Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sounds
Sounds
Uploaded by
mimii irene0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views24 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views24 pagesSounds
Sounds
Uploaded by
mimii ireneCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 24
SOUND
Characteristics, Transmission and Propagation of Sound
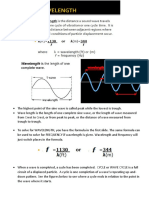
WAVELENGTH
The wavelength of a sound wave refers to the distance
between two consecutive peaks or troughs of the wave.
It is measured in meters (m).
The longer the wavelength, the lower the frequency and the
lower the pitch.
For example, a bass guitar has longer wavelengths and
lower frequencies than a violin.
FREQUENCY
The frequency of a sound wave refers to the number of
vibrations that occur per second.
It is measured in Hertz (Hz).
The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch of the sound.
For example, a high-pitched whistle has a higher frequency
than a low-pitched bass drum.
AMPLITUDE
The amplitude of a sound wave refers to the magnitude or
strength of the wave.
It is measured in decibels (dB).
The greater the amplitude, the louder the sound.
For example, a jet engine has a greater amplitude and is
louder than a whisper.
SPEED:
The speed of sound refers to how fast the sound wave
travels through a medium.
It is measured in meters per second (m/s).
The speed of sound is affected by the temperature, density,
and elasticity of the medium through which it travels.
You might also like
- O Level NotesDocument7 pagesO Level NotesDhanBahadur100% (1)
- Building Services Iii - Sar 1302: Unit - 1Document97 pagesBuilding Services Iii - Sar 1302: Unit - 1Mahamud MusaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I (INTRODUTION)Document30 pagesUnit-I (INTRODUTION)GokulNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Acoustics Bu 03Document56 pagesWeek 1 Acoustics Bu 03Omar Torres ViolaNo ratings yet
- 18 Arc 74 AcousticsDocument25 pages18 Arc 74 Acousticssuryaa ksNo ratings yet
- Propagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Document4 pagesPropagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Piyush RoyNo ratings yet
- Sound 8Document10 pagesSound 8Shanto NiceschoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SOUNDDocument18 pagesChapter 3 SOUNDGaliasis Akoualefo nkefackNo ratings yet
- SOUND - NotesDocument3 pagesSOUND - Notesnandana jammulaNo ratings yet
- Amplitude: Loudness Refers To How Loud or Soft A Sound Seems To A ListenerDocument2 pagesAmplitude: Loudness Refers To How Loud or Soft A Sound Seems To A ListenerTatadarz Auxtero LagriaNo ratings yet
- Wave 7Document2 pagesWave 7Ma. Bernadette EballeNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Presentation SoundDocument33 pagesTopic 7 Presentation SoundPRBMSK50622 Mathilda Durie Anak RowneyNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument1 pageSoundShōyōHinataNo ratings yet
- General NotesDocument19 pagesGeneral NotesAhmedBIowarNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of A SoundDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties of A Soundsergeyka2004No ratings yet
- Measuring Waves 2 3Document19 pagesMeasuring Waves 2 3api-263612989No ratings yet
- Acoustics PDFDocument28 pagesAcoustics PDFCharles Harvey Cabrezos DaabayNo ratings yet
- 01 The Basics of SoundDocument2 pages01 The Basics of SoundFrançois HarewoodNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument28 pagesSoundKunal100% (1)
- SoundDocument25 pagesSoundCookieNo ratings yet
- 2312221519049139Document4 pages2312221519049139Shriya SNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument38 pagesUnit 2 PDFyashaswiniNo ratings yet
- AccousticsDocument62 pagesAccousticsSahil MistryNo ratings yet
- Introduction - AcousticDocument22 pagesIntroduction - Acousticpatel shivanginiNo ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument2 pagesSOUNDROHIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- SOUND Verka (B) AmritsarDocument19 pagesSOUND Verka (B) Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Sound WavesDocument44 pagesLesson 7 Sound WaveskhiananoribsNo ratings yet
- MODULE Class VIII C07Document15 pagesMODULE Class VIII C07gpfphysicsNo ratings yet
- Sound EnergyDocument24 pagesSound EnergyJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Topic 36 Waves - Introduction To Sound WavesDocument8 pagesTopic 36 Waves - Introduction To Sound WavesMarcus GohNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Behaviour of Sound: Submitted by Chitra Rana 5 TH SemDocument18 pagesAssignment 1 Behaviour of Sound: Submitted by Chitra Rana 5 TH SemPrateekNo ratings yet
- BU3 Acoustics PDFDocument257 pagesBU3 Acoustics PDFeyo rimasNo ratings yet
- What Is Sound???Document24 pagesWhat Is Sound???Abhi VallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document38 pagesUnit 2saahasitha 14No ratings yet
- Sound Amplitude PitchDocument19 pagesSound Amplitude PitchVase VaseskiNo ratings yet
- Acoustics - Module 1Document40 pagesAcoustics - Module 1Ashna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument5 pagesSound WavesSun Hee ParkNo ratings yet
- Sound MCQDocument8 pagesSound MCQAdesh Partap SinghNo ratings yet
- Sound: Norazura BT Mizal AzzmiDocument58 pagesSound: Norazura BT Mizal AzzmiWan Mohd SayutiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Architectural AcousticsDocument49 pagesFundamentals of Architectural AcousticsRukminiPriyanka33% (3)
- Techniques de La Prise de Son Et Du Mixage I - Chapitre-1Document4 pagesTechniques de La Prise de Son Et Du Mixage I - Chapitre-1Samah KanaanNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument2 pagesSoundDe Belen, Anjanette ZNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Sound and Human EarDocument26 pagesAcoustic Sound and Human EarEmmanuel EhuronNo ratings yet
- Pitch and FrequencyDocument14 pagesPitch and FrequencyHelmiyanto IsmoyoNo ratings yet
- Section 1 PDFDocument2 pagesSection 1 PDFCallumNo ratings yet
- 2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 1 Lecture 1 Waves and Sound Waves (S)Document34 pages2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 1 Lecture 1 Waves and Sound Waves (S)Sophia Manila SillaNo ratings yet
- NOTES-Speed of Sound - F5Document2 pagesNOTES-Speed of Sound - F5Anonymous OZtBA0FzNo ratings yet
- 1 - SoundDocument26 pages1 - SoundOSHIN BALASINGHNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms Sound TheoryDocument28 pagesDefinition of Terms Sound TheoryAnonymous 5kOS4tNo ratings yet
- Sound and Its CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesSound and Its CharacteristicsGian Louise BarolaNo ratings yet
- Types of Waves, Production and Propagation of Sound WavesDocument7 pagesTypes of Waves, Production and Propagation of Sound WavesDorego TaofeeqNo ratings yet
- 15 Arc 7.3 Mod 1-1Document9 pages15 Arc 7.3 Mod 1-1Prakruthi PrashanthNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledErika ParambitaNo ratings yet
- q1 Lesson4 Sound WavesDocument16 pagesq1 Lesson4 Sound WavesVincent AbucayNo ratings yet
- A Wave Can Be Defined As Follows: A Wave Is A Transfer of Energy From One Point To Another Without Transfer of Material Between The Two PointsDocument4 pagesA Wave Can Be Defined As Follows: A Wave Is A Transfer of Energy From One Point To Another Without Transfer of Material Between The Two PointsCarlos CruzNo ratings yet
- BuildabandDocument7 pagesBuildabandapi-266657445No ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument15 pagesChapter TwoMilat KifluNo ratings yet
- Physics PPT SoundDocument20 pagesPhysics PPT SoundJoshua Chacko PonnachanNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet