Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gay Lussacs Law
Gay Lussacs Law
Uploaded by
chlaire70 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesGay Lussacs Law
Gay Lussacs Law
Uploaded by
chlaire7Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
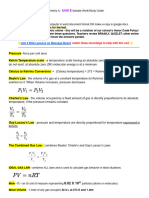
Gay-Lussac’s Law
• There is a direct relationship between the
temperature and pressure of a gas (if one increases
so does the other)
• If volume is held constant:
• P1 = P2 Temperatures must be
T1 T 2 in Kelvin!
KMT – increasing the temperature gets the particles
moving faster causing an increase in the number and
energy involved in collisions; thus an increase in
pressure
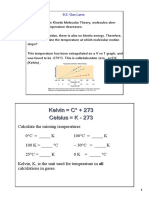
Example
• A gas exerts 1.2 atm of pressure. If the
temperature is raised from 25oC to 100oC, find
the new pressure.
P1 = P2
P1 = 1.2atm T1 T 2
T1 = 298K
? 1.2atm = P
P2 =
373K 298K 373K
T2 =
P = 1.5 atm
A fixed volume of gas exerts a pressure of 1.00
atm at a temperature of 25ºC. What is the
pressure of the gas when it is heated to 100ºC?
A.) 0.250 atm P=P
T T
B.) 1.25 atm
C.) 2.50 atm 1atm = P
D.) 4.00 atm 298K 373K
Which will always decrease the volume of a
sample of methane gas which occupies a volume
of 2.4 L at 25 °C?
A.) An increase in pressure and an increase in
temperature
B.) A decrease in pressure and a decrease in
temperature
C.) An increase in pressure and a decrease in
temperature
D.) A decrease in pressure and an increase in
temperature
Try To Explain This!
The water vapor is removed when cooling
causing a decrease in pressure inside the can.
The internal pressure is no longer able to resist
the atmospheric pressure, causing a collapse.
You might also like
- Mixed Gas Law Worksheet AnswerDocument4 pagesMixed Gas Law Worksheet Answeryiwuwi chiduNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws 2Document33 pagesGas Laws 2Iris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument35 pagesGas Lawsseven.erindejesusNo ratings yet
- The Gas LawsDocument110 pagesThe Gas Lawsapi-266061131No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Gas Laws PPT 2017 GoodDocument34 pagesChapter 14 Gas Laws PPT 2017 GoodBlist ers100% (2)
- Properties of Gases: Rapidly and Collide With Each Other OftenDocument12 pagesProperties of Gases: Rapidly and Collide With Each Other OftenjohnloopsNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument39 pagesGASESKarl Oliver Catabay Ricardo100% (1)
- Gas LawsDocument7 pagesGas LawsRocky vitucciNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument13 pagesChemical ReactionsAprilyn LaribaNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument7 pagesGas Lawsapi-258903855No ratings yet
- Gay Lussac's LawDocument15 pagesGay Lussac's LawAngelyn BarzanaNo ratings yet
- Module 12 - Lesson - 1 - The+Gas+LawsDocument23 pagesModule 12 - Lesson - 1 - The+Gas+LawsMihadNo ratings yet
- 4-3 Physics WK 3 Combined Gas LawDocument3 pages4-3 Physics WK 3 Combined Gas Lawlaisha chanNo ratings yet
- CH 11 GasesDocument67 pagesCH 11 Gasesman supermanNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument55 pagesGASESja_QuinineNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in Science April 8 2024Document1 pageWorksheet in Science April 8 2024Xan Dyre AcoyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in Science April 8 2024Document1 pageWorksheet in Science April 8 2024nataneedelapazNo ratings yet
- Gay Lussac's Law 12 3Document9 pagesGay Lussac's Law 12 3FFF100% (2)
- Unit 5 Study Guide - Sample WorkDocument3 pagesUnit 5 Study Guide - Sample WorkSarinagillNo ratings yet
- GASESSDocument10 pagesGASESSAndrea Martinez ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties and Laws NotesDocument4 pagesGas Properties and Laws NotesAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Document47 pagesTopic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Joshua LaBordeNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Lesson 1 and 2)Document10 pagesModule 3 (Lesson 1 and 2)rocky.mercado2No ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document44 pagesChapter 14Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument26 pagesGASESMaricar SantaceraNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular Theory: General Chemistry 1 Reviewer: 2nd QuarterDocument15 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular Theory: General Chemistry 1 Reviewer: 2nd QuarterJerome jeromeNo ratings yet
- GAS LawDocument50 pagesGAS LawJohn Cailen Barceñas II100% (1)
- Gas Laws 2Document12 pagesGas Laws 2Niel CerezaNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument71 pagesGas LawsIan DaveNo ratings yet
- 10_1143_gaslawsDocument62 pages10_1143_gaslawsMikaela LopezNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gases: Charles' LawDocument20 pagesIdeal Gases: Charles' LawJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- Gas Law: Name: Submitted ToDocument12 pagesGas Law: Name: Submitted ToALLYSA ZYRRE CALIZONo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument18 pagesChemistrywildlife quizNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Differeng Laws of GasesDocument7 pagesChemistry-Differeng Laws of GasesMayette TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument27 pagesGas LawsChese Ann PepinoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Gas Laws This Includes Answer in The Activity SheetDocument7 pagesScience 10 Gas Laws This Includes Answer in The Activity Sheetali tukuranNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Grade 10 Gas LawDocument6 pagesActivity Sheet Grade 10 Gas LawMerlyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q4 Module-2 Week-2Document5 pagesScience-10 Q4 Module-2 Week-2Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Montessori de San Ildefonso, Inc.: Learning KitDocument6 pagesMontessori de San Ildefonso, Inc.: Learning KitAliah Jashel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gases: University of Zakho Collage of Education General Science DepartmentDocument16 pagesProperties of Gases: University of Zakho Collage of Education General Science DepartmentNihad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Gas Law Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesGas Law Lecture NotesHazel Jane JaponNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument66 pagesThermal PhysicsguiNo ratings yet
- Gas Law ProblemsDocument8 pagesGas Law ProblemsHasib Islam JihanNo ratings yet
- 5.3 ChemDocument20 pages5.3 ChemJohnniño Mediran100% (2)
- Intro To Gases and Gas LawsDocument49 pagesIntro To Gases and Gas LawsLianne Grace ParreñasNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws - Problem ExercisesDocument7 pagesGas Laws - Problem Exercisesptyginol4255No ratings yet
- Gay-Lussac's Law: The Third Gas LawDocument11 pagesGay-Lussac's Law: The Third Gas LawJane SalomonNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Anna Marie Roja Rembrant Oniot James Peres Stephen Panadero Annie Oberio Iv-EmeraldDocument52 pagesGroup 5 Anna Marie Roja Rembrant Oniot James Peres Stephen Panadero Annie Oberio Iv-EmeraldDexter EnthusiastsNo ratings yet
- Gases and Gas LawsDocument49 pagesGases and Gas LawsArianne LaruscainNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Volume and Pressure: Temperature Must Be Expressed On The Absolute Temperature or Kelvin ScaleDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law: Volume and Pressure: Temperature Must Be Expressed On The Absolute Temperature or Kelvin ScaleChris Heydenrych100% (1)
- Boyle's Law Charles' Law: Pressure CalculationDocument3 pagesBoyle's Law Charles' Law: Pressure CalculationJensen Ryan LimNo ratings yet
- Section 2Document38 pagesSection 2fabrice ondamaNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument22 pagesGas LawsMichael DianaNo ratings yet
- Thegaslawscomplete 120227061412 Phpapp01Document51 pagesThegaslawscomplete 120227061412 Phpapp01Bustami Muhammad Sidik100% (1)
- Unit 6 Review Sheet KEY - Gas LawsDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Review Sheet KEY - Gas LawsKenna PlayzNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument19 pagesIdeal GasesTheLeaderDimitriosNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument41 pagesGas LawsGrey TapesNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)