Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 Introduction To Networking November 5, 2018
01 Introduction To Networking November 5, 2018
Uploaded by
JOEL P. RODRIGUEZ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views29 pagesThe document provides instructions for creating a UTP network cable with RJ45 connectors. It is a lesson from Casay National High School on computer system servicing. The 9 step process includes preparing the cable, stripping the jacket, arranging the wires according to the 568A or 568B standard, crimping the wires into RJ45 connectors, and repeating for the other end. Key terms defined include UTP cable, crosstalk, straight-through and crossover cables.
Original Description:
introduction to netwprking
Original Title
01 Introduction to Networking November 5, 2018
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides instructions for creating a UTP network cable with RJ45 connectors. It is a lesson from Casay National High School on computer system servicing. The 9 step process includes preparing the cable, stripping the jacket, arranging the wires according to the 568A or 568B standard, crimping the wires into RJ45 connectors, and repeating for the other end. Key terms defined include UTP cable, crosstalk, straight-through and crossover cables.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views29 pages01 Introduction To Networking November 5, 2018
01 Introduction To Networking November 5, 2018
Uploaded by
JOEL P. RODRIGUEZThe document provides instructions for creating a UTP network cable with RJ45 connectors. It is a lesson from Casay National High School on computer system servicing. The 9 step process includes preparing the cable, stripping the jacket, arranging the wires according to the 568A or 568B standard, crimping the wires into RJ45 connectors, and repeating for the other end. Key terms defined include UTP cable, crosstalk, straight-through and crossover cables.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 29
COMPUTER SYSTEM SERVICING NC 2
THIRD QUARTER LESSON 1
CASAY NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Computer System Servicing NC 2
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Warm up
NETWORK
WONTREK
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Computer System Servicing NC 2
Casay National High School
Warm up
RESERV
SERVER
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Warm up
EMMOD
MODEM
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Warm Up
ROUTERS
RETOURS
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Warm up
GATEWAY
AGETWAY
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Definition of Terms
1. Network- is two or more devices capable of communicating and sharing resources between them.
2. LAN- (Local Area Network) A group of devices sharing resources in a single area such as a room
or a building.
3. WAN (Wide Area Network) – Two or more LANs communicating, often across large distances.
The most famous WAN is the Internet
4. Server-Based Network – A basic type of LAN wherein users login to a controlling computer, called
a server and is more secure.
5. Peer-to-Peer Network – One of two basic types of LANs wherein each computer user acts as a
server.
6. Twisted-Pair Cable – Network cable of eight copper wires twisted into four pairs to prevent
crosstalk.
7. UTP (Unshielded Twisted-Pair) – Most common network cable that comes in different categories
for different uses.
8. STP (Shielded Twisted-Pair) – Same as UTP cable, but with extra foil to prevent outside noise
from interfering with data on the cable.
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Definition of Terms
9. Hub - is a small, simple, inexpensive device that joins multiple computers together. Many network
hubs available today support the Ethernet standard.
10. Ethernet switch - is a device that gathers the signals from devices that are connected to it, and
then regenerates a new copy of each signal3.
11. Bridge is a device filters data traffic at a network boundary. Bridges reduce the amount of traffic
on a LAN by dividing it into two segments.
12. Routers - are small physical devices that join multiple networks together.
13. Network gateway- is an internetworking system capable of joining together two networks that
use different base protocols. A network gateway can be implemented completely in software,
completely in hardware, or as a combination of both.
14. Modem - is a contraction of the terms modulator and demodulator. Modems perform a simple
function: They translate digital signals from a computer into analog signals that can travel across
conventional phone lines. The modem modulates the signal at the sending end and demodulates at
the receiving end
15. Network interface- is a device that connects a client computer, server, printer or
other component to your network. Most often, a network interface consists of a small electronic
circuit board that is inserted into a slot inside a computer or printer
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Server-Based Network
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Peer-Peer Network
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
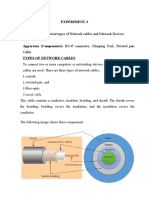
Network Cabling
Cable is normally used as a medium for transporting network data.
The most common types are twisted-pair and fiber-optic, although
coax is still used in some old networks.
• Twisted-Pair Cable – Network cable of eight copper wires twisted
into four pairs to prevent crosstalk.
-UTP (Unshielded Twisted-Pair) – Most common network cable that
comes in different categories for different uses. Categories 3 (voice-
grade), 4, and 5 (data). It is unshielded and more susceptible to
interference. –
-STP (Shielded Twisted-Pair) – Same as UTP cable, but with extra foil
to prevent outside noise from interfering with data onThird
theQuarter
cable. Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
A UTP cable (category 5) is one of the most popular LAN cables. This cable consists of 4
twisted pairs of metal wires (that means there are 8 wires in the cable). Adding RJ45
connectors at both ends of the UTP cable it becomes a LAN cable they usually use.
Preparation
You need a UTP Cable, Crimping Tool, RJ45, and Cutter
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 1
Unroll the required
length of network
cable and add a little
extra wire, just in case.
If a boot is to be fitted,
do so before stripping
away the sleeve and
ensure the boot faces
the correct way.
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 2
Carefully remove the outer
jacket of the cable. Be
careful when stripping the
jacket as to not nick or cut
the internal wiring. One
good way to do this is to
cut lengthwise with snips
or a knife along the side of
the cable, away from
yourself, about an inch
toward the open end.
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 3
Inspect the newly revealed
wires for any cuts or scrapes
that expose the copper wire
inside. If you have breached the
protective sheath of any wire,
you will need to cut the entire
segment of wires off and start
over at step one. Exposed
copper wire will lead to cross-
talk, poor performance or no
connectivity at all. It is
important that the jacket for all
network cables remains intact.
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 4
Untwist the pairs so they
will lay flat between your
fingers. The white piece of
thread can be cut off even
with the jacket and
disposed (see Warnings).
For easier handling, cut the
wires so that they are 3/4"
(19 mm) long from the
base of the jacket and even
in length.
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 5
Arrange the wires based on the
wiring specifications you are
following. There are two
methods set by the TIA, 568A
and 568B. Which one you use
will depend on what is being
connected. A straight-through
cable is used to connect two
different-layer devices (e.g. a
hub and a PC). Two like devices
normally require a cross-over
cable. The difference between
the two is that a straight-
through cable has both ends
wired Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 6
Press all the wires flat and parallel
between your thumb and forefinger.
Verify the colors have remained in the
correct order. Cut the top of the wires
even with one another so that they
are 1/2" (12.5 mm) long from the base
of the jacket, as the jacket needs to go
into the 8P8C connector by about
1/8", meaning that you only have a
1/2" of room for the individual cables.
Leaving more than 1/2" untwisted can
jeopardize connectivity and quality.
Ensure that the cut leaves the wires
even and clean; failure to do so may
cause the wire not to make contact
inside the jack and could lead to
wrongly guided cores inside the plug. Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 7
Keep the wires flat and in order as
you push them into the RJ-45 plug
with the flat surface of the plug on
top. The white/orange wire should be
on the left if you're looking down at
the jack. You can tell if all the wires
made it into the jack and maintain
their positions by looking head-on at
the plug. You should be able to see a
wire located in each hole, as seen at
the bottom right. You may have to use
a little effort to push the pairs firmly
into the plug. The cabling jacket
should also enter the rear of the jack
about 1/4" (6 mm) to help secure the
cable once the plug is crimped.
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 8
Place the wired plug into
the crimping tool. Give the
handle a firm squeeze. You
should hear a ratcheting
noise as you continue.
Once you have completed
the crimp, the handle will
reset to the open position.
To ensure all pins are set,
some prefer to double-
crimp by repeating this
step.
STEP 9
Repeat all of the above
steps with the other end
of the cable. The way you
wire the other end (568A
or 568B) will depend on
whether you're making a
straight-through, rollover,
or cross-over cable (see
Tips).
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
STEP 10
Test the cable to ensure that it will
function in the field. Mis-wired and
incomplete network cables could lead
to headaches down the road. In
addition, with power-over-Ethernet
(PoE) making its way into the
marketplace, crossed wire pairs could
lead to physical damage of computers
or phone system equipment, making it
even more crucial that the pairs are in
the correct order. A simple cable
tester can quickly verify that
information for you. Should you not
have a network cable tester on hand,
simply test connectivity pin to pin.
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
Evaluation
Worksheet no 3.1 ppt presentation
about the steps of making Ethernet
cables with Video Tutorials
Third Quarter Lesson 1
Casay National High School
You might also like
- The OdysseyDocument9 pagesThe OdysseyJacob IlaganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument87 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworkingkaushalvrindaNo ratings yet
- The Soul of An Octopus - Favorite QuotesDocument7 pagesThe Soul of An Octopus - Favorite QuotesTanya RodmanNo ratings yet
- Arthur Clifton GuytonDocument2 pagesArthur Clifton GuytonArlyn SanchezNo ratings yet
- Basic Network Setup DEMODocument23 pagesBasic Network Setup DEMOVenus BoacNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 CNDocument4 pagesLab 1 CNBishal BhandariNo ratings yet
- Server and Client: The Biggest WAN in The World Is The InternetDocument6 pagesServer and Client: The Biggest WAN in The World Is The Internetcesan lianaNo ratings yet
- NET102 Lab Experiment 1 Wiring A Twisted Pair Ethernet NetworkDocument12 pagesNET102 Lab Experiment 1 Wiring A Twisted Pair Ethernet NetworkGleruumarkuuNo ratings yet
- Video Lesson CSS10ccablesDocument28 pagesVideo Lesson CSS10ccablesOrange Chavez MañguneNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet In: Computer Systems ServicingDocument12 pagesLearning Activity Sheet In: Computer Systems ServicingCarvalds 0315No ratings yet
- lab_1Document6 pageslab_1niteshrajbanshi78No ratings yet
- Whlp-Css 10 Week 4 & 5 - q2Document9 pagesWhlp-Css 10 Week 4 & 5 - q2arlyn villanuevaNo ratings yet
- GROUP10 - Assignment 1.2 Practice Set 2 - Network Media - ADocument26 pagesGROUP10 - Assignment 1.2 Practice Set 2 - Network Media - AShyne HazyNo ratings yet
- Review Lesson 3rd QADocument75 pagesReview Lesson 3rd QABiancaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module5 G10 CSSDocument9 pagesQ3 Module5 G10 CSSRhea IsonNo ratings yet
- TLEC SS Grade10 Quarter3 Week2Document4 pagesTLEC SS Grade10 Quarter3 Week2Axel Nicerio RoveloNo ratings yet
- Network Cabling: Making Connections With Cat5Document33 pagesNetwork Cabling: Making Connections With Cat5kerya ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Css Slem Format s2q1 Week 5Document12 pagesCss Slem Format s2q1 Week 5John David Martizano FetalsanaNo ratings yet
- Practical 1: Aim: Study of Different Types of CablesDocument61 pagesPractical 1: Aim: Study of Different Types of CablesYogesh M ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Data Com Lab OneDocument9 pagesData Com Lab OneAyele MitkuNo ratings yet
- COT4 - Lesson Plan in TLE 10 Network CablingDocument3 pagesCOT4 - Lesson Plan in TLE 10 Network CablingMELAIDA CASTANAR GARIBAYNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Practical FileDocument34 pagesComputer Network Practical FileAnupriya JainNo ratings yet
- Cabling 150323050229 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument23 pagesCabling 150323050229 Conversion Gate01 PDFDidith GambaNo ratings yet
- Jaypee University of Engineering & Technology, Guna Deparment of Computer Science & EngineeringDocument4 pagesJaypee University of Engineering & Technology, Guna Deparment of Computer Science & Engineeringgauravsagar311No ratings yet
- CSS - 05-Week 5 - Module 5 - Networking CablingDocument7 pagesCSS - 05-Week 5 - Module 5 - Networking CablingMorelei FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document3 pagesLesson 10Felix BrimonNo ratings yet
- 1.2-7 LOCAL AREA NETWORKS (LANs) SYSTEMS AND CONFIGURATIONSDocument7 pages1.2-7 LOCAL AREA NETWORKS (LANs) SYSTEMS AND CONFIGURATIONSRJ VillamerNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708-21316348873 5815810248475238 4852308856062457441 n.pdfTLE-CSS Grade-9 QRT-2 ModuLE-2-forDocument21 pagesvt59.2708-21316348873 5815810248475238 4852308856062457441 n.pdfTLE-CSS Grade-9 QRT-2 ModuLE-2-forkaye14davidNo ratings yet
- Networking CablesDocument4 pagesNetworking CablesDavid CardenasNo ratings yet
- Network Lab PDFDocument83 pagesNetwork Lab PDFSuhaibb Masalha100% (1)
- Experiment Number: 01 Title:: Study of Existing LANDocument15 pagesExperiment Number: 01 Title:: Study of Existing LANAaizah WaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Lab Lab Manual: Prepared By: Eng. Sireen HiaryDocument80 pagesComputer Network Lab Lab Manual: Prepared By: Eng. Sireen HiaryHamdallah Anwar KhasawnehNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Lab Lab Manual: Prepared By: Eng. Sireen HiaryDocument80 pagesComputer Network Lab Lab Manual: Prepared By: Eng. Sireen HiaryHamdallah Anwar KhasawnehNo ratings yet
- Chs 10 - Lesson 2Document43 pagesChs 10 - Lesson 2Gem Lam SenNo ratings yet
- Network Management-Module MidtermDocument9 pagesNetwork Management-Module MidtermAlvinNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab Report 1tanveer Ahmed (12323)Document7 pagesComputer Networks Lab Report 1tanveer Ahmed (12323)Muhammad Taimoor aslamNo ratings yet
- CCN Lab 2Document11 pagesCCN Lab 2sameen khanNo ratings yet
- Making Network Cables and Connectors ObjectiveDocument7 pagesMaking Network Cables and Connectors ObjectiveTayyaba HussainNo ratings yet
- Ex. No.3Document11 pagesEx. No.3MAYANKNo ratings yet
- Lab2 Network CablesDocument8 pagesLab2 Network Cablesابو عبدالرحمن الحارثيNo ratings yet
- CN FileDocument38 pagesCN Fileyipop57406No ratings yet
- ECE 5102 Data Communications: Patch Cable ConstructionDocument9 pagesECE 5102 Data Communications: Patch Cable ConstructionEdwin Quinlat DevizaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: Name: Pradeep Gupta Div: TE - A Roll No: 112Document9 pagesExperiment No.1: Name: Pradeep Gupta Div: TE - A Roll No: 112Pradeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 DechavezDocument5 pagesChapter6 DechavezCarlos John ManaloNo ratings yet
- Stem 13 Midterm NotesDocument12 pagesStem 13 Midterm NotesitsgracebilangdalNo ratings yet
- Soham ChakrabortyDocument6 pagesSoham ChakrabortySoham ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Gradex Lancabling 160626042418 PDFDocument28 pagesGradex Lancabling 160626042418 PDFMish Lim0% (1)
- Information Sheet 3.1Document10 pagesInformation Sheet 3.1Danica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Script in ICT 11 On Setting Up Computer Networks LO1Document8 pagesScript in ICT 11 On Setting Up Computer Networks LO1julesgajesNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson PlanAlai Siarez50% (2)
- My Lesson - PlanDocument4 pagesMy Lesson - PlanJenelyn RusianaNo ratings yet
- CN FileDocument26 pagesCN FileShaktiNo ratings yet
- Network Devices & CablesDocument8 pagesNetwork Devices & Cablesapi-26530736100% (1)
- CSS4-Q1 Module 1Document9 pagesCSS4-Q1 Module 1Lielanie NavarroNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 CCNDocument4 pagesLab 1 CCNAbdul AhadNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Practical File K. Manisha 2018UIT2523 It Sec-1Document35 pagesComputer Networks: Practical File K. Manisha 2018UIT2523 It Sec-1manishaNo ratings yet
- Engineering College Tuwa: Name: Subject: Branch: Computer Engineering Enrollment NoDocument39 pagesEngineering College Tuwa: Name: Subject: Branch: Computer Engineering Enrollment NoREEYANo ratings yet
- Lab No 2 PDFDocument5 pagesLab No 2 PDFaftab_sweet3024No ratings yet
- Whlp-Css 10 Week 3 - q2Document6 pagesWhlp-Css 10 Week 3 - q2arlyn villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Cabling: What Is Network Cabling?Document7 pagesChapter 4: Cabling: What Is Network Cabling?saboorNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument34 pagesComputer NetworksLalru LalruNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Co 1 202320231213 - 06504323Document4 pagesCo 1 202320231213 - 06504323JOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- White and Red Modern Professional Marketing Optimization PresentationDocument1 pageWhite and Red Modern Professional Marketing Optimization PresentationJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Chess TshirtDocument1 pageChess TshirtJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Credentials Checking ChecklistDocument1 pageCredentials Checking ChecklistJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- CHESS GROUND RULES 2 2023 2024 For Provincial Meet FinalDocument4 pagesCHESS GROUND RULES 2 2023 2024 For Provincial Meet FinalJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Group 5 ActivityDocument1 pageGroup 5 ActivityJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- SHS GRADE 12 Andromeda QRA 2Document27 pagesSHS GRADE 12 Andromeda QRA 2JOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Winninf Coach Champion CertificateDocument1 pageWinninf Coach Champion CertificateJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Casay National High SchoolDocument22 pagesCasay National High SchoolJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Computer Case Labelled DiagramDocument1 pageParts of A Computer Case Labelled DiagramJOEL P. RODRIGUEZ100% (1)
- Khalyce Excuse LetterDocument1 pageKhalyce Excuse LetterJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Introductory ActivityDocument4 pages4.1 Introductory ActivityJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of The Computer System Labelled DiagramDocument1 pageBasic Parts of The Computer System Labelled DiagramJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- NSBI Data Gathering Forms SY 2022 2023 - v3.0Document14 pagesNSBI Data Gathering Forms SY 2022 2023 - v3.0JOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- List of Registered Chess PlayersDocument2 pagesList of Registered Chess PlayersJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Design Hearing FormatDocument2 pagesDesign Hearing FormatJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Cebu Provincial Meet 2023 Entry by Chess Secondary GirlsDocument1 pageCebu Provincial Meet 2023 Entry by Chess Secondary GirlsJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Municipal Meet 2023Document1 pageMunicipal Meet 2023JOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- End User Licensure AgreementDocument8 pagesEnd User Licensure AgreementJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1.2Document1 pagePractical Research 1.2JOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Q3 Tos TQDocument12 pagesQ3 Tos TQJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- COVERDocument1 pageCOVERJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Chess Standing PartialDocument1 pageChess Standing PartialJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Goodle Drive Tutorial # 2Document4 pagesGoodle Drive Tutorial # 2JOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- 3 Ideal Guidelines Using Social MediaDocument1 page3 Ideal Guidelines Using Social MediaJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Anthony Mercado Anthony Mercado Anthony Mercado Anthony MercadoDocument1 pageAnthony Mercado Anthony Mercado Anthony Mercado Anthony MercadoJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Tutorial # 5 How To Create A Gmail AccountDocument1 pageTutorial # 5 How To Create A Gmail AccountJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document2 pagesTutorial 6JOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- SLHT Grade 7 CSS Week 4Document7 pagesSLHT Grade 7 CSS Week 4JOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- SLHT Grade 7 CSS Week 5 Without Answer KeyDocument6 pagesSLHT Grade 7 CSS Week 5 Without Answer KeyJOEL P. RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Case Digest Extinguishment of ObligationsDocument25 pagesCase Digest Extinguishment of ObligationsLyneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- Not in His Image (15th Anniversary Edition) - Preface and IntroDocument17 pagesNot in His Image (15th Anniversary Edition) - Preface and IntroChelsea Green PublishingNo ratings yet
- Study Session8Document1 pageStudy Session8MOSESNo ratings yet
- 2020 Msce Practical Questions TargetDocument30 pages2020 Msce Practical Questions TargetspinyblessingNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals NotesDocument3 pagesMetals and Non Metals NotesVUDATHU SHASHIK MEHERNo ratings yet
- PYF Biennial Conference Vawi 19-NaDocument1 pagePYF Biennial Conference Vawi 19-NaMizoram Presbyterian Church SynodNo ratings yet
- TG0012 enDocument24 pagesTG0012 enDhexter VillaNo ratings yet
- Asfwa Report2008 PDFDocument4 pagesAsfwa Report2008 PDFMesfin DerbewNo ratings yet
- 11.02.2022-PHC ResultsDocument6 pages11.02.2022-PHC ResultsNILAY TEJANo ratings yet
- How To Cook Pork AdoboDocument3 pagesHow To Cook Pork AdoboJennyRoseVelascoNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: Enclosed Type Switching Power Supply (Families: G3, NE, LRS, SE, PFC, HSP, SPV, USP, RST, G5, MSP)Document2 pagesInstallation Manual: Enclosed Type Switching Power Supply (Families: G3, NE, LRS, SE, PFC, HSP, SPV, USP, RST, G5, MSP)Aicky IkrackNo ratings yet
- Linkages and NetworkDocument28 pagesLinkages and NetworkJoltzen GuarticoNo ratings yet
- EoI DocumentDocument45 pagesEoI Documentudi969No ratings yet
- SBC Code 301Document360 pagesSBC Code 301mennnamohsen81No ratings yet
- SG Unit5progresscheckfrq 5e815f88c4fb70Document9 pagesSG Unit5progresscheckfrq 5e815f88c4fb70api-485795043No ratings yet
- Metaverse Report - Thought Leadership 1Document17 pagesMetaverse Report - Thought Leadership 1Tejas KNo ratings yet
- Emcee Script For Kindergarten Recognition (English) - 085301Document3 pagesEmcee Script For Kindergarten Recognition (English) - 085301Felinda ConopioNo ratings yet
- AUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea ODocument3 pagesAUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea OdfsdNo ratings yet
- Mge 4Document17 pagesMge 4RUPAV TIWARINo ratings yet
- Common AddictionsDocument13 pagesCommon AddictionsMaría Cecilia CarattoliNo ratings yet
- Desmand Whitson Resume 1PDFDocument2 pagesDesmand Whitson Resume 1PDFRed RaptureNo ratings yet
- Talent Acquisition Request Form: EducationDocument1 pageTalent Acquisition Request Form: EducationdasfortNo ratings yet
- Design and Synthesis of Zinc (Ii) Complexes With Schiff Base Derived From 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid and Heterocyclic AldehydesDocument6 pagesDesign and Synthesis of Zinc (Ii) Complexes With Schiff Base Derived From 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid and Heterocyclic AldehydesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Schedule CDocument273 pagesSchedule CAzi PaybarahNo ratings yet
- Logging Best Practices Guide PDFDocument12 pagesLogging Best Practices Guide PDFbnanduriNo ratings yet
- Power Point Skripsi UmarDocument12 pagesPower Point Skripsi UmarMuchamad Umar Chatab NasserieNo ratings yet
- Annual Return For A Company Limited by GuaranteeDocument4 pagesAnnual Return For A Company Limited by GuaranteeAtisang Tonny SethNo ratings yet