Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsWeek 1 Tutorials
Week 1 Tutorials
Uploaded by
ashwinraj562The document discusses fire safety regulations and considerations for combustible cladding materials. It then provides tutorials on thermal quantities and units used in heat transfer calculations. Specific examples are given for 1D steady state heat transfer problems with different types of boundary conditions, including temperature boundaries, heat transfer coefficients, and calculating heat flow through layers using thermal resistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Video 1 (Of 13) Introduction - Heat Conduction and Boundary ConditionsDocument9 pagesVideo 1 (Of 13) Introduction - Heat Conduction and Boundary ConditionsEscape VelocityNo ratings yet
- FME9 Lecture Guide 2 - Steady State One Dimensional Conduction Heat TransferDocument7 pagesFME9 Lecture Guide 2 - Steady State One Dimensional Conduction Heat Transfergevgev0929No ratings yet
- Refrigeration Load Sizing For WalkDocument23 pagesRefrigeration Load Sizing For WalkKeioleNo ratings yet
- Basic Heat Transfer - 4101Document105 pagesBasic Heat Transfer - 4101Joy PalitNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Lecture Slide: Dr. Paul S. NnamchiDocument34 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Lecture Slide: Dr. Paul S. NnamchilotannaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document18 pagesLecture 3ssaalleehh340No ratings yet
- GATE Material. Heat Transfer. ChemicalDocument71 pagesGATE Material. Heat Transfer. ChemicalsureshNo ratings yet
- Thermal ConductivityDocument17 pagesThermal ConductivityKennedykimanthiNo ratings yet
- Thermofluids Level5 - Lecture 6 - HeatTransfer ConductionDocument25 pagesThermofluids Level5 - Lecture 6 - HeatTransfer Conductionkanuni41No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument26 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionGeraldine ChanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Unit 4Document28 pagesMechanical Unit 4bhaskarraj1714No ratings yet
- 2019-Me-22 (Waheed Ul Hassan) 02....Document8 pages2019-Me-22 (Waheed Ul Hassan) 02....Amroz AfzalNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity - WikipediaDocument13 pagesThermal Conductivity - WikipediaDomagoj ButumovićNo ratings yet
- Class 03Document11 pagesClass 03Dia' AfanehNo ratings yet
- Cla1 Batch1 Key-1Document5 pagesCla1 Batch1 Key-1Sem 4thNo ratings yet
- Thesis-Thermal ConductityDocument181 pagesThesis-Thermal ConductityAl BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - BTF1513Document21 pagesChapter 3 - BTF1513Amirul HaziqNo ratings yet
- Climatology L7-L8Document20 pagesClimatology L7-L8MansaNo ratings yet
- Transferencia de CalorDocument53 pagesTransferencia de CalorIvonne FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TheoryDocument32 pagesHeat Transfer TheoryNelson LibidoNo ratings yet
- Practical Conduction Heat TransferDocument14 pagesPractical Conduction Heat TransfertskNo ratings yet
- 3 Heat and Solute Transport SlidesDocument52 pages3 Heat and Solute Transport Slidesbugrailgin4No ratings yet
- C17H PDFDocument40 pagesC17H PDFramau619No ratings yet
- Final hmt-1 PDFDocument211 pagesFinal hmt-1 PDFPoyyamozhi Nadesan RanjithNo ratings yet
- 3 Materials Prperties7Document10 pages3 Materials Prperties7ArthurNo ratings yet
- Basic Modes of Heat TransferDocument15 pagesBasic Modes of Heat Transfermeraj100% (1)
- 1) Linear Heat Conduction SlidesDocument11 pages1) Linear Heat Conduction SlidesNael ShunnarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Pr0perties of CeramicsDocument5 pagesThermal Pr0perties of CeramicsaufaNo ratings yet
- Climate and Built Form - IDocument51 pagesClimate and Built Form - IShafnaFawazNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer.: SolnDocument14 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer.: SolnGaettan KatambaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document22 pagesLecture 5ssaalleehh340No ratings yet
- CP: Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure. CV: Heat Capacity at Constant Volume. CP CVDocument10 pagesCP: Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure. CV: Heat Capacity at Constant Volume. CP CVMohammed Al-samarraeNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document3 pagesCH 1Lotfi NaftiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document24 pagesLecture 4ssaalleehh340No ratings yet
- CONDUCTIONDocument53 pagesCONDUCTIONAtharv PahujaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Heat TransferDocument85 pagesBasics of Heat Transferchirag taterNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties (Repaired)Document5 pagesThermal Properties (Repaired)Muhammad Al-BaghdadyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Steady Heat Conduction PDFDocument62 pagesChapter 2 - Steady Heat Conduction PDFAroon KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Guide 1 in Heat TransferDocument4 pagesLecture Guide 1 in Heat TransferCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- HMT Notes-1 PDFDocument85 pagesHMT Notes-1 PDFPraveenNo ratings yet
- Climatology-Unit III 3rd SEMDocument14 pagesClimatology-Unit III 3rd SEMflower lilyNo ratings yet
- HT Ut-1Document67 pagesHT Ut-1P RavisankarNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass TranferDocument331 pagesHeat and Mass TranferVandittJhingranNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Equation Heat Conduction Equation: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDocument50 pagesHeat Conduction Equation Heat Conduction Equation: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsCarmine Di VilioNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer CHE0301 LECTURE 2 Basics of Heat TransferDocument21 pagesHeat Transfer CHE0301 LECTURE 2 Basics of Heat TransfermiraNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lecture NotesDocument66 pagesHeat Transfer Lecture NotesJustin100% (1)
- Insulating RefractoriesDocument10 pagesInsulating RefractoriesAbdulBasitNo ratings yet
- HMT Solved QBDocument85 pagesHMT Solved QBNaveen PrabhuNo ratings yet
- CHE332:Heat Transfer Operations Lecture 2: ConductionDocument20 pagesCHE332:Heat Transfer Operations Lecture 2: ConductionRana Ahsan AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Conduction 2Document17 pagesChapter 2 Conduction 2Diwas GhimireNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction Mec551 AmanDocument91 pagesCH1 - Introduction Mec551 AmanqistinaNo ratings yet
- ZF 72 Gvy 9 L 6 Ynm 0 NDocument44 pagesZF 72 Gvy 9 L 6 Ynm 0 NThaslim ThaslimNo ratings yet
- Thermal ConductivityDocument34 pagesThermal ConductivityBalaji ARNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument68 pagesThermal PhysicsRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Abbas Wahbii1Document15 pagesAbbas Wahbii1gggggggNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Part BDocument6 pagesUnit 3 - Part BMANSOOR REEMANo ratings yet
- Treatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsFrom EverandTreatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
Week 1 Tutorials
Week 1 Tutorials
Uploaded by
ashwinraj5620 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesThe document discusses fire safety regulations and considerations for combustible cladding materials. It then provides tutorials on thermal quantities and units used in heat transfer calculations. Specific examples are given for 1D steady state heat transfer problems with different types of boundary conditions, including temperature boundaries, heat transfer coefficients, and calculating heat flow through layers using thermal resistance.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses fire safety regulations and considerations for combustible cladding materials. It then provides tutorials on thermal quantities and units used in heat transfer calculations. Specific examples are given for 1D steady state heat transfer problems with different types of boundary conditions, including temperature boundaries, heat transfer coefficients, and calculating heat flow through layers using thermal resistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesWeek 1 Tutorials
Week 1 Tutorials
Uploaded by
ashwinraj562The document discusses fire safety regulations and considerations for combustible cladding materials. It then provides tutorials on thermal quantities and units used in heat transfer calculations. Specific examples are given for 1D steady state heat transfer problems with different types of boundary conditions, including temperature boundaries, heat transfer coefficients, and calculating heat flow through layers using thermal resistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
Discussions: fire safety
regulations
- who are interested?
& what are the considerations?
£xxx millions later:
Grenfell: no combustible material
should be used in cladding.
Sensible?
Fire protection to bridges:
necessary?
Heat transfer tutorials
Thermal Quantities & Units
• Temperature
• Time
• Dimensions
• Energy
• Heat
• Density
• Thermal conductivity
• Specific heat
• Heat transfer coefficient
Thermal Quantities & Units
• Temperature (K or C), Time (s),
Dimensions (m)
• Energy (J)/heat (W=J/s)
• Density (kg/m3)
• Thermal conductivity (W/(m.K))
• Specific heat (J/(kg.K) or J/(kg.C))
• Heat transfer coefficient (W/(m2.K))
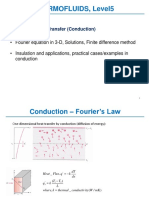
Tutorial: 1-D steady state heat
transfer with heat boundary
conditionns
1. Temperature boundary condition (example: 1-D
steady state heat condition)
Consider a thickness made of n-layers of different materials, each having
the same thermal conductivity. The temperatures of the two sides are T 1
and Tn+1. Assuming steady state heat transfer, find the total heat flow and
temperatures of the different layers.
Example for boundary condition 3: steady state
heat transfer with heat transfer coefficients
The thermal
boundary
conditions in
example 1.1 are
changed to Type
3, with Tf and hf
on the fire side
and Ta and ha on
the air side. Find
the heat transfer.
Thermal resistance
In steady state heat transfer:
Heat flow per unit area through an assembly
of objects = temperature difference between
the two surfaces of the assembly/thermal
resistance of the assembly
Identifying heat transfer
boundary conditions
1. Thermal boundary conditions
You might also like
- Video 1 (Of 13) Introduction - Heat Conduction and Boundary ConditionsDocument9 pagesVideo 1 (Of 13) Introduction - Heat Conduction and Boundary ConditionsEscape VelocityNo ratings yet
- FME9 Lecture Guide 2 - Steady State One Dimensional Conduction Heat TransferDocument7 pagesFME9 Lecture Guide 2 - Steady State One Dimensional Conduction Heat Transfergevgev0929No ratings yet
- Refrigeration Load Sizing For WalkDocument23 pagesRefrigeration Load Sizing For WalkKeioleNo ratings yet
- Basic Heat Transfer - 4101Document105 pagesBasic Heat Transfer - 4101Joy PalitNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Lecture Slide: Dr. Paul S. NnamchiDocument34 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Lecture Slide: Dr. Paul S. NnamchilotannaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document18 pagesLecture 3ssaalleehh340No ratings yet
- GATE Material. Heat Transfer. ChemicalDocument71 pagesGATE Material. Heat Transfer. ChemicalsureshNo ratings yet
- Thermal ConductivityDocument17 pagesThermal ConductivityKennedykimanthiNo ratings yet
- Thermofluids Level5 - Lecture 6 - HeatTransfer ConductionDocument25 pagesThermofluids Level5 - Lecture 6 - HeatTransfer Conductionkanuni41No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument26 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionGeraldine ChanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Unit 4Document28 pagesMechanical Unit 4bhaskarraj1714No ratings yet
- 2019-Me-22 (Waheed Ul Hassan) 02....Document8 pages2019-Me-22 (Waheed Ul Hassan) 02....Amroz AfzalNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity - WikipediaDocument13 pagesThermal Conductivity - WikipediaDomagoj ButumovićNo ratings yet
- Class 03Document11 pagesClass 03Dia' AfanehNo ratings yet
- Cla1 Batch1 Key-1Document5 pagesCla1 Batch1 Key-1Sem 4thNo ratings yet
- Thesis-Thermal ConductityDocument181 pagesThesis-Thermal ConductityAl BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - BTF1513Document21 pagesChapter 3 - BTF1513Amirul HaziqNo ratings yet
- Climatology L7-L8Document20 pagesClimatology L7-L8MansaNo ratings yet
- Transferencia de CalorDocument53 pagesTransferencia de CalorIvonne FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TheoryDocument32 pagesHeat Transfer TheoryNelson LibidoNo ratings yet
- Practical Conduction Heat TransferDocument14 pagesPractical Conduction Heat TransfertskNo ratings yet
- 3 Heat and Solute Transport SlidesDocument52 pages3 Heat and Solute Transport Slidesbugrailgin4No ratings yet
- C17H PDFDocument40 pagesC17H PDFramau619No ratings yet
- Final hmt-1 PDFDocument211 pagesFinal hmt-1 PDFPoyyamozhi Nadesan RanjithNo ratings yet
- 3 Materials Prperties7Document10 pages3 Materials Prperties7ArthurNo ratings yet
- Basic Modes of Heat TransferDocument15 pagesBasic Modes of Heat Transfermeraj100% (1)
- 1) Linear Heat Conduction SlidesDocument11 pages1) Linear Heat Conduction SlidesNael ShunnarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Pr0perties of CeramicsDocument5 pagesThermal Pr0perties of CeramicsaufaNo ratings yet
- Climate and Built Form - IDocument51 pagesClimate and Built Form - IShafnaFawazNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer.: SolnDocument14 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer.: SolnGaettan KatambaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document22 pagesLecture 5ssaalleehh340No ratings yet
- CP: Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure. CV: Heat Capacity at Constant Volume. CP CVDocument10 pagesCP: Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure. CV: Heat Capacity at Constant Volume. CP CVMohammed Al-samarraeNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document3 pagesCH 1Lotfi NaftiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document24 pagesLecture 4ssaalleehh340No ratings yet
- CONDUCTIONDocument53 pagesCONDUCTIONAtharv PahujaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Heat TransferDocument85 pagesBasics of Heat Transferchirag taterNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties (Repaired)Document5 pagesThermal Properties (Repaired)Muhammad Al-BaghdadyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Steady Heat Conduction PDFDocument62 pagesChapter 2 - Steady Heat Conduction PDFAroon KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Guide 1 in Heat TransferDocument4 pagesLecture Guide 1 in Heat TransferCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- HMT Notes-1 PDFDocument85 pagesHMT Notes-1 PDFPraveenNo ratings yet
- Climatology-Unit III 3rd SEMDocument14 pagesClimatology-Unit III 3rd SEMflower lilyNo ratings yet
- HT Ut-1Document67 pagesHT Ut-1P RavisankarNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass TranferDocument331 pagesHeat and Mass TranferVandittJhingranNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Equation Heat Conduction Equation: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDocument50 pagesHeat Conduction Equation Heat Conduction Equation: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsCarmine Di VilioNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer CHE0301 LECTURE 2 Basics of Heat TransferDocument21 pagesHeat Transfer CHE0301 LECTURE 2 Basics of Heat TransfermiraNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lecture NotesDocument66 pagesHeat Transfer Lecture NotesJustin100% (1)
- Insulating RefractoriesDocument10 pagesInsulating RefractoriesAbdulBasitNo ratings yet
- HMT Solved QBDocument85 pagesHMT Solved QBNaveen PrabhuNo ratings yet
- CHE332:Heat Transfer Operations Lecture 2: ConductionDocument20 pagesCHE332:Heat Transfer Operations Lecture 2: ConductionRana Ahsan AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Conduction 2Document17 pagesChapter 2 Conduction 2Diwas GhimireNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction Mec551 AmanDocument91 pagesCH1 - Introduction Mec551 AmanqistinaNo ratings yet
- ZF 72 Gvy 9 L 6 Ynm 0 NDocument44 pagesZF 72 Gvy 9 L 6 Ynm 0 NThaslim ThaslimNo ratings yet
- Thermal ConductivityDocument34 pagesThermal ConductivityBalaji ARNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument68 pagesThermal PhysicsRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Abbas Wahbii1Document15 pagesAbbas Wahbii1gggggggNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Part BDocument6 pagesUnit 3 - Part BMANSOOR REEMANo ratings yet
- Treatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsFrom EverandTreatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)