Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 Skeletal Muscle Relaxants
04 Skeletal Muscle Relaxants
Uploaded by
Filippo Philipp0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views6 pages04 Skeletal Muscle Relaxants
04 Skeletal Muscle Relaxants
Uploaded by
Filippo PhilippCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
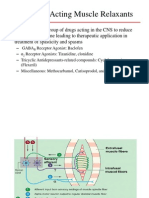
Skeletal muscle relaxants
NMJ blocking drugs
Non-depolarizing
– Tubocurarine, pancuronium, atracurium, vecuronium, rocuronium
Depolarizing
– Succinyl choline
Spasmolytic drugs (antispastic drugs)
• Drugs for chronic spasm
– Diazepam, baclofen, botulinum toxin, tizanidine, dantrolene, mephenesin
• Drugs for acute muscle spasm
– Chlorzoxazone, carisoprodol, metaxalone, methocarbamol,
cyclobenzaprine, chlorphenesin, orphenadrine
Non-depolarizing NM blocking drugs
MOA
• Prevents action of Ach. at skeletal muscle end plate
• Effects reversed by cholinesterase inhibitors- neostigmine
Depolarizing NM blocking drugs
Succinylcholine
• Depolarizes NM end plate
• Has short duration of action
A/E
• Resp. paralysis, hyperkalemia, peripheral nerve dysfunction
• Stimulates autonomic ganglia
Interactions: Inhaled anesthetics, aminoglycosides
Spasmolytic drugs
• Used to Rx skeletal muscle spasms that occur due to injury or a neurologic disease
to compliment physical therapy; or in severe conditions as M Sclerosis. & C Palsy to
control rigidity and pain
• They ↓ abnormally elevated muscle tone(spasm) without causing paralysis e.g.
baclofen, dantrolene
• Action: CNS, skeletal muscle cells
Drugs for Rx of Chronic pain
• Diazepam-GABA mediated inhibition at the spinal cord
• Baclofen - GABAB agonist, acts through G protein–coupled receptors which when
activated, ↓ motor neuron excitability
• Tizanidine- centrally acting α2- agonist; reinforces both pre- and post synaptic
inhibition in the spinal cord resulting in decreased spasticity without a reduction in
muscle strength (contraction)
Dantrolene
- ↓ release of activator Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum, decouples the
excitation-contraction at the muscle endplate & directly relaxes skeletal
muscle
Indications - Rx of
- Malignant hyperthermia mainly due to G/anaesthetics e.g. halothane
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome -high-potency antipsychotics
- Spasticity from such disorders as after strokes, paraplegia, cerebral palsy, or in
patients with MS
Mephenesin - centrally acting muscle relaxant used as an antidote for strychnine
poisoning
Botulinum toxin A(Botox®) - paralyzes muscles by blocking the release of Ach. -
Rx upper- limb spasticity in stroke patients, blepharospasm (spasms of the
eyelids), dystonia & other symptoms of PD, for strabismus (“cross-eyed”),
Others: Progabide, glycine
Drugs for Rx of acute muscle spasm
Chlorzoxazone, carisoprodol, metaxalone, methocarbamol, cyclobenzaprine,
chlorphenesin, orphenadrine
- Thought to act in the spinal cord & brain stem by interfering with polysynaptic reflexes
that maintain skeletal muscle tone
- Most are sedatives
- Used for relief acute muscle spasms due to local trauma or strain
Chlorzoxazone - Centrally acting muscle relaxant used to Rx muscle spasm, acute pain
& tension headache.
• Acts on the spinal cord by depressing reflexes.
• Usually combined with paracetamol
Carisoprodol – A GABAergic drug used for short-term Rx of muscle spasms caused by
musculoskeletal conditions
Metaxalone - a moderately strong muscle relaxant with relatively low A/E used to
relieve pain caused by strains, sprains, & other musculoskeletal conditions.
A/E- N/vomiting, drowsiness, dizziness, headache, & irritability
Methocarbamol: Centrally acting muscle relaxant used for short-term
musculoskeletal pain but ineffective for cerebral palsy and related d/orders. A/E
dizziness, anaphylaxis, confusion, seizures & hepatotoxicity. Not recommended in
pregnancy and breastfeeding mothers
Cyclobenzaprine - indicated for short-term Rx of muscle spasms caused by acute
painful, musculoskeletal conditions
- Ineffective in muscle spasms due to spinal cord injury e.g. MS, ALS or cerebral palsy
but have strong antimuscarinic and sedative effects
- A/E confusion and hallucination in some patients
Chlorphenesin – A centrally acting relaxant that has been withdrawn due to A/E and
availability of better drugs e.g. benzodiazepines
Orphenadrine - An old (1940s) anticholinergic drug closely related to
diphenhydramine that was used to Rx muscle pain and for motor control in
Parkinson's disease, but now superseded by better drugs
You might also like
- Jason Cafer MD - Julianna Link PA-C - Cafer's Psychopharmacology - Visualize To Memorize 270 Medication Mascots - Libgen - LiDocument304 pagesJason Cafer MD - Julianna Link PA-C - Cafer's Psychopharmacology - Visualize To Memorize 270 Medication Mascots - Libgen - LiElectric Amoeba100% (7)
- Orange BookDocument109 pagesOrange BookkayabaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument12 pagesSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsKhemz Dalde LimNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantDocument37 pagesSkeletal Muscle RelaxantNicole Mae DavidNo ratings yet
- CHAP 33Document6 pagesCHAP 33Gwen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Centrally-Acting Muscle RelaxantsDocument11 pagesCentrally-Acting Muscle RelaxantsMerBoughNo ratings yet
- The Drugs in This Chapter Are Divided Into 2 Dissimilar GroupsDocument2 pagesThe Drugs in This Chapter Are Divided Into 2 Dissimilar GroupsAsem AlhazmiNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking Agents and Other Muscle Relaxants: VMED 5223 George M. StrainDocument33 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking Agents and Other Muscle Relaxants: VMED 5223 George M. StrainDhaif dhaifNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking Agents and Other Muscle Relaxants: VMED 5223 George M. StrainDocument32 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking Agents and Other Muscle Relaxants: VMED 5223 George M. Strainsherbaloch922317No ratings yet
- Muscle RelaxantDocument42 pagesMuscle RelaxantMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Muscle RelaxantDocument29 pagesMuscle RelaxantAri Puji AstutiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Relaxant 2015Document29 pagesMuscle Relaxant 2015melanita_99No ratings yet
- 07.muscle RelaxanteDocument28 pages07.muscle RelaxanteLee BoborasNo ratings yet
- Muscular RelaxantsDocument8 pagesMuscular RelaxantsLucia SolerNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument7 pagesSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsRAMNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Musculo-Skeletal, Joints and Bone ProblemsDocument14 pagesPharmacotherapy of Musculo-Skeletal, Joints and Bone ProblemsfateeeNo ratings yet
- Spasmolytic DrugsDocument3 pagesSpasmolytic DrugsVikash LamaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument23 pagesSkeletal Musclerenuka digheNo ratings yet
- Ans DrugsDocument22 pagesAns Drugswww.nathanmengoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Skeletal Muscle RelaxantDocument48 pagesLecture 7 Skeletal Muscle RelaxantMina BiancaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Topic 3 NotesDocument3 pagesPharma Topic 3 NotesAshley Franceska CansanayNo ratings yet
- Disease Spotlight: Neuromuscular AbnormalitiesDocument6 pagesDisease Spotlight: Neuromuscular AbnormalitiesLorie Yvonne Quibin AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Baclofen: Generic: Brand: Class: MoaDocument3 pagesBaclofen: Generic: Brand: Class: MoaCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- SK Musc RelaxDocument27 pagesSK Musc RelaxDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Antianxiety DrugsDocument56 pagesAntianxiety DrugsVictor AlexandreNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Somatic Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesDrugs Acting On Somatic Nervous SystemcchatrumaNo ratings yet
- PCL 312 Modified - 040530Document8 pagesPCL 312 Modified - 040530BrigidNo ratings yet
- Group 6Document37 pagesGroup 6LohithNo ratings yet
- Anti-Depressants: Soumya Mary 1 Year MSC (N)Document22 pagesAnti-Depressants: Soumya Mary 1 Year MSC (N)Salman HabeebNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Mechanical Low BACK PAIN (Cont.)Document7 pagesTreatment of Mechanical Low BACK PAIN (Cont.)Lady Lyn RobinaNo ratings yet
- 4.... NSAIDs 4.4... RADocument14 pages4.... NSAIDs 4.4... RANim DCNo ratings yet
- Muscle RelaxantsDocument42 pagesMuscle RelaxantsDionisio DiaNo ratings yet
- Antiinsomnia and AxyoliticDocument21 pagesAntiinsomnia and AxyoliticGita Tanbao SuselinNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines + Local AnesthesiaDocument5 pagesBenzodiazepines + Local AnesthesiaALNAKINo ratings yet
- 36 Skeletal Muscle Relaxants: Kenneth C. Jackson II and Charles E. ArgoffDocument6 pages36 Skeletal Muscle Relaxants: Kenneth C. Jackson II and Charles E. ArgoffYoga WibowoNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument2 pagesDiazepamgoyaNo ratings yet
- 02 Sedative Hypnotic and Anxiolytic DrugsDocument23 pages02 Sedative Hypnotic and Anxiolytic DrugsFilippo PhilippNo ratings yet
- Pre Medication 2010Document29 pagesPre Medication 2010Anelize MilaréNo ratings yet
- Spasmolitic Muscle RelaxantsDocument12 pagesSpasmolitic Muscle RelaxantsnaotonaoiNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant Pain MedicationDocument20 pagesAdjuvant Pain MedicationAmr SewilamNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Relaxants: DR RC AnakwueDocument24 pagesSkeletal Muscle Relaxants: DR RC AnakwuetemitopeNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking Agents and SpasmolyticsDocument22 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking Agents and Spasmolyticsjanemwanza003No ratings yet
- Drug Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesDrug Cheat SheetSheldon LordNo ratings yet
- Muscle Relaxants: Jake A. Nerio BSN 2ADocument19 pagesMuscle Relaxants: Jake A. Nerio BSN 2AMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Medication For InsomniaDocument32 pagesSleep Medication For InsomniaMelanieNo ratings yet
- Drugs HandoutDocument9 pagesDrugs Handoutekwamboka956No ratings yet
- Autonomo Task-Nervous Central System DiseasesDocument2 pagesAutonomo Task-Nervous Central System DiseasesMaily OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Musclerelaxantandreversalagents 190313130322 PDFDocument48 pagesMusclerelaxantandreversalagents 190313130322 PDFVivek ChNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic DrugsDocument44 pagesAnxiolytic DrugschkiershadiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument21 pagesSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsKetan patilNo ratings yet
- Sedatives and Hypnotics Benzodiazepines, Non Benzodiazepines, BarbituratesDocument37 pagesSedatives and Hypnotics Benzodiazepines, Non Benzodiazepines, BarbituratesAbas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Depression PDFDocument10 pagesDepression PDFLyadelou FortuNo ratings yet
- !KULIAH Adjuvant AnalgesiaDocument31 pages!KULIAH Adjuvant AnalgesiaHilmi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Central Nervous System-1Document163 pagesPharmacology of The Central Nervous System-1Gølà Sèèñàà–baale irraaNo ratings yet
- 02 Sedative Hypnotic and Anxiolytic DrugsDocument16 pages02 Sedative Hypnotic and Anxiolytic DrugsGilbert OsengoNo ratings yet
- Psych DrugsDocument3 pagesPsych DrugsSwarna BanikNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - Skeletal-Muscle-Relaxants-S3-W9Document2 pages1.3 - Skeletal-Muscle-Relaxants-S3-W9FlowerNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant AnalgesicDocument19 pagesAdjuvant AnalgesicKyra KhalidNo ratings yet
- Beberapa Tipe Nyeri KankerDocument5 pagesBeberapa Tipe Nyeri KankerAmalia PutriNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Relaxant (Lecture Notes QIUP 2017)Document9 pagesSkeletal Muscle Relaxant (Lecture Notes QIUP 2017)Monissha ThiaguNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System AgentsDocument20 pagesCentral Nervous System AgentsshannenNo ratings yet
- Daftar Ketersediaan Obat Sesuai Formularium Nasional Puskesmas Candi TAHUN 2020Document18 pagesDaftar Ketersediaan Obat Sesuai Formularium Nasional Puskesmas Candi TAHUN 2020octie0% (1)
- Daftar Obat-ObatanDocument5 pagesDaftar Obat-Obatanklinik warna ayu jaya medikaNo ratings yet
- 2023 - The Clinical Application of Cariprazine in SchizophreniaDocument4 pages2023 - The Clinical Application of Cariprazine in SchizophreniaAna BorgesNo ratings yet
- FORM RKO BPJS 2019.. EditDocument3 pagesFORM RKO BPJS 2019.. EditMitha yuniatyNo ratings yet
- Taper Dosing CalculatorDocument1 pageTaper Dosing Calculatorandirio7486No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Agents: ObjectivesDocument47 pagesCentral Nervous System Agents: ObjectivesKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- HPLC For Analysis ParacetamolDocument29 pagesHPLC For Analysis ParacetamolwwindiastomoNo ratings yet
- TML Issue 1665Document11 pagesTML Issue 1665Dahoom oh yeahNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Sedative DrugsDocument55 pagesPharmacology of Sedative DrugswgalalNo ratings yet
- Active Metabolites As Antidepressant Drugs: The Role of Norquetiapine in The Mechanism of Action of Quetiapine in The Treatment of Mood DisordersDocument8 pagesActive Metabolites As Antidepressant Drugs: The Role of Norquetiapine in The Mechanism of Action of Quetiapine in The Treatment of Mood DisordersNath miaounNo ratings yet
- Tramadol UltramDocument2 pagesTramadol UltramatchiekNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument43 pagesPain ManagementThe AbyssinicansNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Tagihan Detail Landscape-7Document15 pagesRekapitulasi Tagihan Detail Landscape-7dila yatmokoNo ratings yet
- Drug Use and AbuseDocument20 pagesDrug Use and AbuseSergio Ignacio VaccaroNo ratings yet
- The Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Syndrome: H. PeturssonDocument6 pagesThe Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Syndrome: H. PeturssonLucius MarpleNo ratings yet
- Anti Emetic DrugsDocument3 pagesAnti Emetic DrugsFaria Islam JuhiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PsychopharmacologyDocument99 pagesLecture 3 PsychopharmacologyPavan chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MBDocument29 pagesDrug Study MBk4jggjtnz5No ratings yet
- Bu AfniDocument7 pagesBu Afniadila awaludinNo ratings yet
- Emenil PlusDocument2 pagesEmenil PlusMustaf MohamedNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Is A Substance Found in Alcoholic Drinks, While Liquor Is A Name For These Drinks. ... NotDocument7 pagesAlcohol Is A Substance Found in Alcoholic Drinks, While Liquor Is A Name For These Drinks. ... NotGilbert BabolNo ratings yet
- Obat Anti Konvulsan - CompressedDocument52 pagesObat Anti Konvulsan - CompressedNianurmayanti983278No ratings yet
- Product Price ListDocument118 pagesProduct Price ListInfinity TouchNo ratings yet
- AmitiptrinDocument2 pagesAmitiptrinTeguh Fatwa PanuntunNo ratings yet
- Integrated Therapeutics IiiDocument11 pagesIntegrated Therapeutics IiiSalahadinNo ratings yet
- Acacias and Natural AmphetamineDocument2 pagesAcacias and Natural AmphetamineschoolmebroNo ratings yet
- Permintaan Obat Dak Dan BS Triwulan Ke Iii Tahun 2020 JuniDocument3 pagesPermintaan Obat Dak Dan BS Triwulan Ke Iii Tahun 2020 JuniMawar PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesBio Investigatory Projectprism1702No ratings yet