Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3rd ULMuscles of Pectoral Region
3rd ULMuscles of Pectoral Region
Uploaded by
x8w6df2fxw0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views19 pagesThis document describes the muscles of the pectoral region, including the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, subclavius, and associated fascia. The pectoralis major has two heads of origin and inserts via a bilaminar tendon. It functions to flex, adduct, and medially rotate the arm. The pectoralis minor lies deep to the pectoralis major and draws the scapula downwards. The subclavius muscle depresses and steadies the clavicle. The clavipectoral fascia surrounds these muscles and transmits structures like the cephalic vein.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the muscles of the pectoral region, including the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, subclavius, and associated fascia. The pectoralis major has two heads of origin and inserts via a bilaminar tendon. It functions to flex, adduct, and medially rotate the arm. The pectoralis minor lies deep to the pectoralis major and draws the scapula downwards. The subclavius muscle depresses and steadies the clavicle. The clavipectoral fascia surrounds these muscles and transmits structures like the cephalic vein.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views19 pages3rd ULMuscles of Pectoral Region
3rd ULMuscles of Pectoral Region
Uploaded by
x8w6df2fxwThis document describes the muscles of the pectoral region, including the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, subclavius, and associated fascia. The pectoralis major has two heads of origin and inserts via a bilaminar tendon. It functions to flex, adduct, and medially rotate the arm. The pectoralis minor lies deep to the pectoralis major and draws the scapula downwards. The subclavius muscle depresses and steadies the clavicle. The clavipectoral fascia surrounds these muscles and transmits structures like the cephalic vein.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
MSK(101-1)
Academic year: 2022/2023
ANATOMY DEPARTMENT
Pectoral Region
Prof. Dr. Hayam Elsaady Farhoud
Muscles of the pectoral region
Pectoralis major muscle
- It is the most superficial muscle &It is fan shaped.
Pectoralis major muscle
Origin: 1. Clavicular head: from the
medial 1/2 of the anterior surface of the
clavicle
2. Sternocostal head: from half
of the anterior surface of the sternum ,
upper 6 costal cartilages and from
External oblique aponeurosis
Insertion:
into the lateral lip of bicipital groove.
By bilaminar tendon
Nerve supply: medial and lateral pectoral nerves.
Action:1- The clavicular head, flexes the arm at
the shoulder joint.
2- The sternocostal head, bring the
flexed arm to the resting position. In
climbing ,pulls the body upward
3- The 2 heads produce adduction , NB: 2 heads of origin,
2 (bilaminar) tendon of insertion and
flextion and medial rotation of the arm. 2 nerve supply
RELATIONS OF PECTORALIS MAJOR
The pectoralis major lies over the
1-pectoralis minor
2-the clavipectoral fascia
3-separated from the deltoid by the delto-pectoral groove which lodges the cephalic vein
4-deltoid branch of thoraco-acromial artery
5-delto-pectoral lymph nodes.
Pectoralis minor muscle
- The pectoralis minor lies underneath
pectoralis major.
Origin: from the 3 rd to the 5 th ribs
close to their costal cartilages.
Insertion: into the medial border and
upper surface of coracoid process of the
scapula.
Nerve supply: medial and lateral
pectoral nerves.
Action:
1. It pulls the shoulder downwards
and forwards in pushing (It draws
the scapula downwards and
forwards, i.e. it protracts the
scapula. In addition, the muscle
depresses the point of the shoulder).
2. It elevates the 3 rd to 5 th ribs
when the shoulder is fixed.
Relation of pectoralis minor
-lies underneath pectoralis major.
-It bridges over the axillary artery and related cords of brachial plexus.
-lateral pectoral nerve passing above the muscle.
-medial pectoral nerve piercing the muscle.
-lateral thoracic artery and pectoral group of axillary lymph nodes, along the lower border of the muscle.
Subclavius M.- It is a small muscle that lies directly underneath the clavicle.
Origin: from the junction of the first rib and its costal cartilages.
Insertion: into the groove on the inferior surface of the middle 1/3 of the clavicle.
Nerve supply: nerve to subclavius (from upper trunk of brachial plexus)
Action: depresses the clavicle and steadies it during movement of the shoulder girdle.
Pectoral Fascia: is a strong
sheet of connective tissue
that lies deep to pectoralis
major muscle.
1-Axillary fascia: forms
the floor of the axilla
2-Clavipectoral fascia : lies
deep to the clavicular
head of pectoralis major
muscle.
-Clavipectoral fascia is attached to:
Superiorly: divides into 2 layers which surround the subclavius muscle and attaches to the lips
of the groove for subclavius on the inferior surface of the clavicle.
In the middle: divided into 2 layers to surround pectoralis minor muscle.
In the lower part: attached to the fascial floor of the axilla and called suspensory ligament of the axilla.
Medially: attached to the 1st and 2nd costal cartilages and the anterior intercostal membrane between them.
Laterally: attached to coracoid process and coraco-clavicular ligament.
NB: Just below the subclavius the fascia is especially thickened to form the costo-coracoid ligament which
extends along the lower border of the subclavius, from the 1st rib medially to the coracoid process laterally.
The clavipectoral fascia is pierced by (CaLL)
1-- Cephalic vein
2- Thoracoacromial artery.
3- Lateral pectoral nerve
4- Lymph vessels, from the infraclavicular lymph
nodes.
Function:
I) It protects the contents of the axilla by filling the
interval between the clavicle and pectoralis minor
muscle.
2) The suspensory ligament of the axilla raises the
floor of the axilla during abduction of the arm
You might also like
- 4.06 Recording Your Cardiovascular Workout - SchoologyDocument3 pages4.06 Recording Your Cardiovascular Workout - SchoologyMcKayla ChurchNo ratings yet
- OSCE Guide, University of Queensland School of MedicineDocument86 pagesOSCE Guide, University of Queensland School of MedicineDarren Pang100% (2)
- Convict Conditioning LogDocument16 pagesConvict Conditioning Logalxfromplanetx100% (1)
- Applied Strongman Training Part 1Document48 pagesApplied Strongman Training Part 1shaft181100% (10)
- SAMBO WrestlingDocument117 pagesSAMBO WrestlingShaiabbNo ratings yet
- 4 Pectoral RegionDocument62 pages4 Pectoral RegionFarrukh ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Pectoral Region & BreastDocument52 pagesPectoral Region & BreastemanNo ratings yet
- 6.the Pectoral Region and The AxillaDocument97 pages6.the Pectoral Region and The AxillaGish KioiNo ratings yet
- Pectoral Region and AxillaDocument25 pagesPectoral Region and AxillaSelva pandi100% (1)
- 2 - Shoulder Girdle PDFDocument38 pages2 - Shoulder Girdle PDFMayra FlorNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Anatomy 1Document6 pagesUpper Limb Anatomy 1shahab shamsiNo ratings yet
- L1 Anatomy of The Lungs, Pleural Cavities and Respiratory Muscles - L4 - Anatomy of The Chest Wall and DiaphragmDocument8 pagesL1 Anatomy of The Lungs, Pleural Cavities and Respiratory Muscles - L4 - Anatomy of The Chest Wall and DiaphragmAurora TamNo ratings yet
- Summary of Muscles in The ShoulderDocument3 pagesSummary of Muscles in The ShoulderDaniel GraceNo ratings yet
- MUSCLES TabulatedDocument12 pagesMUSCLES Tabulateddncm.alejandroNo ratings yet
- MUSCLES of The UPPER LIMBDocument12 pagesMUSCLES of The UPPER LIMBdncm.alejandroNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of The Forearm: A CAL Package Designed By-Pratik SinhaDocument24 pagesGross Anatomy of The Forearm: A CAL Package Designed By-Pratik SinhaManvi JogiNo ratings yet
- 3-Pectoral RegionDocument39 pages3-Pectoral Regionsama rasmyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper Limb: 1) ClavicleDocument4 pagesAnatomy - Upper Limb: 1) ClavicleJasmine TeoNo ratings yet
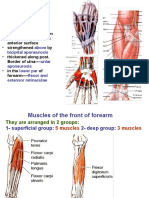
- Front of ForearmDocument19 pagesFront of ForearmAditya AnandNo ratings yet
- RRS Anatomy wordPDF 240210 213926Document56 pagesRRS Anatomy wordPDF 240210 213926beneficialboxer9237No ratings yet
- Front of Forearm LecturesDocument19 pagesFront of Forearm LecturesInsyirah JohariNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 13Document11 pagesAnatomy Lec 13Sajad H. HassanNo ratings yet
- Final W5 L2 Shoulder JointDocument36 pagesFinal W5 L2 Shoulder JointOmar OsamaNo ratings yet
- 02upper L SmmryDocument50 pages02upper L SmmryISMAIL HAMZANo ratings yet
- The Arm PDFDocument19 pagesThe Arm PDFMayra FlorNo ratings yet
- Pectoral Region KJR (1) - 2Document36 pagesPectoral Region KJR (1) - 2MahiNo ratings yet
- 2 Shoulder Girdle JointsDocument29 pages2 Shoulder Girdle JointsFarrukh ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Posterior Triangle of The Neck: Maribel G. Castro-Enano, M.D. CPU College of MedicineDocument28 pagesPosterior Triangle of The Neck: Maribel G. Castro-Enano, M.D. CPU College of MedicineAlexandru GusacinschiNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Bony PelvisDocument5 pagesGRDA Intro Bony PelvisKingNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Inferior Thoracic ApertureDocument7 pagesThoracic Outlet Syndrome Inferior Thoracic ApertureerilarchiNo ratings yet
- Schumann 1. ExtremiitiesDocument12 pagesSchumann 1. ExtremiitiesCrystal AyalaNo ratings yet
- BRACHIAL PLEXUS (Autosaved)Document51 pagesBRACHIAL PLEXUS (Autosaved)Coy EnNo ratings yet
- RRS BlockDocument411 pagesRRS Blockasemashraf390No ratings yet
- Front of ArmDocument23 pagesFront of ArmNicoleta PSNo ratings yet
- Musl of CHESTDocument4 pagesMusl of CHESTVrushab ManojNo ratings yet
- 0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSDocument24 pages0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSArijeet77No ratings yet
- Upper Limp Questions (ANSWERED)Document57 pagesUpper Limp Questions (ANSWERED)kazelio2017No ratings yet
- Special Arthorology of The ForelimbDocument34 pagesSpecial Arthorology of The ForelimbTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Flexor Region of The ForearmDocument13 pagesFlexor Region of The ForearmNeil DolendoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document17 pagesAnatomy 1Uljana NasonovaNo ratings yet
- Pectoral Girdle and Shoulder JointDocument55 pagesPectoral Girdle and Shoulder JointGaurav ThapaNo ratings yet
- DMS (PBL3) Mohamad Arbian Karim FMUI20Document24 pagesDMS (PBL3) Mohamad Arbian Karim FMUI20Mohamad Arbian KarimNo ratings yet
- Back of ForearmDocument25 pagesBack of ForearmAditya AnandNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Shoulder MusclesDocument12 pagesAnatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Shoulder MusclesluizamgoNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Anatomy SummaryDocument4 pagesShoulder Anatomy Summaryapi-246259817No ratings yet
- 02.muscles of Pectoral Girdle and MoreDocument71 pages02.muscles of Pectoral Girdle and MoremathivannaninthujanNo ratings yet
- Erb's PointDocument14 pagesErb's PointRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Topics IA1 AnatDocument9 pagesDiscussion Topics IA1 AnatPhysics TutionNo ratings yet
- Ana 211 The Brachial PlexusDocument10 pagesAna 211 The Brachial PlexusAmadi CedarNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The TRUNKDocument7 pagesMuscles of The TRUNKAjeesh NelsonNo ratings yet
- Special Arthrology of The ForelimbDocument37 pagesSpecial Arthrology of The ForelimbTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Back, Upper Limb, Lower Limb MusclesDocument36 pagesBack, Upper Limb, Lower Limb Muscleseyash.6No ratings yet
- Back Study SheetDocument6 pagesBack Study SheetjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- MSK SummaryDocument5 pagesMSK SummaryRahla KhanNo ratings yet
- neck-FUE FinalDocument84 pagesneck-FUE Finalhannalojo21No ratings yet
- UW Notes - 11 - MSK ArrangedDocument66 pagesUW Notes - 11 - MSK ArrangedDor BenayounNo ratings yet
- Elbow and Antebrachium NotesDocument8 pagesElbow and Antebrachium NoteschadNo ratings yet
- Anat Compart 203Document52 pagesAnat Compart 203Saidu BobbojiNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY: The Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Spaces Axilla The ArmDocument88 pagesANATOMY: The Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Spaces Axilla The ArmNur Liyana MohamadNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Muscular Systemvincealgarme09No ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ Liners by NK PS MBBS Student TVMCHDocument32 pagesAnatomy MCQ Liners by NK PS MBBS Student TVMCHSanjith A.KNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Units 9-12 ObjectivesDocument18 pagesAnatomy Units 9-12 ObjectivespoNo ratings yet
- Thoracic and Coracoid Arteries In Two Families of Birds, Columbidae and HirundinidaeFrom EverandThoracic and Coracoid Arteries In Two Families of Birds, Columbidae and HirundinidaeNo ratings yet
- Ten Key Steps To Learning AnatomyDocument10 pagesTen Key Steps To Learning AnatomypetitelegNo ratings yet
- LCD - Neuroanatomy and Upper LimbDocument125 pagesLCD - Neuroanatomy and Upper LimbLa Woon ChoNo ratings yet
- Aesthetics Vol1Document14 pagesAesthetics Vol1tomNo ratings yet
- HOPEDocument3 pagesHOPEAndrea Venesse NaldaNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Shoulder Are The HumerusDocument4 pagesBones of The Shoulder Are The HumerusHello RainbowNo ratings yet
- Oah Hip Bursitis Exercises r2Document4 pagesOah Hip Bursitis Exercises r2CoupleFF BRNo ratings yet
- First Mbbs Syllabus 21 03 2020 Final FullDocument129 pagesFirst Mbbs Syllabus 21 03 2020 Final FullDeepan rajNo ratings yet
- Kalkaneal OsteotomiDocument11 pagesKalkaneal Osteotomitravma777No ratings yet
- Doppler Ultrasonography of Lower Extremity ArterieDocument35 pagesDoppler Ultrasonography of Lower Extremity Arterierizki100% (1)
- Yoga For Kids Simple First Step PDFDocument74 pagesYoga For Kids Simple First Step PDFAnh DN100% (4)
- Brachial Plexus InjuriesDocument64 pagesBrachial Plexus Injuriesprashanth naikNo ratings yet
- The Bowen Therapy Procedures by Jonathan Damonte...Document39 pagesThe Bowen Therapy Procedures by Jonathan Damonte...czirjak zsofia100% (2)
- Steven Angelo E. Cruz, PTRPDocument130 pagesSteven Angelo E. Cruz, PTRPJoeNo ratings yet
- ITIKITIKDocument2 pagesITIKITIKCyril Mae VillavelezNo ratings yet
- Week 7 notes - HSO202Document5 pagesWeek 7 notes - HSO202eliza.tolfreyNo ratings yet
- Management of Primary Anterior Shoulder Dislocations: A Narrative ReviewDocument8 pagesManagement of Primary Anterior Shoulder Dislocations: A Narrative Reviewamal.fathullahNo ratings yet
- Superior Angle (A) of The Shoulder Blade Just Above The Scapular Spine (FigureDocument4 pagesSuperior Angle (A) of The Shoulder Blade Just Above The Scapular Spine (FigureVanessa Yvonne GurtizaNo ratings yet
- Distal Humeral Fractures - Basic Management Concepts: Dr. Jeffrey Kwee, PGY3 August 22, 2006Document27 pagesDistal Humeral Fractures - Basic Management Concepts: Dr. Jeffrey Kwee, PGY3 August 22, 2006sukhee_baatarNo ratings yet
- 5-Scapular RegionDocument36 pages5-Scapular Regionsama rasmyNo ratings yet
- Posterior Compart. ForearmDocument12 pagesPosterior Compart. ForearmSyed NangyalNo ratings yet
- Summary of Muller's "My System"Document12 pagesSummary of Muller's "My System"andrew colgoni100% (4)
- Activity 2Document6 pagesActivity 2Kairós Isaí Lizarraga DíazNo ratings yet
- Handout of Acupuncture PointsDocument105 pagesHandout of Acupuncture PointsAlexander AntonakakisNo ratings yet
- Trigger Finger: Dr. Aswedi Putra, SP - OT, FICS Universitas MalahayatiDocument9 pagesTrigger Finger: Dr. Aswedi Putra, SP - OT, FICS Universitas MalahayatiJessy WidiyantiNo ratings yet
- K3R WalkingDocument124 pagesK3R WalkingKimkimNo ratings yet