Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsTSEG Lesson 1 Science Framework in The K 12 LMS
TSEG Lesson 1 Science Framework in The K 12 LMS
Uploaded by
Maligo, Renalyn P.Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Unit 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grades: An OverviewDocument43 pagesUnit 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grades: An OverviewJenjen Gammad81% (16)
- Answer The Following Questions BelowDocument3 pagesAnswer The Following Questions BelowJervyn GuiananNo ratings yet
- Screen-Based Online Learning Will Change Kids' Brains. Are We Ready For That - Technology - The GuardianDocument1 pageScreen-Based Online Learning Will Change Kids' Brains. Are We Ready For That - Technology - The GuardianEgemen TanikNo ratings yet
- Lambda Solutions A Guide To Competency Based Training For Organizational Excellence Part 1Document6 pagesLambda Solutions A Guide To Competency Based Training For Organizational Excellence Part 1JStoneNo ratings yet
- 8D TemplateDocument7 pages8D Templatemuhammad_mmd100% (1)
- Malaysia Primary Science Curriculum 1Document19 pagesMalaysia Primary Science Curriculum 1syuhaimisalimNo ratings yet
- The Science Framework in The K To 12Document66 pagesThe Science Framework in The K To 12Tedlyn Joy Pagaling Espino75% (4)
- Elem-9 ReviewerDocument5 pagesElem-9 ReviewerCharisse DeirdreNo ratings yet
- Module Introduction: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: An OverviewDocument8 pagesModule Introduction: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: An OverviewJervyn GuiananNo ratings yet
- Module 2 M. GonzalesDocument3 pagesModule 2 M. GonzalesElton John RestonNo ratings yet
- Module-1 (Science)Document9 pagesModule-1 (Science)Jessa SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Basic Education Curriculum: Luardo Ruel Jr. F. 2A1Document23 pagesK To 12 Basic Education Curriculum: Luardo Ruel Jr. F. 2A1Cilena DomenicinaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science ModuleDocument22 pagesTeaching Science ModuleHassel AbayonNo ratings yet
- Aims of Science: By: Judy Ann Fanuncio Jay Xanderlyn GallegosDocument10 pagesAims of Science: By: Judy Ann Fanuncio Jay Xanderlyn Gallegosjayxanderlyn gallegosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Science Framework in K To 12Document10 pagesLesson 1 The Science Framework in K To 12bpsb4ddzctNo ratings yet
- EEd 4-Lesson 1Document10 pagesEEd 4-Lesson 1Mark Edrill ViñasNo ratings yet
- Science Education Curriculum Oct20Document40 pagesScience Education Curriculum Oct20SAMAR Vernalyn D.No ratings yet
- Vision For Science Education: Scientific PracticesDocument33 pagesVision For Science Education: Scientific PracticesNorlyn Mae ComerosNo ratings yet
- MS 613 Methods of ResearchDocument34 pagesMS 613 Methods of ResearchSelino CruzNo ratings yet
- What Is Science ?: Science Naturalistic Universe NaturalDocument16 pagesWhat Is Science ?: Science Naturalistic Universe NaturalItsna Rona Wahyu AstutiNo ratings yet
- LSK3701 - Notes Unit 1Document14 pagesLSK3701 - Notes Unit 1Annemarie RossouwNo ratings yet
- Tseg 1Document25 pagesTseg 1Mary Ann Andes CaruruanNo ratings yet
- Readings For Week 2 I. The Science Framework in The K To 12Document5 pagesReadings For Week 2 I. The Science Framework in The K To 12StarryGailSanchezNo ratings yet
- Elementary ScienceDocument28 pagesElementary ScienceCilena DomenicinaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Lesson3 ActivitiesDocument4 pagesGroup 1 Lesson3 Activitiesmarvinjay alforqueNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life: Unit I - Nature of Inquiry An D ResearchDocument17 pagesResearch in Daily Life: Unit I - Nature of Inquiry An D ResearchShiro MisakiNo ratings yet
- Spec 1 Modules 1Document10 pagesSpec 1 Modules 1Ann NecdoteNo ratings yet
- Kto12 Science FrameworkDocument31 pagesKto12 Science Frameworkneverc473No ratings yet
- RESEARCH WORKSHOP QualitativeDocument55 pagesRESEARCH WORKSHOP QualitativeAlyssa JaneNo ratings yet
- Ged 102: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: (Physics, Earth and Space Science)Document9 pagesGed 102: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: (Physics, Earth and Space Science)Jean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- The Art of Teaching Science: Introduction and WelcomeDocument30 pagesThe Art of Teaching Science: Introduction and WelcomeQueen Ann NavalloNo ratings yet
- Research I Q1M1W1Document9 pagesResearch I Q1M1W1Friah Mae DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in Elementary Grade ModuleDocument20 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary Grade ModuleSittienor GugoNo ratings yet
- 1.disciplinary Knowledge and Pedagogical Approaches in School SubjectsDocument30 pages1.disciplinary Knowledge and Pedagogical Approaches in School SubjectsANJU SBNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 3 FinalDocument4 pagesModule 2 Week 3 FinalAl Grace DoblonNo ratings yet
- R Donnelly Critical Thinking and Problem SolvingDocument116 pagesR Donnelly Critical Thinking and Problem SolvingBalaji Mahesh Krishnan67% (3)
- Course 1 - Week 1Document18 pagesCourse 1 - Week 1Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- SHS Practical Research 1 Q3 Module 1 SY 2022-2023Document20 pagesSHS Practical Research 1 Q3 Module 1 SY 2022-2023Roland AgraNo ratings yet
- Handouts 3is PDFDocument4 pagesHandouts 3is PDFDe-Andrie GotuatoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 13 ReviewerDocument102 pagesLesson 1 13 ReviewerAngelica Queen Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 in Teaching Science in ElementaryDocument15 pagesModule 1 in Teaching Science in ElementaryJim Ann PamaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science PrelimDocument5 pagesTeaching Science PrelimAizel RuizNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Malaysian Primary Science Curriculum 1Document8 pagesWeek 3: Malaysian Primary Science Curriculum 1noridhka_alienaNo ratings yet
- Research 1 Module 2nd Sem 2021 2022Document24 pagesResearch 1 Module 2nd Sem 2021 2022Ronan TreyesNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Nature of Inquiry and Research PDFDocument17 pagesLESSON 1 Nature of Inquiry and Research PDFDanilo CeraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Teaching Science Physics and Earth ScienceDocument8 pagesLesson 3 Teaching Science Physics and Earth ScienceDaryll QuilantangNo ratings yet
- Elementary Science Curriculum (Physics, Earth and Space Science)Document5 pagesElementary Science Curriculum (Physics, Earth and Space Science)SHARWIN BORDARAISNo ratings yet
- Teacher Leader Ngss PresentationDocument29 pagesTeacher Leader Ngss Presentationapi-573214664No ratings yet
- Local Media8545614879483674203Document33 pagesLocal Media8545614879483674203ShairaNo ratings yet
- Comparison (Task 1 & 2)Document15 pagesComparison (Task 1 & 2)rajaIPSAHNo ratings yet
- Teaching ScienceDocument8 pagesTeaching ScienceSherby May FabiaNo ratings yet
- University of Mindanao: Rolando A. Daraquit, Jr. MBA 101 - Applied Business ResearchDocument19 pagesUniversity of Mindanao: Rolando A. Daraquit, Jr. MBA 101 - Applied Business ResearchJr DaraquitNo ratings yet
- Week1 WatoisresearchDocument121 pagesWeek1 WatoisresearchBian SyahNo ratings yet
- Science Primary 2014 Modified 2Document69 pagesScience Primary 2014 Modified 2ngianbc5802No ratings yet
- Teachingofscience 160207141925Document15 pagesTeachingofscience 160207141925Adam MalikNo ratings yet
- Assessment of LearningDocument3 pagesAssessment of LearningfloresstephaniejoycNo ratings yet
- ESC 8 Chapter 1 Lesson 1 2 2022 23Document13 pagesESC 8 Chapter 1 Lesson 1 2 2022 23Czariane LeeNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy of Science at Upper Primary Stage: National Council of Educational Research and TrainingDocument42 pagesPedagogy of Science at Upper Primary Stage: National Council of Educational Research and TrainingChandan SahuNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Module in Practical Research 1Document18 pagesWeek 1 Module in Practical Research 1lilighhhNo ratings yet
- Sciences PPDocument7 pagesSciences PPosra8242No ratings yet
- Teaching ScienceDocument9 pagesTeaching ScienceIrose JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument6 pagesNature of Inquiry and ResearchJunrey SanchezNo ratings yet
- The Challenges of Culture-based Learning: Indian Students' ExperiencesFrom EverandThe Challenges of Culture-based Learning: Indian Students' ExperiencesNo ratings yet
- BtledDocument10 pagesBtledMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Benlac ReportDocument21 pagesBenlac ReportMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- LmsDocument1 pageLmsMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument8 pagesDocumentMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Social Literacy ReportDocument10 pagesSocial Literacy ReportMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Distance and OnlineDocument1 pageDistance and OnlineMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document17 pagesLesson 1Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Traffic SignsDocument2 pagesTraffic SignsMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- LmsDocument1 pageLmsMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Philosophy and Objectives of Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao 1Document21 pagesPhilosophy and Objectives of Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao 1Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Group 1Document9 pagesGroup 1Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Activity 1-ArtsDocument1 pageActivity 1-ArtsMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- MathDocument14 pagesMathMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- The Teaching of Science in The Elementary GradesDocument40 pagesThe Teaching of Science in The Elementary GradesMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Benlac Melcs CreativeDocument3 pagesBenlac Melcs CreativeMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Functional Literacy 1Document11 pagesFunctional Literacy 1Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Relieved Learning TheoryDocument12 pagesRelieved Learning TheoryMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- AB Learning TheoryDocument7 pagesAB Learning TheoryMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Cil TheoryDocument11 pagesCil TheoryMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 WK 5 5Document7 pagesSCIENCE 5 WK 5 5Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Tips On Facilitating Effective Group Discussions - Sheridan Center - Brown UniversityDocument7 pagesTips On Facilitating Effective Group Discussions - Sheridan Center - Brown UniversityMARY JOY TIMCANGNo ratings yet
- Teach Learn: Confusing WordsDocument6 pagesTeach Learn: Confusing WordsaniNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument10 pagesResearch MethodsAhimbisibwe BenyaNo ratings yet
- Motivation and EmotionDocument15 pagesMotivation and EmotionAasma IsmailNo ratings yet
- Completing MSGDocument17 pagesCompleting MSGZubair Ahmed100% (1)
- Comprehension Toolkit 1Document3 pagesComprehension Toolkit 1api-510893209No ratings yet
- The Bucket List: Activity TypeDocument3 pagesThe Bucket List: Activity TypeAraceliNo ratings yet
- Thomas E W. A Grammar of Spoken Brazilian PortugueseDocument188 pagesThomas E W. A Grammar of Spoken Brazilian PortugueseCassie K L PathakNo ratings yet
- English Grammar CohesionDocument1 pageEnglish Grammar Cohesionbutterball100% (1)
- Interpersonal NeurobiologyDocument28 pagesInterpersonal NeurobiologyNacho Vidal Navarro100% (2)
- RPH 21Document7 pagesRPH 2108hakimiNo ratings yet
- Pba Civil War Day 1Document2 pagesPba Civil War Day 1api-254296463No ratings yet
- EESC Lesson45Document8 pagesEESC Lesson45Liz T.No ratings yet
- Revisiting Comparative Pedagogy - MethodologiesDocument22 pagesRevisiting Comparative Pedagogy - MethodologiesangelaNo ratings yet
- Bioethics SeminarDocument1 pageBioethics Seminarapi-24500288No ratings yet
- ORAL PRESENTATION RUBRIC - 10th GradeDocument2 pagesORAL PRESENTATION RUBRIC - 10th GradeKevin EscobarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8019/01 May/June 2021Document17 pagesCambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8019/01 May/June 2021sbang.alahNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Kurikulum Pendidikan Awal Kanak-KanakpdfDocument30 pagesTopic 4 Kurikulum Pendidikan Awal Kanak-Kanakpdfsiti umminorNo ratings yet
- Ngoc PTBDocument18 pagesNgoc PTBminhlam27061201No ratings yet
- Ai PPT 1Document47 pagesAi PPT 1adĪtYa PàtHakNo ratings yet
- Selection Preliminary Screening: Resume:: Employment TestDocument3 pagesSelection Preliminary Screening: Resume:: Employment Testahmad yassineNo ratings yet
- Well Founded RecursionDocument61 pagesWell Founded Recursionaneto1No ratings yet
- Q1 Week 2 June 11 15 P2Document2 pagesQ1 Week 2 June 11 15 P2Teresa NavarreteNo ratings yet
- ENG133 Dyadic CommunicationDocument2 pagesENG133 Dyadic CommunicationDoctrine Dark0% (1)
- Surveying Metacognitive Reading Strategies Awareness of Fifth-Semester English Department Students Dina Damayanti Sofyan A. Gani Teuku ZulfikarDocument14 pagesSurveying Metacognitive Reading Strategies Awareness of Fifth-Semester English Department Students Dina Damayanti Sofyan A. Gani Teuku Zulfikarmariposa rosaNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Behaviourism, Cognitivism, Social ConstructivismDocument39 pagesLearning Theories Behaviourism, Cognitivism, Social ConstructivismJuan Miguel100% (3)
- Learning Style InventoryDocument3 pagesLearning Style InventorytituspermadiNo ratings yet
TSEG Lesson 1 Science Framework in The K 12 LMS
TSEG Lesson 1 Science Framework in The K 12 LMS
Uploaded by
Maligo, Renalyn P.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views20 pagesOriginal Title
TSEG-Lesson-1-Science-Framework-in-the-K-12-LMS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views20 pagesTSEG Lesson 1 Science Framework in The K 12 LMS
TSEG Lesson 1 Science Framework in The K 12 LMS
Uploaded by
Maligo, Renalyn P.Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
The Science Framework in the K to 12
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
LESSON OUTCOMES
• Describe the science framework in
the K to 12
• Discuss the framework relative to
each grade level
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
Questions to ponder . . .
• What do you expect to teach in science?
• What first come to your mind when you are to teach
Science?
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
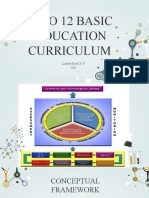
THREE IMPORTANT COMPONENTS
1. Understanding and Applying Scientific Knowledge
2. Developing and Demonstrating Scientific Attitudes and
Values
3. Performing Scientific Inquiry Skills
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
To be scientifically and technologically
literate, one should be:
1. Critical and Creative Problem Solver
2. Responsible Steward of Nature
3. Innovative and Inventive Thinker
4. Informed decision-maker
5. Effective communicator
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
Related Learning Theories:
1. Multidisciplinary - Interdisciplinary Approach
2. Science-Technology Society Approach
3. Problem/Issue Based Learning
4. Inquiry-based Approach
5. Constructivism
6. Social Cognition Learning MOdel
7. Learning Style Theory
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
Goal of science learning:
Science and Technology Literacy
Three Intervening skills to achieve this goal:
1. Understanding and Applying Scientific Knowledge
2. Performing Scientific Inquiry Skills
3. Developing and Demonstrating Scientific Attitudes and
Values
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
A. The Components of Scientific and
Technological Literacy
1. UNDERSTANDING AND APPLYING
SCIENTIFIC KNOWLEDGE
• Science is both (1) body of knowledge and (2)
the process by which that knowledge is produced.
• Scientific knowledge is not absolute or certain.
• Knowledge should be applied.
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
A. The Components of Scientific and
Technological Literacy
2. DEVELOPING AND DEMONSTRATING
SCIENTIFIC ATTITUDES AND VALUES
• Scientific attitudes - way of viewing things, a
way of thinking, feeling, acting, and a disposition
towards science.
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
Some scientific attitudes
• CURIOSITY
• HUMILITY
• OPEN-MINDEDNESS
• INTELLECTUAL HONESTY
• PERSEVERANCE
• SKEPTICISM
• CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE
• RATIONAL
• OBJECTIVITY
• INNOVATIVE
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
A. The Components of Scientific and
Technological Literacy
3. PERFORMING SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY SKILLS
• A science oriented mind is a questioning mind.
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
KINDERGARTEN TO GRADE 5 TO
GRADE 4 GRADE 8
LEARNERS LEARNERS
• Ask question about objects, • Identify questions that can be
organism and events in the answered thru scientific
environment investigations
• Plan and conduct a simple • Design and conduct simple science
investigation investigations
• Employ simple equipment and • Use appropriate tools and
tools to gather data and extend the techniques, gather, analyze and
senses interpret data
• Use data to construct reasonable • Develop descriptions,
explanation explanations, predictions and
• Communicate investigations and models using evidence
explanations • Think critically and logically to
make the relationship between
evidence and explanations
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
3. PERFORMING SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY SKILLS
• A science oriented mind is a questioning mind.
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
B. Approaches, Models and Practices Used in the
Framework
1. Multidisciplinary-Interdisciplinary Approach
• Interaction of different disciplines
2. Science-Technology Society Approach
• Linking science to technology and how it influence
people and ways of life
3. Problem/Issue Based Learning
• Use of identified problem or issues surrounding the
environment
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
Related learning theories (CTD):
4. Inquiry-based Approach
• Anchored in the idea of seeking for truth, information or
knowledge
• Not looking for answer, but seeking for appropriate solution
• Learners take ownership of a problem or a need and the
desire to solve it
5. Constructivism
• Learners are the makers of meaning and knowledge
• People learn by constructing their own understanding and
knowledge through prior experiences and reflection
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
Related learning theories (CTD):
6. Social Cognition Learning Model
• Learning through observing others while interacting and
experiencing
7. Learning Style Theory
• VARK Model identifies Visual, Auditory, Reading/Rifting
and Kinesthetic learners who respond to different kinds of
learning.
• “All learners are created equally but learn differently”
• Each individual has a preference in how they learn.
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
B. Characteristics of a Scientific and
Technologically Literate Person
1. Critical and Creative Problem Solver
• Learners develop skills that enable them to analyze and find
solutions to any perplexing questions of problems.
2. Responsible steward of nature
• Learners demonstrate concern in keeping the environment
safe for themselves and for everybody.
3. Innovative and Inventive Thinker
• Learners create and innovate something for humanity
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
B. Characteristics of a Scientific and
Technologically Literate Person
4. Informed decision maker
• Learners develop skills the ability to make informed
decisions
5. Effective communicator
• Learners convey correct messages to others
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
EVALUATION
| The Science Framework in the K to 12
You might also like
- Unit 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grades: An OverviewDocument43 pagesUnit 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grades: An OverviewJenjen Gammad81% (16)
- Answer The Following Questions BelowDocument3 pagesAnswer The Following Questions BelowJervyn GuiananNo ratings yet
- Screen-Based Online Learning Will Change Kids' Brains. Are We Ready For That - Technology - The GuardianDocument1 pageScreen-Based Online Learning Will Change Kids' Brains. Are We Ready For That - Technology - The GuardianEgemen TanikNo ratings yet
- Lambda Solutions A Guide To Competency Based Training For Organizational Excellence Part 1Document6 pagesLambda Solutions A Guide To Competency Based Training For Organizational Excellence Part 1JStoneNo ratings yet
- 8D TemplateDocument7 pages8D Templatemuhammad_mmd100% (1)
- Malaysia Primary Science Curriculum 1Document19 pagesMalaysia Primary Science Curriculum 1syuhaimisalimNo ratings yet
- The Science Framework in The K To 12Document66 pagesThe Science Framework in The K To 12Tedlyn Joy Pagaling Espino75% (4)
- Elem-9 ReviewerDocument5 pagesElem-9 ReviewerCharisse DeirdreNo ratings yet
- Module Introduction: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: An OverviewDocument8 pagesModule Introduction: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: An OverviewJervyn GuiananNo ratings yet
- Module 2 M. GonzalesDocument3 pagesModule 2 M. GonzalesElton John RestonNo ratings yet
- Module-1 (Science)Document9 pagesModule-1 (Science)Jessa SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Basic Education Curriculum: Luardo Ruel Jr. F. 2A1Document23 pagesK To 12 Basic Education Curriculum: Luardo Ruel Jr. F. 2A1Cilena DomenicinaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science ModuleDocument22 pagesTeaching Science ModuleHassel AbayonNo ratings yet
- Aims of Science: By: Judy Ann Fanuncio Jay Xanderlyn GallegosDocument10 pagesAims of Science: By: Judy Ann Fanuncio Jay Xanderlyn Gallegosjayxanderlyn gallegosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Science Framework in K To 12Document10 pagesLesson 1 The Science Framework in K To 12bpsb4ddzctNo ratings yet
- EEd 4-Lesson 1Document10 pagesEEd 4-Lesson 1Mark Edrill ViñasNo ratings yet
- Science Education Curriculum Oct20Document40 pagesScience Education Curriculum Oct20SAMAR Vernalyn D.No ratings yet
- Vision For Science Education: Scientific PracticesDocument33 pagesVision For Science Education: Scientific PracticesNorlyn Mae ComerosNo ratings yet
- MS 613 Methods of ResearchDocument34 pagesMS 613 Methods of ResearchSelino CruzNo ratings yet
- What Is Science ?: Science Naturalistic Universe NaturalDocument16 pagesWhat Is Science ?: Science Naturalistic Universe NaturalItsna Rona Wahyu AstutiNo ratings yet
- LSK3701 - Notes Unit 1Document14 pagesLSK3701 - Notes Unit 1Annemarie RossouwNo ratings yet
- Tseg 1Document25 pagesTseg 1Mary Ann Andes CaruruanNo ratings yet
- Readings For Week 2 I. The Science Framework in The K To 12Document5 pagesReadings For Week 2 I. The Science Framework in The K To 12StarryGailSanchezNo ratings yet
- Elementary ScienceDocument28 pagesElementary ScienceCilena DomenicinaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Lesson3 ActivitiesDocument4 pagesGroup 1 Lesson3 Activitiesmarvinjay alforqueNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life: Unit I - Nature of Inquiry An D ResearchDocument17 pagesResearch in Daily Life: Unit I - Nature of Inquiry An D ResearchShiro MisakiNo ratings yet
- Spec 1 Modules 1Document10 pagesSpec 1 Modules 1Ann NecdoteNo ratings yet
- Kto12 Science FrameworkDocument31 pagesKto12 Science Frameworkneverc473No ratings yet
- RESEARCH WORKSHOP QualitativeDocument55 pagesRESEARCH WORKSHOP QualitativeAlyssa JaneNo ratings yet
- Ged 102: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: (Physics, Earth and Space Science)Document9 pagesGed 102: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: (Physics, Earth and Space Science)Jean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- The Art of Teaching Science: Introduction and WelcomeDocument30 pagesThe Art of Teaching Science: Introduction and WelcomeQueen Ann NavalloNo ratings yet
- Research I Q1M1W1Document9 pagesResearch I Q1M1W1Friah Mae DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in Elementary Grade ModuleDocument20 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary Grade ModuleSittienor GugoNo ratings yet
- 1.disciplinary Knowledge and Pedagogical Approaches in School SubjectsDocument30 pages1.disciplinary Knowledge and Pedagogical Approaches in School SubjectsANJU SBNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 3 FinalDocument4 pagesModule 2 Week 3 FinalAl Grace DoblonNo ratings yet
- R Donnelly Critical Thinking and Problem SolvingDocument116 pagesR Donnelly Critical Thinking and Problem SolvingBalaji Mahesh Krishnan67% (3)
- Course 1 - Week 1Document18 pagesCourse 1 - Week 1Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- SHS Practical Research 1 Q3 Module 1 SY 2022-2023Document20 pagesSHS Practical Research 1 Q3 Module 1 SY 2022-2023Roland AgraNo ratings yet
- Handouts 3is PDFDocument4 pagesHandouts 3is PDFDe-Andrie GotuatoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 13 ReviewerDocument102 pagesLesson 1 13 ReviewerAngelica Queen Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 in Teaching Science in ElementaryDocument15 pagesModule 1 in Teaching Science in ElementaryJim Ann PamaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science PrelimDocument5 pagesTeaching Science PrelimAizel RuizNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Malaysian Primary Science Curriculum 1Document8 pagesWeek 3: Malaysian Primary Science Curriculum 1noridhka_alienaNo ratings yet
- Research 1 Module 2nd Sem 2021 2022Document24 pagesResearch 1 Module 2nd Sem 2021 2022Ronan TreyesNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Nature of Inquiry and Research PDFDocument17 pagesLESSON 1 Nature of Inquiry and Research PDFDanilo CeraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Teaching Science Physics and Earth ScienceDocument8 pagesLesson 3 Teaching Science Physics and Earth ScienceDaryll QuilantangNo ratings yet
- Elementary Science Curriculum (Physics, Earth and Space Science)Document5 pagesElementary Science Curriculum (Physics, Earth and Space Science)SHARWIN BORDARAISNo ratings yet
- Teacher Leader Ngss PresentationDocument29 pagesTeacher Leader Ngss Presentationapi-573214664No ratings yet
- Local Media8545614879483674203Document33 pagesLocal Media8545614879483674203ShairaNo ratings yet
- Comparison (Task 1 & 2)Document15 pagesComparison (Task 1 & 2)rajaIPSAHNo ratings yet
- Teaching ScienceDocument8 pagesTeaching ScienceSherby May FabiaNo ratings yet
- University of Mindanao: Rolando A. Daraquit, Jr. MBA 101 - Applied Business ResearchDocument19 pagesUniversity of Mindanao: Rolando A. Daraquit, Jr. MBA 101 - Applied Business ResearchJr DaraquitNo ratings yet
- Week1 WatoisresearchDocument121 pagesWeek1 WatoisresearchBian SyahNo ratings yet
- Science Primary 2014 Modified 2Document69 pagesScience Primary 2014 Modified 2ngianbc5802No ratings yet
- Teachingofscience 160207141925Document15 pagesTeachingofscience 160207141925Adam MalikNo ratings yet
- Assessment of LearningDocument3 pagesAssessment of LearningfloresstephaniejoycNo ratings yet
- ESC 8 Chapter 1 Lesson 1 2 2022 23Document13 pagesESC 8 Chapter 1 Lesson 1 2 2022 23Czariane LeeNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy of Science at Upper Primary Stage: National Council of Educational Research and TrainingDocument42 pagesPedagogy of Science at Upper Primary Stage: National Council of Educational Research and TrainingChandan SahuNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Module in Practical Research 1Document18 pagesWeek 1 Module in Practical Research 1lilighhhNo ratings yet
- Sciences PPDocument7 pagesSciences PPosra8242No ratings yet
- Teaching ScienceDocument9 pagesTeaching ScienceIrose JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument6 pagesNature of Inquiry and ResearchJunrey SanchezNo ratings yet
- The Challenges of Culture-based Learning: Indian Students' ExperiencesFrom EverandThe Challenges of Culture-based Learning: Indian Students' ExperiencesNo ratings yet
- BtledDocument10 pagesBtledMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Benlac ReportDocument21 pagesBenlac ReportMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- LmsDocument1 pageLmsMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument8 pagesDocumentMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Social Literacy ReportDocument10 pagesSocial Literacy ReportMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Distance and OnlineDocument1 pageDistance and OnlineMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document17 pagesLesson 1Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Traffic SignsDocument2 pagesTraffic SignsMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- LmsDocument1 pageLmsMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Philosophy and Objectives of Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao 1Document21 pagesPhilosophy and Objectives of Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao 1Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Group 1Document9 pagesGroup 1Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Activity 1-ArtsDocument1 pageActivity 1-ArtsMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- MathDocument14 pagesMathMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- The Teaching of Science in The Elementary GradesDocument40 pagesThe Teaching of Science in The Elementary GradesMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Benlac Melcs CreativeDocument3 pagesBenlac Melcs CreativeMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Functional Literacy 1Document11 pagesFunctional Literacy 1Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Relieved Learning TheoryDocument12 pagesRelieved Learning TheoryMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- AB Learning TheoryDocument7 pagesAB Learning TheoryMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Cil TheoryDocument11 pagesCil TheoryMaligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 WK 5 5Document7 pagesSCIENCE 5 WK 5 5Maligo, Renalyn P.No ratings yet
- Tips On Facilitating Effective Group Discussions - Sheridan Center - Brown UniversityDocument7 pagesTips On Facilitating Effective Group Discussions - Sheridan Center - Brown UniversityMARY JOY TIMCANGNo ratings yet
- Teach Learn: Confusing WordsDocument6 pagesTeach Learn: Confusing WordsaniNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument10 pagesResearch MethodsAhimbisibwe BenyaNo ratings yet
- Motivation and EmotionDocument15 pagesMotivation and EmotionAasma IsmailNo ratings yet
- Completing MSGDocument17 pagesCompleting MSGZubair Ahmed100% (1)
- Comprehension Toolkit 1Document3 pagesComprehension Toolkit 1api-510893209No ratings yet
- The Bucket List: Activity TypeDocument3 pagesThe Bucket List: Activity TypeAraceliNo ratings yet
- Thomas E W. A Grammar of Spoken Brazilian PortugueseDocument188 pagesThomas E W. A Grammar of Spoken Brazilian PortugueseCassie K L PathakNo ratings yet
- English Grammar CohesionDocument1 pageEnglish Grammar Cohesionbutterball100% (1)
- Interpersonal NeurobiologyDocument28 pagesInterpersonal NeurobiologyNacho Vidal Navarro100% (2)
- RPH 21Document7 pagesRPH 2108hakimiNo ratings yet
- Pba Civil War Day 1Document2 pagesPba Civil War Day 1api-254296463No ratings yet
- EESC Lesson45Document8 pagesEESC Lesson45Liz T.No ratings yet
- Revisiting Comparative Pedagogy - MethodologiesDocument22 pagesRevisiting Comparative Pedagogy - MethodologiesangelaNo ratings yet
- Bioethics SeminarDocument1 pageBioethics Seminarapi-24500288No ratings yet
- ORAL PRESENTATION RUBRIC - 10th GradeDocument2 pagesORAL PRESENTATION RUBRIC - 10th GradeKevin EscobarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8019/01 May/June 2021Document17 pagesCambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8019/01 May/June 2021sbang.alahNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Kurikulum Pendidikan Awal Kanak-KanakpdfDocument30 pagesTopic 4 Kurikulum Pendidikan Awal Kanak-Kanakpdfsiti umminorNo ratings yet
- Ngoc PTBDocument18 pagesNgoc PTBminhlam27061201No ratings yet
- Ai PPT 1Document47 pagesAi PPT 1adĪtYa PàtHakNo ratings yet
- Selection Preliminary Screening: Resume:: Employment TestDocument3 pagesSelection Preliminary Screening: Resume:: Employment Testahmad yassineNo ratings yet
- Well Founded RecursionDocument61 pagesWell Founded Recursionaneto1No ratings yet
- Q1 Week 2 June 11 15 P2Document2 pagesQ1 Week 2 June 11 15 P2Teresa NavarreteNo ratings yet
- ENG133 Dyadic CommunicationDocument2 pagesENG133 Dyadic CommunicationDoctrine Dark0% (1)
- Surveying Metacognitive Reading Strategies Awareness of Fifth-Semester English Department Students Dina Damayanti Sofyan A. Gani Teuku ZulfikarDocument14 pagesSurveying Metacognitive Reading Strategies Awareness of Fifth-Semester English Department Students Dina Damayanti Sofyan A. Gani Teuku Zulfikarmariposa rosaNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Behaviourism, Cognitivism, Social ConstructivismDocument39 pagesLearning Theories Behaviourism, Cognitivism, Social ConstructivismJuan Miguel100% (3)
- Learning Style InventoryDocument3 pagesLearning Style InventorytituspermadiNo ratings yet