagesFisher - Paykel DD60SCW9 DishDrawer User ManualTho MasNo ratings yet
- Dawson 2002 - Upper-Extremity Problems Caused by Playing InstrumentsDocument6 pagesDawson 2002 - Upper-Extremity Problems Caused by Playing InstrumentsDiana MatiasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemVinDiesel Balag-eyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Clients With Life Threatening Conditions / Medical EmergenciesDocument23 pagesAssessment Clients With Life Threatening Conditions / Medical EmergenciesJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Revision of SpacesDocument6 pagesRevision of SpacesFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Civil Appeal 133 of 2005Document12 pagesCivil Appeal 133 of 2005vusNo ratings yet
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Runner's Knee) - Symptoms & CausesDocument9 pagesPatellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Runner's Knee) - Symptoms & CausesAndy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- حلول جراحه ماينر 11Document14 pagesحلول جراحه ماينر 11Yousif AlaaNo ratings yet
- Cold Case File: Black Dahlia: Presented by Esperanza DazaDocument11 pagesCold Case File: Black Dahlia: Presented by Esperanza DazaEsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Controversias en El Manejo de Las Fracturas Abiertas (2014)Document7 pagesControversias en El Manejo de Las Fracturas Abiertas (2014)J. Adrian NogueraNo ratings yet
- Free Mobility AssessmentDocument12 pagesFree Mobility AssessmentCapuNo ratings yet
- Trauma in ChildrenDocument11 pagesTrauma in ChildrenEdwardRazvanNo ratings yet
- HEAD AND SPINAL INJURY - DR RetnoDocument22 pagesHEAD AND SPINAL INJURY - DR RetnoJackNo ratings yet
- Joseph Pilates - 34 Classic Mat Exercises - LongversionDocument14 pagesJoseph Pilates - 34 Classic Mat Exercises - LongversionMarta GomesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology TerminologyDocument31 pagesClinical Pathology Terminologyirenezach88No ratings yet
- Abused and Neglected ChildrenDocument76 pagesAbused and Neglected ChildrenSam Raven Andres100% (1)
- Anatomy I: by Dr. Ziyad M. Al Zeer Orthopedic Surgeon MD - PHDDocument36 pagesAnatomy I: by Dr. Ziyad M. Al Zeer Orthopedic Surgeon MD - PHDMOHAMMAD ALSWEITYNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12 Answer Sheet AbellanaornopiaDocument5 pagesExercise 12 Answer Sheet AbellanaornopiaMarlie TobiseNo ratings yet
- Emergency Neurological Life Support - Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument13 pagesEmergency Neurological Life Support - Traumatic Brain Injurybrian leonardo gonzalez gomezNo ratings yet
- Pokemon - Pearl Version - Manual - NDS PDFDocument32 pagesPokemon - Pearl Version - Manual - NDS PDFpika chuNo ratings yet
- Athletic RecoveryDocument7 pagesAthletic Recoverylala2000_roNo ratings yet
- Prehab RehabDocument277 pagesPrehab Rehabradarm2018555No ratings yet
- Assessment of The AbdomenDocument186 pagesAssessment of The AbdomenFaith madayag100% (1)
- Patient Positioning During SurgeryDocument30 pagesPatient Positioning During SurgeryKristine AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of The Breast T-HAZEM - CompressedDocument28 pagesSurgical Anatomy of The Breast T-HAZEM - CompressedmohamedhazemelfollNo ratings yet