Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsLesson 5motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctions
Lesson 5motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctions
Uploaded by
Jason BaloroThe document summarizes the key components found on a motherboard and their functions. The components include:
1. Back panel connectors and ports that connect the computer to external devices like displays, audio, USB, Ethernet, and more.
2. Expansion slots like PCI, PCIe x1, and PCIe x16 that accommodate devices like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards.
3. Chipsets like the Northbridge and Southbridge that allow the CPU to communicate with components like RAM, graphics cards, hard drives, and ports.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Cartilla ElectricaDocument135 pagesCartilla ElectricaOsvaldo UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument14 pagesParts of MotherboardNoelyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Bahasa Inggris Reading Dan VocabularyDocument3 pagesWeek 7 - Bahasa Inggris Reading Dan VocabularyRizal QoironNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument20 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument20 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsavinmanzanoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionCherrisNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument2 pagesParts of MotherboardThomas James P. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument29 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsChristian Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument4 pagesMotherboardDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functions PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functions PDFMaria Norberta MandacNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument39 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsJamer AmpongNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsErwin BenitezNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument5 pagesMotherboardRichard Melvin GarciaNo ratings yet
- A Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataDocument11 pagesA Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataPenchalaiah NarasapuramNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.6 Motherboard: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesInformation Sheet 1.6 Motherboard: Learning Objectivesjezreel csNo ratings yet
- ITP421 WEEK 2 - MotherboardsDocument29 pagesITP421 WEEK 2 - MotherboardsJaira Mae DiazNo ratings yet
- Computer MotherboardDocument15 pagesComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Parts of The MotherboardDocument17 pagesLesson 3 Parts of The MotherboardrommelNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functionsjoel lacayNo ratings yet
- M2 Yash AllabadiDocument7 pagesM2 Yash Allabadidegijon661No ratings yet
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryDocument8 pagesMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462No ratings yet
- Computer ComponentsDocument53 pagesComputer ComponentsAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- 4 Computer MotherboardDocument5 pages4 Computer MotherboardStar Boy DavieNo ratings yet
- CMN Lab Expt-1Document3 pagesCMN Lab Expt-1Aaryan SinghNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument30 pagesSeminarShweta Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Class NotesDocument12 pagesClass NotesHeart WeyganNo ratings yet
- What Is A MotherboardDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MotherboardManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of The MotherboardDocument2 pagesParts and Function of The MotherboardTorreja JonjiNo ratings yet
- CHN EXPDocument32 pagesCHN EXPAnanduNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Hardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519Document46 pagesHardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519crecbhoomi21No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardKurk DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- PartsandFunctions 302911981992807Document1 pagePartsandFunctions 302911981992807lotusvanhardt0099No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Final Notes of Second Yr 2022Document269 pagesFinal Notes of Second Yr 2022RAM KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard EnglishDocument9 pagesMotherboard EnglishallamNo ratings yet
- Computer System Parts of MotherboardDocument28 pagesComputer System Parts of MotherboardJohn Adams Budomo100% (2)
- Motherboard SlidesDocument21 pagesMotherboard Slidesmubiru moses100% (1)
- CahmDocument3 pagesCahmakkivish37No ratings yet
- A MotherboardDocument4 pagesA MotherboardOttonniel BenNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument20 pagesMotherboardJeyc RapperNo ratings yet
- Description of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Document4 pagesDescription of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Nain khanNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument6 pagesMotherboardj9694052No ratings yet
- PC TroubleshootingDocument112 pagesPC TroubleshootingMosul VictoriaNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument15 pagesMotherboardDragoon GamingNo ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- What Is A Motherboard ?Document13 pagesWhat Is A Motherboard ?Ian OffemariaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsRige Mae MuescoNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document6 pagesLab 117b-012-peNo ratings yet
- II Puc CS 1st and 4th Chapters NotesDocument17 pagesII Puc CS 1st and 4th Chapters NotesRyuNo ratings yet
- Aim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)Document15 pagesAim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)VanessaNo ratings yet
- G9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardDocument10 pagesG9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemSohum VenkatadriNo ratings yet
- 2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardDocument3 pages2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardAashish KandelNo ratings yet
- 1.pci Peripheral Component Interconnected 2.what Is Troubleshooting?Document6 pages1.pci Peripheral Component Interconnected 2.what Is Troubleshooting?no fake NewsNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4CABADONGA, Justin M.No ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- Chapter No 3 Air CompressorsDocument59 pagesChapter No 3 Air Compressorsahsan8arshad-4No ratings yet
- Arja AL Khaleej Group.: Quantities To Hold The Implementation of Sewage Networks Turaif Second PhaseDocument14 pagesArja AL Khaleej Group.: Quantities To Hold The Implementation of Sewage Networks Turaif Second PhasesalmanNo ratings yet
- Light BulbsDocument5 pagesLight BulbsMiguelito GuballaNo ratings yet
- Starting Methods of 3-Phase Induction MotorsDocument5 pagesStarting Methods of 3-Phase Induction MotorsroshanzoonNo ratings yet
- 2.5 SQ - MM Pluggable Feed Through Spring Clamp Terminal BlockDocument2 pages2.5 SQ - MM Pluggable Feed Through Spring Clamp Terminal BlockNitinNo ratings yet
- Wedgegard CatalogDocument20 pagesWedgegard CatalogJose RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 03) Mazda-Allegro Manual de Taller Tren DelanteroDocument35 pages03) Mazda-Allegro Manual de Taller Tren DelanteroJohn Jairo MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Codigos SP y SC Aficio 2075Document212 pagesCodigos SP y SC Aficio 2075Xelcop RojasNo ratings yet
- Data0305 MX832+Document3 pagesData0305 MX832+Abdelhamid SammoudiNo ratings yet
- gs450h Lexus Emergency Guide PDFDocument29 pagesgs450h Lexus Emergency Guide PDFlukasz_b7100% (1)
- AHB Vs AXI Vs APBDocument2 pagesAHB Vs AXI Vs APBSorabh Dung75% (4)
- At90pwm2 3Document365 pagesAt90pwm2 3flo72afNo ratings yet
- Truck-Mounted UNIC Crane UR-V230 Series For Light-Duty TruckDocument3 pagesTruck-Mounted UNIC Crane UR-V230 Series For Light-Duty Truckwongnggantheng100% (1)
- Telligent Brake System (BS) : Differential Slip Control (D S R)Document23 pagesTelligent Brake System (BS) : Differential Slip Control (D S R)Sameh MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cargo Van SizesDocument7 pagesCargo Van Sizesangelfelix28No ratings yet
- Mounting Instructions: 75900 Models Top ViewDocument6 pagesMounting Instructions: 75900 Models Top ViewMarioNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Dump Truck 930e 2 Shop Manual Cebm007001Document20 pagesKomatsu Dump Truck 930e 2 Shop Manual Cebm007001alvera100% (51)
- N13201 - DR B R Ambedkar NIT Jalandhar - Supra Sae India 2014 - Design Spec SheetDocument4 pagesN13201 - DR B R Ambedkar NIT Jalandhar - Supra Sae India 2014 - Design Spec Sheetsatbirsingh123No ratings yet
- 1LAB 000280 EasyDry DMB OA Bushing Nov 2012Document12 pages1LAB 000280 EasyDry DMB OA Bushing Nov 2012Jason BourneNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Engine Saa6d170e 5 Workshop ManualsDocument20 pagesKomatsu Engine Saa6d170e 5 Workshop Manualslucy100% (54)
- 5717-Datasheet-8Zone - LAN - Expander 2Document2 pages5717-Datasheet-8Zone - LAN - Expander 2Iain PerrieNo ratings yet
- Spare Part List HC HCL HCH 6100 8100Document28 pagesSpare Part List HC HCL HCH 6100 8100yoye1968100% (1)
- 50Hz B TO200B47.5 5Document4 pages50Hz B TO200B47.5 5Thu Hiền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Asme B30.22 (2005)Document42 pagesAsme B30.22 (2005)Omar Ramirez100% (1)
- TC 1000 BrochureDocument2 pagesTC 1000 BrochureerniewatersNo ratings yet
- P-223.2013 (GIS Plant)Document58 pagesP-223.2013 (GIS Plant)NasrullahNo ratings yet
- Vue EclateeDocument12 pagesVue EclateeBlacheNo ratings yet
- Mic VerticalDocument139 pagesMic VerticalRavi KrishnanNo ratings yet
Lesson 5motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctions
Lesson 5motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctions
Uploaded by
Jason Baloro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views20 pagesThe document summarizes the key components found on a motherboard and their functions. The components include:
1. Back panel connectors and ports that connect the computer to external devices like displays, audio, USB, Ethernet, and more.
2. Expansion slots like PCI, PCIe x1, and PCIe x16 that accommodate devices like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards.
3. Chipsets like the Northbridge and Southbridge that allow the CPU to communicate with components like RAM, graphics cards, hard drives, and ports.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the key components found on a motherboard and their functions. The components include:
1. Back panel connectors and ports that connect the computer to external devices like displays, audio, USB, Ethernet, and more.
2. Expansion slots like PCI, PCIe x1, and PCIe x16 that accommodate devices like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards.
3. Chipsets like the Northbridge and Southbridge that allow the CPU to communicate with components like RAM, graphics cards, hard drives, and ports.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views20 pagesLesson 5motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctions
Lesson 5motherboardcomponentsandtheirfunctions
Uploaded by
Jason BaloroThe document summarizes the key components found on a motherboard and their functions. The components include:
1. Back panel connectors and ports that connect the computer to external devices like displays, audio, USB, Ethernet, and more.
2. Expansion slots like PCI, PCIe x1, and PCIe x16 that accommodate devices like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards.
3. Chipsets like the Northbridge and Southbridge that allow the CPU to communicate with components like RAM, graphics cards, hard drives, and ports.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
Motherboard Components
and Their Functions
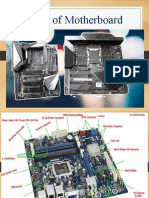
1- Back Panel Connectors &
Ports
Connectors and ports for connecting
the computer to external devices
such as display ports, audio ports,
USB ports, Ethernet ports, PS/2 ports
etc.
2. PCI Slots PCI: Peripheral Component
Interconnect
Slot for older expansion cards such as
sound cards, network cards,
connector cards. See image below for
a close-up view.
3. PCI Express x1
Slots
Slot for modern expansion cards such as
sound cards, network cards (Wi-Fi, Ethernet,
Bluetooth), connector cards (USB, FireWire,
eSATA) and certain low-end graphics cards.
See image below for a close-up view
4. PCI Express x16
Slot
Slot for discrete graphic cards and high
bandwidth devices such as top-end solid
state drives. See image below for a
close- up view
5.
Also known as Memory Controller Hub (MCH).
Northbridge
Chipset that allows the CPU to
communicate with the RAM and graphics
card.
Beginning from Intel Sandy Bridge in 2011, this
motherboard component is no longer present
as it has been integrated within the CPU itself.
6. CPU Socket
A CPU socket or CPU slot is a mechanical
component(s) that provides mechanical and
electrical connections between a microprocessor
and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows
the CPU to be placed and replaced without
soldering.
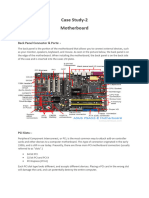
7. ATX 12V Power
Connector
Connects to the 4-pin power cable of a
power supply unit which supplies power
to the CPU.
8. Front Panel USB 2.0
Connectors
Connects to USB 2.0 ports at the front or top
of a computer case. See image above for a
close- up view.
9. Front Panel
Connectors
Connects to the power switch, reset switch,
power LED, hard drive LED and front audio
ports of a computer case. See image above for
a
close-up view.
10. IDE Connector
Connects to older hard drive disks and optical
drives for data transfer. See image above for a
close-up view. Have been replaced over by
SATA connectors (see motherboard component
#13 below).
11. CMOS Battery
Supplies power to store BIOS settings and keep
the real-time clock running. See image above
for a close-up view. The CMOS battery found
on most motherboards is the CR2032 lithium
coin cell.
12. Southbridge
Also known as the Input/output Controller Hub
(ICH).Chipset that allows the CPU to communicate
with PCI slots, PCI-Express x 1 slots (expansion
cards), SATA connectors (hard drives, optical
drives), USB ports (USB devices), Ethernet ports
and on-board audio.
13. SATA
Connectors
Connects to modern hard disk drives, solid
state drives and optical drives for data
transfer. See image above for a close-up
view.
14. Fan Header
Supplies power to the CPU heat sink fan
and computer case fans. See image
above for a close-up view.
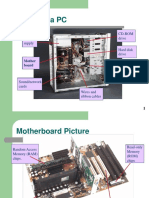
15. RAM Slots
A memory slot, memory socket, or RAM slot is what
allows computer memory (RAM) to be inserted into the
computer. Depending on the motherboard, there may
be 2 to 4 memory slots (sometimes more on high-end
motherboards) and are what determine the type of
RAM used with the computer.
16. mSATA Connector
Connects to a mSATA solid state drive. In most
cases, this SSD is used as cache to speed up
hard disk drives, but it's possible to re-purpose
it as a regular hard drive.
17. Power & Reset
Button
he reset button could be an actual button or concept.
The reset button would typically kick off a soft boot,
instructing the computer to go through the process of
shutting down, which would clear memory and reset
devices to their initialized state. Contrary to the 'Power
Button', which would simply remove power
immediately.
THANK
YOU
You might also like
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Cartilla ElectricaDocument135 pagesCartilla ElectricaOsvaldo UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument14 pagesParts of MotherboardNoelyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Bahasa Inggris Reading Dan VocabularyDocument3 pagesWeek 7 - Bahasa Inggris Reading Dan VocabularyRizal QoironNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument20 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsHerwin CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument20 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsavinmanzanoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionCherrisNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument2 pagesParts of MotherboardThomas James P. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument29 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsChristian Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument4 pagesMotherboardDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functions PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functions PDFMaria Norberta MandacNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument39 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsJamer AmpongNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsErwin BenitezNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument5 pagesMotherboardRichard Melvin GarciaNo ratings yet
- A Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataDocument11 pagesA Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataPenchalaiah NarasapuramNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.6 Motherboard: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesInformation Sheet 1.6 Motherboard: Learning Objectivesjezreel csNo ratings yet
- ITP421 WEEK 2 - MotherboardsDocument29 pagesITP421 WEEK 2 - MotherboardsJaira Mae DiazNo ratings yet
- Computer MotherboardDocument15 pagesComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Parts of The MotherboardDocument17 pagesLesson 3 Parts of The MotherboardrommelNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Different Motherboard Components and Their Functionsjoel lacayNo ratings yet
- M2 Yash AllabadiDocument7 pagesM2 Yash Allabadidegijon661No ratings yet
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryDocument8 pagesMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462No ratings yet
- Computer ComponentsDocument53 pagesComputer ComponentsAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- 4 Computer MotherboardDocument5 pages4 Computer MotherboardStar Boy DavieNo ratings yet
- CMN Lab Expt-1Document3 pagesCMN Lab Expt-1Aaryan SinghNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument30 pagesSeminarShweta Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Class NotesDocument12 pagesClass NotesHeart WeyganNo ratings yet
- What Is A MotherboardDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MotherboardManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of The MotherboardDocument2 pagesParts and Function of The MotherboardTorreja JonjiNo ratings yet
- CHN EXPDocument32 pagesCHN EXPAnanduNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Hardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519Document46 pagesHardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519crecbhoomi21No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardKurk DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- PartsandFunctions 302911981992807Document1 pagePartsandFunctions 302911981992807lotusvanhardt0099No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Reading3 - MotherboardChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Final Notes of Second Yr 2022Document269 pagesFinal Notes of Second Yr 2022RAM KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard EnglishDocument9 pagesMotherboard EnglishallamNo ratings yet
- Computer System Parts of MotherboardDocument28 pagesComputer System Parts of MotherboardJohn Adams Budomo100% (2)
- Motherboard SlidesDocument21 pagesMotherboard Slidesmubiru moses100% (1)
- CahmDocument3 pagesCahmakkivish37No ratings yet
- A MotherboardDocument4 pagesA MotherboardOttonniel BenNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument20 pagesMotherboardJeyc RapperNo ratings yet
- Description of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Document4 pagesDescription of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Nain khanNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument6 pagesMotherboardj9694052No ratings yet
- PC TroubleshootingDocument112 pagesPC TroubleshootingMosul VictoriaNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument15 pagesMotherboardDragoon GamingNo ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- What Is A Motherboard ?Document13 pagesWhat Is A Motherboard ?Ian OffemariaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsRige Mae MuescoNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document6 pagesLab 117b-012-peNo ratings yet
- II Puc CS 1st and 4th Chapters NotesDocument17 pagesII Puc CS 1st and 4th Chapters NotesRyuNo ratings yet
- Aim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)Document15 pagesAim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)VanessaNo ratings yet
- G9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardDocument10 pagesG9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemSohum VenkatadriNo ratings yet
- 2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardDocument3 pages2.10 Inside A Computer Cabinet: 2.10.1 MotherboardAashish KandelNo ratings yet
- 1.pci Peripheral Component Interconnected 2.what Is Troubleshooting?Document6 pages1.pci Peripheral Component Interconnected 2.what Is Troubleshooting?no fake NewsNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4CABADONGA, Justin M.No ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- Chapter No 3 Air CompressorsDocument59 pagesChapter No 3 Air Compressorsahsan8arshad-4No ratings yet
- Arja AL Khaleej Group.: Quantities To Hold The Implementation of Sewage Networks Turaif Second PhaseDocument14 pagesArja AL Khaleej Group.: Quantities To Hold The Implementation of Sewage Networks Turaif Second PhasesalmanNo ratings yet
- Light BulbsDocument5 pagesLight BulbsMiguelito GuballaNo ratings yet
- Starting Methods of 3-Phase Induction MotorsDocument5 pagesStarting Methods of 3-Phase Induction MotorsroshanzoonNo ratings yet
- 2.5 SQ - MM Pluggable Feed Through Spring Clamp Terminal BlockDocument2 pages2.5 SQ - MM Pluggable Feed Through Spring Clamp Terminal BlockNitinNo ratings yet
- Wedgegard CatalogDocument20 pagesWedgegard CatalogJose RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 03) Mazda-Allegro Manual de Taller Tren DelanteroDocument35 pages03) Mazda-Allegro Manual de Taller Tren DelanteroJohn Jairo MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Codigos SP y SC Aficio 2075Document212 pagesCodigos SP y SC Aficio 2075Xelcop RojasNo ratings yet
- Data0305 MX832+Document3 pagesData0305 MX832+Abdelhamid SammoudiNo ratings yet
- gs450h Lexus Emergency Guide PDFDocument29 pagesgs450h Lexus Emergency Guide PDFlukasz_b7100% (1)
- AHB Vs AXI Vs APBDocument2 pagesAHB Vs AXI Vs APBSorabh Dung75% (4)
- At90pwm2 3Document365 pagesAt90pwm2 3flo72afNo ratings yet
- Truck-Mounted UNIC Crane UR-V230 Series For Light-Duty TruckDocument3 pagesTruck-Mounted UNIC Crane UR-V230 Series For Light-Duty Truckwongnggantheng100% (1)
- Telligent Brake System (BS) : Differential Slip Control (D S R)Document23 pagesTelligent Brake System (BS) : Differential Slip Control (D S R)Sameh MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cargo Van SizesDocument7 pagesCargo Van Sizesangelfelix28No ratings yet
- Mounting Instructions: 75900 Models Top ViewDocument6 pagesMounting Instructions: 75900 Models Top ViewMarioNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Dump Truck 930e 2 Shop Manual Cebm007001Document20 pagesKomatsu Dump Truck 930e 2 Shop Manual Cebm007001alvera100% (51)
- N13201 - DR B R Ambedkar NIT Jalandhar - Supra Sae India 2014 - Design Spec SheetDocument4 pagesN13201 - DR B R Ambedkar NIT Jalandhar - Supra Sae India 2014 - Design Spec Sheetsatbirsingh123No ratings yet
- 1LAB 000280 EasyDry DMB OA Bushing Nov 2012Document12 pages1LAB 000280 EasyDry DMB OA Bushing Nov 2012Jason BourneNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Engine Saa6d170e 5 Workshop ManualsDocument20 pagesKomatsu Engine Saa6d170e 5 Workshop Manualslucy100% (54)
- 5717-Datasheet-8Zone - LAN - Expander 2Document2 pages5717-Datasheet-8Zone - LAN - Expander 2Iain PerrieNo ratings yet
- Spare Part List HC HCL HCH 6100 8100Document28 pagesSpare Part List HC HCL HCH 6100 8100yoye1968100% (1)
- 50Hz B TO200B47.5 5Document4 pages50Hz B TO200B47.5 5Thu Hiền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Asme B30.22 (2005)Document42 pagesAsme B30.22 (2005)Omar Ramirez100% (1)
- TC 1000 BrochureDocument2 pagesTC 1000 BrochureerniewatersNo ratings yet
- P-223.2013 (GIS Plant)Document58 pagesP-223.2013 (GIS Plant)NasrullahNo ratings yet
- Vue EclateeDocument12 pagesVue EclateeBlacheNo ratings yet
- Mic VerticalDocument139 pagesMic VerticalRavi KrishnanNo ratings yet