Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metabolism - Amino Acids
Metabolism - Amino Acids
Uploaded by
Clara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesMetabolism - Amino Acids
Metabolism - Amino Acids
Uploaded by
ClaraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
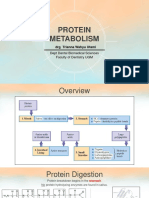
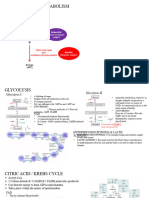
AMINO ACID METABOLISM
Types Of Amino Acids
• ESSENTIAL = Unable to produce inside the body so must beSynthesis Of Non-Essential Amino Acid
included in human diet • GLUTAMATE & GLUTAMINE donate their amino group to various carbon skeleton
• NON-ESSENTIAL = Able to produce inside the body so that exist in the cell = Produce majority of non-essential amino acids
don’t need be included in human diet • Needs AMINOTRANSFERASE enzyme (transfer amino acids) and VITAMIN B6 co-
enzymes
Serum Level Of AST Use For Clinical Diagnosis Of Liver Injury
• ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE (ALT) & ASPARTATE AMINOTRANSFERASE (AST)
• Both enzymes abundantly expressed in liver, HEPATOCYTES
• Damage to HEPATOCYTES during liver injury = Leakage of enzyme into bloodstream = Serum levels of ALT & AST released due to
leakage = Increased levels of ALT & AST as sensitive biomarker of liver injury
• BUT Level might be elevated in other medical conditions (ex: CARDIOMYOCYTE’s express AST Serum AST level increases
significantly after MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION) = Not a very specific diagnostic tool
CATABOLISM OF AMINO ACID
Proteins and amino acids are not primarily a source of energy = But when cells experience a shortage of energy, amino acids
may undergo catabolism
DEAMINATION = Removal of an amine group from a molecule as initial step for catabolism
AMMONIA: Toxic; Detoxified in hepatocytes in urea cycle
DEAMINATED PRODUCT: Deamination of amino acids produces molecules that can – Enter the citric acid cycle OR Be
converted to glucose (gluconeogenesis)
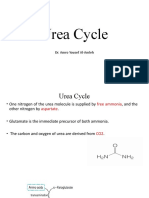
Gluconeogenesis Urea Cycle
• = Metabolic pathway that results in the • Detoxification of ammonia in the liver
generation of glucose from non- • Ammonia is a highly toxic compound formed in the body during amino acids catabolism
carbohydrate carbon substrates (amino • Gut bacteria produce ammonia that is absorbed in the gut and reaches the liver through hepatic portal vein
acids, pyruvate, lactate) • Liver converts ammonia to urea (non-toxic), which is excreted in the urine
You might also like
- 03 - Metabolisme Protein - MonogastrikDocument25 pages03 - Metabolisme Protein - MonogastrikHerni Bustam100% (1)
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument35 pagesAmino Acid MetabolismRajkishor YadavNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Catabolism-Part-1: Biochemistry For Medics - Lecture Notes Professor (DR.) Namrata ChhabraDocument43 pagesAmino Acid Catabolism-Part-1: Biochemistry For Medics - Lecture Notes Professor (DR.) Namrata Chhabrashree devNo ratings yet
- Introduction Amino Acid Matabolism and CatabolismDocument45 pagesIntroduction Amino Acid Matabolism and CatabolismAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'd100% (1)
- Protein and Amino Acid MetabolismDocument32 pagesProtein and Amino Acid MetabolismVirag0% (1)
- Protein MetabolismDocument182 pagesProtein MetabolismSimra ZahidNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Metabolism Final For Pharm 2014Document57 pagesAmino Acids Metabolism Final For Pharm 2014Getu LuchesaNo ratings yet
- Protein and Amino Acid MetabolismDocument52 pagesProtein and Amino Acid MetabolismRisky OpponentNo ratings yet
- Bio Synthesis of Amino Acid Tabisa Gcobo 1Document18 pagesBio Synthesis of Amino Acid Tabisa Gcobo 1Tabisa GcoboNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Amino Acid and Protein-EditedDocument36 pagesTopic 3 Amino Acid and Protein-Editedشيكين LurveJellabiesNo ratings yet
- Protien and Urea CycleDocument33 pagesProtien and Urea CycleTAUQEER Ali shahNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument29 pagesAmino Acid MetabolismERIAS TENYWANo ratings yet
- 3 Metabolism of Proteins & Amino AcidsDocument79 pages3 Metabolism of Proteins & Amino AcidsYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture PPT 7Document16 pagesBiochemistry Lecture PPT 7Chiranjeevi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen MetabolismDocument36 pagesNitrogen Metabolism202210034No ratings yet
- Proteins and Amino Acids Metabolism: Tahun Ajar 2016/2017Document47 pagesProteins and Amino Acids Metabolism: Tahun Ajar 2016/2017Aswar AyuNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle and Protein MetabolismDocument39 pagesUrea Cycle and Protein Metabolismikramullahkhan211No ratings yet
- BIO 202 Biochemistry II by Seyhun YURDUGÜL: Amino Acid Metabolism I: Amino Acid BiosynthesisDocument65 pagesBIO 202 Biochemistry II by Seyhun YURDUGÜL: Amino Acid Metabolism I: Amino Acid BiosynthesisYasin Çağrı KılıçerNo ratings yet
- Glucogenic & Ketogenic Amino AcidsDocument20 pagesGlucogenic & Ketogenic Amino AcidsDivine GamingNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle and Its DefectsDocument48 pagesUrea Cycle and Its DefectsStevia NdoeNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Proteins: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman M.D. Ph.D. Clinical Biochemistry HucomDocument27 pagesMetabolism of Proteins: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman M.D. Ph.D. Clinical Biochemistry HucomHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis and Degradation of Amino AcidsDocument22 pagesBiosynthesis and Degradation of Amino Acidsإضحك وبين سنانك Laugh and show your teethNo ratings yet
- Protein MetaboilisamDocument18 pagesProtein MetaboilisamSumit PandyaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Unit 03 PDFDocument66 pagesBiochemistry Unit 03 PDFDhanush kannanNo ratings yet
- 15BT103 Biochem-UNIT 3Document53 pages15BT103 Biochem-UNIT 3Adityanair RA1711009010128No ratings yet
- Amino Acid CatabolismDocument19 pagesAmino Acid Catabolismwmdpr4x64fNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Asam Amino - Blok 2.2.maret 2017Document55 pagesMetabolisme Asam Amino - Blok 2.2.maret 2017Avlya ZelykaNo ratings yet
- Catabolism of Amino Acids: DR - Ula Abbas ZekiDocument49 pagesCatabolism of Amino Acids: DR - Ula Abbas ZekinameNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Metabolism (Catabolism) and Clinical SignificantDocument33 pagesAmino Acids Metabolism (Catabolism) and Clinical SignificantBehailu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid & Protein MetabolismDocument59 pagesAmino Acid & Protein MetabolismAndualemNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of ProteinsDocument46 pagesPhysical Properties of ProteinsTasneem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle LehningerDocument34 pagesUrea Cycle LehningerMohamadJamaludinNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Aminoacids 2Document68 pagesMetabolism of Aminoacids 2Mi PatelNo ratings yet
- Special Functions of Amino AcidsDocument24 pagesSpecial Functions of Amino Acidsgeralynmodesto1No ratings yet
- Amino Acid CatabolismDocument24 pagesAmino Acid CatabolismAnonymous 0ha8TmNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle: Dr. Amro Yousef Al-AmlehDocument45 pagesUrea Cycle: Dr. Amro Yousef Al-AmlehDr. Amro YousefNo ratings yet
- C10 Protein and Amino Acid MetabolismDocument8 pagesC10 Protein and Amino Acid MetabolismSoraya D. Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Protein Metabolism 1Document18 pagesLecture 4 Protein Metabolism 1beneficialboxer9237No ratings yet
- Amino Acid For B.TechDocument4 pagesAmino Acid For B.TechAnushka AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Protein MetabolismDocument19 pagesProtein MetabolismAnn Michelle Tarrobago100% (1)
- 9a. Metabolisme Asam AminoDocument62 pages9a. Metabolisme Asam AminohimawarumNo ratings yet
- Protein Metabolism DikonversiDocument13 pagesProtein Metabolism DikonversiCat cuteNo ratings yet
- 202synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids - Lec 02 PDFDocument35 pages202synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids - Lec 02 PDFnyasha chinyangaNo ratings yet
- Protein Metabolism Part 1 Prepared By: CST, RMT 2020Document44 pagesProtein Metabolism Part 1 Prepared By: CST, RMT 2020Acel Jone CayotNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-05-25 at 1.47.14 PMDocument7 pagesScreenshot 2021-05-25 at 1.47.14 PMAynaz ChanNo ratings yet
- Protein Turn OverDocument29 pagesProtein Turn Overabdullah zaheerNo ratings yet
- Ch18 - Amino Acid Oxidation Production of UreaDocument50 pagesCh18 - Amino Acid Oxidation Production of UreaSalma KhoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- Ni Nyoman Ayu Dewi Dept. of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine Udayana University Ayu - Dewi@unud - Ac.idDocument37 pagesNi Nyoman Ayu Dewi Dept. of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine Udayana University Ayu - Dewi@unud - Ac.idWida Utami100% (1)
- 10 Protein MetabolismDocument21 pages10 Protein Metabolismlexjm7605No ratings yet
- B. Katabolisme Asam Amino-1Document19 pagesB. Katabolisme Asam Amino-1M Sifal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Pencernaan Protein Dan Penyerapan Asam AminoDocument33 pagesPencernaan Protein Dan Penyerapan Asam AminoAnonymous DVg2tmBINo ratings yet
- Protein Metabolism Dental and Physiotherapy Part 1Document17 pagesProtein Metabolism Dental and Physiotherapy Part 1Nada Atef KoraitemNo ratings yet
- 9 Metabolism of AAsDocument25 pages9 Metabolism of AAsyasingadaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Oxidation andDocument23 pagesAmino Acid Oxidation andRahma FauziahNo ratings yet
- 5 Nutrition and Metabloism Protein-UpdatedDocument38 pages5 Nutrition and Metabloism Protein-UpdatedAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Protein - En.idDocument51 pagesMetabolisme Protein - En.idMarissa AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Dr. Dra. Trini Suryowati, MsDocument49 pagesBiochemistry: Dr. Dra. Trini Suryowati, MsDaud ParluhutanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Proteins MetabolismDocument10 pagesIntro To Proteins MetabolismAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- Nirogen Metabolism Part 1Document13 pagesNirogen Metabolism Part 1Talha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cell & Tissue Engineering Strategies - Development & Replacement Of Musculoskeletal TissuesDocument7 pagesCell & Tissue Engineering Strategies - Development & Replacement Of Musculoskeletal TissuesClaraNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument8 pagesSkeletal MuscleClaraNo ratings yet
- BoneDocument18 pagesBoneClaraNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument16 pagesCartilageClaraNo ratings yet
- Jimin - Lesson50.2P (J)Document6 pagesJimin - Lesson50.2P (J)ClaraNo ratings yet
- Jimin - Lesson67P (J)Document2 pagesJimin - Lesson67P (J)ClaraNo ratings yet
- Jimin - Lesson14.2B (J)Document1 pageJimin - Lesson14.2B (J)ClaraNo ratings yet
- Tendon & LigamentDocument11 pagesTendon & LigamentClaraNo ratings yet
- Jimin - Lesson12B (J)Document1 pageJimin - Lesson12B (J)ClaraNo ratings yet
- Jimin - Lesson19.3C (J)Document1 pageJimin - Lesson19.3C (J)ClaraNo ratings yet
- Jimin - Lesson15.2C (J)Document1 pageJimin - Lesson15.2C (J)ClaraNo ratings yet
- Cell SignallingDocument7 pagesCell SignallingClaraNo ratings yet
- Genetics & Inheritance - QuestionsDocument10 pagesGenetics & Inheritance - QuestionsClaraNo ratings yet
- Metabolism - CarbohydrateDocument5 pagesMetabolism - CarbohydrateClaraNo ratings yet
- Metabolism - Nucleic AcidDocument2 pagesMetabolism - Nucleic AcidClaraNo ratings yet
- Jimin - Lesson10P (J)Document10 pagesJimin - Lesson10P (J)ClaraNo ratings yet
- Metabolism - LipidDocument2 pagesMetabolism - LipidClaraNo ratings yet
- DNA To CellsDocument4 pagesDNA To CellsClaraNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDocument8 pagesProkaryotes & EukaryotesClaraNo ratings yet
- Lipids, Membranes, TransportDocument9 pagesLipids, Membranes, TransportClaraNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument6 pagesCarbohydrateClaraNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure & Replication + RNADocument8 pagesDNA Structure & Replication + RNAClaraNo ratings yet
- Cells & TissuesDocument17 pagesCells & TissuesClaraNo ratings yet
- Cellular Compartments & EnvironmentsDocument5 pagesCellular Compartments & EnvironmentsClaraNo ratings yet
- Cell TraffickingDocument7 pagesCell TraffickingClaraNo ratings yet
- Cell Adaptation - DefenceDocument8 pagesCell Adaptation - DefenceClaraNo ratings yet
- Transcriptional & Chromatin RegulationDocument11 pagesTranscriptional & Chromatin RegulationClaraNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionClaraNo ratings yet
- Protein Translation ControlDocument8 pagesProtein Translation ControlClaraNo ratings yet
- ATP & Energy MetabolismDocument3 pagesATP & Energy MetabolismClaraNo ratings yet