Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsExcretion & Homeostasis
Excretion & Homeostasis
Uploaded by
Varun GoseinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ebook First Aid For The Basic Sciences General Principles PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook First Aid For The Basic Sciences General Principles PDF Full Chapter PDFgwendolyn.jordan283100% (34)
- DR. SEBI KIDNEY FAILURE SOLUTION: Dialysis-Free Living. A Natural Approach to Treating and Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease (2022 Guide for Beginners)From EverandDR. SEBI KIDNEY FAILURE SOLUTION: Dialysis-Free Living. A Natural Approach to Treating and Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease (2022 Guide for Beginners)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Occams Protocol Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesOccams Protocol Cheat Sheetfnandow4lNo ratings yet
- 2007 - Framework For Product ExperienceDocument10 pages2007 - Framework For Product ExperiencePallavi RayNo ratings yet
- Programming For Athletic PerformanceDocument7 pagesProgramming For Athletic Performancemike100% (2)
- Bio 10, Excretion in HumansDocument14 pagesBio 10, Excretion in HumansSephoraNo ratings yet
- Excretion in HumansDocument6 pagesExcretion in HumansMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: Function and PartsDocument15 pagesExcretory System: Function and PartsVladStoenescuNo ratings yet
- Effects of Exercise and Training On Human Excretory System: Rahul Arya Amit Singh Rishi Chaubey Vishal ThakranDocument13 pagesEffects of Exercise and Training On Human Excretory System: Rahul Arya Amit Singh Rishi Chaubey Vishal ThakranAnonymous Dx0S9QlNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Excretory SystemDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Excretory Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- Excretion and KidneysDocument39 pagesExcretion and KidneyselizabethNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument11 pagesExcretory Systemcmillica1176No ratings yet
- EXCRETIONDocument36 pagesEXCRETIONIbrahim NOORZADNo ratings yet
- Excretion 3Document139 pagesExcretion 3Princess NtleleNo ratings yet
- Excretion: Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesExcretion: Urinary SystemDiana PriyaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument19 pagesExcretory SystemElliz DoctoraNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument11 pagesExcretory Systemcmillica1176100% (1)
- Excretion: Excretory Organ Excretory ProductDocument3 pagesExcretion: Excretory Organ Excretory ProductKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: Function and PartsDocument18 pagesExcretory System: Function and PartsChandra AdieNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument18 pagesExcretory SystemRochell CabahugNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Excretion in HumansDocument11 pages4.3 Excretion in Humansnyanmoemyat2010No ratings yet
- Exvretion: Removal of Waste MaterialsDocument20 pagesExvretion: Removal of Waste MaterialsQazi QaziNo ratings yet
- Za NST 1642930204 Systems in The Human Body Excretory System Powerpoint - Ver - 2Document12 pagesZa NST 1642930204 Systems in The Human Body Excretory System Powerpoint - Ver - 2Eunice HuangNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument61 pagesExcretory Systemalayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes IGCSE Excretion NoteDocument9 pagesBiology Notes IGCSE Excretion NoteCorina HuNo ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument46 pagesThe Excretory SystemRand NasserNo ratings yet
- 10 Excretion Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document10 pages10 Excretion Biology Notes IGCSE 2014pyf2nq6gdrNo ratings yet
- Y10 Chapter+13 ExcretionDocument67 pagesY10 Chapter+13 ExcretionLOW YUEBEI RIJNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Excretion in HumansDocument15 pagesIGCSE Excretion in HumansYashodhaNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: Function and PartsDocument9 pagesExcretory System: Function and PartsalvitakhoridatulNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Excretion in Humans (Edited)Document59 pagesIGCSE Excretion in Humans (Edited)elizabethNo ratings yet
- Urinary System and ExcretionDocument36 pagesUrinary System and ExcretionAngel CepedaNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument4 pagesExcretiontalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- 10 Excretion Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument10 pages10 Excretion Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans67% (3)
- Homeostasis 1Document23 pagesHomeostasis 1mandimutsiradoreen8No ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans - NotesDocument10 pagesExcretion in Humans - NotesPranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Excretion in HumansDocument17 pages4.3 Excretion in HumanskaverinmohiteNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 4Document16 pagesPDF Document 4johnmazuba12No ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument15 pagesThe Excretory SystemHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument17 pagesExcretionMaria adeelNo ratings yet
- Excretory SyestemDocument13 pagesExcretory SyestemAnnaya RazaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument32 pagesExcretory SystemJeanie uyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - ExcretionDocument46 pagesChapter 11 - Excretionapi-372850875% (4)
- Bped 65 Urinary SystemDocument26 pagesBped 65 Urinary SystemDollie May Maestre-TejidorNo ratings yet
- Al Wadi International School Biology Grade 9 13. Excretion in Humans NotesDocument42 pagesAl Wadi International School Biology Grade 9 13. Excretion in Humans NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument11 pagesExcretory Systemapi-245979635No ratings yet
- THE Excretory SystemDocument24 pagesTHE Excretory SystemZain HaiderNo ratings yet
- 4.lessons 23-24, Excretory System, PP 453-459Document20 pages4.lessons 23-24, Excretory System, PP 453-459Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - ExcretionDocument51 pagesChapter 12 - ExcretionKareem DmourNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 Excretion in HumansDocument7 pagesCh-13 Excretion in Humansdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- Excretion NOTESDocument2 pagesExcretion NOTESabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotesDocument27 pagesUNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotescyumadripNo ratings yet
- Human Excretory SystemDocument51 pagesHuman Excretory SystemVinoj MnoNo ratings yet
- Overview of RENAL: Dr. Wilson Arthur Zein, M. BiomedDocument34 pagesOverview of RENAL: Dr. Wilson Arthur Zein, M. BiomedAnnisNo ratings yet
- Excretory System PresentationDocument13 pagesExcretory System Presentationcristobal melegritoNo ratings yet
- Excretory System PresentationDocument13 pagesExcretory System PresentationNelson DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Checkpoint Notes ExcretionDocument3 pagesCambridge Checkpoint Notes Excretionanimemaster2kNo ratings yet
- Complete ExcretionDocument61 pagesComplete Excretionethankhoo2007No ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument37 pagesExcretory SystemPatrick DeeNo ratings yet
- ExcretoryDocument31 pagesExcretoryJevin IndaNo ratings yet
- Revision ExcretionDocument24 pagesRevision Excretionjanling82No ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument14 pagesExcretionAuthor ClubNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument39 pagesExcretory SystemTajXNo ratings yet
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 11 Energy FlowDocument7 pages11 Energy FlowVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- 3 ReproductionDocument17 pages3 ReproductionVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- 2 Cells Chemicals and Processes of LifeDocument9 pages2 Cells Chemicals and Processes of LifeVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Questions PHYSICS CDocument20 pagesPast Paper Questions PHYSICS CVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- Water Treading in SwimmingDocument11 pagesWater Treading in SwimmingPavitra VitraNo ratings yet
- Atrial Systole: The End of DiastoleDocument9 pagesAtrial Systole: The End of DiastoleSophia MahboobNo ratings yet
- Neck Pain Questionnaire FormDocument1 pageNeck Pain Questionnaire FormSeptyan Dwi Witjaksana100% (1)
- E C I R P: Shoulder RehabilitationDocument7 pagesE C I R P: Shoulder RehabilitationMelisa Agustina TobarNo ratings yet
- ContinueDocument3 pagesContinueJúÑi ØrNo ratings yet
- 71170-Article Text-218870-1-10-20210401Document9 pages71170-Article Text-218870-1-10-20210401San LocardoNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Chapter 1 Form 5Document3 pagesTopical Test Chapter 1 Form 5Rubi AnnNo ratings yet
- Cultivo de CianobacteriasDocument35 pagesCultivo de CianobacteriasArmando Chiclla SalazarNo ratings yet
- Basics of Cardiopulmonary Bypass.10Document8 pagesBasics of Cardiopulmonary Bypass.10Chaaru ShaarmaNo ratings yet
- Animal Respiratory SystemDocument80 pagesAnimal Respiratory SystemPutri Maharani75% (8)
- Applications of Calcium and Its Supplement Derived From Marine OrganismsDocument8 pagesApplications of Calcium and Its Supplement Derived From Marine OrganismsDewi SariNo ratings yet
- Blalock Taussig Thomas PDFDocument11 pagesBlalock Taussig Thomas PDFFer45No ratings yet
- Micro B - Ascending Tracts SummaryDocument1 pageMicro B - Ascending Tracts SummaryMitchu Tan100% (1)
- Chapter 10 BloodDocument3 pagesChapter 10 BloodinitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- DR. MARK HYMAN - Simplifying Weight Loss.Document6 pagesDR. MARK HYMAN - Simplifying Weight Loss.Mihaela Cristina MunteanuNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast PanabangiDocument7 pagesChloroplast PanabangiPatrick Rómulo CabilingNo ratings yet
- Action Observation and Execution Network: An Extended ViewDocument16 pagesAction Observation and Execution Network: An Extended ViewAndreia SilvaNo ratings yet
- LifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionDocument173 pagesLifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionSamanta Arijit100% (1)
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 48Document7 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 48sarasjunkNo ratings yet
- Nat MurDocument19 pagesNat MurSun BNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Muscle AttachmentDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Muscle Attachmenterwilli5No ratings yet
- IV ComputationDocument11 pagesIV ComputationSheniel VariacionNo ratings yet
- Virtual Microscopy Histology Manual: University of Alabama at Birmingham School of MedicineDocument6 pagesVirtual Microscopy Histology Manual: University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Medicinelucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- Cell & Tissue StructureDocument19 pagesCell & Tissue StructureBrintha Kani KumarNo ratings yet
- Unlock Brains Full PotentialDocument3 pagesUnlock Brains Full PotentialMiguel Antonio Platon Torres100% (1)
- Faecal Incontinence in Adults - ReviewDocument12 pagesFaecal Incontinence in Adults - Reviewi can always make u smile :DNo ratings yet
Excretion & Homeostasis
Excretion & Homeostasis
Uploaded by
Varun Gosein0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views20 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views20 pagesExcretion & Homeostasis
Excretion & Homeostasis
Uploaded by
Varun GoseinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
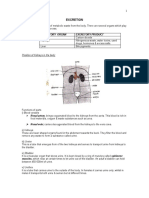
The removal of metabolic waste products and
excess substances from the body.
CO2 is a waste product of Respiration
CO2 is toxic in large amounts
Excretion is NOT the same as Egestion
The material in feces is not MWP’s; it was never
digested or absorbed.
Do you remember them all?
Carbon Dioxide
MWP of cell Respiration
Urea
MWP of Liver, removed by kidneys
Water
In excess, removed by kidneys
• First, you eat proteins, which get digested into
amino acids and absorbed into your blood.
• The AA’s travel to the Liver (thru the hepatic
portal vein)
• Extra AA’s get broken down into urea.
– This involves deamination; removing the part of the
AA that contains Nitrogen.
• The part with N will be excreted as Urea.
• So Urea is a “nitrogenous excretory product.”
The urea goes back into the blood and travels
to the kidneys.
Kidneys take urea out of the blood and mix it
with water to make urine.
The urine flows from the kidneys thru 2 ureters
to the bladder.
Then it’s excreted thru the urethra.
You eat a protein and break it down into amino
acids. Where do the amino acids go next?
To the Liver (thru the Hepatic Portal Vein)
What happens to extra amino acidsin the
Liver?
They get deaminated and made into urea
Where does the urea go next?
To the kidneys, then out of the body thru the
ureters bladder urethra.
# Event
6 AA’s are deaminated in Liver
10 Kidneys remove urea from blood
4 AA’s travel through hepatic portal vein
8 Urea passes into blood
1 Proteins are eaten
14 Urine flows into urethra
2 Proteins are digested into AA’s
13 Urine is stored in the bladder
3 AA’s are absorbed into blood
5 AA’s enter liver cells
7 Urea is produced
9 Urea is carried to kidneys
11 Urine is produced
12 Urine flows through the ureter
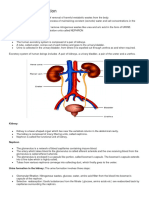
• Kidneys consist of tiny units of tubules called
nephrons.
• The nephron is where urea is filtered out of the
blood.
• An intricate network of blood capillaries
around the nephron helps urea diffuse down
its concentration gradient into the urinary
tubules.
• Other substances also diffuse out of the blood
in the same way.
• When kidneys fail, people still need their blood
“cleaned” of urea and other harmful
substances.
• They have to undergo dialysis treatment
several times a week.
• Dialysis = a mechanical means of filtering
blood, using concentration gradients to remove
urea and other substances.
• Blood is filtered outside of the body and
pumped back in!
What if you had too much water in your body?
What if you didn’t have enough?
Kidneys excrete lots of watery urine when you
have too much.
Kidneys excrete only small amounts when
you’re short on water.
So the urine is very concentrated.
Hormones
Broken down in liver, excreted by kidneys in urine
Alcohol
Also broken down in liver
Toxic to cells; even liver cells!
Liver damage or failure can result from drinking too
much alcohol.
Why should a person with kidney failure avoid
eating salty foods?
The kidneys will be unable to filter out the
extra salt.
You might also like
- Ebook First Aid For The Basic Sciences General Principles PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook First Aid For The Basic Sciences General Principles PDF Full Chapter PDFgwendolyn.jordan283100% (34)
- DR. SEBI KIDNEY FAILURE SOLUTION: Dialysis-Free Living. A Natural Approach to Treating and Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease (2022 Guide for Beginners)From EverandDR. SEBI KIDNEY FAILURE SOLUTION: Dialysis-Free Living. A Natural Approach to Treating and Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease (2022 Guide for Beginners)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Occams Protocol Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesOccams Protocol Cheat Sheetfnandow4lNo ratings yet
- 2007 - Framework For Product ExperienceDocument10 pages2007 - Framework For Product ExperiencePallavi RayNo ratings yet
- Programming For Athletic PerformanceDocument7 pagesProgramming For Athletic Performancemike100% (2)
- Bio 10, Excretion in HumansDocument14 pagesBio 10, Excretion in HumansSephoraNo ratings yet
- Excretion in HumansDocument6 pagesExcretion in HumansMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: Function and PartsDocument15 pagesExcretory System: Function and PartsVladStoenescuNo ratings yet
- Effects of Exercise and Training On Human Excretory System: Rahul Arya Amit Singh Rishi Chaubey Vishal ThakranDocument13 pagesEffects of Exercise and Training On Human Excretory System: Rahul Arya Amit Singh Rishi Chaubey Vishal ThakranAnonymous Dx0S9QlNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Excretory SystemDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Excretory Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- Excretion and KidneysDocument39 pagesExcretion and KidneyselizabethNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument11 pagesExcretory Systemcmillica1176No ratings yet
- EXCRETIONDocument36 pagesEXCRETIONIbrahim NOORZADNo ratings yet
- Excretion 3Document139 pagesExcretion 3Princess NtleleNo ratings yet
- Excretion: Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesExcretion: Urinary SystemDiana PriyaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument19 pagesExcretory SystemElliz DoctoraNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument11 pagesExcretory Systemcmillica1176100% (1)
- Excretion: Excretory Organ Excretory ProductDocument3 pagesExcretion: Excretory Organ Excretory ProductKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: Function and PartsDocument18 pagesExcretory System: Function and PartsChandra AdieNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument18 pagesExcretory SystemRochell CabahugNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Excretion in HumansDocument11 pages4.3 Excretion in Humansnyanmoemyat2010No ratings yet
- Exvretion: Removal of Waste MaterialsDocument20 pagesExvretion: Removal of Waste MaterialsQazi QaziNo ratings yet
- Za NST 1642930204 Systems in The Human Body Excretory System Powerpoint - Ver - 2Document12 pagesZa NST 1642930204 Systems in The Human Body Excretory System Powerpoint - Ver - 2Eunice HuangNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument61 pagesExcretory Systemalayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes IGCSE Excretion NoteDocument9 pagesBiology Notes IGCSE Excretion NoteCorina HuNo ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument46 pagesThe Excretory SystemRand NasserNo ratings yet
- 10 Excretion Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document10 pages10 Excretion Biology Notes IGCSE 2014pyf2nq6gdrNo ratings yet
- Y10 Chapter+13 ExcretionDocument67 pagesY10 Chapter+13 ExcretionLOW YUEBEI RIJNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Excretion in HumansDocument15 pagesIGCSE Excretion in HumansYashodhaNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: Function and PartsDocument9 pagesExcretory System: Function and PartsalvitakhoridatulNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Excretion in Humans (Edited)Document59 pagesIGCSE Excretion in Humans (Edited)elizabethNo ratings yet
- Urinary System and ExcretionDocument36 pagesUrinary System and ExcretionAngel CepedaNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument4 pagesExcretiontalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- 10 Excretion Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument10 pages10 Excretion Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans67% (3)
- Homeostasis 1Document23 pagesHomeostasis 1mandimutsiradoreen8No ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans - NotesDocument10 pagesExcretion in Humans - NotesPranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Excretion in HumansDocument17 pages4.3 Excretion in HumanskaverinmohiteNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 4Document16 pagesPDF Document 4johnmazuba12No ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument15 pagesThe Excretory SystemHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument17 pagesExcretionMaria adeelNo ratings yet
- Excretory SyestemDocument13 pagesExcretory SyestemAnnaya RazaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument32 pagesExcretory SystemJeanie uyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - ExcretionDocument46 pagesChapter 11 - Excretionapi-372850875% (4)
- Bped 65 Urinary SystemDocument26 pagesBped 65 Urinary SystemDollie May Maestre-TejidorNo ratings yet
- Al Wadi International School Biology Grade 9 13. Excretion in Humans NotesDocument42 pagesAl Wadi International School Biology Grade 9 13. Excretion in Humans NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument11 pagesExcretory Systemapi-245979635No ratings yet
- THE Excretory SystemDocument24 pagesTHE Excretory SystemZain HaiderNo ratings yet
- 4.lessons 23-24, Excretory System, PP 453-459Document20 pages4.lessons 23-24, Excretory System, PP 453-459Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - ExcretionDocument51 pagesChapter 12 - ExcretionKareem DmourNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 Excretion in HumansDocument7 pagesCh-13 Excretion in Humansdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- Excretion NOTESDocument2 pagesExcretion NOTESabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotesDocument27 pagesUNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotescyumadripNo ratings yet
- Human Excretory SystemDocument51 pagesHuman Excretory SystemVinoj MnoNo ratings yet
- Overview of RENAL: Dr. Wilson Arthur Zein, M. BiomedDocument34 pagesOverview of RENAL: Dr. Wilson Arthur Zein, M. BiomedAnnisNo ratings yet
- Excretory System PresentationDocument13 pagesExcretory System Presentationcristobal melegritoNo ratings yet
- Excretory System PresentationDocument13 pagesExcretory System PresentationNelson DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Checkpoint Notes ExcretionDocument3 pagesCambridge Checkpoint Notes Excretionanimemaster2kNo ratings yet
- Complete ExcretionDocument61 pagesComplete Excretionethankhoo2007No ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument37 pagesExcretory SystemPatrick DeeNo ratings yet
- ExcretoryDocument31 pagesExcretoryJevin IndaNo ratings yet
- Revision ExcretionDocument24 pagesRevision Excretionjanling82No ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument14 pagesExcretionAuthor ClubNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument39 pagesExcretory SystemTajXNo ratings yet
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 11 Energy FlowDocument7 pages11 Energy FlowVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- 3 ReproductionDocument17 pages3 ReproductionVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- 2 Cells Chemicals and Processes of LifeDocument9 pages2 Cells Chemicals and Processes of LifeVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Questions PHYSICS CDocument20 pagesPast Paper Questions PHYSICS CVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- Water Treading in SwimmingDocument11 pagesWater Treading in SwimmingPavitra VitraNo ratings yet
- Atrial Systole: The End of DiastoleDocument9 pagesAtrial Systole: The End of DiastoleSophia MahboobNo ratings yet
- Neck Pain Questionnaire FormDocument1 pageNeck Pain Questionnaire FormSeptyan Dwi Witjaksana100% (1)
- E C I R P: Shoulder RehabilitationDocument7 pagesE C I R P: Shoulder RehabilitationMelisa Agustina TobarNo ratings yet
- ContinueDocument3 pagesContinueJúÑi ØrNo ratings yet
- 71170-Article Text-218870-1-10-20210401Document9 pages71170-Article Text-218870-1-10-20210401San LocardoNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Chapter 1 Form 5Document3 pagesTopical Test Chapter 1 Form 5Rubi AnnNo ratings yet
- Cultivo de CianobacteriasDocument35 pagesCultivo de CianobacteriasArmando Chiclla SalazarNo ratings yet
- Basics of Cardiopulmonary Bypass.10Document8 pagesBasics of Cardiopulmonary Bypass.10Chaaru ShaarmaNo ratings yet
- Animal Respiratory SystemDocument80 pagesAnimal Respiratory SystemPutri Maharani75% (8)
- Applications of Calcium and Its Supplement Derived From Marine OrganismsDocument8 pagesApplications of Calcium and Its Supplement Derived From Marine OrganismsDewi SariNo ratings yet
- Blalock Taussig Thomas PDFDocument11 pagesBlalock Taussig Thomas PDFFer45No ratings yet
- Micro B - Ascending Tracts SummaryDocument1 pageMicro B - Ascending Tracts SummaryMitchu Tan100% (1)
- Chapter 10 BloodDocument3 pagesChapter 10 BloodinitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- DR. MARK HYMAN - Simplifying Weight Loss.Document6 pagesDR. MARK HYMAN - Simplifying Weight Loss.Mihaela Cristina MunteanuNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast PanabangiDocument7 pagesChloroplast PanabangiPatrick Rómulo CabilingNo ratings yet
- Action Observation and Execution Network: An Extended ViewDocument16 pagesAction Observation and Execution Network: An Extended ViewAndreia SilvaNo ratings yet
- LifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionDocument173 pagesLifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionSamanta Arijit100% (1)
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 48Document7 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 48sarasjunkNo ratings yet
- Nat MurDocument19 pagesNat MurSun BNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Muscle AttachmentDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Muscle Attachmenterwilli5No ratings yet
- IV ComputationDocument11 pagesIV ComputationSheniel VariacionNo ratings yet
- Virtual Microscopy Histology Manual: University of Alabama at Birmingham School of MedicineDocument6 pagesVirtual Microscopy Histology Manual: University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Medicinelucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- Cell & Tissue StructureDocument19 pagesCell & Tissue StructureBrintha Kani KumarNo ratings yet
- Unlock Brains Full PotentialDocument3 pagesUnlock Brains Full PotentialMiguel Antonio Platon Torres100% (1)
- Faecal Incontinence in Adults - ReviewDocument12 pagesFaecal Incontinence in Adults - Reviewi can always make u smile :DNo ratings yet