Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsChapter 4 Slides
Chapter 4 Slides
Uploaded by
vanshitCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 11/20/2018 MIST.3030 Database Management Systems by Xiaobai Li 1Document6 pages11/20/2018 MIST.3030 Database Management Systems by Xiaobai Li 1Nina LeNo ratings yet
- Section 6 QuizDocument9 pagesSection 6 Quiznafetsboy100% (1)
- MySQL2 Query1Table (Murach 3e Slides Chap 03)Document59 pagesMySQL2 Query1Table (Murach 3e Slides Chap 03)Gia Cát HuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SlidesDocument41 pagesChapter 1 SlidesvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document48 pagesChapter 4Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4murachDocument48 pagesChapter 4murachMariaBufneaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SlidesDocument17 pagesChapter 5 SlidesvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Slides MurachDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Slides MurachvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document54 pagesChapter 3Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document35 pagesChapter 03Munir SalemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document34 pagesChapter 6Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document21 pagesChapter 5Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Slides MurachDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Slides MurachvanshitNo ratings yet
- AX2012 User Interfaces 03Document24 pagesAX2012 User Interfaces 03indusaNo ratings yet
- How To Retrieve Data From Two or More TablesDocument41 pagesHow To Retrieve Data From Two or More TablesDerick Blacido ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document69 pagesChapter 02Munir SalemNo ratings yet
- 9713 Y08 SP 2 PDFDocument6 pages9713 Y08 SP 2 PDFAhmed ZiadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document28 pagesChapter 11Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- 411 Max or inDocument124 pages411 Max or inmchansekarNo ratings yet
- 9713 Y08 SP 2Document6 pages9713 Y08 SP 2HamzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 BroussardDocument11 pagesAssignment 4 Broussardapi-635217861No ratings yet
- Com 318 Database Systems 2015 2016 Sept DecDocument4 pagesCom 318 Database Systems 2015 2016 Sept DecGabriel ANGELNo ratings yet
- Report Programming Model For Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012Document37 pagesReport Programming Model For Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012senthil_suruliNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office Access 2013: Relational Databases and SubformsDocument19 pagesMicrosoft Office Access 2013: Relational Databases and SubformsAhamed ImranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document56 pagesChapter 10Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Belair High School Csec Information Technology Sba: Description of The ProjectDocument7 pagesBelair High School Csec Information Technology Sba: Description of The ProjectNicole TuckerNo ratings yet
- Finally, A Tool For Business Users! A Step-By-Step Practical Approach To Pharma Sales Reporting Using SAS® Enterprise Guide® 4.3Document18 pagesFinally, A Tool For Business Users! A Step-By-Step Practical Approach To Pharma Sales Reporting Using SAS® Enterprise Guide® 4.3av0224atgmailcomNo ratings yet
- DBMS NEP Lab ManualDocument57 pagesDBMS NEP Lab Manualdharanendrabillionaire1No ratings yet
- Half Yearly Examination 2018 DmaDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly Examination 2018 DmaJacinth EsupadamNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument7 pagesAssessmentShailesh ShitoleNo ratings yet
- Dbms 1 To 18updatedDocument39 pagesDbms 1 To 18updatedVimal MishraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 005 - JoinsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Exercise 005 - JoinsTeri CulaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 FinalDocument10 pagesAssignment 4 Finalapi-571488031No ratings yet
- DBMS Lab SyllabusDocument5 pagesDBMS Lab SyllabusHARICHANDANA DIGAVINTINo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelAl-Sami MashrafeeNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 08 PDFDocument9 pagesLab Manual 08 PDFShahid ZikriaNo ratings yet
- AR Invoice InterfaceDocument4 pagesAR Invoice InterfaceprinjurpNo ratings yet
- Database Worksheet 1-1Document2 pagesDatabase Worksheet 1-1Avakash RaghavNo ratings yet
- Basic Lab For MySQLDocument6 pagesBasic Lab For MySQLleulNo ratings yet
- Sba 2026Document4 pagesSba 2026kimesha waltersNo ratings yet
- AXXXDocument20 pagesAXXXChristianAlessiNo ratings yet
- MSCDA601 - August 2020 - December 2020 NORMALDocument4 pagesMSCDA601 - August 2020 - December 2020 NORMALMcebisi NcubeNo ratings yet
- HRMS Version 2.0Document143 pagesHRMS Version 2.0Saravana Kumar100% (1)
- Dbms Lab ManualDocument44 pagesDbms Lab ManualBilal ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage Via Business Processes: Figure 3-13Document4 pagesCompetitive Advantage Via Business Processes: Figure 3-13Quynh TrangNo ratings yet
- Link Between Supplier and Customer in R12Document6 pagesLink Between Supplier and Customer in R12AzizzulHassanNo ratings yet
- Outer Joins in Visual Foxpro 5.0: Issue Date: Foxtalk October 1996Document17 pagesOuter Joins in Visual Foxpro 5.0: Issue Date: Foxtalk October 1996gurubarandNo ratings yet
- MySQL Query Browser Activity 4Document8 pagesMySQL Query Browser Activity 4Jeremias C. EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Database Systems MQs 2014-2015Document12 pagesDatabase Systems MQs 2014-2015Hon seif MwabegeNo ratings yet
- Sql-Joins: Inner, Outer, Full: Session 6 (Week 4)Document24 pagesSql-Joins: Inner, Outer, Full: Session 6 (Week 4)Subhadip SinhaNo ratings yet
- Heckaman Jeremy Final Project ReportDocument12 pagesHeckaman Jeremy Final Project ReportukamaluddinmbaNo ratings yet
- Model MidTerm QBank DBMSDocument1 pageModel MidTerm QBank DBMSyashpatelykpNo ratings yet
- Ire Port WizardDocument10 pagesIre Port WizardSanderson SaNo ratings yet
- Data Source Enhancement With BadisDocument11 pagesData Source Enhancement With BadisSirajuddin MohdNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3: Complete Problems #5, #9 and #27 On Pages 186, 187 and 192 Respectively of The TextDocument4 pagesAssignment #3: Complete Problems #5, #9 and #27 On Pages 186, 187 and 192 Respectively of The TextKobinaNo ratings yet
- Database Design DBT1111C 5Document7 pagesDatabase Design DBT1111C 5Abhay Kumar Sharma BOODHOONo ratings yet
- 100+ SQL Queries Jet SQL for Microsoft Office AccessFrom Everand100+ SQL Queries Jet SQL for Microsoft Office AccessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Querying with SQL T-SQL for Microsoft SQL ServerFrom EverandQuerying with SQL T-SQL for Microsoft SQL ServerRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Chapter 2 Slides MurachDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Slides MurachvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Slides MurachDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Slides MurachvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SlidesDocument41 pagesChapter 1 SlidesvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SlidesDocument17 pagesChapter 5 SlidesvanshitNo ratings yet
- Actividad 13 Evidencia 4 InglesDocument7 pagesActividad 13 Evidencia 4 InglesfredypiraconNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of InfotypesDocument8 pagesEnhancement of InfotypesAshok KancharlaNo ratings yet
- PLC Transmit Instruction Mov Smov Cmov Bmov FmovDocument2 pagesPLC Transmit Instruction Mov Smov Cmov Bmov FmovNatKThNo ratings yet
- Career at PrachayDocument15 pagesCareer at PrachayGirish LakhotiyaNo ratings yet
- Mcdonald'S History ListingDocument9 pagesMcdonald'S History Listinghimanshu-guntewar-4431No ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument1 pageChecklistLarrytate15100% (2)
- Top 42 Electrical Machines Interview Questions (2023) - JavatpointDocument15 pagesTop 42 Electrical Machines Interview Questions (2023) - JavatpointeeeshijaNo ratings yet
- Reducer: Sweat Reducer Hydraulic Concentric Eccentric ReducersDocument1 pageReducer: Sweat Reducer Hydraulic Concentric Eccentric ReducersMayur MandrekarNo ratings yet
- Fawaz HadiDocument1 pageFawaz HadiAnonymous LuvhmxPNo ratings yet
- m4l27 Lesson 27 The Direct Stiffness Method: BeamsDocument17 pagesm4l27 Lesson 27 The Direct Stiffness Method: BeamsVitor Vale100% (1)
- Cannes Lions 2019: Digital Craft Lions ShortlistDocument18 pagesCannes Lions 2019: Digital Craft Lions Shortlistadobo magazineNo ratings yet
- Program of WorksDocument2 pagesProgram of WorksSimply RoseNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5 Chap 5 AnswerDocument4 pagesQuiz 5 Chap 5 AnswerPhương NgaNo ratings yet
- 2012rap BRC PDFDocument185 pages2012rap BRC PDFFarikhNo ratings yet
- Name Email Phone Hometown: Authorized To Work in The US For Any EmployerDocument3 pagesName Email Phone Hometown: Authorized To Work in The US For Any EmployerR.T. CoffmanNo ratings yet
- New Salary Scales Updated February 2023 NAC ExtendedDocument2 pagesNew Salary Scales Updated February 2023 NAC ExtendedIon NNo ratings yet
- 3 Gimp Size Color Contrast Crop RedeyeDocument2 pages3 Gimp Size Color Contrast Crop Redeyeapi-370628488No ratings yet
- Manejadora - Cba25uh - 018 Al 060 - Lennox - Ficha Tecnica - I LennoxDocument16 pagesManejadora - Cba25uh - 018 Al 060 - Lennox - Ficha Tecnica - I LennoxWalter BernalNo ratings yet
- Legal Provisions Relating To Managing Director / Whole-Time DirectorDocument10 pagesLegal Provisions Relating To Managing Director / Whole-Time DirectorSoumitra ChawatheNo ratings yet
- Modeling Wood Structural Panel Portal Frame ResponseDocument2 pagesModeling Wood Structural Panel Portal Frame ResponseGuillaumeHNONo ratings yet
- Pricelist Laptop & PrinterDocument7 pagesPricelist Laptop & PrinterKharis FreefireNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Getting Data From The Client (Form Handling)Document43 pagesChapter 6 Getting Data From The Client (Form Handling)shariifcqaadir985No ratings yet
- S7 M WE4 RWBu QCCJs EDocument8 pagesS7 M WE4 RWBu QCCJs Eindasijames06No ratings yet
- Formal-Relational Query Languages: Practice ExercisesDocument4 pagesFormal-Relational Query Languages: Practice ExercisesDivyanshu BoseNo ratings yet
- Jameco Part Number 838680: Distributed byDocument20 pagesJameco Part Number 838680: Distributed byAlan FuentesNo ratings yet
- Globe Valves: Standard SpecificationDocument26 pagesGlobe Valves: Standard SpecificationHammad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Lipidomics Methods and Protocols 2Nd Edition Sanjoy K Bhattacharya Editor Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Lipidomics Methods and Protocols 2Nd Edition Sanjoy K Bhattacharya Editor Online PDF All Chapterandrewmolina926227100% (4)
- Pilot/Escort Vehicle Operators: Training ManualDocument140 pagesPilot/Escort Vehicle Operators: Training ManualD Rider CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Shea Davis - Rocket Project ReflectionDocument8 pagesShea Davis - Rocket Project Reflectionapi-583382380No ratings yet
- Lean Thinking Banish Waste and Create Wealth in YoDocument9 pagesLean Thinking Banish Waste and Create Wealth in YoKandan KarunaiNo ratings yet
Chapter 4 Slides
Chapter 4 Slides
Uploaded by
vanshit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views38 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter 4 slides
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views38 pagesChapter 4 Slides
Chapter 4 Slides
Uploaded by
vanshitCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 38
Chapter 4
How to retrieve data
from two or more tables
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 1
Objectives
Applied
1. Use the explicit syntax to code an inner join that returns data
from a single table or multiple tables.
2. Use the explicit syntax to code an outer join.
3. Code a union that combines data from a single table or multiple
tables.
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 2
Objectives (continued)
Knowledge
1. Explain when column names need to be qualified.
2. Describe the proper use of a table alias.
3. Describe the differences between an inner join, a left outer join, a
right outer join, a full outer join, and a cross join.
4. Describe how to combine inner and outer joins.
5. Describe the use of the implicit syntax for coding joins.
6. Describe the use of the USING and NATURAL keywords for
coding joins.
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 3
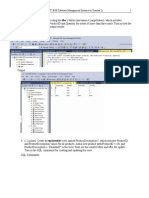
The explicit syntax for an inner join
SELECT select_list
FROM table_1
[INNER] JOIN table_2
ON join_condition_1
[[INNER] JOIN table_3
ON join_condition_2]...
An inner join of the Vendors and Invoices tables
SELECT invoice_number, vendor_name
FROM vendors INNER JOIN invoices
ON vendors.vendor_id = invoices.vendor_id
ORDER BY invoice_number
(114 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 4
The syntax for an inner join that uses table aliases
SELECT select_list
FROM table_1 a1
[INNER] JOIN table_2 a2
ON a1.column_name operator a2.column_name
[[INNER] JOIN table_3 a3
ON a2.column_name operator a3.column_name]...
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 5
An inner join with aliases for all tables
SELECT invoice_number, vendor_name, invoice_due_date,
invoice_total - payment_total - credit_total
AS balance_due
FROM vendors v JOIN invoices i
ON v.vendor_id = i.vendor_id
WHERE invoice_total - payment_total - credit_total > 0
ORDER BY invoice_due_date DESC
(11 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 6
An inner join with an alias for only one table
SELECT invoice_number, line_item_amount,
line_item_description
FROM invoices JOIN invoice_line_items line_items
ON invoices.invoice_id = line_items.invoice_id
WHERE account_number = 540
ORDER BY invoice_date
(6 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 7
The syntax of a table name that’s qualified
with a database name
database_name.table_name
A join to a table in another database
SELECT vendor_name, customer_last_name,
customer_first_name, vendor_state AS state,
vendor_city AS city
FROM vendors v
JOIN om.customers c
ON v.vendor_zip_code = c.customer_zip
ORDER BY state, city
(37 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 8
The Customers table
(24 rows)
The Employees table
(9 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 9
An inner join with two conditions
SELECT customer_first_name, customer_last_name
FROM customers c JOIN employees e
ON c.customer_first_name = e.first_name
AND c.customer_last_name = e.last_name
(1 row)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 10
A self-join that returns vendors from cities
in common with other vendors
SELECT DISTINCT v1.vendor_name, v1.vendor_city,
v1.vendor_state
FROM vendors v1 JOIN vendors v2
ON v1.vendor_city = v2.vendor_city AND
v1.vendor_state = v2.vendor_state AND
v1.vendor_name <> v2.vendor_name
ORDER BY v1.vendor_state, v1.vendor_city
(84 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 11
A statement that joins four tables
SELECT vendor_name, invoice_number, invoice_date,
line_item_amount, account_description
FROM vendors v
JOIN invoices i
ON v.vendor_id = i.vendor_id
JOIN invoice_line_items li
ON i.invoice_id = li.invoice_id
JOIN general_ledger_accounts gl
ON li.account_number = gl.account_number
WHERE invoice_total - payment_total - credit_total > 0
ORDER BY vendor_name, line_item_amount DESC
(11 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 12
The implicit syntax for an inner join
SELECT select_list
FROM table_1, table_2 [, table_3]...
WHERE table_1.column_name operator table_2.column_name
[AND table_2.column_name operator table_3.column_name]...
Join the Vendors and Invoices tables
SELECT invoice_number, vendor_name
FROM vendors v, invoices i
WHERE v.vendor_id = i.vendor_id
ORDER BY invoice_number
(114 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 13
Join four tables
SELECT vendor_name, invoice_number, invoice_date,
line_item_amount, account_description
FROM vendors v, invoices i, invoice_line_items li,
general_ledger_accounts gl
WHERE v.vendor_id = i.vendor_id
AND i.invoice_id = li.invoice_id
AND li.account_number = gl.account_number
AND invoice_total - payment_total - credit_total > 0
ORDER BY vendor_name, line_item_amount DESC
(11 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 14
Terms to know about inner joins
Join
Join condition
Inner join
Ad hoc relationship
Qualified column name
Table alias
Schema
Self-join
Explicit syntax (SQL-92)
Implicit syntax
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 15
The explicit syntax for an outer join
SELECT select_list
FROM table_1
{LEFT|RIGHT} [OUTER] JOIN table_2
ON join_condition_1
[{LEFT|RIGHT} [OUTER] JOIN table_3
ON join_condition_2]...
What outer joins do
Joins of this type Retrieve unmatched rows from
Left outer join The first (left) table
Right outer join The second (right) table
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 16
A left outer join of the Vendors and Invoices tables
SELECT vendor_name, invoice_number, invoice_total
FROM vendors LEFT JOIN invoices
ON vendors.vendor_id = invoices.vendor_id
ORDER BY vendor_name
(202 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 17
The Departments table
The Employees table
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 18
The Projects table
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 19
A left outer join
SELECT department_name, d.department_number, last_name
FROM departments d
LEFT JOIN employees e
ON d.department_number = e.department_number
ORDER BY department_name
(8 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 20
A right outer join
SELECT department_name, e.department_number, last_name
FROM departments d
RIGHT JOIN employees e
ON d.department_number = e.department_number
ORDER BY department_name
(9 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 21
Join three tables using left outer joins
SELECT department_name, last_name, project_number
FROM departments d
LEFT JOIN employees e
ON d.department_number = e.department_number
LEFT JOIN projects p
ON e.employee_id = p.employee_id
ORDER BY department_name, last_name
(8 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 22
Combine an outer and an inner join
SELECT department_name, last_name, project_number
FROM departments d
JOIN employees e
ON d.department_number = e.department_number
LEFT JOIN projects p
ON e.employee_id = p.employee_id
ORDER BY department_name, last_name
(7 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 23
The syntax for a join that uses the USING keyword
SELECT select_list
FROM table_1
[{LEFT|RIGHT} [OUTER]] JOIN table_2
USING (join_column_1[, join_column_2]...)
[[{LEFT|RIGHT} [OUTER]] JOIN table_3
USING (join_column_1[, join_column_2]...)]...
Use the USING keyword to join two tables
SELECT invoice_number, vendor_name
FROM vendors
JOIN invoices USING (vendor_id)
ORDER BY invoice_number
(114 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 24
Use the USING keyword to join three tables
SELECT department_name, last_name, project_number
FROM departments
JOIN employees USING (department_number)
LEFT JOIN projects USING (employee_id)
ORDER BY department_name
(7 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 25
The syntax for a join
that uses the NATURAL keyword
SELECT select_list
FROM table_1
NATURAL JOIN table_2
[NATURAL JOIN table_3]...
Use the NATURAL keyword to join tables
SELECT invoice_number, vendor_name
FROM vendors
NATURAL JOIN invoices
ORDER BY invoice_number
(114 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 26
Use the NATURAL keyword in a statement
that joins three tables
SELECT department_name AS dept_name, last_name,
project_number
FROM departments
NATURAL JOIN employees
LEFT JOIN projects USING (employee_id)
ORDER BY department_name
(7 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 27
The explicit syntax for a cross join
SELECT select_list
FROM table_1 CROSS JOIN table_2
A cross join that uses the explicit syntax
SELECT departments.department_number, department_name,
employee_id, last_name
FROM departments CROSS JOIN employees
ORDER BY departments.department_number
(45 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 28
The implicit syntax for a cross join
SELECT select_list
FROM table_1, table_2
A cross join that uses the implicit syntax
SELECT departments.department_number, department_name,
employee_id, last_name
FROM departments, employees
ORDER BY departments.department_number
(45 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 29
Terms to know about other types of joins
Outer join
Left outer join
Right outer join
Equijoin
Natural join
Cross join
Cartesian product
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 30
The syntax for a union operation
SELECT_statement_1
UNION [ALL]
SELECT_statement_2
[UNION [ALL]
SELECT_statement_3]...
[ORDER BY order_by_list]
Rules for a union
• Each result set must return the same number of columns.
• The corresponding columns in each result set must have
compatible data types.
• The column names in the final result set are taken from the first
SELECT clause.
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 31
A union that combines result sets
from two different tables
SELECT 'Active' AS source, invoice_number,
invoice_date, invoice_total
FROM active_invoices
WHERE invoice_date >= '2018-06-01'
UNION
SELECT 'Paid' AS source, invoice_number,
invoice_date, invoice_total
FROM paid_invoices
WHERE invoice_date >= '2018-06-01'
ORDER BY invoice_total DESC
(22 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 32
A union that combines result sets
from a single table
SELECT 'Active' AS source, invoice_number,
invoice_date, invoice_total
FROM invoices
WHERE invoice_total - payment_total - credit_total > 0
UNION
SELECT 'Paid' AS source, invoice_number,
invoice_date, invoice_total
FROM invoices
WHERE invoice_total - payment_total - credit_total <= 0
ORDER BY invoice_total DESC
(114 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 33
A union that combines result sets
from the same two tables
SELECT invoice_number, vendor_name,
'33% Payment' AS payment_type,
invoice_total AS total,
invoice_total * 0.333 AS payment
FROM invoices JOIN vendors
ON invoices.vendor_id = vendors.vendor_id
WHERE invoice_total > 10000
UNION
SELECT invoice_number, vendor_name,
'50% Payment' AS payment_type,
invoice_total AS total,
invoice_total * 0.5 AS payment
FROM invoices JOIN vendors
ON invoices.vendor_id = vendors.vendor_id
WHERE invoice_total BETWEEN 500 AND 10000
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 34
A union that combines result sets
from the same two tables (continued)
UNION
SELECT invoice_number, vendor_name,
'Full amount' AS payment_type,
invoice_total AS total,
invoice_total AS payment
FROM invoices JOIN vendors
ON invoices.vendor_id = vendors.vendor_id
WHERE invoice_total < 500
ORDER BY payment_type, vendor_name, invoice_number
(114 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 35
A union that simulates a full outer join
SELECT department_name AS dept_name,
d.department_number AS d_dept_no,
e.department_number AS e_dept_no, last_name
FROM departments d
LEFT JOIN employees e
ON d.department_number = e.department_number
UNION
SELECT department_name AS dept_name,
d.department_number AS d_dept_no,
e.department_number AS e_dept_no, last_name
FROM departments d
RIGHT JOIN employees e
ON d.department_number = e.department_number
ORDER BY dept_name
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 36
A union that simulates a full outer join (result set)
(10 rows)
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 37
Terms to know about unions
Union
Full outer join
© 2019, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.
Murach’s MySQL 3rd Edition C4, Slide 38
You might also like
- 11/20/2018 MIST.3030 Database Management Systems by Xiaobai Li 1Document6 pages11/20/2018 MIST.3030 Database Management Systems by Xiaobai Li 1Nina LeNo ratings yet
- Section 6 QuizDocument9 pagesSection 6 Quiznafetsboy100% (1)
- MySQL2 Query1Table (Murach 3e Slides Chap 03)Document59 pagesMySQL2 Query1Table (Murach 3e Slides Chap 03)Gia Cát HuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SlidesDocument41 pagesChapter 1 SlidesvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document48 pagesChapter 4Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4murachDocument48 pagesChapter 4murachMariaBufneaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SlidesDocument17 pagesChapter 5 SlidesvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Slides MurachDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Slides MurachvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document54 pagesChapter 3Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document35 pagesChapter 03Munir SalemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document34 pagesChapter 6Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document21 pagesChapter 5Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Slides MurachDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Slides MurachvanshitNo ratings yet
- AX2012 User Interfaces 03Document24 pagesAX2012 User Interfaces 03indusaNo ratings yet
- How To Retrieve Data From Two or More TablesDocument41 pagesHow To Retrieve Data From Two or More TablesDerick Blacido ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document69 pagesChapter 02Munir SalemNo ratings yet
- 9713 Y08 SP 2 PDFDocument6 pages9713 Y08 SP 2 PDFAhmed ZiadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document28 pagesChapter 11Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- 411 Max or inDocument124 pages411 Max or inmchansekarNo ratings yet
- 9713 Y08 SP 2Document6 pages9713 Y08 SP 2HamzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 BroussardDocument11 pagesAssignment 4 Broussardapi-635217861No ratings yet
- Com 318 Database Systems 2015 2016 Sept DecDocument4 pagesCom 318 Database Systems 2015 2016 Sept DecGabriel ANGELNo ratings yet
- Report Programming Model For Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012Document37 pagesReport Programming Model For Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012senthil_suruliNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office Access 2013: Relational Databases and SubformsDocument19 pagesMicrosoft Office Access 2013: Relational Databases and SubformsAhamed ImranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document56 pagesChapter 10Eckart SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Belair High School Csec Information Technology Sba: Description of The ProjectDocument7 pagesBelair High School Csec Information Technology Sba: Description of The ProjectNicole TuckerNo ratings yet
- Finally, A Tool For Business Users! A Step-By-Step Practical Approach To Pharma Sales Reporting Using SAS® Enterprise Guide® 4.3Document18 pagesFinally, A Tool For Business Users! A Step-By-Step Practical Approach To Pharma Sales Reporting Using SAS® Enterprise Guide® 4.3av0224atgmailcomNo ratings yet
- DBMS NEP Lab ManualDocument57 pagesDBMS NEP Lab Manualdharanendrabillionaire1No ratings yet
- Half Yearly Examination 2018 DmaDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly Examination 2018 DmaJacinth EsupadamNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument7 pagesAssessmentShailesh ShitoleNo ratings yet
- Dbms 1 To 18updatedDocument39 pagesDbms 1 To 18updatedVimal MishraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 005 - JoinsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Exercise 005 - JoinsTeri CulaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 FinalDocument10 pagesAssignment 4 Finalapi-571488031No ratings yet
- DBMS Lab SyllabusDocument5 pagesDBMS Lab SyllabusHARICHANDANA DIGAVINTINo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelAl-Sami MashrafeeNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 08 PDFDocument9 pagesLab Manual 08 PDFShahid ZikriaNo ratings yet
- AR Invoice InterfaceDocument4 pagesAR Invoice InterfaceprinjurpNo ratings yet
- Database Worksheet 1-1Document2 pagesDatabase Worksheet 1-1Avakash RaghavNo ratings yet
- Basic Lab For MySQLDocument6 pagesBasic Lab For MySQLleulNo ratings yet
- Sba 2026Document4 pagesSba 2026kimesha waltersNo ratings yet
- AXXXDocument20 pagesAXXXChristianAlessiNo ratings yet
- MSCDA601 - August 2020 - December 2020 NORMALDocument4 pagesMSCDA601 - August 2020 - December 2020 NORMALMcebisi NcubeNo ratings yet
- HRMS Version 2.0Document143 pagesHRMS Version 2.0Saravana Kumar100% (1)
- Dbms Lab ManualDocument44 pagesDbms Lab ManualBilal ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage Via Business Processes: Figure 3-13Document4 pagesCompetitive Advantage Via Business Processes: Figure 3-13Quynh TrangNo ratings yet
- Link Between Supplier and Customer in R12Document6 pagesLink Between Supplier and Customer in R12AzizzulHassanNo ratings yet
- Outer Joins in Visual Foxpro 5.0: Issue Date: Foxtalk October 1996Document17 pagesOuter Joins in Visual Foxpro 5.0: Issue Date: Foxtalk October 1996gurubarandNo ratings yet
- MySQL Query Browser Activity 4Document8 pagesMySQL Query Browser Activity 4Jeremias C. EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Database Systems MQs 2014-2015Document12 pagesDatabase Systems MQs 2014-2015Hon seif MwabegeNo ratings yet
- Sql-Joins: Inner, Outer, Full: Session 6 (Week 4)Document24 pagesSql-Joins: Inner, Outer, Full: Session 6 (Week 4)Subhadip SinhaNo ratings yet
- Heckaman Jeremy Final Project ReportDocument12 pagesHeckaman Jeremy Final Project ReportukamaluddinmbaNo ratings yet
- Model MidTerm QBank DBMSDocument1 pageModel MidTerm QBank DBMSyashpatelykpNo ratings yet
- Ire Port WizardDocument10 pagesIre Port WizardSanderson SaNo ratings yet
- Data Source Enhancement With BadisDocument11 pagesData Source Enhancement With BadisSirajuddin MohdNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3: Complete Problems #5, #9 and #27 On Pages 186, 187 and 192 Respectively of The TextDocument4 pagesAssignment #3: Complete Problems #5, #9 and #27 On Pages 186, 187 and 192 Respectively of The TextKobinaNo ratings yet
- Database Design DBT1111C 5Document7 pagesDatabase Design DBT1111C 5Abhay Kumar Sharma BOODHOONo ratings yet
- 100+ SQL Queries Jet SQL for Microsoft Office AccessFrom Everand100+ SQL Queries Jet SQL for Microsoft Office AccessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Querying with SQL T-SQL for Microsoft SQL ServerFrom EverandQuerying with SQL T-SQL for Microsoft SQL ServerRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Chapter 2 Slides MurachDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Slides MurachvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Slides MurachDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Slides MurachvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SlidesDocument41 pagesChapter 1 SlidesvanshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SlidesDocument17 pagesChapter 5 SlidesvanshitNo ratings yet
- Actividad 13 Evidencia 4 InglesDocument7 pagesActividad 13 Evidencia 4 InglesfredypiraconNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of InfotypesDocument8 pagesEnhancement of InfotypesAshok KancharlaNo ratings yet
- PLC Transmit Instruction Mov Smov Cmov Bmov FmovDocument2 pagesPLC Transmit Instruction Mov Smov Cmov Bmov FmovNatKThNo ratings yet
- Career at PrachayDocument15 pagesCareer at PrachayGirish LakhotiyaNo ratings yet
- Mcdonald'S History ListingDocument9 pagesMcdonald'S History Listinghimanshu-guntewar-4431No ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument1 pageChecklistLarrytate15100% (2)
- Top 42 Electrical Machines Interview Questions (2023) - JavatpointDocument15 pagesTop 42 Electrical Machines Interview Questions (2023) - JavatpointeeeshijaNo ratings yet
- Reducer: Sweat Reducer Hydraulic Concentric Eccentric ReducersDocument1 pageReducer: Sweat Reducer Hydraulic Concentric Eccentric ReducersMayur MandrekarNo ratings yet
- Fawaz HadiDocument1 pageFawaz HadiAnonymous LuvhmxPNo ratings yet
- m4l27 Lesson 27 The Direct Stiffness Method: BeamsDocument17 pagesm4l27 Lesson 27 The Direct Stiffness Method: BeamsVitor Vale100% (1)
- Cannes Lions 2019: Digital Craft Lions ShortlistDocument18 pagesCannes Lions 2019: Digital Craft Lions Shortlistadobo magazineNo ratings yet
- Program of WorksDocument2 pagesProgram of WorksSimply RoseNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5 Chap 5 AnswerDocument4 pagesQuiz 5 Chap 5 AnswerPhương NgaNo ratings yet
- 2012rap BRC PDFDocument185 pages2012rap BRC PDFFarikhNo ratings yet
- Name Email Phone Hometown: Authorized To Work in The US For Any EmployerDocument3 pagesName Email Phone Hometown: Authorized To Work in The US For Any EmployerR.T. CoffmanNo ratings yet
- New Salary Scales Updated February 2023 NAC ExtendedDocument2 pagesNew Salary Scales Updated February 2023 NAC ExtendedIon NNo ratings yet
- 3 Gimp Size Color Contrast Crop RedeyeDocument2 pages3 Gimp Size Color Contrast Crop Redeyeapi-370628488No ratings yet
- Manejadora - Cba25uh - 018 Al 060 - Lennox - Ficha Tecnica - I LennoxDocument16 pagesManejadora - Cba25uh - 018 Al 060 - Lennox - Ficha Tecnica - I LennoxWalter BernalNo ratings yet
- Legal Provisions Relating To Managing Director / Whole-Time DirectorDocument10 pagesLegal Provisions Relating To Managing Director / Whole-Time DirectorSoumitra ChawatheNo ratings yet
- Modeling Wood Structural Panel Portal Frame ResponseDocument2 pagesModeling Wood Structural Panel Portal Frame ResponseGuillaumeHNONo ratings yet
- Pricelist Laptop & PrinterDocument7 pagesPricelist Laptop & PrinterKharis FreefireNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Getting Data From The Client (Form Handling)Document43 pagesChapter 6 Getting Data From The Client (Form Handling)shariifcqaadir985No ratings yet
- S7 M WE4 RWBu QCCJs EDocument8 pagesS7 M WE4 RWBu QCCJs Eindasijames06No ratings yet
- Formal-Relational Query Languages: Practice ExercisesDocument4 pagesFormal-Relational Query Languages: Practice ExercisesDivyanshu BoseNo ratings yet
- Jameco Part Number 838680: Distributed byDocument20 pagesJameco Part Number 838680: Distributed byAlan FuentesNo ratings yet
- Globe Valves: Standard SpecificationDocument26 pagesGlobe Valves: Standard SpecificationHammad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Lipidomics Methods and Protocols 2Nd Edition Sanjoy K Bhattacharya Editor Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Lipidomics Methods and Protocols 2Nd Edition Sanjoy K Bhattacharya Editor Online PDF All Chapterandrewmolina926227100% (4)
- Pilot/Escort Vehicle Operators: Training ManualDocument140 pagesPilot/Escort Vehicle Operators: Training ManualD Rider CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Shea Davis - Rocket Project ReflectionDocument8 pagesShea Davis - Rocket Project Reflectionapi-583382380No ratings yet
- Lean Thinking Banish Waste and Create Wealth in YoDocument9 pagesLean Thinking Banish Waste and Create Wealth in YoKandan KarunaiNo ratings yet