Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 1 Unit of Measurement
Week 1 Unit of Measurement
Uploaded by
kobep48940 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views22 pagesOriginal Title
Week 1 Unit of Measurement (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views22 pagesWeek 1 Unit of Measurement
Week 1 Unit of Measurement
Uploaded by
kobep4894Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 22
UNIT I
LESSON I- UNIT OF MEASUREMENT
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Is the study of the structure, properties, composition, reaction, and preparation of
carbon-containing compounds
Most organic compound contain carbon and hydrogen, but they may also include any
number of other element (e.g. nitrogen, oxygen, halogen,, phosphorus, silicon, sulfur)
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Is the study of behavior of compound along with their properties, their physical and
chemical characteristic.
The element of the periodic table except for carbon and hydrogen and in the list of
inorganic compounds.
BIOCHEMISTRY
Is used to learn about the biological processes which take place in cells and organism.
Biochemistry maybe used to study the properties of biological molecules for a variety of
properties.
UNIT OF MEASUREMENT
THE INTERNATIONA UNIT
We use measurements everyday of our lives.
we measure gasoline by gallon, and milk by the quart, we buy meat by the kilo/pound. A
recipe may call for a cup of flour, a tablespoon of butter and teaspoon for alt.
In chemistry all measurement are made in the metric system or in its expanded
modernized version the SI from the French le systeme internationale unites.
The main advantages of the SI system is that it is decimal system, that is, the units are all
multiples of ten (10) of larger or smaller units.
In the English system there is no such common number.
EX:
3 feet in a yard
4 quart in a gallon
16 ounces in a pound
MASS and WEIGHT
The mass an object is measure of the amount of matter it contains.
The weight of an object depends on the pull of gravity.
mass remain constant regardless of location, whereas weight can vary slightly from place
on the surface of the Earth.
FUNDAMETAL OF UNITS
The fundamental of unit of length in the SI system is the meter
A meter is a little longer than a yard.
The word meter is abbreviated as m.
The fundamental SI unit of mass (weight) is the kilogram. A kilogram is slight more 2
pounds
The basic laboratory unit of mass (weight) is the gram. A gram is 1/454 pound.
The fundamental SI unit of time is the second(s). Decimal-based multiples and
submultiples can also be used, but the older units such as minutes, hours, and days are still
in common use.
The fundamental SI unit of temperature is the kelvin (k)
Note:
the words degree and the symbols for degree are not used.
In medical application, however, temperature is usually measured in degrees Celsius (°C).
DERIVED UNITS
Volume is not a fundamental SI unit because it can be derived from length(the volume of
rectangular object can be calculated from the relationship
Volume = length x width x length
In the SI system, volume is expressed in the unit cubic meter (m3)
The cubic meter contains approximately 250 gallons
A more common unit of volume is the liter (abbreviated by chemist as L by some others
as l).
A liter is slightly more than one(1) quart
The basic unit most commonly used in medicine are the meter, the gram, and the liter.
In the SI system prefixes are used to designate various multiples or submultiples.
EX:
Kilo – means one thousand (1000)
Centi – means one-hundredth (100)
Thus , a kilometer (km) is one thousand meter, or 1000m
Centigram (cg) is 1/100 gram or 0.01g
Likewise, a milliliter (ml) is 0.001L
Another unit of volume is the cubic meter (cm3), 1cm3 is equal to 1 ml, so these
two units may be used interchangeably.
Although the term cubic centimeter is abbreviated as cm3 by chemist, the older
abbreviation cc is still seen at a times.
Likewise 1MCi (1 megacurie) means 1 million Ci and 1 µg or 1mcg (1 microgram) means
0.000001 g
Note:
That the letter m indicates both meter and milli; however, when used itself, it
indicates meter.
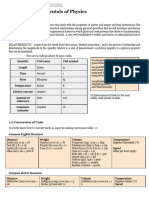
Table 1.1 Some Prefixes used in the SI System
Prefix Abbreviation decimal Expression Exponential expression
Mega M 1,000,000 106
Kilo k 1,000 103
hekto h 100 102
deka da 1 101
deci d 0.1 10-1
Prefix Abbreviation Decimal Expression Exponential Expression
centi c 0.01 10-2
milli m 0.001 10-3
micro µ (or mc) 0.000001 10-6
nano n 0.0000000001 10-9
Table 1.2 Metric Conversion
Mass (Weight)
1 g = 1000 mg one gram = one thousand milligram
1 g = 100 cg one gram = one hundred centigram
1g = 10 dg one gram = ten decigrams
1 kg = 1000 g one kilogram = one thousand grams
Length
1 m = mm one meter = one thousand millimeters
1 m = 100 cm one meter = one hundred centimeters
1 m = 10 dm one meter = ten decimeters
1 km = 1000 m one kilometer = one thousand meter
Volume
1 L = 1000 mL one liter = one thousand milliliters
1 L = 100 cl one liter = one hundred centiliters
1 L = dL one liter = ten deciliters
1 kL = 1000 L one kiloliter = one thousand liter
EXERCISE:
Complete the equation for each metric relationship
1.) 1 LITER = ________mL
2.) 1 cm =
Solution:
refer to the metric prefix in Table 1.1 if necessary
1.) The prefix milli is 0.000 of a basic unit; 1000 units are in 1
basic unit, therefore, 1 liter = 1000mL
2.) The prefix centi is 0.01 of a basic unit, 100 centi; units are
in basic unit, therefore , 1 cm = 0.01 meter
FACTOR LABEL METHOD
Considered the following English - English conversion units.
12 in = 1 ft
3 ft – 1 yd
1760 yd = 1 mi
EXERCISE:
Convert 6ft to inches, many students merely multiply by 12.
However mathematically, the correct procedure is to multiply by
the conversion unit 12in /1 ft so the result is correct both
numerically and in unit.
6 ft = 6ft x 12 in x 72
1 ft
Likewise, to convert 657.5 yd to mi
657.5 yd x 1 mi = 0.3736 mi
1760 yd
Convert 68 grams to kilograms
Solution
68 g x 1kg = 0.068 kg
1000 g
Metric – Metric Conversion
In this exercises you will apply the factor – label method using signifant figures.
Exercise:
Convert 150 cm to m.
Solution:
since 1 m = to 100 cm
150 cm x 1m = 150 m
100 cm
Convert 3.76 l to mL
Solution:
3.76 L x 1000 mL = 3760
1L
= 3.76 x 103 mL ( to those significant figures)
Convert 512 mg to kg
Solution:
since 1 g = 1000 mg and 1 kg = to 1000 g, then
512 mg x 1g x 1 kg = 5.12 x 104 kg
1000 mg 1000 g
TEMPERATURE SCALE
Temperature is a measure of the availability of heat or cold or, in simpler terms, of how
hot or cold a substance is.
It can be measured by means of a thermometer.
When we speak of body temperature as being 98.6 degrees or when we say that the
outside temperature is 80 degrees or 40 degrees or even 2 degrees below zero, we are
usually speaking in terms of degrees Fahrenheit (°F), even though we may not express the
unit itself.
In chemistry, the Celsius (C) and Kelvin (K) temperature scale are commonly used.
If Fahrenheit and a Celsius thermometer are placed in a mixture of ice ad water, the
reading on the Fahrenheit scale will be 32° and the reading on the Celsius scale 0° - that is,
32 °F correspond to 0°C.
These temperature is indicate the freezing point of water. They also indicate the melting
If the same two thermometer are placed in boiling water at 1 atmosphere pressure, the
reading on the Fahrenheit scale will be 212° and the reading on the Celsius scale will be 100°.
These temperatures indicate the boiling point of water.
Thus there is a 180-degree different between the boiling point and the freezing point of
water on the Fahrenheit scale (212° to 32°) and a 100-degree difference between boiling and
freezing points of water on the Celsius scale (100° to 0°).
The difference between the freezing point of water on the Fahrenheit and Celsius scale is 32°
(32° - 0).
FORMULA
from Fahrenheit to Celsius
from Celsius to Fahrenheit
from kelvin to Celsius
°F = 9/5 °C + 32 and ° C = 5/9 (°F - 32°)
Exercise:
Change 80.0° C to °F
Solution:
Using the formula:
°F = 9 °C + 32°
5
°F = 9 (80.0) + 32°
5
= 144° + 32
= 176° F
Thus 80.0° C = 176° F
POST –TEST
QUIZ # 1
1.) 1 kg = ______ g
2.) 1 sec = ________ µsec
3.) 1 mm = ________ m
QUIZ # 2
QUIZ # 3
QUIZ # 4
You might also like
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry Structure and Function 6th Edition by VollhardtDocument13 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry Structure and Function 6th Edition by Vollhardta492222920No ratings yet
- BOD5 APHA 5210B 23rdDocument6 pagesBOD5 APHA 5210B 23rdahmad munawir100% (1)
- CH 11 Solutions Meissler PDFDocument12 pagesCH 11 Solutions Meissler PDFFerdinand Tamayo Cayabyab Jr.0% (1)
- Grade 7 Math Week 2Document4 pagesGrade 7 Math Week 2Tina SayconNo ratings yet
- m100 MetricshandoutDocument12 pagesm100 Metricshandoutapi-234377298No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math (2nd Quarter)Document22 pagesGrade 7 Math (2nd Quarter)Euclid Pogi100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document65 pagesChapter 5Pirate CaribbeanNo ratings yet
- 0 Reviewer MeasurementsDocument17 pages0 Reviewer MeasurementsCylle Jerone BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Problem SolvingDocument13 pagesChemical Problem SolvingChristian DuranaNo ratings yet
- Scientific MeasurementDocument64 pagesScientific MeasurementAbishaNo ratings yet
- The English System of UnitsDocument77 pagesThe English System of UnitsAnwer AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Numbers and Measurements in ChemistryDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Numbers and Measurements in ChemistryMido IzukuNo ratings yet
- 1.6a DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 1Document41 pages1.6a DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 1Guile MacaNo ratings yet
- Convertion of Units OutputDocument4 pagesConvertion of Units Outputjerico raquizaNo ratings yet
- Co2 2023-2024Document45 pagesCo2 2023-2024RICHELLE L. HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- 20171101131130chapter 1 - Measurement in ChemistryDocument43 pages20171101131130chapter 1 - Measurement in ChemistryShahNo ratings yet
- How UnitDocument2 pagesHow UnitHatdogNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Q2 Week 2Document17 pagesMath 7 Q2 Week 2Joshrel V. CieloNo ratings yet
- Chm1025 Chapter 3Document92 pagesChm1025 Chapter 3deniz.mammadova2002No ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument42 pagesMeasurementappleNo ratings yet
- Units, Physical Quantities, and MeasurementDocument46 pagesUnits, Physical Quantities, and MeasurementChristian CincoNo ratings yet
- Measurements and UnitsDocument18 pagesMeasurements and UnitsSrynnENo ratings yet
- AnnouncementsDocument29 pagesAnnouncementsJay-anne CruzNo ratings yet
- Physics - Summer ExercisesDocument11 pagesPhysics - Summer ExercisesDIEGO FERNANDO BARRIOS DIAZNo ratings yet
- Funmath Module 5 - Measurements and ConversionsDocument13 pagesFunmath Module 5 - Measurements and ConversionsRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument4 pagesConversion of UnitsJairhiz AnnNo ratings yet
- Conversion ChartDocument2 pagesConversion ChartMack AmansecNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Measurement L - A 1Document30 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Measurement L - A 1Vea Patricia AngeloNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.4 UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS v2Document43 pagesLESSON 2.4 UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS v2Reign CallosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Lecture NotesAhmad KamalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MeasurementsDocument0 pagesChemistry MeasurementsAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module1Document15 pagesGrade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module1Josue NaldaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module1Document17 pagesGrade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module1Krystian BonghanoyNo ratings yet
- Drilling Calculations CD Complete CourseDocument177 pagesDrilling Calculations CD Complete CoursecarmenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1-2.3 PDFDocument7 pagesLesson 2.1-2.3 PDFMicha E.No ratings yet
- Physics1 MeasurementsDocument69 pagesPhysics1 MeasurementsCAITHLENE MARIE ALFONSONo ratings yet
- Metric Measurement Lab: Standard UnitsDocument7 pagesMetric Measurement Lab: Standard UnitsmdslaniaNo ratings yet
- Units: Unit Is Internationally Accepted Reference Standard To Measure A Physical QuantityDocument52 pagesUnits: Unit Is Internationally Accepted Reference Standard To Measure A Physical Quantitysusmita waghmareNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - MechanicsDocument4 pagesWeek 7 - MechanicsRafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- The Metric System and Scientific Method AnsweredDocument11 pagesThe Metric System and Scientific Method AnsweredKenn CollinsNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument14 pagesMeasurementOyi Lorenzo-LibanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - LAS 2022-2023 1st QuarterDocument25 pagesPHYSICS - LAS 2022-2023 1st QuarterMonique MangubatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CHEM 106Document4 pagesChapter 2 CHEM 106Marjorie GawalaNo ratings yet
- Topik 1 DBS10012 Physical Quantities MeasurementDocument60 pagesTopik 1 DBS10012 Physical Quantities MeasurementᴍᴜʜᴀᴍᴍᴀᴅNo ratings yet
- Metric System: Exercises Exercise A: Changing The Value of A NumberDocument5 pagesMetric System: Exercises Exercise A: Changing The Value of A NumberlvminhtrietNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Unit & MeasurementDocument54 pagesChapter 1 Unit & MeasurementnisaarNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Measurements: Chapter 1 - Essential Ideas 29Document7 pages1.4 Measurements: Chapter 1 - Essential Ideas 29Urvi MohanNo ratings yet
- Ass #1.0 ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesAss #1.0 ThermodynamicsJosh BarriosNo ratings yet
- Ass #1 ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesAss #1 ThermodynamicsJosh BarriosNo ratings yet
- HW #1 Thermodynamics 1Document7 pagesHW #1 Thermodynamics 1Josh BarriosNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Principles of Measurement and Laboratory Mathematics in Clinical ChemistryDocument6 pagesModule 4-Principles of Measurement and Laboratory Mathematics in Clinical ChemistryAllyah Ross DuqueNo ratings yet
- 3.module 2. Measuremsnts in Analytical ChemistryDocument19 pages3.module 2. Measuremsnts in Analytical ChemistryKim MalangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Measurements and SF - RozainaDocument42 pagesChapter 1 - Measurements and SF - RozainaNUR AUNI SAHIRA S ROSLINo ratings yet
- General Physics ReviewerDocument12 pagesGeneral Physics ReviewerfelixiefairyNo ratings yet
- General Physics Module 1 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGeneral Physics Module 1 ReviewerIca Safra100% (2)
- Technical System Unit SI MeasurementDocument16 pagesTechnical System Unit SI MeasurementManish PatelNo ratings yet
- Chemical MeasurementsDocument5 pagesChemical Measurementspeaky blinderNo ratings yet
- PCT Unit II - Units and MeasurementsDocument32 pagesPCT Unit II - Units and MeasurementsEuna De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Conversions in The Metric System PDFDocument5 pagesConversions in The Metric System PDFJaythan Vincent CorderoNo ratings yet
- Math and Basic Geometr1Document36 pagesMath and Basic Geometr1king100% (1)
- Uty ReviewerDocument3 pagesUty Reviewerkobep4894No ratings yet
- Topography AP1-REPORTING FinalDocument36 pagesTopography AP1-REPORTING Finalkobep4894No ratings yet
- AbleismDocument12 pagesAbleismkobep4894No ratings yet
- What Are The Three Examples of CorrectionDocument1 pageWhat Are The Three Examples of Correctionkobep4894No ratings yet
- Scan 20240319Document1 pageScan 20240319kobep4894No ratings yet
- Assignmnt DoxcDocument1 pageAssignmnt Doxckobep4894No ratings yet
- ComparativeDocument14 pagesComparativekobep4894No ratings yet
- Work Immersion Parents FeedbackDocument1 pageWork Immersion Parents Feedbackkobep4894No ratings yet
- Week 7 and 8 2.3.4 Effects of Abiotic FactorsDocument13 pagesWeek 7 and 8 2.3.4 Effects of Abiotic Factorskobep4894No ratings yet
- When Rizal Arrived in Barcelona On June 16Document7 pagesWhen Rizal Arrived in Barcelona On June 16kobep4894No ratings yet
- Week 4 The Relationship of Ecology With Other Science The Ecosystem and Basic Unit of EcosystemDocument13 pagesWeek 4 The Relationship of Ecology With Other Science The Ecosystem and Basic Unit of Ecosystemkobep4894No ratings yet
- Asssignment # 5Document3 pagesAsssignment # 5kobep4894No ratings yet
- Reaction Paper of 3RD PillarDocument2 pagesReaction Paper of 3RD Pillarkobep4894No ratings yet
- Forensic 1Document10 pagesForensic 1kobep4894No ratings yet
- Assignemnt 2Document1 pageAssignemnt 2kobep4894No ratings yet
- Prsonal InfoDocument1 pagePrsonal Infokobep4894No ratings yet
- Wing 2024 Nolcom Reservist Convention Letter Order 03 22 24 09Document2 pagesWing 2024 Nolcom Reservist Convention Letter Order 03 22 24 09kobep4894No ratings yet
- Group 3 Bravo EC 2 Post TestDocument1 pageGroup 3 Bravo EC 2 Post Testkobep4894No ratings yet
- ForensicDocument1 pageForensickobep4894No ratings yet
- Vibrating Mill PDFDocument6 pagesVibrating Mill PDFPhanHathamNo ratings yet
- THE COMPLETE General Science Notes (Chemistry) For Railway ExamsDocument39 pagesTHE COMPLETE General Science Notes (Chemistry) For Railway ExamsPravinNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Qns With Answers - Haloalkanes&Haloarenes 2Document8 pagesReasoning Qns With Answers - Haloalkanes&Haloarenes 2tanishka0307No ratings yet
- Chemaflex 276 HDocument4 pagesChemaflex 276 HghazanfarNo ratings yet
- IB Organic Chemistry Note SL (Note Cards)Document31 pagesIB Organic Chemistry Note SL (Note Cards)陳定均No ratings yet
- Corrosion: Prepared By: Engr Derik R de CastroDocument22 pagesCorrosion: Prepared By: Engr Derik R de CastroMatthew SilabNo ratings yet
- Polyurethane ReviewDocument30 pagesPolyurethane Reviewivan192010No ratings yet
- Biochem. Lab (Handouts)Document23 pagesBiochem. Lab (Handouts)Jhamylla Difuntorum EstocapioNo ratings yet
- Water Management in Chemical IndustriesDocument40 pagesWater Management in Chemical IndustriesBelgaumNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 P Block ElementsDocument17 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 P Block ElementsVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document1 pageHomework 2Study StudyNo ratings yet
- Proteins AS Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexcelDocument3 pagesProteins AS Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexceljanaNo ratings yet
- Delta Mks (Zinc Flake) - Pea ProjectDocument32 pagesDelta Mks (Zinc Flake) - Pea ProjectTAEWARAT RAKRUANGNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Cell Shape Membrane Internal STRDocument39 pagesTopic 1 Cell Shape Membrane Internal STRMuhammed Shafi Tk0% (1)
- InsertosDocument48 pagesInsertosDuvan VillaNo ratings yet
- Versatile Polyethylenimine: A Vector For Gene and Oligonucleotide Transfer Into Cells in Culture and in VivoDocument5 pagesVersatile Polyethylenimine: A Vector For Gene and Oligonucleotide Transfer Into Cells in Culture and in VivoLuiz Filipe BezerraNo ratings yet
- 212labexp06 NitrationOfToluene RDocument3 pages212labexp06 NitrationOfToluene REngrAneelKumarAkhaniNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Method For Analysis of Inorganic Phosphate in The Presence of Interfering Substances.Document9 pagesA Simplified Method For Analysis of Inorganic Phosphate in The Presence of Interfering Substances.muratout3447No ratings yet
- CPP - Balancing EquationsDocument6 pagesCPP - Balancing EquationsAarchi SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: SyllabusDocument51 pagesChemistry: SyllabusYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Chemical AnalysisDocument4 pages1.1 Introduction To Chemical Analysismasitule nkombisaNo ratings yet
- Polyflex 304 EnglishDocument2 pagesPolyflex 304 EnglishcesarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HalogensDocument9 pagesIntroduction To HalogensReyyan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationDocument14 pagesOrganic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationSomesh MishraNo ratings yet
- 1Q2016EXCELDocument779 pages1Q2016EXCELMd.Mazed Abdullah0% (2)
- Rapid, Continuous Solution-Phase Peptide Synthesis: Application To Peptides of Pharmaceutical InterestDocument10 pagesRapid, Continuous Solution-Phase Peptide Synthesis: Application To Peptides of Pharmaceutical InterestStefania Claudia JitaruNo ratings yet
- Fpai ReportDocument23 pagesFpai ReportJohn Lerrie AdonayNo ratings yet