Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsEREF Pinheiro
EREF Pinheiro
Uploaded by
RASHEED YUSUFThe document discusses renewable energy in Europe. It describes EREF, an organization of renewable energy producers from 10 EU countries. EREF's goals are to actively support growth of renewable energy use in Europe to meet targets. It discusses EU climate change programs and policies to promote renewable energy, including national targets in the RES Directive. Charts show current renewable energy use is still below targets, and policies have had varying levels of success promoting different technologies like wind, hydro, and biomass. Barriers include inconsistent support mechanisms and administrative hurdles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Solved Problems Axial DeformationDocument6 pagesSolved Problems Axial DeformationChristopher Largado67% (3)
- Carbon Market Year in Review 2022Document30 pagesCarbon Market Year in Review 2022ThomasNo ratings yet
- Pooie GF 2019 1Document7 pagesPooie GF 2019 1nedp18No ratings yet
- Energy Union Factsheet Spain enDocument26 pagesEnergy Union Factsheet Spain entrovatore48No ratings yet
- Energy Union and Climate Action: Driving Europe's Transition To A Low-Carbon EconomyDocument3 pagesEnergy Union and Climate Action: Driving Europe's Transition To A Low-Carbon EconomyLuís CastroNo ratings yet
- Road EnergiamappingDocument20 pagesRoad EnergiamappingJTHNo ratings yet
- A New Directive On Energy Efficiency: - Challenges Addressed & Solutions ProposedDocument16 pagesA New Directive On Energy Efficiency: - Challenges Addressed & Solutions ProposedIgor NeagaNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy ContributionDocument104 pagesWind Energy ContributionTown Obio EteteNo ratings yet
- RagwitzDocument28 pagesRagwitzmaria_alexandraNo ratings yet
- EEA - 2017 - RESinEU2017 - TH AL 17 024 EN NDocument74 pagesEEA - 2017 - RESinEU2017 - TH AL 17 024 EN NbuhmoohNo ratings yet
- Wpiea2022220 Print PDFDocument22 pagesWpiea2022220 Print PDFMikeNo ratings yet
- Key World Energy Statistics 2020Document81 pagesKey World Energy Statistics 2020Amin DehghaniNo ratings yet
- EEA 2014 Country Profile CroatiaDocument5 pagesEEA 2014 Country Profile CroatiaSaša MartinovićNo ratings yet
- MLT Out Look 2023 EditionDocument46 pagesMLT Out Look 2023 EditionhambaliNo ratings yet
- Carbon Tax: What Environmental and Economic Impact in The French Manufacturing Sector?Document21 pagesCarbon Tax: What Environmental and Economic Impact in The French Manufacturing Sector?Josua Desmonda SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Energy Economic Developments in EuropaDocument160 pagesEnergy Economic Developments in EuropaAna AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Renewables Se enDocument3 pagesRenewables Se enAmir FauwazNo ratings yet
- 4 - 610 - ms16 - Sander - 0Document16 pages4 - 610 - ms16 - Sander - 0Karim IsmailNo ratings yet
- European Union 2020 Energy Policy ReviewDocument310 pagesEuropean Union 2020 Energy Policy ReviewFenhia RivasNo ratings yet
- 2050 EU Energy StrategyDocument12 pages2050 EU Energy StrategyHector Parra MolinaNo ratings yet
- A One Gigawatt Green PlantDocument45 pagesA One Gigawatt Green PlantIsabelMaríaGarcíaNo ratings yet
- SimcockDocument13 pagesSimcockJusuwa JusuwaNo ratings yet
- Smart GridDocument90 pagesSmart Gridjose girotNo ratings yet
- Florou PresentationDocument19 pagesFlorou Presentationayeletariku092No ratings yet
- 5 Industry IndicatorsDocument47 pages5 Industry IndicatorsBülent BulutNo ratings yet
- Renewable Factsheet PDFDocument34 pagesRenewable Factsheet PDFdep25No ratings yet
- GT2005-68014 Axial Compressor MaintenanceDocument48 pagesGT2005-68014 Axial Compressor MaintenanceRaden MasNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Prospects for Central and South-Eastern Europe Energy Connectivity (CESEC)From EverandRenewable Energy Prospects for Central and South-Eastern Europe Energy Connectivity (CESEC)No ratings yet
- Waste To Hydrogen Webinar Presentation Post Event FINALDocument35 pagesWaste To Hydrogen Webinar Presentation Post Event FINALImed ChoukiNo ratings yet
- Renewables 2021 - Analysis and Forecast To 2026 - IeaDocument175 pagesRenewables 2021 - Analysis and Forecast To 2026 - IeaMohammad ShofieNo ratings yet
- PV Status Report 2011Document130 pagesPV Status Report 2011AndreiCeagleiNo ratings yet
- Ace TrendsDocument4 pagesAce TrendsZerohedge JanitorNo ratings yet
- Net Oil Zero PDFDocument33 pagesNet Oil Zero PDFRizal FauziNo ratings yet
- H1 Report 2021 US FinalDocument48 pagesH1 Report 2021 US FinalnemoNo ratings yet
- 09 - EP - Gestione Dei RischiDocument26 pages09 - EP - Gestione Dei RischiantonioNo ratings yet
- Training Webinar #8Document174 pagesTraining Webinar #8Vale PiscoyaNo ratings yet
- EDF Study For Download On EPDocument25 pagesEDF Study For Download On EPlitteraeinvitaeNo ratings yet
- Global Gas Market and Its ChallengesDocument15 pagesGlobal Gas Market and Its ChallengesjosealvaroNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage Needs in SpainDocument56 pagesEnergy Storage Needs in SpainAhmed WestministerNo ratings yet
- France 2021Document211 pagesFrance 2021Madiha KhanNo ratings yet
- EbstbDocument12 pagesEbstbapi-292520116No ratings yet
- Transformers ScopeDocument60 pagesTransformers ScopeSathiya KumarNo ratings yet
- CE - Delft - 200247 - UCO - As - Biofuel - Feedstock - in - EU - FINAL - v5 - 0Document65 pagesCE - Delft - 200247 - UCO - As - Biofuel - Feedstock - in - EU - FINAL - v5 - 0LelosPinelos123No ratings yet
- 2018 02 21 - RRIF - Explanatory - Document - Public ConsultationDocument17 pages2018 02 21 - RRIF - Explanatory - Document - Public ConsultationLuiza GhitaNo ratings yet
- EU Climate Policy FailureDocument90 pagesEU Climate Policy FailureCasimir de BonnevalNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Project Analysis Using Retscreen SoftwareDocument28 pagesPhotovoltaic Project Analysis Using Retscreen SoftwarehazimeNo ratings yet
- Korea 2020 Energy Policy ReviewDocument204 pagesKorea 2020 Energy Policy ReviewSunderjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Global Hydrogen Review 2021Document224 pagesGlobal Hydrogen Review 2021Rajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Excerpt From: Electricity InformationDocument7 pagesExcerpt From: Electricity InformationCarlosNo ratings yet
- Biofuels Directive - Implications For IrelandDocument40 pagesBiofuels Directive - Implications For IrelandBharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Prezentare WAGES 2007Document36 pagesPrezentare WAGES 2007Ionut DraganNo ratings yet
- IEA G20 Hydrogen Report: AssumptionsDocument14 pagesIEA G20 Hydrogen Report: Assumptionspragya89No ratings yet
- IEA-Clean Energy MFGDocument36 pagesIEA-Clean Energy MFGManokaran KNo ratings yet
- Technology Roadmap Wind EnergyDocument63 pagesTechnology Roadmap Wind EnergyEdgard Leonardo Castaneda GarciaNo ratings yet
- PHEV White Paper Sept2020 0Document57 pagesPHEV White Paper Sept2020 0Simon AlvarezNo ratings yet
- PV The Cheapest Electricity Source Almost EverywheDocument2 pagesPV The Cheapest Electricity Source Almost Everywhem.armadaNo ratings yet
- Energy Policies of IEA Countries United Kingdom 2019 ReviewDocument220 pagesEnergy Policies of IEA Countries United Kingdom 2019 ReviewPranay MahawarNo ratings yet
- $$$ACER H2 Paper - VFinal - CleanDocument61 pages$$$ACER H2 Paper - VFinal - CleanMahjoub AmriNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Policy Progress Index: Sector End-Use Performance Level MetricDocument3 pagesEfficiency Policy Progress Index: Sector End-Use Performance Level MetricGerardo AguirreNo ratings yet
- EU-China Energy Magazine 2021 Summer Issue: 2021, #2From EverandEU-China Energy Magazine 2021 Summer Issue: 2021, #2No ratings yet
- EU-China Energy Magazine 2020 Christmas Double Issue: 2020, #4From EverandEU-China Energy Magazine 2020 Christmas Double Issue: 2020, #4No ratings yet
- Wipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2Document65 pagesWipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- 66 Commonwealth Parliamentary Conference Accra, Ghana 30 September - 6 October 2023 Hon 'Ble Chairperson and Distinguished DelegatesDocument19 pages66 Commonwealth Parliamentary Conference Accra, Ghana 30 September - 6 October 2023 Hon 'Ble Chairperson and Distinguished DelegatesRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- External ContentDocument542 pagesExternal ContentRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grade Math Worksheets FractionsDocument2 pages3rd Grade Math Worksheets FractionsRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Anhydrous Ammonia:: Managing The RisksDocument16 pagesAnhydrous Ammonia:: Managing The RisksRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Operator Installation & Instruction Manual: Auto-Purger Plus, App Non-Condensible Gas (Air) & Water Purger For AmmoniaDocument20 pagesOperator Installation & Instruction Manual: Auto-Purger Plus, App Non-Condensible Gas (Air) & Water Purger For AmmoniaRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Selection of Condensers and Chillers: Systems & Components (India) Pvt. LTDDocument34 pagesSelection of Condensers and Chillers: Systems & Components (India) Pvt. LTDRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Float Switch: Product Bulletin 61-12 ADocument12 pagesRefrigerant Float Switch: Product Bulletin 61-12 ARASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Ab 538 Integrity Management Requirements For Mechanical Refrigeration Systems Containing AmmoniaDocument18 pagesAb 538 Integrity Management Requirements For Mechanical Refrigeration Systems Containing AmmoniaRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Ab 275 General Requirements For Mechanical Refrigeration SystemsDocument7 pagesAb 275 General Requirements For Mechanical Refrigeration SystemsRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Gas Detection Bump Testing Ammonia (NH) Sensors: TF: +1.877.940.8741 - T: +1.604.940.8741 - F: +1.604.940.8745Document2 pagesGas Detection Bump Testing Ammonia (NH) Sensors: TF: +1.877.940.8741 - T: +1.604.940.8741 - F: +1.604.940.8745RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Piping Registration - Pressure Vessel EngineeringDocument6 pagesPiping Registration - Pressure Vessel EngineeringRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- IB18-004 (Reporting Unsafe Conditions, Accidents and Fires)Document5 pagesIB18-004 (Reporting Unsafe Conditions, Accidents and Fires)RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Defrosting Industrial Refrigeration Evaporators Reindl Jekel August 2009Document13 pagesDefrosting Industrial Refrigeration Evaporators Reindl Jekel August 2009RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Manitoba RequirementDocument15 pagesManitoba RequirementRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Document Title: Installation Instruction: Pacific Co., LTDDocument13 pagesDocument Title: Installation Instruction: Pacific Co., LTDRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Management of Change (Hazard Screening)Document2 pagesManagement of Change (Hazard Screening)RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- O F R M e P P P A C T, I e L U e W, TX G, LaDocument253 pagesO F R M e P P P A C T, I e L U e W, TX G, LaRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Novel Technologies For Wear Protection and Monitoring in DredgingDocument23 pagesNovel Technologies For Wear Protection and Monitoring in DredgingRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Location Written By: Approved By: Date Created Last RevisionDocument2 pagesLocation Written By: Approved By: Date Created Last RevisionRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Coagulation/Flocculation Process For Produced Water TreatmentDocument6 pagesCoagulation/Flocculation Process For Produced Water TreatmentRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Ifage Bachelor 1 General English Chapter 1 Basics 1 2023 2024Document22 pagesIfage Bachelor 1 General English Chapter 1 Basics 1 2023 2024coordinateurlpa coordinateurlpaNo ratings yet
- 510 - Sps Vega vs. SSS, 20 Sept 2010Document2 pages510 - Sps Vega vs. SSS, 20 Sept 2010anaNo ratings yet
- The Mavericks MNIT 1st Year 2022-23Document3 pagesThe Mavericks MNIT 1st Year 2022-23Shantul KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Enhanced Flooded Battery For Smart Mild Hybrid Power TrainsDocument29 pagesRecent Advances in Enhanced Flooded Battery For Smart Mild Hybrid Power Trains3 GamerNo ratings yet
- Prolin Termassist Operating Guide: Pax Computer Technology Shenzhen Co.,LtdDocument29 pagesProlin Termassist Operating Guide: Pax Computer Technology Shenzhen Co.,Ltdhenry diazNo ratings yet
- Httpsrvce Edu Insitesdefaultfiles7 20EC20III202620IV PDFDocument51 pagesHttpsrvce Edu Insitesdefaultfiles7 20EC20III202620IV PDFNANDITA SNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument16 pagesCash Flow Statementrajesh337masssNo ratings yet
- Master Key To Imagination GuideDocument60 pagesMaster Key To Imagination GuideAnonymous ecgjAAD98% (45)
- Module 5 Introduction To Stochastic Processes Eec605Document89 pagesModule 5 Introduction To Stochastic Processes Eec605daniel developerNo ratings yet
- Examining The Relationship BetDocument24 pagesExamining The Relationship BetMariaNo ratings yet
- NDT Basics GuideDocument29 pagesNDT Basics Guideravindra_jivaniNo ratings yet
- Bestiary of The Rosewood Highlands Draft 1-4-08!07!19Document82 pagesBestiary of The Rosewood Highlands Draft 1-4-08!07!19Stefano Chiaramonti100% (2)
- Mixers FinalDocument44 pagesMixers FinalDharmender KumarNo ratings yet
- Simbol A4Document3 pagesSimbol A4ibnu100% (1)
- Diploma Thesis Digital DiplomacyDocument56 pagesDiploma Thesis Digital DiplomacyShagadamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Steam and Gas TurbinesDocument64 pagesChapter 5 Steam and Gas TurbinesKeba Del Ray100% (2)
- 18 - Thalamus and Limbic System (Edited)Document22 pages18 - Thalamus and Limbic System (Edited)Fotocopias LulisNo ratings yet
- Gospel Steel TrussDocument18 pagesGospel Steel TrussJoseph Cloyd L. LamberteNo ratings yet
- John Hopkins IbdDocument38 pagesJohn Hopkins IbdNovita ApramadhaNo ratings yet
- Amusement Events and Recreation Award Ma000080 Pay GuideDocument17 pagesAmusement Events and Recreation Award Ma000080 Pay GuideCol. O'NeillNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Titanium Sponge Formation in The Kroll Reduction ReactorDocument11 pagesMechanism of Titanium Sponge Formation in The Kroll Reduction ReactorSrinivasulu PuduNo ratings yet
- D Internet Myiemorgmy Intranet Assets Doc Alldoc Document 15367 JURUTERA OCTOBER 2018Document52 pagesD Internet Myiemorgmy Intranet Assets Doc Alldoc Document 15367 JURUTERA OCTOBER 2018Leanne ChewNo ratings yet
- Contoh Financial PlanDocument4 pagesContoh Financial PlanJonathan ChandhikaNo ratings yet
- Siun Sote Objection Related To Social Welfare and Health Care Services or Treatment FormDocument2 pagesSiun Sote Objection Related To Social Welfare and Health Care Services or Treatment FormShahnaz NawazNo ratings yet
- Electric Rebar Cutter Owener'S Manual: Item# 999321Document10 pagesElectric Rebar Cutter Owener'S Manual: Item# 999321Mahmoud AliNo ratings yet
- ACMV and Acoustic Comfort in BuildingsDocument13 pagesACMV and Acoustic Comfort in BuildingsTuan Suhaimi SallehNo ratings yet
- Coldharbour/Wrotham Road GravesendDocument28 pagesColdharbour/Wrotham Road GravesendWessex ArchaeologyNo ratings yet
- Salt Market StructureDocument8 pagesSalt Market StructureASBMailNo ratings yet
- M As1 Formative Task: Review Questions: Star Alliance Sky Team OneworldDocument4 pagesM As1 Formative Task: Review Questions: Star Alliance Sky Team OneworldSharlyne PimentelNo ratings yet
EREF Pinheiro
EREF Pinheiro
Uploaded by
RASHEED YUSUF0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views17 pagesThe document discusses renewable energy in Europe. It describes EREF, an organization of renewable energy producers from 10 EU countries. EREF's goals are to actively support growth of renewable energy use in Europe to meet targets. It discusses EU climate change programs and policies to promote renewable energy, including national targets in the RES Directive. Charts show current renewable energy use is still below targets, and policies have had varying levels of success promoting different technologies like wind, hydro, and biomass. Barriers include inconsistent support mechanisms and administrative hurdles.
Original Description:
Original Title
EREF-Pinheiro
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses renewable energy in Europe. It describes EREF, an organization of renewable energy producers from 10 EU countries. EREF's goals are to actively support growth of renewable energy use in Europe to meet targets. It discusses EU climate change programs and policies to promote renewable energy, including national targets in the RES Directive. Charts show current renewable energy use is still below targets, and policies have had varying levels of success promoting different technologies like wind, hydro, and biomass. Barriers include inconsistent support mechanisms and administrative hurdles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views17 pagesEREF Pinheiro
EREF Pinheiro
Uploaded by
RASHEED YUSUFThe document discusses renewable energy in Europe. It describes EREF, an organization of renewable energy producers from 10 EU countries. EREF's goals are to actively support growth of renewable energy use in Europe to meet targets. It discusses EU climate change programs and policies to promote renewable energy, including national targets in the RES Directive. Charts show current renewable energy use is still below targets, and policies have had varying levels of success promoting different technologies like wind, hydro, and biomass. Barriers include inconsistent support mechanisms and administrative hurdles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
Sustainable Energy for Europe
- INFORSE-Europe Seminar, Brussels -
André Vieira Pinheiro – Brüssel
November 2002
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
Introduction (I)
About EREF
A federation made up of national associations of renewable
energy producers, belonging to 10 different countries of the
European Union, that have decided to unite their powers by
creating a European network that defends and promotes ‚green‘
energy
EREF unites the powers of thousands of European companies,
who work in the field of energy production through the use of
renewable energy sources such as small hydro, wind, tidal,
wave, solar, geothermal and bioenergy
Associations coming from the sector of non-biological waste
generation are not included in EREF, and will not be invited to
join.
join
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
Introduction (II)
What has EREF observed?
That the emissions caused by carbon dioxide and other harmful
gaseous substances impose a great risk on the climate and on
the general welfare
Conventional energy resources are at risk of being exhausted
within a time period of only a few generations
Nuclear energy presents inherent risks as much in regards to
safety as to the unsolved problem of radioactive waste
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
•
The last couple of years renewable energy has experienced a
considerable boom within those countries of the European Union
that have implemented legal standards such as minimum pricing
schemes, purchase obligation and priority access to the grid
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
Introduction (III)
What are our aims?
Actively support the rapid and sustainable growth of the usage of
renewable energy in Europe, with the hope to at least meet the
fixed objective of the White Book of Renewable Energies
Promote the expansion of legal mechanisms that work in favour
of renewable energy into the European Union
Support the establishment of a realistic and fair pricing scheme
on the basis of the European internal market for energy
respecting the principle of subsidiary of each member state
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
Ensure that transmission system operators grant priority access
to the transmission of electricity from renewable energy sources
under standard rules based on objective, transparent and non-
discriminatory criteria
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
European Climate Change
Programme (ECCP)
since 1991 several climate-related initiatives (e.g. RES-
electricity, voluntary commitments by car makers to
improve fuel economy, proposal for emission trading
scheme etc.)
Target to cut EU greenhouse gas emissions to 8 %
below 1990 levels by 2008-2012
June 2000 - launch of the ECCP
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
ECCP - First Phase
Focus on energy, transport and industry sectors
Set up of working groups (summer 2000)
Result: ECCP - report june 2001, identifying 42
possible measures, with emission reduction potential
of about 664 - 765 MtCO2 equivalent
Action Plan for the ECCP in form of a Communication
from the Commission
Proposal for ratification of the Kyoto Protocol
Proposal for Emissions Trading
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
ECCP - Second Phase
Aims to facilitate and support the actual
implementation of the priorities identified in the first
phase
Measures:
– Proposal for EU framework for emissions trading (see above)
– Proposal for a Directive on the promotion of biofuels
– Proposal for a Directive to promote combined heat and power
(CHP)
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
Directive 2001/77/EC
of 27 September on the Promotion of Electricity
Produced from Renewable Energy Sources (RES-
directive)
Follow-up to the 1997 White Paper on RES
Target of 12% of gross inland energy consumption
from RES for the Community as a whole by 2010, with
electricity representing 22, 1%
promotion of RES as an essential part of the package
of measures needed to comply with the commitments
made by the EU under the 1997 Kyoto Protocol
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
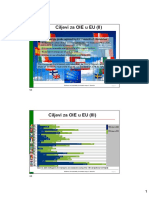
Table: Annex of the RES-directive 2001/77/EC
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
RES-directive
Where do we stand?
Defintion of renewable energies
(Article 2 lit. a RES-directive)
National targets for renewables
(Annex of the RES-directive)
Support mechanism, e.g. Feed-in systems, Quota
system, tendering system
(Article 4 RES directive)
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
RES-directive
What is the expected gap?
Table
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
Table : Scenarios for the uptake of renewably
generated electricity
1999 2001
EU Current scenario Active scenario
Targets 2010
% % % %
AT 72% 78% 63% 63.00%
BE 1% 6% 1% 3.00%
DE 6% 13% 11% 12.00%
DK 13% 29% 23% 32.00%
ES 19% 29% 22% 28.00%
FI 26% 32% 31% 31.00%
FR 15% 21% 13% 16.00%
GR 10% 20% 12% 15.00%
IE 5% 13% 11% 15.00%
IT 17% 25% 17% 18.00%
LU 3% 6% 5% 5.00%
NL 2% 9% 6% 8.50%
PT 36% 39% 27% 38.00%
SE 50% 60% 57% 57.00%
UK 2% 10% 4% 4.00%
EU 14% 22% 15% 17.00%
Sources: calculations based on Ecofys 2002.
Active Policy: results implementing the current policies.
Continued Policy: results assuming that policies will be continued.
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
RES-Directive
What does work and what doesn‘t?
Support mechanisms
– Feed-in systems
– Quota systems:
Adminstrative implementation
Uncertainty about actual invetsment
Voltaile revenues
Adminstrative procedures (almost no fast-track-
planning)
Grid connection
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
RES-directive - Technologies -
White Paper targets for renewable technologies vs. current
situation 1999 Scenario 2010
Imple Active Continued White
Unit mented Policy Policy Paper
Wind GWe 9 37 54 40
Hydro-large (>10 MWe) GWe 85 85 87 91
Hydro-small (<10 MWe) GWe 9 11 12 14
Photovoltaic GWp 0,1 0,5 0,7 3,0
Biomass (fuel input) Mtoe 55 86 118 135
Geothermal: electricity GWe 0,6 0,6 0,9 1,0
Geothermal: heat GWth 1,2 1,8 1,9 5,0
2
Active solar thermal million. m 9 18 28 100
Total electricity production TWhe 364 466 539 675
Total primary energy* Mtoe 85 122 159 182
Share renewable energy % 6% 8% 10% 12%
* Eurostat convention
Source: Ecofys 2002
Active Policy: results implementing the current policies.
Continued Policy: results assuming that policies will be continued .
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
RES-directive
- Conclusions -
Adopt national feed-in systems when implemeting the
RES-directive
Remove rigorously all adminstrative barriers for new
renewable electricty generation
Develop planning guidelines for siting of renewable
energy projects
Implement guarantee of origin for all electricty sources
EREF - European Renewable Ene
rgy Federation
You might also like
- Solved Problems Axial DeformationDocument6 pagesSolved Problems Axial DeformationChristopher Largado67% (3)
- Carbon Market Year in Review 2022Document30 pagesCarbon Market Year in Review 2022ThomasNo ratings yet
- Pooie GF 2019 1Document7 pagesPooie GF 2019 1nedp18No ratings yet
- Energy Union Factsheet Spain enDocument26 pagesEnergy Union Factsheet Spain entrovatore48No ratings yet
- Energy Union and Climate Action: Driving Europe's Transition To A Low-Carbon EconomyDocument3 pagesEnergy Union and Climate Action: Driving Europe's Transition To A Low-Carbon EconomyLuís CastroNo ratings yet
- Road EnergiamappingDocument20 pagesRoad EnergiamappingJTHNo ratings yet
- A New Directive On Energy Efficiency: - Challenges Addressed & Solutions ProposedDocument16 pagesA New Directive On Energy Efficiency: - Challenges Addressed & Solutions ProposedIgor NeagaNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy ContributionDocument104 pagesWind Energy ContributionTown Obio EteteNo ratings yet
- RagwitzDocument28 pagesRagwitzmaria_alexandraNo ratings yet
- EEA - 2017 - RESinEU2017 - TH AL 17 024 EN NDocument74 pagesEEA - 2017 - RESinEU2017 - TH AL 17 024 EN NbuhmoohNo ratings yet
- Wpiea2022220 Print PDFDocument22 pagesWpiea2022220 Print PDFMikeNo ratings yet
- Key World Energy Statistics 2020Document81 pagesKey World Energy Statistics 2020Amin DehghaniNo ratings yet
- EEA 2014 Country Profile CroatiaDocument5 pagesEEA 2014 Country Profile CroatiaSaša MartinovićNo ratings yet
- MLT Out Look 2023 EditionDocument46 pagesMLT Out Look 2023 EditionhambaliNo ratings yet
- Carbon Tax: What Environmental and Economic Impact in The French Manufacturing Sector?Document21 pagesCarbon Tax: What Environmental and Economic Impact in The French Manufacturing Sector?Josua Desmonda SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Energy Economic Developments in EuropaDocument160 pagesEnergy Economic Developments in EuropaAna AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Renewables Se enDocument3 pagesRenewables Se enAmir FauwazNo ratings yet
- 4 - 610 - ms16 - Sander - 0Document16 pages4 - 610 - ms16 - Sander - 0Karim IsmailNo ratings yet
- European Union 2020 Energy Policy ReviewDocument310 pagesEuropean Union 2020 Energy Policy ReviewFenhia RivasNo ratings yet
- 2050 EU Energy StrategyDocument12 pages2050 EU Energy StrategyHector Parra MolinaNo ratings yet
- A One Gigawatt Green PlantDocument45 pagesA One Gigawatt Green PlantIsabelMaríaGarcíaNo ratings yet
- SimcockDocument13 pagesSimcockJusuwa JusuwaNo ratings yet
- Smart GridDocument90 pagesSmart Gridjose girotNo ratings yet
- Florou PresentationDocument19 pagesFlorou Presentationayeletariku092No ratings yet
- 5 Industry IndicatorsDocument47 pages5 Industry IndicatorsBülent BulutNo ratings yet
- Renewable Factsheet PDFDocument34 pagesRenewable Factsheet PDFdep25No ratings yet
- GT2005-68014 Axial Compressor MaintenanceDocument48 pagesGT2005-68014 Axial Compressor MaintenanceRaden MasNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Prospects for Central and South-Eastern Europe Energy Connectivity (CESEC)From EverandRenewable Energy Prospects for Central and South-Eastern Europe Energy Connectivity (CESEC)No ratings yet
- Waste To Hydrogen Webinar Presentation Post Event FINALDocument35 pagesWaste To Hydrogen Webinar Presentation Post Event FINALImed ChoukiNo ratings yet
- Renewables 2021 - Analysis and Forecast To 2026 - IeaDocument175 pagesRenewables 2021 - Analysis and Forecast To 2026 - IeaMohammad ShofieNo ratings yet
- PV Status Report 2011Document130 pagesPV Status Report 2011AndreiCeagleiNo ratings yet
- Ace TrendsDocument4 pagesAce TrendsZerohedge JanitorNo ratings yet
- Net Oil Zero PDFDocument33 pagesNet Oil Zero PDFRizal FauziNo ratings yet
- H1 Report 2021 US FinalDocument48 pagesH1 Report 2021 US FinalnemoNo ratings yet
- 09 - EP - Gestione Dei RischiDocument26 pages09 - EP - Gestione Dei RischiantonioNo ratings yet
- Training Webinar #8Document174 pagesTraining Webinar #8Vale PiscoyaNo ratings yet
- EDF Study For Download On EPDocument25 pagesEDF Study For Download On EPlitteraeinvitaeNo ratings yet
- Global Gas Market and Its ChallengesDocument15 pagesGlobal Gas Market and Its ChallengesjosealvaroNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage Needs in SpainDocument56 pagesEnergy Storage Needs in SpainAhmed WestministerNo ratings yet
- France 2021Document211 pagesFrance 2021Madiha KhanNo ratings yet
- EbstbDocument12 pagesEbstbapi-292520116No ratings yet
- Transformers ScopeDocument60 pagesTransformers ScopeSathiya KumarNo ratings yet
- CE - Delft - 200247 - UCO - As - Biofuel - Feedstock - in - EU - FINAL - v5 - 0Document65 pagesCE - Delft - 200247 - UCO - As - Biofuel - Feedstock - in - EU - FINAL - v5 - 0LelosPinelos123No ratings yet
- 2018 02 21 - RRIF - Explanatory - Document - Public ConsultationDocument17 pages2018 02 21 - RRIF - Explanatory - Document - Public ConsultationLuiza GhitaNo ratings yet
- EU Climate Policy FailureDocument90 pagesEU Climate Policy FailureCasimir de BonnevalNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Project Analysis Using Retscreen SoftwareDocument28 pagesPhotovoltaic Project Analysis Using Retscreen SoftwarehazimeNo ratings yet
- Korea 2020 Energy Policy ReviewDocument204 pagesKorea 2020 Energy Policy ReviewSunderjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Global Hydrogen Review 2021Document224 pagesGlobal Hydrogen Review 2021Rajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Excerpt From: Electricity InformationDocument7 pagesExcerpt From: Electricity InformationCarlosNo ratings yet
- Biofuels Directive - Implications For IrelandDocument40 pagesBiofuels Directive - Implications For IrelandBharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Prezentare WAGES 2007Document36 pagesPrezentare WAGES 2007Ionut DraganNo ratings yet
- IEA G20 Hydrogen Report: AssumptionsDocument14 pagesIEA G20 Hydrogen Report: Assumptionspragya89No ratings yet
- IEA-Clean Energy MFGDocument36 pagesIEA-Clean Energy MFGManokaran KNo ratings yet
- Technology Roadmap Wind EnergyDocument63 pagesTechnology Roadmap Wind EnergyEdgard Leonardo Castaneda GarciaNo ratings yet
- PHEV White Paper Sept2020 0Document57 pagesPHEV White Paper Sept2020 0Simon AlvarezNo ratings yet
- PV The Cheapest Electricity Source Almost EverywheDocument2 pagesPV The Cheapest Electricity Source Almost Everywhem.armadaNo ratings yet
- Energy Policies of IEA Countries United Kingdom 2019 ReviewDocument220 pagesEnergy Policies of IEA Countries United Kingdom 2019 ReviewPranay MahawarNo ratings yet
- $$$ACER H2 Paper - VFinal - CleanDocument61 pages$$$ACER H2 Paper - VFinal - CleanMahjoub AmriNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Policy Progress Index: Sector End-Use Performance Level MetricDocument3 pagesEfficiency Policy Progress Index: Sector End-Use Performance Level MetricGerardo AguirreNo ratings yet
- EU-China Energy Magazine 2021 Summer Issue: 2021, #2From EverandEU-China Energy Magazine 2021 Summer Issue: 2021, #2No ratings yet
- EU-China Energy Magazine 2020 Christmas Double Issue: 2020, #4From EverandEU-China Energy Magazine 2020 Christmas Double Issue: 2020, #4No ratings yet
- Wipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2Document65 pagesWipo Idb Ip Ryd 07 2RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- 66 Commonwealth Parliamentary Conference Accra, Ghana 30 September - 6 October 2023 Hon 'Ble Chairperson and Distinguished DelegatesDocument19 pages66 Commonwealth Parliamentary Conference Accra, Ghana 30 September - 6 October 2023 Hon 'Ble Chairperson and Distinguished DelegatesRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- External ContentDocument542 pagesExternal ContentRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grade Math Worksheets FractionsDocument2 pages3rd Grade Math Worksheets FractionsRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Anhydrous Ammonia:: Managing The RisksDocument16 pagesAnhydrous Ammonia:: Managing The RisksRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Operator Installation & Instruction Manual: Auto-Purger Plus, App Non-Condensible Gas (Air) & Water Purger For AmmoniaDocument20 pagesOperator Installation & Instruction Manual: Auto-Purger Plus, App Non-Condensible Gas (Air) & Water Purger For AmmoniaRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Selection of Condensers and Chillers: Systems & Components (India) Pvt. LTDDocument34 pagesSelection of Condensers and Chillers: Systems & Components (India) Pvt. LTDRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Float Switch: Product Bulletin 61-12 ADocument12 pagesRefrigerant Float Switch: Product Bulletin 61-12 ARASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Ab 538 Integrity Management Requirements For Mechanical Refrigeration Systems Containing AmmoniaDocument18 pagesAb 538 Integrity Management Requirements For Mechanical Refrigeration Systems Containing AmmoniaRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Ab 275 General Requirements For Mechanical Refrigeration SystemsDocument7 pagesAb 275 General Requirements For Mechanical Refrigeration SystemsRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Gas Detection Bump Testing Ammonia (NH) Sensors: TF: +1.877.940.8741 - T: +1.604.940.8741 - F: +1.604.940.8745Document2 pagesGas Detection Bump Testing Ammonia (NH) Sensors: TF: +1.877.940.8741 - T: +1.604.940.8741 - F: +1.604.940.8745RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Piping Registration - Pressure Vessel EngineeringDocument6 pagesPiping Registration - Pressure Vessel EngineeringRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- IB18-004 (Reporting Unsafe Conditions, Accidents and Fires)Document5 pagesIB18-004 (Reporting Unsafe Conditions, Accidents and Fires)RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Defrosting Industrial Refrigeration Evaporators Reindl Jekel August 2009Document13 pagesDefrosting Industrial Refrigeration Evaporators Reindl Jekel August 2009RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Manitoba RequirementDocument15 pagesManitoba RequirementRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Document Title: Installation Instruction: Pacific Co., LTDDocument13 pagesDocument Title: Installation Instruction: Pacific Co., LTDRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Management of Change (Hazard Screening)Document2 pagesManagement of Change (Hazard Screening)RASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- O F R M e P P P A C T, I e L U e W, TX G, LaDocument253 pagesO F R M e P P P A C T, I e L U e W, TX G, LaRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Novel Technologies For Wear Protection and Monitoring in DredgingDocument23 pagesNovel Technologies For Wear Protection and Monitoring in DredgingRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Location Written By: Approved By: Date Created Last RevisionDocument2 pagesLocation Written By: Approved By: Date Created Last RevisionRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Coagulation/Flocculation Process For Produced Water TreatmentDocument6 pagesCoagulation/Flocculation Process For Produced Water TreatmentRASHEED YUSUFNo ratings yet
- Ifage Bachelor 1 General English Chapter 1 Basics 1 2023 2024Document22 pagesIfage Bachelor 1 General English Chapter 1 Basics 1 2023 2024coordinateurlpa coordinateurlpaNo ratings yet
- 510 - Sps Vega vs. SSS, 20 Sept 2010Document2 pages510 - Sps Vega vs. SSS, 20 Sept 2010anaNo ratings yet
- The Mavericks MNIT 1st Year 2022-23Document3 pagesThe Mavericks MNIT 1st Year 2022-23Shantul KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Enhanced Flooded Battery For Smart Mild Hybrid Power TrainsDocument29 pagesRecent Advances in Enhanced Flooded Battery For Smart Mild Hybrid Power Trains3 GamerNo ratings yet
- Prolin Termassist Operating Guide: Pax Computer Technology Shenzhen Co.,LtdDocument29 pagesProlin Termassist Operating Guide: Pax Computer Technology Shenzhen Co.,Ltdhenry diazNo ratings yet
- Httpsrvce Edu Insitesdefaultfiles7 20EC20III202620IV PDFDocument51 pagesHttpsrvce Edu Insitesdefaultfiles7 20EC20III202620IV PDFNANDITA SNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument16 pagesCash Flow Statementrajesh337masssNo ratings yet
- Master Key To Imagination GuideDocument60 pagesMaster Key To Imagination GuideAnonymous ecgjAAD98% (45)
- Module 5 Introduction To Stochastic Processes Eec605Document89 pagesModule 5 Introduction To Stochastic Processes Eec605daniel developerNo ratings yet
- Examining The Relationship BetDocument24 pagesExamining The Relationship BetMariaNo ratings yet
- NDT Basics GuideDocument29 pagesNDT Basics Guideravindra_jivaniNo ratings yet
- Bestiary of The Rosewood Highlands Draft 1-4-08!07!19Document82 pagesBestiary of The Rosewood Highlands Draft 1-4-08!07!19Stefano Chiaramonti100% (2)
- Mixers FinalDocument44 pagesMixers FinalDharmender KumarNo ratings yet
- Simbol A4Document3 pagesSimbol A4ibnu100% (1)
- Diploma Thesis Digital DiplomacyDocument56 pagesDiploma Thesis Digital DiplomacyShagadamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Steam and Gas TurbinesDocument64 pagesChapter 5 Steam and Gas TurbinesKeba Del Ray100% (2)
- 18 - Thalamus and Limbic System (Edited)Document22 pages18 - Thalamus and Limbic System (Edited)Fotocopias LulisNo ratings yet
- Gospel Steel TrussDocument18 pagesGospel Steel TrussJoseph Cloyd L. LamberteNo ratings yet
- John Hopkins IbdDocument38 pagesJohn Hopkins IbdNovita ApramadhaNo ratings yet
- Amusement Events and Recreation Award Ma000080 Pay GuideDocument17 pagesAmusement Events and Recreation Award Ma000080 Pay GuideCol. O'NeillNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Titanium Sponge Formation in The Kroll Reduction ReactorDocument11 pagesMechanism of Titanium Sponge Formation in The Kroll Reduction ReactorSrinivasulu PuduNo ratings yet
- D Internet Myiemorgmy Intranet Assets Doc Alldoc Document 15367 JURUTERA OCTOBER 2018Document52 pagesD Internet Myiemorgmy Intranet Assets Doc Alldoc Document 15367 JURUTERA OCTOBER 2018Leanne ChewNo ratings yet
- Contoh Financial PlanDocument4 pagesContoh Financial PlanJonathan ChandhikaNo ratings yet
- Siun Sote Objection Related To Social Welfare and Health Care Services or Treatment FormDocument2 pagesSiun Sote Objection Related To Social Welfare and Health Care Services or Treatment FormShahnaz NawazNo ratings yet
- Electric Rebar Cutter Owener'S Manual: Item# 999321Document10 pagesElectric Rebar Cutter Owener'S Manual: Item# 999321Mahmoud AliNo ratings yet
- ACMV and Acoustic Comfort in BuildingsDocument13 pagesACMV and Acoustic Comfort in BuildingsTuan Suhaimi SallehNo ratings yet
- Coldharbour/Wrotham Road GravesendDocument28 pagesColdharbour/Wrotham Road GravesendWessex ArchaeologyNo ratings yet
- Salt Market StructureDocument8 pagesSalt Market StructureASBMailNo ratings yet
- M As1 Formative Task: Review Questions: Star Alliance Sky Team OneworldDocument4 pagesM As1 Formative Task: Review Questions: Star Alliance Sky Team OneworldSharlyne PimentelNo ratings yet