Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth and Life Magmatism
Earth and Life Magmatism
Uploaded by
Marvin Melis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views21 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views21 pagesEarth and Life Magmatism
Earth and Life Magmatism
Uploaded by
Marvin MelisCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
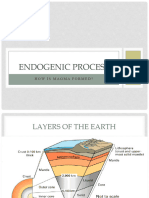
The Earth and Life Sciences:
Geologic Process that Occur
within the Earth
(Magmatism)
Geologic Process that Occur
within the Earth
Learning Objectives
•Describe how magma is formed (magmatism)
Magma
Magma
• Composed of semi-liquid hot molten rocks
located beneath the Earth; in the melted mantle
rock and oceanic plate.
• Solidified, creates igneous rock found on the
surface of the Earth
• Magma and Lava; both molten rocks, Magma
found in the chamber of the volcano, Lava found
on the surface of the Earth
Magma and Lava
Magma
Magmatism
The process under the earth’s crust where
formation of magma occur.
Happen in the lower part of the Earth’s crust
and in the upper portion of the mantle, known as
asthenosphere
Magma
Magmatism
oAsthenosphere
Magma
How is magma formed?
The magma present in the lower crust and
upper mantle of the Earth is formed or generated
through the process of partial melting
oPartial melting:
Different minerals in rock melt at different
temperature and pressure.
Magma
How is magma formed?
Another factor considered in this process is
the addition of volatile materials such as water
and carbon dioxide
Magma
o Partial Melting
Magma
oMelting
Magma
o Melting
- Requires one of the three possible events to occur
1. An increase in temperature
Conduction in mantle happens when heat is
transferred from hotter molten rocks to the Earth’s
cold crust
Process known as heat transfer
As magma rises, it is often hot enough to melt the
rocks it touches.
Magma
oMelting
1. An increase in temperature
happens at convergent boundaries, where
tectonic plates are crashing together
Magma
oMelting
1. An increase in temperature
Magma
o Melting
1. An increase in temperature
Rocks are composed of minerals; start to melt once
the temperature in the lower crust and upper mantle
increases or exceeds the melting point of minerals.
Temperature of mantle reaches 1200 degrees Celsius
Rock minerals such as quartz and feldspar begin to
partially melt at around 650 – 850 oC
Magma
oMelting
2. A decrease of pressure
Mantle rocks remain solid when exposed to high
pressure
During convection, these rocks tend to go upward
(shallower level) and the pressure is reduced;
triggering the melting of magma, know as
decompression melting
Magma
oMelting
2. A decrease of pressure
oDecompression melting
Process occurs at the Mid-Ocean Ridge, an
underwater mountain system
Magma
oMelting
2. A decrease of pressure
oDecompression melting
Magma
o Melting
3. Addition of volatiles
Water or carbon dioxides is added to hot rocks occurs
flux melting
Melting points of minerals within the rocks decrease.
If a rock is already close to its melting point, the
effect of adding these volatiles can be enough to
trigger partial melting
Magma
oMelting
3. Addition of volatiles
It occurs around subduction zones
Magma
Sources:
https://depedtambayan.net/wp-content/uploads/
2021/10/ELS_Q1_Module-7_Magmatism_v2.pdf
You might also like
- Star CCM TutorialDocument2 pagesStar CCM TutorialMuralidharan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Silviculture (2019)Document218 pagesSilviculture (2019)TUSHAR SAHUNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument43 pagesEndogenic ProcessesMeryNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document13 pagesGroup 1Donamae D. DelacruzNo ratings yet
- MagmatismDocument15 pagesMagmatismjadenn busiaNo ratings yet
- MagmatismDocument18 pagesMagmatismgardenshadow139No ratings yet
- Batch 2 Topic 6Document24 pagesBatch 2 Topic 6Mikhael HerreraNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1-Module 7: Magmatism Endogenic ProcessDocument13 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1-Module 7: Magmatism Endogenic ProcessJulius GamayanNo ratings yet
- Demo Presentation - Earth-and-Life-Science-MagmatismDocument8 pagesDemo Presentation - Earth-and-Life-Science-MagmatismCrystel ParNo ratings yet
- MAGMATISMDocument27 pagesMAGMATISMMini Ivan JayNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ProcessesDocument52 pagesEarth Materials and ProcessesMay Lyn BerondoNo ratings yet
- Magmatism Group 3Document29 pagesMagmatism Group 3MARY JOSEPH OCONo ratings yet
- Magma FormationDocument12 pagesMagma FormationAliyana Trisha HarunNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesModule 3 ReviewerMikyla DulinNo ratings yet
- Q1 M7 Magma FormationDocument40 pagesQ1 M7 Magma FormationTheo AugustusNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes, Magma, and Volcanic Eruptions: Characteristics of Magma Types of MagmaDocument12 pagesVolcanoes, Magma, and Volcanic Eruptions: Characteristics of Magma Types of MagmaJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- How Magma Is FormedDocument21 pagesHow Magma Is FormedJAY ANDRESNo ratings yet
- Earth's and Life Science Module 1 Quarter 7 MagmatismDocument9 pagesEarth's and Life Science Module 1 Quarter 7 MagmatismRene Rey B. SulapasNo ratings yet
- MAGMATISMDocument30 pagesMAGMATISMRyan CortezNo ratings yet
- Q1 W1 Lesson 5 and 6Document13 pagesQ1 W1 Lesson 5 and 6Teacher BearNo ratings yet
- Name: Cesar John Catuburan Grade/ Section: Stem CDocument8 pagesName: Cesar John Catuburan Grade/ Section: Stem CMakapikon NagudNo ratings yet
- Nature and Generation of MagmaDocument42 pagesNature and Generation of MagmaMuzmmil MianNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 8.2 Magmatism - How Magma Is FormedDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 8.2 Magmatism - How Magma Is FormedTrishanne PilapilNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument8 pagesEarth ScienceJommel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Magma FormationDocument23 pagesLesson 2.1 Magma FormationRexTheKingNo ratings yet
- ELS-Q1-Week 4-Magmatism and MetamorphismDocument38 pagesELS-Q1-Week 4-Magmatism and MetamorphismRoldan Bibat BoresNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Earth Science Semi FinalsDocument7 pagesReviewer in Earth Science Semi Finalsmarkdexter leynesNo ratings yet
- Earths Internal Heat and MagmatismDocument23 pagesEarths Internal Heat and MagmatismJoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- Reporting About MagmatismDocument9 pagesReporting About MagmatismRene Rey B. SulapasNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessDocument9 pagesEndogenic ProcessKrysfer SecusanaNo ratings yet
- MAGMATISMDocument2 pagesMAGMATISMRaven Chastity EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes Plutonism and VolcanismDocument21 pagesEndogenic Processes Plutonism and VolcanismBen Josiah BayotNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Grade 11 - Lesson 3Document24 pagesQ2 - Grade 11 - Lesson 3Francheska AbandoNo ratings yet
- FOR STUDENTS. MagmatismDocument13 pagesFOR STUDENTS. Magmatismangelmae.estrellaNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes Plutonism and Volcanism PRESENTATION 0F GROUP 1 G 11 STEM EARTH AND SCIENCEDocument25 pagesEndogenic Processes Plutonism and Volcanism PRESENTATION 0F GROUP 1 G 11 STEM EARTH AND SCIENCEjeffrey bacayNo ratings yet
- Els Chapter 5Document12 pagesEls Chapter 5Jelly Joy CampomayorNo ratings yet
- Zayzay Earth Sci (Magma)Document12 pagesZayzay Earth Sci (Magma)ZayNo ratings yet
- Q2 M2 Presentation MWFDocument34 pagesQ2 M2 Presentation MWFEspinosa , Lance G.No ratings yet
- Magma and Volcanism Reviewer GROUP 4Document7 pagesMagma and Volcanism Reviewer GROUP 4muhamsumandresNo ratings yet
- Formation of MagmaDocument2 pagesFormation of MagmaBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- How Endogenic Processes OccurDocument2 pagesHow Endogenic Processes OccurCamille BaylonNo ratings yet
- Geo Chapter 7Document4 pagesGeo Chapter 7Montoya KylaNo ratings yet
- Group 7BDocument5 pagesGroup 7BKate Ashley HugoNo ratings yet
- Magmatism PDFDocument24 pagesMagmatism PDFParis ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Geologic ProcessesDocument84 pagesGeologic ProcessesHenry DuterteNo ratings yet
- Elsci Report PresentationDocument22 pagesElsci Report PresentationArnel DelingonNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of MagmaDocument18 pagesCharacteristics of MagmaCanggahNo ratings yet
- Magma PT.2Document10 pagesMagma PT.2zin GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument6 pagesEndogenic ProcessesBenjamin AmbiaNo ratings yet
- Magma Formation StemDocument38 pagesMagma Formation StemAzu RiteNo ratings yet
- How Magma FormsDocument2 pagesHow Magma FormsSoh Ail GamingNo ratings yet
- How Magma Was FormedDocument11 pagesHow Magma Was FormedPaolo RapanizaNo ratings yet
- Endo GenicDocument38 pagesEndo GenicKate ParanaNo ratings yet
- Plutonism and VolcanismDocument42 pagesPlutonism and VolcanismAthenaNo ratings yet
- Geochemical CycleDocument13 pagesGeochemical CycleSOCKYNo ratings yet
- Igneous Rocks PDFDocument43 pagesIgneous Rocks PDFJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- MAGMATISMDocument30 pagesMAGMATISMJoshua Laurence PalconNo ratings yet
- Notes VolcanoesDocument11 pagesNotes VolcanoesAmeen MtNo ratings yet
- Thermal and Pressure Change-: Exposed To Water and Gases in TheDocument11 pagesThermal and Pressure Change-: Exposed To Water and Gases in TheDonna Libres100% (1)
- Group 2Document1 pageGroup 2zin GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Geology For Kids - Pictionary | Geology Encyclopedia Of Terms | Children's Rock & Mineral BooksFrom EverandGeology For Kids - Pictionary | Geology Encyclopedia Of Terms | Children's Rock & Mineral BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Energy of LightDocument2 pagesEnergy of LightMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Variance and Standard Deviation of A Discrete Random VariableDocument4 pagesVariance and Standard Deviation of A Discrete Random VariableMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Folds and FaultsDocument23 pagesEarth and Life Folds and FaultsMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Geological HazardsDocument42 pagesGeological HazardsMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument5 pagesNutritionMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Rocks IntroductionDocument11 pagesRocks IntroductionMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument27 pagesOrigin of LifeMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- The Basic Principles of The EcosystemDocument15 pagesThe Basic Principles of The EcosystemMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- The Earth and SubsystemsDocument30 pagesThe Earth and SubsystemsMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument3 pagesElasticity of DemandMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- The Earth Internal StructureDocument19 pagesThe Earth Internal StructureMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Environmental LawDocument2 pagesEnvironmental LawMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Expansion in SolidsDocument2 pagesExpansion in SolidsDhana AryalNo ratings yet
- 5 ReactorsDocument28 pages5 ReactorsatulsemiloNo ratings yet
- Weathering and Erosion Reading Questions 091Document7 pagesWeathering and Erosion Reading Questions 091eros0% (1)
- Soarno ™ DC3203FDocument3 pagesSoarno ™ DC3203FMehdi SaouriNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise Chapter 2 3Document8 pagesLab Exercise Chapter 2 3Andy BirdieNo ratings yet
- Etude de Faisabilité INGA AecomDocument21 pagesEtude de Faisabilité INGA AecomL'Usine Nouvelle100% (1)
- TB02 Bearing Capacity of Geopier Supported Foundations PDFDocument16 pagesTB02 Bearing Capacity of Geopier Supported Foundations PDFDavid Garces MesaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 4Document27 pagesPhysical Science Module 4Florence-j Pelayo TupazNo ratings yet
- Experiences in Designing and Operating The Latest 1,050-MW Coal-Fired BoilerDocument5 pagesExperiences in Designing and Operating The Latest 1,050-MW Coal-Fired BoilerswatkoolNo ratings yet
- 5 Mark Paper 3Document25 pages5 Mark Paper 3YogaAnandNo ratings yet
- Bisrat AlemayehuDocument105 pagesBisrat Alemayehuሄኖክ ብርሃነNo ratings yet
- Morning Forecast 06042024Document1 pageMorning Forecast 06042024nana enguahNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Agri-Power: Utilizing of Plant Spacing in Shared-Anolyte CalamansiDocument11 pagesSustainable Agri-Power: Utilizing of Plant Spacing in Shared-Anolyte CalamansiVinson Josaiah KasilagNo ratings yet
- A Parametric Study of Layered Bed PSA For Hydrogen PurificationDocument16 pagesA Parametric Study of Layered Bed PSA For Hydrogen PurificationMateo PosadaNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 7586Document6 pagesRepublic Act No. 7586Carol TerradoNo ratings yet
- Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full QuestionsDocument3 pagesPages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questionslakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- MFC Second ReviewDocument26 pagesMFC Second Reviewvlharikrishnan19No ratings yet
- Sba3 (2019) Year 5 Science Paper 2Document12 pagesSba3 (2019) Year 5 Science Paper 2azmidaNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4492574Document16 pagesSSRN Id4492574Sai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Energy AuditingDocument28 pagesThe Basics of Energy Auditingghoyarbide9599No ratings yet
- Module 5A - Minerals, Definition & ClassesDocument32 pagesModule 5A - Minerals, Definition & ClassesDia FebriyandiNo ratings yet
- Zainal (2001) - Prediction of Performance of A Downdraft Gasifier Using Equilibrium Modeling For Different Biomass MaterialsDocument17 pagesZainal (2001) - Prediction of Performance of A Downdraft Gasifier Using Equilibrium Modeling For Different Biomass MaterialsAbraham AvNo ratings yet
- PureCell Model 400 DatasheetDocument2 pagesPureCell Model 400 DatasheetJaikumar PettikkattilNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials Applied in Asphalt Modi Fication: A Review: Changqing Fang, Ruien Yu, Shaolong Liu, Yan LiDocument6 pagesNanomaterials Applied in Asphalt Modi Fication: A Review: Changqing Fang, Ruien Yu, Shaolong Liu, Yan LiGiannis PappasNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Analysis of Evaporation From An Inactive Outdoor Swimming PoolDocument5 pagesMeasurement and Analysis of Evaporation From An Inactive Outdoor Swimming PoolAyaEzzNo ratings yet
- Manish (Green Building)Document22 pagesManish (Green Building)Manish kumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science and MaterialsDocument21 pagesEngineering Science and MaterialsCASTRO, JANELLA T.No ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE RocksDocument26 pagesEARTH SCIENCE RocksDAKSINo ratings yet