Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modal Verbs of Deduction and Speculation Picture Description Exercises 123770
Modal Verbs of Deduction and Speculation Picture Description Exercises 123770
Uploaded by
Maryna Bakalo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesModal verbs can be used to express:
1) Certainty or possibility through deduction and speculation. Modals like must, may, might, could express different levels of certainty or possibility.
2) Actions that are ongoing or continuous through the modal continuous structure of modal verb + be + present participle.
3) Past actions through the modal perfect structure of modal verb + have + past participle. This expresses speculation or certainty about past events.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentModal verbs can be used to express:
1) Certainty or possibility through deduction and speculation. Modals like must, may, might, could express different levels of certainty or possibility.
2) Actions that are ongoing or continuous through the modal continuous structure of modal verb + be + present participle.
3) Past actions through the modal perfect structure of modal verb + have + past participle. This expresses speculation or certainty about past events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesModal Verbs of Deduction and Speculation Picture Description Exercises 123770
Modal Verbs of Deduction and Speculation Picture Description Exercises 123770
Uploaded by
Maryna BakaloModal verbs can be used to express:
1) Certainty or possibility through deduction and speculation. Modals like must, may, might, could express different levels of certainty or possibility.
2) Actions that are ongoing or continuous through the modal continuous structure of modal verb + be + present participle.
3) Past actions through the modal perfect structure of modal verb + have + past participle. This expresses speculation or certainty about past events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Modal verbs
Modals of Deduction and Speculation
Miss Anna's Marvellous Grammar Presentation
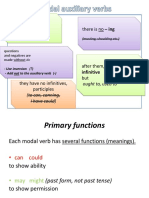
Modal verbs:
•Common characteristics:
• They only have one form
• They are followed by an infinitive without to
(bare-infinitive)
• They form questions using inversion (change
their place with the subject of the sentence)
• They form the negative taking “not”
• They indicate modality:
• ability or capacity – can / could
• permission – may / might
• request – will (as “Will you give me a
pen?”)
• suggestions or advice – should, ought
to
• order or obligation – must
Miss Anna's Marvellous Grammar Presentation
Modal verbs to express certainty,
uncertainty, deduction and speculation:
• Must
– certainty: we are 100% sure that something is true:
• He must speak French. He used to live in France.
– deduction: we ask for confirmation
• You must be tired after such a long trip.
• May, might, could
– possibily: we think that something is posible now or in the future.
• He might be at home. He may help you.
– speculation about future events:
• You may win the game if you practice a lot.
• Can´t
– certainty: we are 100% sure that something is NOT true:
• He can´t be at home. I just saw him at the supermarket.
– impossibility: we know that something is not true because it´s impossible:
• It can´t be a ghost. Ghosts do no exists.
Miss Anna's Marvellous Grammar Presentation
Modal Continuous
Structure: modal verb + be + present participle (-ing) of the verb
Must / May /
She must work hard. She must be working hard. Might / Could /
Can´t
They might come home. They might be coming home.
be
She can´t speak seriously. She can´t be speaking seriously.
This structure can be used with all modals! Sleeping / eating
/ reading
Make sentences what you can deduce
or speculate about this picture.
Miss Anna's Marvellous Grammar Presentation
Past modals or modal perfect
Structure: modal verb + have + past participle (third form) of the verb
She must love you. She must have loved you.
I´m sure she loves you. I´m sure she loved you.
They might win the game. They might have won the game.
It´s possibile that they will win. I don´t know the results – but it´s possible.
She can´t solve the puzzle. She can´t have solved the puzzle.
It will be impossible for her. She must have had some help – it was
impossible for someone with her capacity.
This structure can be used with all modals!
Miss Anna's Marvellous Grammar Presentation
Describe what you think
might have happened.
Miss Anna's Marvellous Grammar Presentation
You might also like
- Math 87 Mathematics 8 - 7 Textbook An Incremental Development Stephen Hake John SaxonDocument696 pagesMath 87 Mathematics 8 - 7 Textbook An Incremental Development Stephen Hake John Saxonnitikanehi100% (8)
- Modal Verbs PDFDocument3 pagesModal Verbs PDFSara Albaladejo Albaladejo100% (1)
- Filter Separator SizingDocument3 pagesFilter Separator SizingChem.EnggNo ratings yet
- 4 NBT 4Document9 pages4 NBT 4api-29514981950% (2)
- Gyro Error by Sun & Amplitude RDRDocument2 pagesGyro Error by Sun & Amplitude RDRCan T. ErbayNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs of Deduction and SpeculationDocument7 pagesModal Verbs of Deduction and SpeculationAinhoa MariaNo ratings yet
- Seminar 4Document8 pagesSeminar 4Teodora AvramNo ratings yet
- Problems Students Have With ModalsDocument17 pagesProblems Students Have With ModalsLUIS IVAN LLUMIQUINGA GUAMANNo ratings yet
- L2 - Modals LamDocument35 pagesL2 - Modals LamQui RainNo ratings yet
- VERBS (2) Modal VerbsDocument8 pagesVERBS (2) Modal VerbsKaterine Lorena BAQUERO AMAYANo ratings yet
- Modal and Semimodal VerbsDocument11 pagesModal and Semimodal Verbsniko_blue55No ratings yet
- Activity Modal VerbsDocument9 pagesActivity Modal VerbsAlex OspinaNo ratings yet
- Inglés - MODAL VERBS WORKSHEET - 2nd GradeDocument3 pagesInglés - MODAL VERBS WORKSHEET - 2nd GradeValentina Vasquez salamancaNo ratings yet
- Modals BacDocument6 pagesModals BacTeacher MonicaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Present PastDocument4 pagesModal Verbs: Present PastmariaNo ratings yet
- Activity Modal VerbsDocument8 pagesActivity Modal VerbsJenniifer EliianaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 ModalsDocument5 pagesLesson 9 ModalsAngelica Jusay IbusNo ratings yet
- Idioma Tecnico 4Document4 pagesIdioma Tecnico 4Ainsley FergusonNo ratings yet
- Bhs - Inggris KLMPK 4Document13 pagesBhs - Inggris KLMPK 4Fitriah Nur JannahNo ratings yet
- 3 Perfect ModalsDocument4 pages3 Perfect ModalsGeraldjose EspinozañNo ratings yet
- 8 TheHappinessApp 1bach EnglishDocument4 pages8 TheHappinessApp 1bach EnglishJose.rt06 from CHI StudentNo ratings yet
- Gestión de Formación Profesional Integral Procedimiento Desarrollo Curricular Guía de AprendizajeDocument8 pagesGestión de Formación Profesional Integral Procedimiento Desarrollo Curricular Guía de AprendizajeWilson OspinaNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument8 pagesModal VerbsMily MaciasNo ratings yet
- Ought Rachel To Be Here So Early? Ought They To Live There?Document12 pagesOught Rachel To Be Here So Early? Ought They To Live There?Roy ToyNo ratings yet
- 2020 English 6Document34 pages2020 English 6carlossuarez2014No ratings yet
- English Modal VerbsDocument37 pagesEnglish Modal VerbsDeniz FerahNo ratings yet
- Modals and Semi-ModalsDocument12 pagesModals and Semi-ModalsGEORGIANA VIOLETA CRISTACHENo ratings yet
- Can or Could For AbilityDocument46 pagesCan or Could For AbilitySarah McLeanNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Structure & USEDocument26 pagesModal Verbs: Structure & USEsandra razoNo ratings yet
- Modals TheoryDocument5 pagesModals TheorykiiinNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument44 pagesModal VerbsHicynty CostamNo ratings yet
- ModalsDocument27 pagesModalsThess Flores CabreraNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument20 pagesTensesMiftahul JannahNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument5 pagesModal VerbsItzel VenturaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs Uses: Lexical Modal Verbs: To Be Able To, To Have To, To Be Allowed To, To Be Permitted ToDocument9 pagesModal Verbs Uses: Lexical Modal Verbs: To Be Able To, To Have To, To Be Allowed To, To Be Permitted ToDiana GonzaliNo ratings yet
- English 9 Activity Sheet Q 1 ModalsDocument6 pagesEnglish 9 Activity Sheet Q 1 ModalsLiza TradioNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument16 pagesModal VerbsBlueberry LatteNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs USE Formation (Affirmative, Interrogative, Negative)Document4 pagesModal Verbs USE Formation (Affirmative, Interrogative, Negative)MartaAndreiaSousaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs For DeductionDocument14 pagesModal Verbs For DeductionRicardo VázquezNo ratings yet
- Clase 3Document16 pagesClase 3mariaNo ratings yet
- 2022.01.07 - Basic GrammarDocument5 pages2022.01.07 - Basic Grammarkaryda christinaNo ratings yet
- MODALSDocument4 pagesMODALSMitzi Daniele BatistaNo ratings yet
- Page 17, C-Grammar: May, Might, and Be Able ToDocument9 pagesPage 17, C-Grammar: May, Might, and Be Able ToBethany ShawNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs USE Formation (Affirmative, Interrogative, Negative)Document3 pagesModal Verbs USE Formation (Affirmative, Interrogative, Negative)yuki melaniNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs USE Formation (Affirmative, Interrogative, Negative)Document4 pagesModal Verbs USE Formation (Affirmative, Interrogative, Negative)BIBIANA BELTRANNo ratings yet
- English Department English III 17th February: Vicerrectoria Regional OrinoquiaDocument30 pagesEnglish Department English III 17th February: Vicerrectoria Regional OrinoquiaSantiago HernándezNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs First PartDocument18 pagesModal Verbs First PartJosé MiraldaNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument11 pagesModal VerbsAna LugliNo ratings yet
- Examen Ingles Avanzado 5Document6 pagesExamen Ingles Avanzado 5AreNo ratings yet
- Finding Out About Grammar - 2 PDFDocument74 pagesFinding Out About Grammar - 2 PDFLorena GalvisNo ratings yet
- Modals and Semi-ModalsDocument11 pagesModals and Semi-Modalsmarinela100% (1)
- ModalDocument10 pagesModalhoang quangNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs of Speculation and DeductionDocument5 pagesModal Verbs of Speculation and DeductionДияна ДимитроваNo ratings yet
- Ought To ShouldDocument5 pagesOught To ShouldTriggered KampungNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs and Their Substitutes 1Document9 pagesModal Verbs and Their Substitutes 1Roy ToyNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument5 pagesModal VerbsCarlos Paz ChanganaNo ratings yet
- Modality: Introduction: English Grammar TodayDocument13 pagesModality: Introduction: English Grammar TodaySilvia Alejandra SuarezNo ratings yet
- Modals Form StructuresDocument62 pagesModals Form StructuresKarla Iliana RomeroNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Full Bai Giang-SvDocument68 pagesUnit 1 - Full Bai Giang-SvThư Nguyễn Ngọc MinhNo ratings yet
- All ModalsDocument5 pagesAll ModalsstacyNo ratings yet
- Guessing Game: Job DescriptionsDocument39 pagesGuessing Game: Job DescriptionsGIRLNo ratings yet
- 6 Auxiliary VerbsDocument7 pages6 Auxiliary Verbsxzha809No ratings yet
- Modals 2Document24 pagesModals 2ade ayuningsih utamiNo ratings yet
- Computer Languages PDFDocument2 pagesComputer Languages PDFSelvaraj Villy50% (2)
- 09 Flight Techniques 747 400 v10Document18 pages09 Flight Techniques 747 400 v10flightstudent100% (1)
- Bosch Gear Reducers Re 76108Document30 pagesBosch Gear Reducers Re 76108K.K GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Syntactic Classification of Verbs Intransitive Verbs of Incomplete PredicationDocument4 pagesLesson 14 Syntactic Classification of Verbs Intransitive Verbs of Incomplete PredicationLaydy HanccoNo ratings yet
- Chuka Fred Complete Project EditedDocument117 pagesChuka Fred Complete Project EditedSunday LazarusNo ratings yet
- Decoding Raw Frames - Generic - Libre Space CommunityDocument7 pagesDecoding Raw Frames - Generic - Libre Space CommunityGeneration GenerationNo ratings yet
- Tollefson Pattern Drafting 1 AssignmentsDocument10 pagesTollefson Pattern Drafting 1 Assignmentstauqeer_141No ratings yet
- PL23XX DriverInstallerv 4.0.0 ReleaseNoteDocument4 pagesPL23XX DriverInstallerv 4.0.0 ReleaseNoteAmir VahidiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Activity SheetDocument3 pages3rd Quarter Activity SheetMa. Teresa BajaoNo ratings yet
- Caccs I: Advanced Computing & Communication SystemsDocument4 pagesCaccs I: Advanced Computing & Communication SystemsMohan Kumar MNo ratings yet
- PR Linear Encoders For Numerically Controlled Machine Tools ID571470 enDocument25 pagesPR Linear Encoders For Numerically Controlled Machine Tools ID571470 ensundhar mohanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International As A Level Mathematics Probability Statistics 2 Practice Book Cambridge International Z LibDocument85 pagesCambridge International As A Level Mathematics Probability Statistics 2 Practice Book Cambridge International Z LibSukanya DattaNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Structures Unit-3Document15 pagesPrestressed Concrete Structures Unit-3chinnaNo ratings yet
- Yella Terra Roller Rocker Geometry GuideDocument1 pageYella Terra Roller Rocker Geometry GuideDave BournNo ratings yet
- 2020 DES Combined Extractive Dearomatization Desulfurization and Denitrogenation Oil FuelsDocument29 pages2020 DES Combined Extractive Dearomatization Desulfurization and Denitrogenation Oil FuelsBaraa AlmahameedNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design by Wayne C Teng - Single Portrait Page VersionDocument542 pagesFoundation Design by Wayne C Teng - Single Portrait Page Versionzakaria200811060100% (5)
- Geschlecht Der Substantive Theorie: Noun Gender Der Mann Die Frau Das KindDocument4 pagesGeschlecht Der Substantive Theorie: Noun Gender Der Mann Die Frau Das Kindl1624242No ratings yet
- Ricoh Aficio MPC2500 Trouble Error CodesDocument23 pagesRicoh Aficio MPC2500 Trouble Error CodesnafeesNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Implementation of National Curriculum For Secondary School Biology and Academic Achievement in Taraba State, NigeriaDocument8 pagesEvaluation of The Implementation of National Curriculum For Secondary School Biology and Academic Achievement in Taraba State, NigeriaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Sig Wave HeightDocument2 pagesSig Wave HeightPaul OnionsNo ratings yet
- Noise HTMLDocument14 pagesNoise HTMLIndika TisseraNo ratings yet
- Sysmex SEED Platelet Detection and The Importance of A Reliable CountDocument7 pagesSysmex SEED Platelet Detection and The Importance of A Reliable CountMuhammad Khoirut TNo ratings yet
- DIP Lecture 9Document34 pagesDIP Lecture 9Sukanti PalNo ratings yet
- 5020-250-S12-P04-0027 - TOFD-20113 - Rev.1Document53 pages5020-250-S12-P04-0027 - TOFD-20113 - Rev.1ahmed elezabyNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Groundwater Recharge in The Lake Haramaya WatershedDocument67 pagesEstimation of Groundwater Recharge in The Lake Haramaya Watershedshamsu100% (1)
- L4 RocksDocument33 pagesL4 RocksFARHA NAAZNo ratings yet