Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry Alkanes
Organic Chemistry Alkanes
Uploaded by
Mathieu CarringtonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry Alkanes
Organic Chemistry Alkanes
Uploaded by
Mathieu CarringtonCopyright:
Available Formats
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Organic Chemistry
Organic nomenclature: Naming alkanes, alkenes, a
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
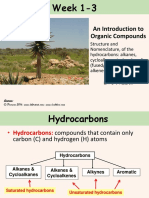
Hydrocarbons
• A saturated hydrocarbon is made up
of carbon and hydrogen and contains
no multiple bonds.
• All alkanes have the general formula:
CnH2n+2
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Naming Alkanes
• Straight-chain (unbranched) hydrocarbons are
named as follows:
1. A prefix indicates the number of carbons
and the name ends in “-ane”
Meth – 1 Hex – 6
Eth – 2 Hept – 7
Prop – 3 Oct – 8
But – 4 Non – 9
Pent – 5 Dec - 10
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Naming Alkanes
• Therefore, H
CH4 is methane H C H
H
H H
C2H6 is ethane H C C H
H H
H H H
C3H8 is propane H C C C H
H H H
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Isomers
• Starting with butane, alkanes will exhibit
structural isomerism. Structural isomers have
the same molecular formula, but the atoms are
bonded in a different arrangement.
• Butane has 2 structural isomers: H
H H
H H H H C
H H
H C C C C H C C C
H H
H H H H H H H
n-butane isobutane
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
• Pentane has 3 structural isomers:
CH3
H3C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 H3C CH CH2 CH3
n-pentane isopentane
CH3
H3C C CH3
CH3
neopentane
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
But be careful!
• The following may look different, but
they are the same as isopentane!
CH3 H3C CH2 CH CH3
H3C CH CH2 CH3
CH3
H3C CH CH2 CH3
CH3
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Substituents
• For branched hydrocarbons, always use the parent
name of the longest chain.
• A substituent is a different group on the hydrocarbon
chain instead of a hydrogen.
• When alkane groups appear as substituents, drop
“-ane” ending and add “-yl”
-CH3 is methyl
-CH2CH3 is ethyl
-CH2CH2CH3 is propyl
-CH3CHCH3 is isopropyl
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Naming Alkanes
• Number the carbons on the parent
chain from the end that gives the
substituent the lowest number and
indicate this number in front of the
substituent.
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Example:
Name the following alkane:
Longest carbon chain? (Parent)
1 2 3
H3C CH2 CH CH2 CH2 CH3
Substituent?
CH3
3-methyl hexane
Note: This is the same structure as the structure above.
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Example:
Name the following alkane:
Longest carbon chain? (Parent)
H3C 2
CH2 Substituent?
H3C CH
CH2 CH3
3-methyl pentane
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Naming Alkanes
• If there is more than one substituent, list
them in alphabetical order.
• Prefixes such as di-, tri- , tetra- etc. are
used to indicate multiple identical
substituents.
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Example:
Name the following alkane:
Longest carbon chain? (Parent)
1 2 3
H3C CH CH CH3
Substituent?
CH3 CH3
2,3-dimethyl butane
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Example:
Name the following alkane:
Longest carbon chain? (Parent) CH3
H2C Substituents?
CH2 CH2 5 CH
4
3 CH2 1
H3C CH2 CH CH CH3
CH3 CH3
4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl nonane
Note: Prefixes such as di-, tri- etc. are ignored for alphabetical arrangements of the
substituents.
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Cyclic Alkanes
• Carbon atoms can form rings containing only
saturated C-C (single) bonds.
• General formula: CnH2n
cyclopropane cyclobutane cyclopentane
H H H H
H H
H C H
C H H
C C C C
H H H H
C C C C C C
H H H H
H H H H H H
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Naming Cyclic Alkanes
• Use the same naming rules as before
except attach the prefix “cyclo-” to
name the parent.
• Use the same substituent naming
rules as before.
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Example:
Name the following cycloalkane:
Parent name?
CH3
H3C HC
CH
1 2
CH2 Substituents?
H2C 3
CH
CH2 CH3
1-isopropyl-3-methyl cyclopentane
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
Example:
Name the following cycloalkane:
Parent name?
H3C
CH2 Substituents?
H2C CH2
2 1 CH3
CH CH
H2C CH2
1-ethyl-2-propyl cyclobutane
Copyright © 2011-present MsRazz ChemClass
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Product Information Vamin 18 PDFDocument7 pagesProduct Information Vamin 18 PDFportosinNo ratings yet
- Deductive Tasting Grid Dec 2016Document1 pageDeductive Tasting Grid Dec 2016stanciu virgilNo ratings yet
- Alkanes HQDocument28 pagesAlkanes HQHaslimi Bin HassanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry CCDocument77 pagesOrganic Chemistry CCmunthalipeggy4No ratings yet
- Week1-3 OrgChem1 UpdatedStructureNomenclatureLecture 2023Document182 pagesWeek1-3 OrgChem1 UpdatedStructureNomenclatureLecture 2023happy cyenoNo ratings yet
- IB Organic Chemistry Note SL (Note Cards)Document31 pagesIB Organic Chemistry Note SL (Note Cards)陳定均No ratings yet
- 19a Organic Chemistry 1 DetailedDocument55 pages19a Organic Chemistry 1 DetailedKarel BrionesNo ratings yet
- 12 - Alkanes Lecture NotesDocument15 pages12 - Alkanes Lecture Notesقاتل مستأجرNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry:: Functional GroupsDocument43 pagesOrganic Chemistry:: Functional GroupsprincesschemistNo ratings yet
- Note On AlkenesDocument8 pagesNote On Alkenes1danfammy1No ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Carbon CompoundDocument12 pagesNomenclature of Carbon CompoundTj NovalNo ratings yet
- 2022 H2 Alkanes Lect 1 - 4augDocument24 pages2022 H2 Alkanes Lect 1 - 4augcaseypokemon088No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For AlevelDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry For AlevelNahida HossainNo ratings yet
- Basic Nomenclature AlkanesDocument12 pagesBasic Nomenclature AlkanesPsychoPak OfficialNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument88 pagesOrganic Chemistrys17m0582No ratings yet
- 2 AlkaneDocument22 pages2 AlkaneNatashamazukiNo ratings yet
- Organic Naming RulesDocument50 pagesOrganic Naming Rulesjg2No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - AlkanesDocument7 pagesTopic 2 - AlkanesRichard WalkerNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument10 pagesHydrocarbonAstuti GendaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesOrganic ChemistryAnonymous 1c0HNRTC9GNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Organic ChemistryDocument104 pagesChapter 8 - Organic Chemistryhiu nok kwanNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1 Basic ConceptsDocument35 pages4.1.1 Basic Conceptsaioplayz951No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Section 2Document14 pagesHydrocarbons: Section 2Karam AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry (Lesson Only) - 0Document42 pagesOrganic Chemistry (Lesson Only) - 0osimp3095No ratings yet
- 4 Introductory Organic Chemistry and AlkanesDocument12 pages4 Introductory Organic Chemistry and AlkanesChristina HerculesNo ratings yet
- Naming Organic CompoundsDocument33 pagesNaming Organic CompoundsCorpus, Irene Zen P.No ratings yet
- Alkanes Lecture - 1Document54 pagesAlkanes Lecture - 1hagshhsiauhagah516525No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument44 pagesChapter 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsKaran Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapters 7 & 8Document66 pagesChapters 7 & 8Amirabbas SaffariNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 1Document12 pagesAlkanes 1Wasajja NajibNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1&2Document142 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1&2Kennedy ChitayiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Aromatic Compounds: 4.1 Some Facts About BenzeneDocument20 pagesChapter 4. Aromatic Compounds: 4.1 Some Facts About Benzenehanna liuNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons & Functional GroupsDocument62 pagesHydrocarbons & Functional GroupsNINO DOLINONo ratings yet
- AlkaneDocument2 pagesAlkaneMukisa Esther graceNo ratings yet
- 2021 Chapter 9 Notes - Organic CompoundsDocument16 pages2021 Chapter 9 Notes - Organic CompoundsJoshua GouralnikNo ratings yet
- Erica Jane L. Sulit Rhoyelle D. Mag-IsaDocument28 pagesErica Jane L. Sulit Rhoyelle D. Mag-IsaErica Jane SulitNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument14 pages1.5 Introduction To Organic Chemistrymaya 1DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NewDocument35 pagesChapter 5 NewNoor farahin bainNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC ChemistryDocument150 pagesORGANIC ChemistryAhmad AlShahrourNo ratings yet
- Naming HydrocarbonsDocument28 pagesNaming HydrocarbonsavreljeaneboncalesNo ratings yet
- Chem 100 Unit 4 Organic ChemistryDocument27 pagesChem 100 Unit 4 Organic ChemistryIsah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument44 pagesChapter - 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsElaine McDholicNo ratings yet
- MEQ L (Introductory Organic Chemistry)Document62 pagesMEQ L (Introductory Organic Chemistry)Furious SKNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Aldehyds, KetonesDocument54 pagesLesson 8 Aldehyds, KetonesIris BallajNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry SlidesDocument53 pagesOrganic Chemistry SlidesmbaguleekaristiNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument22 pagesCH 4 Carbon and Its Compoundsmanojsinghbagi56No ratings yet
- Organic NomenclatureDocument12 pagesOrganic Nomenclatureitbwng100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry WorksheetDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry WorksheetOrane CassanovaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HYDROCARBONDocument12 pagesIntroduction To HYDROCARBONMohamad AzaniNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1: Prof. Dr. Fakhri ElabbarDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1: Prof. Dr. Fakhri ElabbarFakhri ElabbarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 2SPPDocument53 pagesChapter 02 2SPProugeaiden143No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons PDFDocument48 pagesHydrocarbons PDFAniruddha KawadeNo ratings yet
- Novel TutorialsDocument2 pagesNovel TutorialsUrjita DasNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1 - Chem - f3 - v1 1Document77 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1 - Chem - f3 - v1 1Lubanga N JamesNo ratings yet
- Xkis Organic Chemistry 18-19 - Abhishek KumarDocument7 pagesXkis Organic Chemistry 18-19 - Abhishek KumarSwastik Dutta RoyNo ratings yet
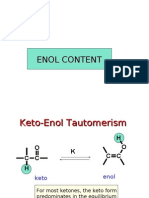
- Enol ContentDocument13 pagesEnol Contentsally gomaa100% (2)
- Universty: UrdanetaDocument7 pagesUniversty: UrdanetaMello DiaxNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry 2019Document127 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry 2019Nonhlanhla NdlovuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 202: Reactions of Alkenes, Part 1Document28 pagesChemistry 202: Reactions of Alkenes, Part 1CindyNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument8 pagesNomenclatureNarjis FatimaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and AlkenesDocument17 pagesAlkanes and AlkenesChristopher gotemNo ratings yet
- Bs Architecture 1C: Name Address Contact NoDocument2 pagesBs Architecture 1C: Name Address Contact NoAlven T BactadNo ratings yet
- Kingston College Valency and Writing Formulae Home Work: Name: - Grade 10Document2 pagesKingston College Valency and Writing Formulae Home Work: Name: - Grade 1012&13 SciencesNo ratings yet
- Fibre-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) CompositesDocument56 pagesFibre-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) CompositesEsmailAlshogaryNo ratings yet
- Denatured Alcohol: Jump ToDocument13 pagesDenatured Alcohol: Jump ToDr_Asma86No ratings yet
- 2018 Bioprocessing of FoodDocument85 pages2018 Bioprocessing of FoodSaheed AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Copyofapchemistrytakehometest 2Document7 pagesCopyofapchemistrytakehometest 2api-311739848No ratings yet
- Final Draft of Sodium Acetate Lab ReportDocument2 pagesFinal Draft of Sodium Acetate Lab ReportAaron LiNo ratings yet
- Training Courses On Polyurethane AdhesivesDocument67 pagesTraining Courses On Polyurethane AdhesivesCarlotta C.No ratings yet
- Ppe Hazard Assessment AnalysisDocument3 pagesPpe Hazard Assessment AnalysisArief FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Metabolism in The Fed and Fasting States-2010Document24 pagesMetabolism in The Fed and Fasting States-2010Mousa SuhailNo ratings yet
- Chau Fasman Using MATLABDocument4 pagesChau Fasman Using MATLABrawatpooran05No ratings yet
- Amino Acids BiochemistryDocument21 pagesAmino Acids BiochemistryAhmed Talal100% (1)
- Is 1448 (P 1) 2002 Determination of Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Potentiometric TitrationDocument17 pagesIs 1448 (P 1) 2002 Determination of Acid Number of Petroleum Products by Potentiometric TitrationMalouk CheniouniNo ratings yet
- MDCAT 2017 Reconduct-UnlockedDocument30 pagesMDCAT 2017 Reconduct-UnlockedArsalan Khan GhauriNo ratings yet
- Coconut Fatty Acid Diethanolamide - CDE 85Document6 pagesCoconut Fatty Acid Diethanolamide - CDE 85Iqbal batchaNo ratings yet
- STEREOISOMERISMDocument11 pagesSTEREOISOMERISMSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Food Technology Fact Sheet: Edible Oil QualityDocument4 pagesFood Technology Fact Sheet: Edible Oil QualityyohannesNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids: Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Organic ChemistryHezron BumbunganNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of The Partial Oxidation of MethanolDocument16 pagesKinetics of The Partial Oxidation of MethanolmagierezNo ratings yet
- Biohydrogen, Biomethane and Bioelectricity As Crucial Components of Biorefinery of Organic Wastes - A ReviewDocument13 pagesBiohydrogen, Biomethane and Bioelectricity As Crucial Components of Biorefinery of Organic Wastes - A ReviewIvanNo ratings yet
- Flexible Displays Using TFT'SDocument16 pagesFlexible Displays Using TFT'SRaghavendra RaghavNo ratings yet
- SESE 115 Biochemistry: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union PhilippinesDocument13 pagesSESE 115 Biochemistry: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union PhilippinesVhenz MapiliNo ratings yet
- Phet - Activity 1Document4 pagesPhet - Activity 1api-306913723No ratings yet
- C ProfileDocument16 pagesC ProfileResky Ervaldi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Systematic Analysis of A Mixture Containing Two SaltsDocument10 pagesScheme For Systematic Analysis of A Mixture Containing Two SaltsMuhammad Shaheer JavedNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies For The Conversion of ResiduesDocument24 pagesEmerging Technologies For The Conversion of ResiduesRuth AbelloNo ratings yet
- Liquid Liquid Equilibrium For Ternary System N Butanol + N Hexane + Ethylene Glycol at 298.15 323.15 KDocument6 pagesLiquid Liquid Equilibrium For Ternary System N Butanol + N Hexane + Ethylene Glycol at 298.15 323.15 KWilo JaraNo ratings yet
- HL P2 Exam Chem2020Document12 pagesHL P2 Exam Chem2020rania samirNo ratings yet