Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsOfel Thesis CD
Ofel Thesis CD
Uploaded by
Armel Grace Lugod-VianzonThe document outlines the architectural design process in 5 steps: (1) define the problem, (2) inventory, (3) analysis, (4) synthesis, and (5) interpretation. It then discusses architectural programming, including considerations for space requirements, building codes, site conditions, cost estimating, and functional and sociological factors. The goal is to demonstrate the process and knowledge needed to develop a feasible architectural design that addresses the problem statement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Tietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics 7th Edition Burtis Test BankDocument8 pagesTietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics 7th Edition Burtis Test BankRicardoCarsonnbgda94% (17)
- Big Data Analytics in HealthcareDocument193 pagesBig Data Analytics in HealthcareMuhammad Alkahfi100% (3)
- Quarter 1 - Module 1 Nature Goals and Perspectives in Anthropology Sociology and Political ScienceDocument24 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 1 Nature Goals and Perspectives in Anthropology Sociology and Political Science완83% (12)
- Pre Design OutlineDocument5 pagesPre Design Outlineapi-3831280100% (1)
- Architectural Design ProcessDocument35 pagesArchitectural Design ProcessVholts Villa VitugNo ratings yet
- DraughtmanshipDocument39 pagesDraughtmanshiphanihusainiNo ratings yet
- General Design Approach For Architectural Design Board ExamDocument8 pagesGeneral Design Approach For Architectural Design Board ExamVanessa RafaelNo ratings yet
- Analisa SiteDocument51 pagesAnalisa SiteAzayaka MikuNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design Studio IDocument81 pagesArchitectural Design Studio IPoii GNo ratings yet
- Literature Review and Case StudyDocument4 pagesLiterature Review and Case StudyNimNo ratings yet
- Case Study MethodologyDocument12 pagesCase Study Methodologyshravani wodeyarNo ratings yet
- AD5 Space Planning Module 2 1Document4 pagesAD5 Space Planning Module 2 1Deanna RentegradoNo ratings yet
- Architectural DesignDocument56 pagesArchitectural DesignBiniam AssefaNo ratings yet
- Prethesis Final Report Redevelopment of Rythubazar in MehidepatnamDocument40 pagesPrethesis Final Report Redevelopment of Rythubazar in MehidepatnamAkhi Akhila50% (2)
- Desktop Case Study VIII SemDocument3 pagesDesktop Case Study VIII SemsamNo ratings yet
- Land SurveyingDocument102 pagesLand SurveyingAbdissa Bekele50% (4)
- Structural Design in IDPDocument65 pagesStructural Design in IDPMuhd IbrahimNo ratings yet
- SEM 6 - AD - Check List For Case StudyDocument1 pageSEM 6 - AD - Check List For Case StudyMohiniNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document18 pagesGroup 4Marvin GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Design ServicesDocument1 pageDesign ServicesToptop OreNo ratings yet
- Architect Scope of Services (Typical) : 1417 Palo Duro Rd. Austin, Texas 78757Document2 pagesArchitect Scope of Services (Typical) : 1417 Palo Duro Rd. Austin, Texas 78757Clarisse OdayanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Landscape Design - HamnaDocument52 pagesLecture 1 Landscape Design - HamnaHamza NaseemNo ratings yet
- By: Olyad G. (MSC)Document22 pagesBy: Olyad G. (MSC)samuelhailu853No ratings yet
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessDocument18 pagesFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessTadi Fresco Royce100% (2)
- Design 2016 SRMDocument3 pagesDesign 2016 SRMAnoop KothariNo ratings yet
- UD Brief TofR July 2009Document11 pagesUD Brief TofR July 2009Debasis DasNo ratings yet
- StuffDocument23 pagesStuffFreyaNo ratings yet
- Programing ArsDocument40 pagesPrograming ArsCandra Semakin SharappzNo ratings yet
- Case Study, Site Analysis, & Design ProgrameDocument16 pagesCase Study, Site Analysis, & Design ProgrameShruti NandiwdekarNo ratings yet
- Presentation SSESL1Document47 pagesPresentation SSESL1Ajith VandebonaNo ratings yet
- IDP III Arch5471 2016EC Research Concept DeliverablesDocument3 pagesIDP III Arch5471 2016EC Research Concept Deliverablesras yoniNo ratings yet
- Arc209-Architectural Design I: CourseDocument5 pagesArc209-Architectural Design I: CourseMurat ArapogluNo ratings yet
- Spatial Planning and Building DesignDocument50 pagesSpatial Planning and Building DesignManchala AyeshNo ratings yet
- Design ProcessDocument18 pagesDesign ProcessNejib MohNo ratings yet
- 2018-10-22 - Week 09 - Considerations SAPPK & FSRD - EnglishDocument53 pages2018-10-22 - Week 09 - Considerations SAPPK & FSRD - Englishraissa damiriNo ratings yet
- RSW#1 Basic Description of TermsDocument12 pagesRSW#1 Basic Description of TermsPrescilo Nato Palor IVNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design ProcessDocument38 pagesArchitectural Design ProcessUwaoma Uchenna Emmanuel100% (1)
- Unit - 1BDocument36 pagesUnit - 1BnihaNo ratings yet
- AR 171 P Site Planning and Landscape Architecture: Module 1.0 IntroductionDocument5 pagesAR 171 P Site Planning and Landscape Architecture: Module 1.0 IntroductionAlmae IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Deliverables For Pre-Final Thesis ReportDocument19 pagesDeliverables For Pre-Final Thesis ReportmonikaNo ratings yet
- Syallbus 3rd SemsterDocument19 pagesSyallbus 3rd Semstervishal yaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot - 2023-08-20-19-59-46-244 - Com - Android.chrome-Edit (2 Files Merged)Document2 pagesScreenshot - 2023-08-20-19-59-46-244 - Com - Android.chrome-Edit (2 Files Merged)Ar. Vignesh DhanapalNo ratings yet
- Arch Thesis - Building Programme & Design RationaleDocument21 pagesArch Thesis - Building Programme & Design RationaleSam CharlesNo ratings yet
- Arch Thesis - Building Programme & Design RationaleDocument21 pagesArch Thesis - Building Programme & Design RationaleSam CharlesNo ratings yet
- ARCH 311 - Week 1 PresentationDocument17 pagesARCH 311 - Week 1 PresentationEugeneNo ratings yet
- Site Grading SyllabusDocument7 pagesSite Grading SyllabusBabulalSahuNo ratings yet
- F2020 Urban Design Studio ARC500: To Analyze An Alike Project, The Objective Is To Evaluate: Activities Included in ADocument2 pagesF2020 Urban Design Studio ARC500: To Analyze An Alike Project, The Objective Is To Evaluate: Activities Included in AMario MagdyNo ratings yet
- Annex I Thesis Book Outline and Drawing Requirements 2023.Document7 pagesAnnex I Thesis Book Outline and Drawing Requirements 2023.Francis SubiacoNo ratings yet
- Ar 242 Module 2Document31 pagesAr 242 Module 2Andrei Nicole De VeraNo ratings yet
- Salvador Pires - Architecture As A Tool For Transformative Physical DevelopmentDocument29 pagesSalvador Pires - Architecture As A Tool For Transformative Physical DevelopmentPapers and Powerpoints from UNTL-VU Joint Conferenes in Dili100% (1)
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessDocument18 pagesFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design Process9rq5cj4w25No ratings yet
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessDocument18 pagesFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessHabtamu Hailemariam AsfawNo ratings yet
- Concrete Design NotesDocument253 pagesConcrete Design NotesBishwajit Chowdhury100% (1)
- Urban Design Lecture 1Document16 pagesUrban Design Lecture 1Maryam HeshamNo ratings yet
- Structural Layout (Key Plan) PlanningDocument12 pagesStructural Layout (Key Plan) Planningzures gustiabaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Planning and Low-Cost DesignDocument13 pagesLecture 2-Planning and Low-Cost DesignAstorianbooNo ratings yet
- Architectural Site AnalysisDocument11 pagesArchitectural Site AnalysisSrishti Dokras100% (1)
- Geotechnical EngineerDocument5 pagesGeotechnical EngineeryehnafarNo ratings yet
- Site Planning and Urban DesignDocument35 pagesSite Planning and Urban Designrain06021992No ratings yet
- The Principles of Landscape Design - 015104Document18 pagesThe Principles of Landscape Design - 015104Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- IDP III Arch5471 2016EC Final DeliverablesDocument5 pagesIDP III Arch5471 2016EC Final Deliverablesras yoniNo ratings yet
- 01 Architectural Design Process PDFDocument25 pages01 Architectural Design Process PDFashok100% (3)
- Progressive Steps in Architectural Drawing - A Step-by-Step Method for Student Draughtsmen Together with Details of Construction and DesignFrom EverandProgressive Steps in Architectural Drawing - A Step-by-Step Method for Student Draughtsmen Together with Details of Construction and DesignRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Capstone-Midterm ExamDocument11 pagesCapstone-Midterm ExamRenz PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Anin Eka SulistyawatiDocument96 pagesThesis - Anin Eka Sulistyawatisalie29296No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering NotesDocument17 pagesCivil Engineering Notesaamir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- ML Lab - Sukanya RajaDocument23 pagesML Lab - Sukanya RajaRick MitraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 About Mental HealthDocument6 pagesChapter 4 About Mental HealthPinsanity GoalsNo ratings yet
- Organisational Psychology Dissertation TopicsDocument6 pagesOrganisational Psychology Dissertation TopicsWebsiteThatWillWriteAPaperForYouSavannah100% (1)
- Ambo University College of Business and Economics Department of Economics Research Method in Economics (Econ 5042)Document75 pagesAmbo University College of Business and Economics Department of Economics Research Method in Economics (Econ 5042)Ballemi TolossaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Societal Perceptions Towards Gender Domestic ViolenceDocument31 pagesUnit 9 Societal Perceptions Towards Gender Domestic ViolenceKhalil UllahNo ratings yet
- Hexagon PPM Digital Twin Solution Sheet USDocument2 pagesHexagon PPM Digital Twin Solution Sheet USAbhishek GadhwalNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Instruction in Secondary MathematicsDocument3 pagesDifferentiated Instruction in Secondary MathematicsEditha Cuenco100% (1)
- Creative Leaders - A Decade of Contributions From Creativity and Innovation Management JournalDocument15 pagesCreative Leaders - A Decade of Contributions From Creativity and Innovation Management JournalHumberto Jacobo SolísNo ratings yet
- Https:/cbseacademic - Nic.in/web material/Curriculum22/SQP MS X/417 AI MDocument6 pagesHttps:/cbseacademic - Nic.in/web material/Curriculum22/SQP MS X/417 AI MSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hist Bang Maths B: Fatema Aynoon JuienaDocument2 pagesHist Bang Maths B: Fatema Aynoon JuienaKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning Curve 1693642530Document10 pagesDeep Learning Curve 1693642530omar4programmingNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Evidences of Outreach ActivityDocument7 pagesSAMPLE Evidences of Outreach ActivityMaria Christine TorionNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 1Document294 pagesLecture-1 1Ben Ritche LayosNo ratings yet
- Summary ChomskyDocument3 pagesSummary ChomskyPriska GintingNo ratings yet
- Currere Quizzes Group1 Group5 - 020932Document8 pagesCurrere Quizzes Group1 Group5 - 020932jessagadon05No ratings yet
- ETI UNIT 1 MCQsDocument15 pagesETI UNIT 1 MCQsScary NightmareNo ratings yet
- EED422 202430 W D-Version 1Document47 pagesEED422 202430 W D-Version 1Maddison WillisNo ratings yet
- Tri Yuliono - KEEFEKTIFAN MEDIA PEMELAJARAN AUGMENTED REALITY TERHADAP PENGUASAAN KONSEP SISTEM PENCERNAAN MANUSIADocument20 pagesTri Yuliono - KEEFEKTIFAN MEDIA PEMELAJARAN AUGMENTED REALITY TERHADAP PENGUASAAN KONSEP SISTEM PENCERNAAN MANUSIAHSJNNo ratings yet
- A Sample of Quantitative Study - Chapter3Document20 pagesA Sample of Quantitative Study - Chapter3ANNISA FITRIANINo ratings yet
- Week 2: How To Write A Concept Paper: at The End of The Lesson, You Should Be Able ToDocument8 pagesWeek 2: How To Write A Concept Paper: at The End of The Lesson, You Should Be Able ToDharyn KhaiNo ratings yet
- 3 Robert Sokolowski - Natural and Artificial IntelligenceDocument20 pages3 Robert Sokolowski - Natural and Artificial IntelligenceVan Tien LeNo ratings yet
- Surrogate Partners' ExperienceDocument203 pagesSurrogate Partners' ExperienceDARSHINI A/P BALASINGAMNo ratings yet
- Colorful Culture and Communication PresentationDocument15 pagesColorful Culture and Communication PresentationBea Nicole BacuyagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Educ 211Document5 pagesLesson 1 Educ 211John Ralph Perez SilvaNo ratings yet
Ofel Thesis CD
Ofel Thesis CD
Uploaded by
Armel Grace Lugod-Vianzon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views15 pagesThe document outlines the architectural design process in 5 steps: (1) define the problem, (2) inventory, (3) analysis, (4) synthesis, and (5) interpretation. It then discusses architectural programming, including considerations for space requirements, building codes, site conditions, cost estimating, and functional and sociological factors. The goal is to demonstrate the process and knowledge needed to develop a feasible architectural design that addresses the problem statement.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ofel_Thesis_CD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the architectural design process in 5 steps: (1) define the problem, (2) inventory, (3) analysis, (4) synthesis, and (5) interpretation. It then discusses architectural programming, including considerations for space requirements, building codes, site conditions, cost estimating, and functional and sociological factors. The goal is to demonstrate the process and knowledge needed to develop a feasible architectural design that addresses the problem statement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views15 pagesOfel Thesis CD
Ofel Thesis CD
Uploaded by
Armel Grace Lugod-VianzonThe document outlines the architectural design process in 5 steps: (1) define the problem, (2) inventory, (3) analysis, (4) synthesis, and (5) interpretation. It then discusses architectural programming, including considerations for space requirements, building codes, site conditions, cost estimating, and functional and sociological factors. The goal is to demonstrate the process and knowledge needed to develop a feasible architectural design that addresses the problem statement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
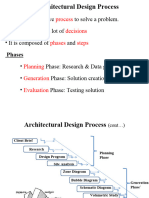
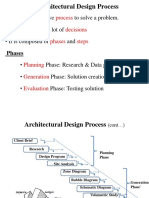
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN PROCESS
Arch. Annie Corpuz Pugeda, uap, M.A. Ed.
CONTENTS:
Steps in Architectural Design Process
Architectural Programming
Exercise on Form/Shape Consideration
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN PROCESS
1. Define the Problem (30 minutes)
2. Inventory (1hour)
3. Analysis (1 – 1 ½ hours)
4. Synthesis (4 hours)
5. Interpretation (30 minutes)
1. DESIGN PROCESS
• Scrutinize the problem title
• “hint”
• General idea of what the problem is
2. INVENTORY
• Read/highlight given requirements
• Prepare/plot site plan (scaled)
• Bubble diagram of site (zone)
• Bubble diagram of space requirements
• Modular grid of site/building plan(s)
• Location of utilities – building(s)/site
• Preliminary planning scheme(s)
3. ANALYSIS
• Review given data/requirements
• Input design considerations/criteria
• Put emphasis on the grade criteria
4. SYNTHESIS
• Schematic plan(s)
• Elevations (put character on facade)
• Sections (cut through utilities/structural)
• Perspective (site or building?)
• SDP (orientation, placement on paper,
entourages, utilities)
5. INTERPRETATION
• Refinement/finishing touches
• “wrap – up” (30 minutes before the time)
Architectural Programming
• Familiarity with basic space requirements
and parameters
Approximate square meter floor area required
per person
Room utilization
• Methods of estimation of space needs
• Limits of building efficiency
Architectural Programming
• Knowledge of content/applicability of
building/zoning code
• Easements/restrictions (site planning)
• Easements/restrictions (design)
Floor area limitations
Building height limitations
Exit requirements
Fire – proofing requirements
Corridor lengths
Stairs requirements
Construction types
Setbackss, party walls, etc.
City utility easements and right of ways
Private deed restrictions
Architectural Programming
• Familiar with basic functional considerations
• Understand influence of site conditions on
building programming/cost
Climate
Topography
Drainage
Sun and wind
Geology and soils
Vegetation
Architectural Programming
• Consider cost estimating/budget analysis
• Capable of assessing concepts and
principles
single level vs. multi – level
centralized vs. decentralized planning
linear vs. radial planning
compact vs. extended
single access vs. multi – access
Architectural Programming
• Familiar with basic
sociological/psychological aspects of
activities
“Territoriality”
Sociology of human groupings
Human “role playing”
Human perceptual characteristics
Architectural Programming
• Demonstrate judgment with respect to
feasible design
CONGRATULATIONS!
June 2006
ARCHITECTS!
You might also like
- Tietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics 7th Edition Burtis Test BankDocument8 pagesTietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics 7th Edition Burtis Test BankRicardoCarsonnbgda94% (17)
- Big Data Analytics in HealthcareDocument193 pagesBig Data Analytics in HealthcareMuhammad Alkahfi100% (3)
- Quarter 1 - Module 1 Nature Goals and Perspectives in Anthropology Sociology and Political ScienceDocument24 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 1 Nature Goals and Perspectives in Anthropology Sociology and Political Science완83% (12)
- Pre Design OutlineDocument5 pagesPre Design Outlineapi-3831280100% (1)
- Architectural Design ProcessDocument35 pagesArchitectural Design ProcessVholts Villa VitugNo ratings yet
- DraughtmanshipDocument39 pagesDraughtmanshiphanihusainiNo ratings yet
- General Design Approach For Architectural Design Board ExamDocument8 pagesGeneral Design Approach For Architectural Design Board ExamVanessa RafaelNo ratings yet
- Analisa SiteDocument51 pagesAnalisa SiteAzayaka MikuNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design Studio IDocument81 pagesArchitectural Design Studio IPoii GNo ratings yet
- Literature Review and Case StudyDocument4 pagesLiterature Review and Case StudyNimNo ratings yet
- Case Study MethodologyDocument12 pagesCase Study Methodologyshravani wodeyarNo ratings yet
- AD5 Space Planning Module 2 1Document4 pagesAD5 Space Planning Module 2 1Deanna RentegradoNo ratings yet
- Architectural DesignDocument56 pagesArchitectural DesignBiniam AssefaNo ratings yet
- Prethesis Final Report Redevelopment of Rythubazar in MehidepatnamDocument40 pagesPrethesis Final Report Redevelopment of Rythubazar in MehidepatnamAkhi Akhila50% (2)
- Desktop Case Study VIII SemDocument3 pagesDesktop Case Study VIII SemsamNo ratings yet
- Land SurveyingDocument102 pagesLand SurveyingAbdissa Bekele50% (4)
- Structural Design in IDPDocument65 pagesStructural Design in IDPMuhd IbrahimNo ratings yet
- SEM 6 - AD - Check List For Case StudyDocument1 pageSEM 6 - AD - Check List For Case StudyMohiniNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document18 pagesGroup 4Marvin GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Design ServicesDocument1 pageDesign ServicesToptop OreNo ratings yet
- Architect Scope of Services (Typical) : 1417 Palo Duro Rd. Austin, Texas 78757Document2 pagesArchitect Scope of Services (Typical) : 1417 Palo Duro Rd. Austin, Texas 78757Clarisse OdayanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Landscape Design - HamnaDocument52 pagesLecture 1 Landscape Design - HamnaHamza NaseemNo ratings yet
- By: Olyad G. (MSC)Document22 pagesBy: Olyad G. (MSC)samuelhailu853No ratings yet
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessDocument18 pagesFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessTadi Fresco Royce100% (2)
- Design 2016 SRMDocument3 pagesDesign 2016 SRMAnoop KothariNo ratings yet
- UD Brief TofR July 2009Document11 pagesUD Brief TofR July 2009Debasis DasNo ratings yet
- StuffDocument23 pagesStuffFreyaNo ratings yet
- Programing ArsDocument40 pagesPrograming ArsCandra Semakin SharappzNo ratings yet
- Case Study, Site Analysis, & Design ProgrameDocument16 pagesCase Study, Site Analysis, & Design ProgrameShruti NandiwdekarNo ratings yet
- Presentation SSESL1Document47 pagesPresentation SSESL1Ajith VandebonaNo ratings yet
- IDP III Arch5471 2016EC Research Concept DeliverablesDocument3 pagesIDP III Arch5471 2016EC Research Concept Deliverablesras yoniNo ratings yet
- Arc209-Architectural Design I: CourseDocument5 pagesArc209-Architectural Design I: CourseMurat ArapogluNo ratings yet
- Spatial Planning and Building DesignDocument50 pagesSpatial Planning and Building DesignManchala AyeshNo ratings yet
- Design ProcessDocument18 pagesDesign ProcessNejib MohNo ratings yet
- 2018-10-22 - Week 09 - Considerations SAPPK & FSRD - EnglishDocument53 pages2018-10-22 - Week 09 - Considerations SAPPK & FSRD - Englishraissa damiriNo ratings yet
- RSW#1 Basic Description of TermsDocument12 pagesRSW#1 Basic Description of TermsPrescilo Nato Palor IVNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design ProcessDocument38 pagesArchitectural Design ProcessUwaoma Uchenna Emmanuel100% (1)
- Unit - 1BDocument36 pagesUnit - 1BnihaNo ratings yet
- AR 171 P Site Planning and Landscape Architecture: Module 1.0 IntroductionDocument5 pagesAR 171 P Site Planning and Landscape Architecture: Module 1.0 IntroductionAlmae IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Deliverables For Pre-Final Thesis ReportDocument19 pagesDeliverables For Pre-Final Thesis ReportmonikaNo ratings yet
- Syallbus 3rd SemsterDocument19 pagesSyallbus 3rd Semstervishal yaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot - 2023-08-20-19-59-46-244 - Com - Android.chrome-Edit (2 Files Merged)Document2 pagesScreenshot - 2023-08-20-19-59-46-244 - Com - Android.chrome-Edit (2 Files Merged)Ar. Vignesh DhanapalNo ratings yet
- Arch Thesis - Building Programme & Design RationaleDocument21 pagesArch Thesis - Building Programme & Design RationaleSam CharlesNo ratings yet
- Arch Thesis - Building Programme & Design RationaleDocument21 pagesArch Thesis - Building Programme & Design RationaleSam CharlesNo ratings yet
- ARCH 311 - Week 1 PresentationDocument17 pagesARCH 311 - Week 1 PresentationEugeneNo ratings yet
- Site Grading SyllabusDocument7 pagesSite Grading SyllabusBabulalSahuNo ratings yet
- F2020 Urban Design Studio ARC500: To Analyze An Alike Project, The Objective Is To Evaluate: Activities Included in ADocument2 pagesF2020 Urban Design Studio ARC500: To Analyze An Alike Project, The Objective Is To Evaluate: Activities Included in AMario MagdyNo ratings yet
- Annex I Thesis Book Outline and Drawing Requirements 2023.Document7 pagesAnnex I Thesis Book Outline and Drawing Requirements 2023.Francis SubiacoNo ratings yet
- Ar 242 Module 2Document31 pagesAr 242 Module 2Andrei Nicole De VeraNo ratings yet
- Salvador Pires - Architecture As A Tool For Transformative Physical DevelopmentDocument29 pagesSalvador Pires - Architecture As A Tool For Transformative Physical DevelopmentPapers and Powerpoints from UNTL-VU Joint Conferenes in Dili100% (1)
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessDocument18 pagesFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design Process9rq5cj4w25No ratings yet
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessDocument18 pagesFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessHabtamu Hailemariam AsfawNo ratings yet
- Concrete Design NotesDocument253 pagesConcrete Design NotesBishwajit Chowdhury100% (1)
- Urban Design Lecture 1Document16 pagesUrban Design Lecture 1Maryam HeshamNo ratings yet
- Structural Layout (Key Plan) PlanningDocument12 pagesStructural Layout (Key Plan) Planningzures gustiabaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Planning and Low-Cost DesignDocument13 pagesLecture 2-Planning and Low-Cost DesignAstorianbooNo ratings yet
- Architectural Site AnalysisDocument11 pagesArchitectural Site AnalysisSrishti Dokras100% (1)
- Geotechnical EngineerDocument5 pagesGeotechnical EngineeryehnafarNo ratings yet
- Site Planning and Urban DesignDocument35 pagesSite Planning and Urban Designrain06021992No ratings yet
- The Principles of Landscape Design - 015104Document18 pagesThe Principles of Landscape Design - 015104Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- IDP III Arch5471 2016EC Final DeliverablesDocument5 pagesIDP III Arch5471 2016EC Final Deliverablesras yoniNo ratings yet
- 01 Architectural Design Process PDFDocument25 pages01 Architectural Design Process PDFashok100% (3)
- Progressive Steps in Architectural Drawing - A Step-by-Step Method for Student Draughtsmen Together with Details of Construction and DesignFrom EverandProgressive Steps in Architectural Drawing - A Step-by-Step Method for Student Draughtsmen Together with Details of Construction and DesignRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Capstone-Midterm ExamDocument11 pagesCapstone-Midterm ExamRenz PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Anin Eka SulistyawatiDocument96 pagesThesis - Anin Eka Sulistyawatisalie29296No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering NotesDocument17 pagesCivil Engineering Notesaamir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- ML Lab - Sukanya RajaDocument23 pagesML Lab - Sukanya RajaRick MitraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 About Mental HealthDocument6 pagesChapter 4 About Mental HealthPinsanity GoalsNo ratings yet
- Organisational Psychology Dissertation TopicsDocument6 pagesOrganisational Psychology Dissertation TopicsWebsiteThatWillWriteAPaperForYouSavannah100% (1)
- Ambo University College of Business and Economics Department of Economics Research Method in Economics (Econ 5042)Document75 pagesAmbo University College of Business and Economics Department of Economics Research Method in Economics (Econ 5042)Ballemi TolossaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Societal Perceptions Towards Gender Domestic ViolenceDocument31 pagesUnit 9 Societal Perceptions Towards Gender Domestic ViolenceKhalil UllahNo ratings yet
- Hexagon PPM Digital Twin Solution Sheet USDocument2 pagesHexagon PPM Digital Twin Solution Sheet USAbhishek GadhwalNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Instruction in Secondary MathematicsDocument3 pagesDifferentiated Instruction in Secondary MathematicsEditha Cuenco100% (1)
- Creative Leaders - A Decade of Contributions From Creativity and Innovation Management JournalDocument15 pagesCreative Leaders - A Decade of Contributions From Creativity and Innovation Management JournalHumberto Jacobo SolísNo ratings yet
- Https:/cbseacademic - Nic.in/web material/Curriculum22/SQP MS X/417 AI MDocument6 pagesHttps:/cbseacademic - Nic.in/web material/Curriculum22/SQP MS X/417 AI MSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hist Bang Maths B: Fatema Aynoon JuienaDocument2 pagesHist Bang Maths B: Fatema Aynoon JuienaKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning Curve 1693642530Document10 pagesDeep Learning Curve 1693642530omar4programmingNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Evidences of Outreach ActivityDocument7 pagesSAMPLE Evidences of Outreach ActivityMaria Christine TorionNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 1Document294 pagesLecture-1 1Ben Ritche LayosNo ratings yet
- Summary ChomskyDocument3 pagesSummary ChomskyPriska GintingNo ratings yet
- Currere Quizzes Group1 Group5 - 020932Document8 pagesCurrere Quizzes Group1 Group5 - 020932jessagadon05No ratings yet
- ETI UNIT 1 MCQsDocument15 pagesETI UNIT 1 MCQsScary NightmareNo ratings yet
- EED422 202430 W D-Version 1Document47 pagesEED422 202430 W D-Version 1Maddison WillisNo ratings yet
- Tri Yuliono - KEEFEKTIFAN MEDIA PEMELAJARAN AUGMENTED REALITY TERHADAP PENGUASAAN KONSEP SISTEM PENCERNAAN MANUSIADocument20 pagesTri Yuliono - KEEFEKTIFAN MEDIA PEMELAJARAN AUGMENTED REALITY TERHADAP PENGUASAAN KONSEP SISTEM PENCERNAAN MANUSIAHSJNNo ratings yet
- A Sample of Quantitative Study - Chapter3Document20 pagesA Sample of Quantitative Study - Chapter3ANNISA FITRIANINo ratings yet
- Week 2: How To Write A Concept Paper: at The End of The Lesson, You Should Be Able ToDocument8 pagesWeek 2: How To Write A Concept Paper: at The End of The Lesson, You Should Be Able ToDharyn KhaiNo ratings yet
- 3 Robert Sokolowski - Natural and Artificial IntelligenceDocument20 pages3 Robert Sokolowski - Natural and Artificial IntelligenceVan Tien LeNo ratings yet
- Surrogate Partners' ExperienceDocument203 pagesSurrogate Partners' ExperienceDARSHINI A/P BALASINGAMNo ratings yet
- Colorful Culture and Communication PresentationDocument15 pagesColorful Culture and Communication PresentationBea Nicole BacuyagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Educ 211Document5 pagesLesson 1 Educ 211John Ralph Perez SilvaNo ratings yet