Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnetic Forces PowerPoint 2023
Magnetic Forces PowerPoint 2023
Uploaded by
jared.demars0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views10 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views10 pagesMagnetic Forces PowerPoint 2023
Magnetic Forces PowerPoint 2023
Uploaded by
jared.demarsCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
WHAT IS MAGNETISM?
• Magnetism is a force created by
magnets. What is
• Magnetism is also called magnetism?
magnetic force.
• Only magnets produce
magnetic force.
• Magnetic force is invisible and
can be felt by objects around or
near a magnet.
• Magnetic force attracts or
repels other objects or magnets.
Magnetism & Electricity 1 © Stephanie Elkowitz
MAGNETS
• A magnet is an object that produces magnetic force.
• The strength of a magnet’s magnetic force depends on the size
of the magnet and the material the magnet is made of.
• Most magnets are made of iron, nickel or cobalt. However, not
all iron, nickel or cobalt objects produce magnetic force.
• The strongest magnets are made of rare Earth metals. The
strongest and most commonly used rare Earth metal magnet is
called the Neodymium magnet.
Magnetism & Electricity 2 © Stephanie Elkowitz
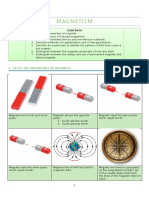
MAGNETS
• A magnet has ends called poles. One
pole is called the north pole (N). The
other is called the south pole (S).
• A bar magnet is a straight, rectangular
magnet. One end of the bar magnet is
the north pole. The other end is the south
pole.
• A horseshoe magnet is a curved,
horseshoe-shaped magnet. One end of
the curve is the north pole. The other
end is the south pole.
• Magnets can also be shaped like disks,
rings and cylinders.
Magnetism & Electricity 3 © Stephanie Elkowitz
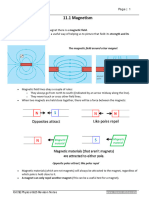
MAGNETS
• The north pole of one magnet is attracted to the south pole of
a second magnet.
• The north pole of one magnet is repelled by the north pole of a
second magnet.
• For this reason, we say like poles repel and unlike poles
attract.
Magnetism & Electricity 4 © Stephanie Elkowitz
MAGNETS
• You cannot separate the north and south pole of a magnet.
• If you cut a bar magnet in half, you get two smaller bar
magnets. You do not get a “north pole magnet” and a “south
pole magnet.”
Magnetism & Electricity 5 © Stephanie Elkowitz
MAGNETS
• All matter is made of atoms. Atoms What makes
have magnetic fields. Atoms group a magnet
together when their magnetic fields magnetic?
align. These groups are called domains.
• In a magnet, domains point in the same
direction. This produces an object with
a uniform magnetic field.
• In a non-magnet, the domains point in
random directions.
Magnetism & Electricity 6 © Stephanie Elkowitz
TYPES of MAGNETS
• There are 3 main types of magnets:
1. A permanent magnet is an object made of matter that is
permanently magnetized. Some iron, nickel or cobalt
objects are permanent magnets.
2. A temporary magnet is an object that becomes a magnet
through magnetization. Over time, a temporary magnet
loses its magnetism. Iron, nickel and cobalt objects can
become temporary magnets.
3. An electromagnet is a temporary magnet produced by an
electric current. You will learn more about electromagnets
later in this presentation.
Magnetism & Electricity 7 © Stephanie Elkowitz
CREDIT CARDS
• The stripe on the back of a credit
card is a magnetic stripe. It is
called a magstripe.
• The magstripe is made of tiny
iron-based magnetic particles.
These particles are selectively
magnetized to store data or
information.
• A credit card that is exposed to a
strong magnetic field or heat no
longer works because the
magstripe becomes
demagnetized.
Magnetism & Electricity 8 © Stephanie Elkowitz
COMPUTER HARD DRIVE
• A computer hard drive is made of
magnetic material that can be
magnetized to store data and
demagnetized to erase it.
• Data is stored in extremely small
magnetic domains on platters on the
hard drive.
• The arm stores, reads or erases the
information on the platters.
• The information on a hard drive can
be erased if the computer is exposed
to extreme heat or strong magnetic
fields.
Magnetism & Electricity 9 © Stephanie Elkowitz
MRI
• MRI (magnetic resonance
imaging) is a type of medical
imaging that produces images of
the body. These images are used
to diagnosis diseases and
anatomy abnormalities.
• An MRI scanner uses strong
magnets and magnetic fields to
create images of the body.
• Unlike X-ray and CT-Scan, MRI
does not expose a patient to
radiation.
Magnetism & Electricity 10 © Stephanie Elkowitz
You might also like
- Magnetism - Science Year 8Document15 pagesMagnetism - Science Year 8b_syiera100% (7)
- Delmar Unit 04 Magnetism 3edDocument44 pagesDelmar Unit 04 Magnetism 3eddale gillNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theory of FerromagnetismDocument331 pagesIntroduction To The Theory of FerromagnetismCledson Santana50% (2)
- Magnet Therapy and Protocols For Osteoporosis 2004 (Pag 18) by William H. Philpott - Negative Field On Brain and Spine For Pain, TreatmentsDocument25 pagesMagnet Therapy and Protocols For Osteoporosis 2004 (Pag 18) by William H. Philpott - Negative Field On Brain and Spine For Pain, Treatmentsitetejac100% (2)
- Magnetic Components Design and ApplicationsDocument354 pagesMagnetic Components Design and Applicationseugene67% (3)
- Magnetism QRDocument35 pagesMagnetism QRJared PataniNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Simple Phenomena of MagnetismDocument6 pages4.1 Simple Phenomena of MagnetismAbdul Hadi Tahir100% (1)
- Physics - Magnetism Summary & WorksheetDocument10 pagesPhysics - Magnetism Summary & Worksheetsanjayrecruitment003No ratings yet
- MagnetDocument20 pagesMagnetHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13Document4 pagesCbse Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13rohinimr007No ratings yet
- Y11 Chapter 16Document5 pagesY11 Chapter 16JIYAS SNo ratings yet
- Magnetism G10 ScienceDocument16 pagesMagnetism G10 ScienceVianca Rein MilanNo ratings yet
- What Is MagnetDocument9 pagesWhat Is Magnetarsc123No ratings yet
- Magnetism Notes FinalDocument29 pagesMagnetism Notes FinalMuryum SalmanNo ratings yet
- Magnetism QRDocument36 pagesMagnetism QRJohn Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- Course: Basic Electrical TechnologyDocument18 pagesCourse: Basic Electrical TechnologyUsman ShahidNo ratings yet
- MAGNETISMDocument52 pagesMAGNETISMUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Magnets Class6Document34 pagesMagnets Class6Moumita DasNo ratings yet
- MagnetDocument6 pagesMagnetdjamalNo ratings yet
- ''Magnets in Orthodontics''Document102 pages''Magnets in Orthodontics''Anubha VermaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: 1. State The Properties of MagnetsDocument4 pagesMagnetism: 1. State The Properties of Magnets23maabNo ratings yet
- Twig Magnets PDFDocument10 pagesTwig Magnets PDFMuqtasidNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Types of Magnets - Monday 22nd NovemberDocument14 pages2021 - Types of Magnets - Monday 22nd NovemberSheldon MusiinzaNo ratings yet
- MagnetsDocument25 pagesMagnetsnkoan12No ratings yet
- KD 3.4 MagnetismDocument8 pagesKD 3.4 MagnetismPlaystation SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MagnetismDocument17 pagesUnit 5 MagnetismTofe YusufNo ratings yet
- Electricity & MagnetismDocument10 pagesElectricity & MagnetismReynald AntasoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism For Printing ModuleDocument24 pagesElectromagnetism For Printing ModuleBob PhigglebottomNo ratings yet
- Magnetic ForcesDocument11 pagesMagnetic ForcesDash TomarNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: How Do We Use Magnets?Document45 pagesMagnetism: How Do We Use Magnets?Noroña S.R.No ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument12 pagesMagnetismblazemwangi59No ratings yet
- Notes - Fun With Magnets-2023-24Document5 pagesNotes - Fun With Magnets-2023-24shamshadNo ratings yet
- Magnets and Electricity: Write-On Grade 5Document13 pagesMagnets and Electricity: Write-On Grade 5tica1118No ratings yet
- Lesson Note - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument9 pagesLesson Note - Magnetism and Electromagnetismyashmiganegoda13No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Circuit AnalysisDocument32 pagesElectromagnetic Circuit AnalysisSM FerdousNo ratings yet
- Magnetism For o LevelDocument54 pagesMagnetism For o LevelKYALISIIMA ODRAENo ratings yet
- Magnetic Force-OnlineDocument25 pagesMagnetic Force-Onlinelizbeth martinezNo ratings yet
- MAGNESTISMDocument14 pagesMAGNESTISMAbjyot SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetism pg1Document1 pageMagnetism pg1sachinNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument26 pagesMagnetismHanna MercadoNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Demo 171022065922Document26 pagesMagnetism Demo 171022065922Raghu Nadh100% (1)
- PHYSICS FORM 5 NewDocument29 pagesPHYSICS FORM 5 NewIdriss DjatsaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current-Alok SirDocument21 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current-Alok Sirchashish2792008No ratings yet
- Magnetism PowerPoint 0Document19 pagesMagnetism PowerPoint 0Kristine Mae Dizon RelobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document45 pagesChapter 16farhanasikder123No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesPhysics ProjectMandeep TanwarNo ratings yet
- EM1 MagnetismDocument7 pagesEM1 MagnetismNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- August Monthly Year 9 Physics PresentationDocument142 pagesAugust Monthly Year 9 Physics PresentationalannachetsNo ratings yet
- All About MagnetsDocument2 pagesAll About MagnetsFátima Delgado PolloNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Physics MagnetsDocument6 pagesForm 3 Physics MagnetsChibale Mchere BandaNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument17 pagesMagnetismSomdebNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETISMDocument90 pagesELECTROMAGNETISMAllsher Diega100% (2)
- Basic Principles of MagnetsDocument24 pagesBasic Principles of MagnetsMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- 2021 Magnets - FridayDocument19 pages2021 Magnets - FridaySheldon MusiinzaNo ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields (2) - Lecture 1 Spring 2021-2022Document21 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields (2) - Lecture 1 Spring 2021-2022Ahmed tarek gaballahNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Magnetic FieldsDocument12 pagesMagnetism: Magnetic FieldsShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- Open Magnetic Forces and Magnetic FieldsDocument44 pagesOpen Magnetic Forces and Magnetic Fieldss6wzygmxcwNo ratings yet
- Science Notes 14 LsDocument5 pagesScience Notes 14 LsM CHETHANA M CHETHANANo ratings yet
- Magnetism 140818123730 Phpapp012 PDFDocument20 pagesMagnetism 140818123730 Phpapp012 PDFmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism Review2Document35 pagesMagnetism and Electromagnetism Review2Kenneth JacksonNo ratings yet
- Magnets and Magnetic Fields: Cambridge IGCSE PhysicsDocument24 pagesMagnets and Magnetic Fields: Cambridge IGCSE PhysicsSajayanKS100% (1)
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Design of A Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor Controller: April 2014Document7 pagesDesign of A Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor Controller: April 2014Janet WaldeNo ratings yet
- Design and Modelling of BLDC Motor For ADocument7 pagesDesign and Modelling of BLDC Motor For AShubhzsNo ratings yet
- App Lie Physics IDocument8 pagesApp Lie Physics Ishiva sravan sangabathulaNo ratings yet
- EEU NotesDocument5 pagesEEU NotesNero MonNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Relays and Their Working Principles: A Relay Is A Switching DeviceDocument17 pagesDifferent Types of Relays and Their Working Principles: A Relay Is A Switching DeviceVIPIN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Coexisting Nanoscale Inverse Spinel and Rock Salt Crystallographic Phases in Nico2O4 Epitaxial Thin Films Grown by Pulsed Laser DepositionDocument9 pagesCoexisting Nanoscale Inverse Spinel and Rock Salt Crystallographic Phases in Nico2O4 Epitaxial Thin Films Grown by Pulsed Laser DepositionUshaNo ratings yet
- Reluctance Synchronous Motors HendershotDocument31 pagesReluctance Synchronous Motors HendershotLatisha CarterNo ratings yet
- Magnetism NotesDocument14 pagesMagnetism Notesapi-277818647No ratings yet
- What Is Moving Iron or MI Instrument? - Definition, Construction, Working, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages - Circuit GlobeDocument3 pagesWhat Is Moving Iron or MI Instrument? - Definition, Construction, Working, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages - Circuit GlobeJoseph MarzanNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Physics OnDocument26 pagesMagnetism: A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Physics OnKevin CalidroNo ratings yet
- Relay: Group 3Document30 pagesRelay: Group 3Wilmark R. CahiligNo ratings yet
- Winsem2023-24 Beee215l TH Ch2023240502407 Assignment I Assignment 1 Beee215l MergedDocument17 pagesWinsem2023-24 Beee215l TH Ch2023240502407 Assignment I Assignment 1 Beee215l Mergedkrayush2801No ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Magnetic Properties of MaterialsDocument21 pagesChapter 20 Magnetic Properties of MaterialsGepel OntanillasNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Compass ErrorDocument36 pagesMagnetic Compass ErrorNimesh Perera67% (3)
- Making A Flynn Motor - Circuit Diagram Attached: Parallel Path Magnetic TheoryDocument5 pagesMaking A Flynn Motor - Circuit Diagram Attached: Parallel Path Magnetic Theorydewidewi76No ratings yet
- Assignments 1, 2, 3Document7 pagesAssignments 1, 2, 3Mude Kishore NaikNo ratings yet
- PHY568 Lec 1 IntroductionDocument36 pagesPHY568 Lec 1 IntroductionzulhaimirasheedNo ratings yet
- Guntur Engineering College: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesGuntur Engineering College: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringharimadhavareddyNo ratings yet
- A Novel Magnetic Gear For High Speed Motor System: Kohei Aiso, Kan Akatsu, Yasuaki AoyamaDocument7 pagesA Novel Magnetic Gear For High Speed Motor System: Kohei Aiso, Kan Akatsu, Yasuaki AoyamabnbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 PDFDocument18 pagesChapter 22 PDFneivaprojetosNo ratings yet
- Transformer Vector GroupDocument11 pagesTransformer Vector GroupjohnNo ratings yet
- ELEN 3084 OBE Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesELEN 3084 OBE Course SyllabusGillianne Mae VargasNo ratings yet
- Geoelectric Strike and Its Application in MagnetotelluricsDocument40 pagesGeoelectric Strike and Its Application in MagnetotelluricsamiruddinNo ratings yet
- Emassignment 1Document3 pagesEmassignment 1Pushkar GuptaNo ratings yet
- University of MauritiusDocument6 pagesUniversity of MauritiushansleyNo ratings yet
- EM Induction MindmapDocument1 pageEM Induction MindmapJulio Alvarez SNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument10 pagesTransformerilias ahmedNo ratings yet