Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsNoun Clause
Noun Clause
Uploaded by
Dyah Ayu Widya EganingrumCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 6328 - Grammar Minutes Book 2 Finished)Document113 pages6328 - Grammar Minutes Book 2 Finished)Clare Geoghegan75% (8)
- Noun Clause: Her Man ToDocument15 pagesNoun Clause: Her Man ToJasmine PutriNo ratings yet
- The Story Her House: 1. Question WordsDocument6 pagesThe Story Her House: 1. Question WordsAhmad AryaNo ratings yet
- Noun ClauseDocument15 pagesNoun ClauseFafa PunyaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechapi-3806123No ratings yet
- Class X-Study Material (2020-21)Document17 pagesClass X-Study Material (2020-21)Sangam SinghNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechDocument12 pagesIndirect SpeechElaine OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect NarrationDocument39 pagesDirect Indirect NarrationCT.Sadia Munir/17570100% (1)
- DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH-KLAS XI KurmerDocument10 pagesDIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH-KLAS XI KurmerVanesa Dwi FebriyantiNo ratings yet
- Tense Change D and IDDocument4 pagesTense Change D and IDkunti robiyatunNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Ingles IiiDocument31 pagesReported Speech Ingles IiiOscar Andres Rojo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Gómez Henao, J. I. (2019) - Reported Speech. University of Antioquia.Document18 pagesGómez Henao, J. I. (2019) - Reported Speech. University of Antioquia.Daniel ArenasNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PPT 140311051942 Phpapp01Document34 pagesReported Speech PPT 140311051942 Phpapp01Liezel LebarnesNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument10 pagesEnglishAvior Bagas ErtansyahNo ratings yet
- Course OneDocument120 pagesCourse OneRoberto Carlos CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechWILLIAM JOSE ACEVEDO JULIONo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument37 pagesReported SpeechFlying FriendsNo ratings yet
- Direct, Indirect, Reported SpeechDocument24 pagesDirect, Indirect, Reported SpeechKHALIDOO6No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledAsad RzayevNo ratings yet
- Sessions 12 and 13Document16 pagesSessions 12 and 13Francisco Milton SiueiaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PPTDocument37 pagesReported Speech PPTJITENDRA YADAV0% (1)
- Active and PassiveDocument9 pagesActive and Passivevishu_86No ratings yet
- Dokumen PDFDocument27 pagesDokumen PDFKhairun NizamNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument20 pagesReported Speechpocky-66100% (5)
- Reported SpeechDocument24 pagesReported SpeechjuliareveronraNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech in EnglishDocument4 pagesIndirect Speech in EnglishDaniela CraciunNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument20 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Noun Clauses 3Document49 pagesNoun Clauses 3Olcay HavalanNo ratings yet
- REPORTED SPEECh Intermediate 1Document4 pagesREPORTED SPEECh Intermediate 1Zorica ArnaudovaNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech or Reported Speech 2Document21 pagesIndirect Speech or Reported Speech 2Constanza Farfán100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument5 pagesReported SpeechPatricia López RasteuNo ratings yet
- English 7 Q1 WK5Document22 pagesEnglish 7 Q1 WK5RamilNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeecheditfotiNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocument6 pagesAdverbs of FrequencyPermata HatiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech REVIEWDocument31 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech REVIEWjamrockerNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFDocument35 pagesReported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFArabic&English NonoooNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument30 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechGiridhar Suresh KitturNo ratings yet
- Direct SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect SpeechSomaSanubariNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument11 pagesReported SpeechCibotari MihaiNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFDocument28 pagesReported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFIVAN ANDRE AGUILAR ALVARADONo ratings yet
- Unit 0:introduce Yourself and Holiday Anecdotes: by Daniela RossiDocument23 pagesUnit 0:introduce Yourself and Holiday Anecdotes: by Daniela Rossi3roB_LdeA100% (1)
- Direct and ReportedDocument22 pagesDirect and ReportedMaria Vallerie FulgarNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument42 pagesReported SpeechMaria Eduarda LinsNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument34 pagesReported SpeechRubicel Cordova0% (1)
- Relative Clauses N ExerciseDocument15 pagesRelative Clauses N ExerciseTiara D'Silva100% (2)
- Unit Iv ModificadaDocument9 pagesUnit Iv Modificadawalquiria cabezaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Reported Speech Is Often Also Called Indirect Speech in English. When We Use Reported Speech, We AreDocument4 pagesReported Speech: Reported Speech Is Often Also Called Indirect Speech in English. When We Use Reported Speech, We AreLoredanaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported SpeechJaviera Gálvez PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Transformation Negatives InterrogativesDocument14 pagesTransformation Negatives InterrogativesTasneem Khan100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument10 pagesReported SpeechAlbertoyJavier Sancho CamposNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechHienNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument62 pagesReported SpeechUtsav LalNo ratings yet
- Tense Direct Speech Reported Speech: Click Here To Practise Reported StatementsDocument4 pagesTense Direct Speech Reported Speech: Click Here To Practise Reported StatementsSlimaneNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech Definition and ExamplesDocument14 pagesDirect Speech Definition and Examplesintiw_23No ratings yet
- Reported Speech StudentsDocument37 pagesReported Speech StudentsphobyuNo ratings yet
- EstiloindirectoDocument19 pagesEstiloindirectoTatiana García SolanoNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument19 pagesDirect and IndirectSaqib ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Direct-Indirect Speech EnglishDocument82 pagesDirect-Indirect Speech EnglishYanuar NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechJopa FebiolaNo ratings yet
- Mastering The English Langyage, Communication Arts and Skills, Gayo Publishing, 2006Document4 pagesMastering The English Langyage, Communication Arts and Skills, Gayo Publishing, 2006Graciella FaeNo ratings yet
- UGC-NET Dec 2018Document66 pagesUGC-NET Dec 2018Partha Sarathi PatraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Norwegian - Word List Day 1Document5 pagesIntroduction To Norwegian - Word List Day 1AntonioNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 8 GN XIDocument6 pagesLearning Material 8 GN XIJuli DikariNo ratings yet
- Thuthuyck@tuu - Edu: Student's Book With AnswersDocument200 pagesThuthuyck@tuu - Edu: Student's Book With AnswersTâm GiaNo ratings yet
- Concise Book of English Linkers and ConnectivesDocument32 pagesConcise Book of English Linkers and Connectivesbishwabengalitola100% (1)
- Listado VerbosDocument8 pagesListado VerbosMARBELLA GELENA GUASHPA RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle Infinitive Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument2 pagesInfinitive Past Simple Past Participle Infinitive Past Simple Past Participleanas0lNo ratings yet
- Grammar Quarter Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3Document3 pagesGrammar Quarter Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3Yasmin G. BaoitNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument20 pagesRelative ClausesDaniela A. Huerta Parra0% (1)
- Word FormsDocument15 pagesWord FormsШухрат ТоймуратовNo ratings yet
- Longer List of Grammar Terms HereDocument2 pagesLonger List of Grammar Terms HereNuhaNo ratings yet
- Adverb Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAdverb Lesson Planapi-288610471No ratings yet
- English Gen - Ed ReviewerDocument10 pagesEnglish Gen - Ed ReviewerSantiago Jr KadusaleNo ratings yet
- The MatrixDocument12 pagesThe MatrixKarina FernandesNo ratings yet
- German AP Summer WorkDocument14 pagesGerman AP Summer WorkDina MapoonNo ratings yet
- English Paper Group 5 Material 7Document12 pagesEnglish Paper Group 5 Material 7zakia cacaNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: Pronoun Ialah Kata Yang Digunakan Atau Difungsikan Sebagai Pengganti Kata Benda (Noun)Document4 pagesPronoun: Pronoun Ialah Kata Yang Digunakan Atau Difungsikan Sebagai Pengganti Kata Benda (Noun)ryo apriansyahNo ratings yet
- Modul Basic English 1 Print 4Document72 pagesModul Basic English 1 Print 4Apriana SalimNo ratings yet
- Possessive Pronoun ActivityDocument3 pagesPossessive Pronoun ActivityMario A. Sánchez PabónNo ratings yet
- DETERMINERDocument7 pagesDETERMINERBhanu Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- A - Add Capital Letters and Punctuation To The SentencesDocument2 pagesA - Add Capital Letters and Punctuation To The SentencesShosho AlmaeNo ratings yet
- Taller Personal PronounsDocument2 pagesTaller Personal PronounsLuis Fernando SáenzNo ratings yet
- Review of Verb Tenses 2 BachDocument2 pagesReview of Verb Tenses 2 BachcmvvmcNo ratings yet
- Adverb of TimeDocument5 pagesAdverb of TimeIsha kaleNo ratings yet
- French Gcse 2024 Vocabulary ListDocument145 pagesFrench Gcse 2024 Vocabulary Listdinaafreen hussainNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous TenseDocument28 pagesPresent Continuous TenseJhon Rider100% (1)
- Word BuildingDocument7 pagesWord BuildingNatia LashqareishviliNo ratings yet
- Word Order in English Questions - SummaryDocument3 pagesWord Order in English Questions - SummaryMena CabralNo ratings yet
Noun Clause
Noun Clause
Uploaded by
Dyah Ayu Widya Eganingrum0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesNoun Clause
Noun Clause
Uploaded by
Dyah Ayu Widya EganingrumCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
NOUN CLAUSE
Keep in your mind!
Noun: is used as a subject or object.
Example: The story is interesting.
I know her house.
Noun clause: is used as a subject or object. In
other words, a noun clause is used in the
same ways as a noun.
Example: What he said is interesting.
I know where she lives.
Words to introduce NC
• Question words:
- who - whom
- what - which
- when - where
- why - how
- whose
• Whether/If
• That
Noun Clause with ‘Question Words’
Where does she live? I don’t know where she lives.
What did he say? I couldn’t hear what he said.
Who lives there? No body knows who lives there.
Who is at the door? I wonder who is at the door.
Who is she? I don’t know who she is.
Who are those girls? I don’t know who those girls are.
Whose house is that? I wonder whose house that is.
What did he say? What he said surprised me.
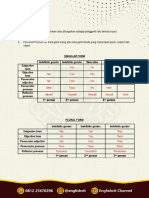
Noun Clause with ‘whether’ or ‘if’
Yes – No Question Noun Clause
Will she come? I don’t know whether she will come.
I don’t know if she will come.
I wonder whether he needs help.
I wonder if he needs help.
Does he need help? I wonder whether or not he needs help.
I wonder whether he needs help or not.
I wonder if he needs help or not.
Whether he needs help or not is not obvious to me.
Noun clause with ‘that’
Statement Noun clause
He is an excellent student Everybody thinks that he is an excellent student.
I think he is an excellent student.
The earth is round We know (that) the earth is round.
Computer is basic need for modern life That computer is basic need for modern life
is obvious.
It is obvious (that) computer is basic need for
modern life.
English is world language That English is world language is fact.
It is a fact that English is world language.
Question Words followed by Infinitive
• I don’t know what I should do.
= I don’t know what to do.
• She can’t decide whether she should go or stay
home.
= She can’t decide whether to go or (to) stay
home.
• Please tell me how I can get the information.
=Please tell me how to get the information.
• A boy told us where we could find the address.
=A boy told us where to find the address.
Reported /Indirect Speech
Indirect Speech (also referred to as 'reported
speech') refers to a sentence reporting what
someone has said.
Reporting Verb
• If the reporting verb (i.e. said) is in the past, the reported
clause will be in a past form.
• This form is usually one step back into the past from the
original.
• For example:
– He said, “The test is difficult.”
He said the test was difficult.
– She said, “She watches TV every day.”
She said she watched TV every day.
-- Jack said, “I come to school every day.
Jack said he came to school every day.”
Reporting Verb
• If simple present, present perfect or the future is
used in the reporting verb (i.e. says) the tense is
retained.
• For example:
– He says the test is difficult.
– She has said that she watches TV every day.
– Jack will say that he comes to school every day.
General truth
• If reporting a general truth the present tense
will be retained.
• For example:
- The teacher said, “Phrasal verbs are very
important.
The teacher said that phrasal verbs are
very important.
Changing Pronouns and Time Signifiers
• When changing from direct speech to indirect
speech, it is often necessary to change the pronouns
to match the subject of the sentence.
• For example:
- She said, "I want to present my report.“
She said that she wanted to present her report.
- Jack said, "My friend went to the class with me.“
Jack said his friend had gone to the class with him.
Changing Pronouns and Time Signifiers
• It is also important to change time words (signifiers)
when referring to present, past or future time to match
the moment of speaking.
• For example:
- She said, "I want to submit my report tomorrow.“
She said that she wanted to submit her report the next day.
- Jack said, " My friend went to the class with me
yesterday.“
Jack said that his friend had gone to the class with him
the day before.
Indirect Questions
• When reporting questions, it is especially important to
pay attention to sentence order.
• When reporting yes/ no questions connect the reported
question using 'if'.
• When reporting questions using question words (why,
where, when, etc.) use the question word + S+ V.
Example:
She asked, "Do you want to come with me?“
She asked me if I wanted to come with her.
Dave asked, "Where did you go last weekend?“
Dave asked me where I had gone the previous weekend.
He asked, "Why are you studying English?“
She asked me why I was studying English.
Indirect command
• When reporting command, change the
infinitive verb to ‘to infinitive verb’.
Example:
• He said, “Close the door.”
He said to close the door.
• She ordered him, “Don’t come to my house.”
She ordered him not to come to her house.
You might also like
- 6328 - Grammar Minutes Book 2 Finished)Document113 pages6328 - Grammar Minutes Book 2 Finished)Clare Geoghegan75% (8)
- Noun Clause: Her Man ToDocument15 pagesNoun Clause: Her Man ToJasmine PutriNo ratings yet
- The Story Her House: 1. Question WordsDocument6 pagesThe Story Her House: 1. Question WordsAhmad AryaNo ratings yet
- Noun ClauseDocument15 pagesNoun ClauseFafa PunyaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect Speechapi-3806123No ratings yet
- Class X-Study Material (2020-21)Document17 pagesClass X-Study Material (2020-21)Sangam SinghNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechDocument12 pagesIndirect SpeechElaine OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect NarrationDocument39 pagesDirect Indirect NarrationCT.Sadia Munir/17570100% (1)
- DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH-KLAS XI KurmerDocument10 pagesDIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH-KLAS XI KurmerVanesa Dwi FebriyantiNo ratings yet
- Tense Change D and IDDocument4 pagesTense Change D and IDkunti robiyatunNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Ingles IiiDocument31 pagesReported Speech Ingles IiiOscar Andres Rojo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Gómez Henao, J. I. (2019) - Reported Speech. University of Antioquia.Document18 pagesGómez Henao, J. I. (2019) - Reported Speech. University of Antioquia.Daniel ArenasNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PPT 140311051942 Phpapp01Document34 pagesReported Speech PPT 140311051942 Phpapp01Liezel LebarnesNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument10 pagesEnglishAvior Bagas ErtansyahNo ratings yet
- Course OneDocument120 pagesCourse OneRoberto Carlos CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechWILLIAM JOSE ACEVEDO JULIONo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument37 pagesReported SpeechFlying FriendsNo ratings yet
- Direct, Indirect, Reported SpeechDocument24 pagesDirect, Indirect, Reported SpeechKHALIDOO6No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledAsad RzayevNo ratings yet
- Sessions 12 and 13Document16 pagesSessions 12 and 13Francisco Milton SiueiaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech PPTDocument37 pagesReported Speech PPTJITENDRA YADAV0% (1)
- Active and PassiveDocument9 pagesActive and Passivevishu_86No ratings yet
- Dokumen PDFDocument27 pagesDokumen PDFKhairun NizamNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument20 pagesReported Speechpocky-66100% (5)
- Reported SpeechDocument24 pagesReported SpeechjuliareveronraNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech in EnglishDocument4 pagesIndirect Speech in EnglishDaniela CraciunNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument20 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Noun Clauses 3Document49 pagesNoun Clauses 3Olcay HavalanNo ratings yet
- REPORTED SPEECh Intermediate 1Document4 pagesREPORTED SPEECh Intermediate 1Zorica ArnaudovaNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech or Reported Speech 2Document21 pagesIndirect Speech or Reported Speech 2Constanza Farfán100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument5 pagesReported SpeechPatricia López RasteuNo ratings yet
- English 7 Q1 WK5Document22 pagesEnglish 7 Q1 WK5RamilNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeecheditfotiNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocument6 pagesAdverbs of FrequencyPermata HatiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech REVIEWDocument31 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech REVIEWjamrockerNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFDocument35 pagesReported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFArabic&English NonoooNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument30 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechGiridhar Suresh KitturNo ratings yet
- Direct SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect SpeechSomaSanubariNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument11 pagesReported SpeechCibotari MihaiNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFDocument28 pagesReported Speech: Click Here For A List of Reported Speech Exercises. Click Here To Download This Explanation in PDFIVAN ANDRE AGUILAR ALVARADONo ratings yet
- Unit 0:introduce Yourself and Holiday Anecdotes: by Daniela RossiDocument23 pagesUnit 0:introduce Yourself and Holiday Anecdotes: by Daniela Rossi3roB_LdeA100% (1)
- Direct and ReportedDocument22 pagesDirect and ReportedMaria Vallerie FulgarNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument42 pagesReported SpeechMaria Eduarda LinsNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument34 pagesReported SpeechRubicel Cordova0% (1)
- Relative Clauses N ExerciseDocument15 pagesRelative Clauses N ExerciseTiara D'Silva100% (2)
- Unit Iv ModificadaDocument9 pagesUnit Iv Modificadawalquiria cabezaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Reported Speech Is Often Also Called Indirect Speech in English. When We Use Reported Speech, We AreDocument4 pagesReported Speech: Reported Speech Is Often Also Called Indirect Speech in English. When We Use Reported Speech, We AreLoredanaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported SpeechJaviera Gálvez PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Transformation Negatives InterrogativesDocument14 pagesTransformation Negatives InterrogativesTasneem Khan100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument10 pagesReported SpeechAlbertoyJavier Sancho CamposNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechHienNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument62 pagesReported SpeechUtsav LalNo ratings yet
- Tense Direct Speech Reported Speech: Click Here To Practise Reported StatementsDocument4 pagesTense Direct Speech Reported Speech: Click Here To Practise Reported StatementsSlimaneNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech Definition and ExamplesDocument14 pagesDirect Speech Definition and Examplesintiw_23No ratings yet
- Reported Speech StudentsDocument37 pagesReported Speech StudentsphobyuNo ratings yet
- EstiloindirectoDocument19 pagesEstiloindirectoTatiana García SolanoNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument19 pagesDirect and IndirectSaqib ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Direct-Indirect Speech EnglishDocument82 pagesDirect-Indirect Speech EnglishYanuar NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechJopa FebiolaNo ratings yet
- Mastering The English Langyage, Communication Arts and Skills, Gayo Publishing, 2006Document4 pagesMastering The English Langyage, Communication Arts and Skills, Gayo Publishing, 2006Graciella FaeNo ratings yet
- UGC-NET Dec 2018Document66 pagesUGC-NET Dec 2018Partha Sarathi PatraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Norwegian - Word List Day 1Document5 pagesIntroduction To Norwegian - Word List Day 1AntonioNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 8 GN XIDocument6 pagesLearning Material 8 GN XIJuli DikariNo ratings yet
- Thuthuyck@tuu - Edu: Student's Book With AnswersDocument200 pagesThuthuyck@tuu - Edu: Student's Book With AnswersTâm GiaNo ratings yet
- Concise Book of English Linkers and ConnectivesDocument32 pagesConcise Book of English Linkers and Connectivesbishwabengalitola100% (1)
- Listado VerbosDocument8 pagesListado VerbosMARBELLA GELENA GUASHPA RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle Infinitive Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument2 pagesInfinitive Past Simple Past Participle Infinitive Past Simple Past Participleanas0lNo ratings yet
- Grammar Quarter Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3Document3 pagesGrammar Quarter Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3Yasmin G. BaoitNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument20 pagesRelative ClausesDaniela A. Huerta Parra0% (1)
- Word FormsDocument15 pagesWord FormsШухрат ТоймуратовNo ratings yet
- Longer List of Grammar Terms HereDocument2 pagesLonger List of Grammar Terms HereNuhaNo ratings yet
- Adverb Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAdverb Lesson Planapi-288610471No ratings yet
- English Gen - Ed ReviewerDocument10 pagesEnglish Gen - Ed ReviewerSantiago Jr KadusaleNo ratings yet
- The MatrixDocument12 pagesThe MatrixKarina FernandesNo ratings yet
- German AP Summer WorkDocument14 pagesGerman AP Summer WorkDina MapoonNo ratings yet
- English Paper Group 5 Material 7Document12 pagesEnglish Paper Group 5 Material 7zakia cacaNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: Pronoun Ialah Kata Yang Digunakan Atau Difungsikan Sebagai Pengganti Kata Benda (Noun)Document4 pagesPronoun: Pronoun Ialah Kata Yang Digunakan Atau Difungsikan Sebagai Pengganti Kata Benda (Noun)ryo apriansyahNo ratings yet
- Modul Basic English 1 Print 4Document72 pagesModul Basic English 1 Print 4Apriana SalimNo ratings yet
- Possessive Pronoun ActivityDocument3 pagesPossessive Pronoun ActivityMario A. Sánchez PabónNo ratings yet
- DETERMINERDocument7 pagesDETERMINERBhanu Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- A - Add Capital Letters and Punctuation To The SentencesDocument2 pagesA - Add Capital Letters and Punctuation To The SentencesShosho AlmaeNo ratings yet
- Taller Personal PronounsDocument2 pagesTaller Personal PronounsLuis Fernando SáenzNo ratings yet
- Review of Verb Tenses 2 BachDocument2 pagesReview of Verb Tenses 2 BachcmvvmcNo ratings yet
- Adverb of TimeDocument5 pagesAdverb of TimeIsha kaleNo ratings yet
- French Gcse 2024 Vocabulary ListDocument145 pagesFrench Gcse 2024 Vocabulary Listdinaafreen hussainNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous TenseDocument28 pagesPresent Continuous TenseJhon Rider100% (1)
- Word BuildingDocument7 pagesWord BuildingNatia LashqareishviliNo ratings yet
- Word Order in English Questions - SummaryDocument3 pagesWord Order in English Questions - SummaryMena CabralNo ratings yet