Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Forests 1
Forests 1
Uploaded by
Raahim Usmani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views25 pagesOriginal Title
forests-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views25 pagesForests 1
Forests 1
Uploaded by
Raahim UsmaniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 25
Forests: Importance
Productive Forests: Natural, high tree density,
close canopy, high commercial value, timber is
extracted from them.
Protection Forests: planted along roads, in parks
and along railway lines, protect soil from erosion,
keep environment pleasant by regulating
temperature.
Importance
Forests check pollution, prevent soil
erosion, intercept rainfall, reduce flood risks.
Decomposition of leaves form humus
(natural fertilizers) that keeps soil fertile.
Provide commercial use for various
industries eg paper, timber etc.
Help in promotion of tourism through scenic
beauty.
Distributed according to their altitude.
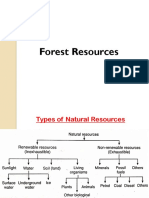
Types of forests
Alpine Forest
Coniferous Forest
Tropical Thorn Forest
Sub-Tropical Scrub Forest
Riverain or Bela Forest
Mangrove Forest
Irrigated Forest
Alpine
Alpine
Coniferous Forest
Coniferous Forest
Tropical Thorn Forest
Tropical Thorn Forest
Sub-Tropical Scrub Forest
Sub-Tropical Scrub Forest
Riverain or Bela Forest
Riverain or Bela Forest
Mangrove Forests
Mangrove Forests
Mangrove Forests
Irrigated Forests
Irrigated Forests
Advantages and disadvantages of
Irrigated Plantations
Advantages:
Source of timber
Leaves provide food for animals
Leaf fall; humus formation
Transpiration
Provide shade or shelter, protect agriculture.
Release oxygen and absorb carbon dioxide
Scenic beauty
Control run off and soil erosion, waterlogging
Provide employment
Disadvantages
High initial investment, no short term
economic benefits.
Maintenance ; expensive.
Extra burden on limited water supply.
Loss of lands for settlements, industries and
transport.
Difficult to monitor illegal cutting of trees.
Forest fire can lead to environmental
damage.
Diterminents of forests
Altitude
Aridity
Ratio of precipitation
Deltas ; alluvium deposit encourages
mangrove vegetation
Edaphic factor (type of soil)
Deforestation
Causes:
Mining activities.
Infrastructure; dams, and barrages to meet
the need of growing population lead to
forest clearing.
Urbanization
Transportation ; construction of roads
Industrial and domestic use.
Used as a fuel in underdeveloped areas
Overgrazing
Effects of deforestation
Soil erosion, land sliding.
Floods
Global warming
Smog
Increase silt in reservoirs of the dams
Increase in temperature
Loss of habitat
Loss of fodder
Afforestation
Afforestation is the process of introducing
trees and tree seedlings to an area that has
previously not been forested. Afforestation
can be done through tree planting and
seeding, naturally or artificially.
Projects consists of
Selection of areas to be afforested
Management of plantations
Development of ways of using forest
products.
Sustainability of forestry
We should manage the forest resources
in such a way as to ensure that we will be
able to obtain the things that we want
from the forests on regular basis while
conserving the natural environment.
You might also like
- Forests Day 1Document27 pagesForests Day 1Ayo TeoNo ratings yet
- ForestsDocument25 pagesForestsahmadirfan021094No ratings yet
- Forests NotesDocument14 pagesForests Notesalishba mohsinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ForestDocument3 pagesUnit 4 Forestm.furqanullahNo ratings yet
- Mity Niversity Harkhand: Subject: Environmental ScienceDocument36 pagesMity Niversity Harkhand: Subject: Environmental ScienceRakeshagentNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument25 pagesNatural Resourcessurveys4yougovNo ratings yet
- Rangelands: Overgrazing Deforestation DesertificationDocument35 pagesRangelands: Overgrazing Deforestation DesertificationNoah AusejoNo ratings yet
- ForestDocument20 pagesForestJaveria AfzaalNo ratings yet
- 01 ForestDocument36 pages01 Forestrehan.amd.khanNo ratings yet
- Forest by ADIL DURRANIDocument12 pagesForest by ADIL DURRANIADIL DURRANINo ratings yet
- Forestsofpakistan 180401124356Document20 pagesForestsofpakistan 180401124356satayishNo ratings yet
- What Are Forests and Its Types ?: Presented by Saqib Abdul Jabbar Saqib Javed Advisor: Sir Iazaz Ahmed BukhariDocument42 pagesWhat Are Forests and Its Types ?: Presented by Saqib Abdul Jabbar Saqib Javed Advisor: Sir Iazaz Ahmed Bukharishahzaibrasool31No ratings yet
- FOREST in PakistanDocument29 pagesFOREST in Pakistanrussia russiaNo ratings yet
- Battle For The Biosphere RevisionDocument15 pagesBattle For The Biosphere RevisionMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesDocument114 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesPatricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Conservation Protecting Our Plant ResourcesDocument33 pagesTopic 10 Conservation Protecting Our Plant ResourcesChuan Ung SiiNo ratings yet
- Forest ResourceDocument26 pagesForest Resourceswainananta336No ratings yet
- Program Persediaan Ijazah Sarjana Muda Perguruan (Ppismp) Ambilan Julai 2009Document16 pagesProgram Persediaan Ijazah Sarjana Muda Perguruan (Ppismp) Ambilan Julai 2009Han AmranNo ratings yet
- Background of The StudyDocument2 pagesBackground of The StudyAeron AlburoNo ratings yet
- ES Unit 2Document13 pagesES Unit 2InstagramNo ratings yet
- Forests: Deforestation and DesertificationDocument15 pagesForests: Deforestation and DesertificationFaiza NoorNo ratings yet
- What Does Deforestation MeanDocument6 pagesWhat Does Deforestation MeanPankaj hedaooNo ratings yet
- Geography ForestDocument4 pagesGeography ForestAzka GilaniNo ratings yet
- Deforest RationDocument29 pagesDeforest RationSaif MohammadNo ratings yet
- GCSE GEO 3 - Making Geographical Decisions - Forests Under ThreatDocument6 pagesGCSE GEO 3 - Making Geographical Decisions - Forests Under ThreatRomani PathakNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument18 pagesDeforestationYzel DuroyNo ratings yet
- Forest and WaterDocument32 pagesForest and WaterAllen Rey TicarNo ratings yet
- Harmful Effects of DeforestationDocument2 pagesHarmful Effects of Deforestationgenster828282No ratings yet
- Forests Extension Information SheetDocument2 pagesForests Extension Information SheetMuskanNo ratings yet
- ForestsDocument7 pagesForestsHooria AmjadNo ratings yet
- FORESTRYDocument30 pagesFORESTRYkimeujackson92No ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument6 pagesDeforestationJhonsenn Escosio RudioNo ratings yet
- Rangelands: 1. GrasslandsDocument10 pagesRangelands: 1. GrasslandsNoah AusejoNo ratings yet
- Forest Ecosystem PDFDocument51 pagesForest Ecosystem PDFs41401718No ratings yet
- Forest Resources: - Amiya NaushadDocument9 pagesForest Resources: - Amiya NaushadOppo A83No ratings yet
- CHE110 Compatibility ModeDocument95 pagesCHE110 Compatibility ModeCool CupNo ratings yet
- Forestry Geo111Document6 pagesForestry Geo111Tiffany MurrayNo ratings yet
- Preserving and Protecting Woods by SlidesgoDocument17 pagesPreserving and Protecting Woods by Slidesgotq260904No ratings yet
- Icelin Glora - Commercial, Ecological and Aesthetic Benefits of ForestDocument4 pagesIcelin Glora - Commercial, Ecological and Aesthetic Benefits of ForestIcelin GloraNo ratings yet
- Deforestation Sub By:bryan Jasper D. Ruiz Sub To: Sir Jilbert Bong GumaruDocument8 pagesDeforestation Sub By:bryan Jasper D. Ruiz Sub To: Sir Jilbert Bong GumaruJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- FORESTRYDocument10 pagesFORESTRYkwambokasly21No ratings yet
- 'Tropical Rainforest: Conservation EffortsDocument2 pages'Tropical Rainforest: Conservation Effortsyohana yunusNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument85 pagesNatural Resourcesapi-2658989480% (5)
- Module 4 Natural ResourcesDocument7 pagesModule 4 Natural ResourcesKarl angelo LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Geo - X - Handout 5-Natural Vegetation of IndiaDocument5 pagesGeo - X - Handout 5-Natural Vegetation of IndiaAdvait BajoriaNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument6 pagesNatural ResourcesMadhurGuptaNo ratings yet
- Deforestation Is The Permanent Destruction of Indigenous Forests and WoodlandsDocument3 pagesDeforestation Is The Permanent Destruction of Indigenous Forests and WoodlandsTara Idzni AshilaNo ratings yet
- Geography Project 9N Group BDocument8 pagesGeography Project 9N Group BAinna AliNo ratings yet
- Deforestation Causes, Effects, and Solutions: TOPIC: For The Month MAY 2019Document5 pagesDeforestation Causes, Effects, and Solutions: TOPIC: For The Month MAY 2019Marlon BongatoNo ratings yet
- Forest ResourcesDocument23 pagesForest ResourcesLevi LeviNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Natural ResourcesDocument52 pagesUnit 1-Natural ResourcesRidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Water Farming FlyerDocument2 pagesWater Farming FlyerwoodlandtrustNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Sciencelukay123No ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument8 pagesNatural Resourcessandhyarani beheraNo ratings yet
- Examples of Natural Resources-1Document4 pagesExamples of Natural Resources-1Nathan KemboNo ratings yet
- Deforestation: - Background ReadingDocument4 pagesDeforestation: - Background ReadingMinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science - PPTDocument41 pagesEnvironmental Science - PPTJM RoxasNo ratings yet
- Forest Conservation: Roque Helio InacioDocument6 pagesForest Conservation: Roque Helio InacioQuízio BaptistaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2BalaKrishna Batta100% (1)
- Infografía Simulacro de Incendios Ilustrado Rojo y AmarilloDocument1 pageInfografía Simulacro de Incendios Ilustrado Rojo y AmarilloDANIELA MICHELLE GUTIERREZ HIGUERANo ratings yet
- Pap 19 Port Louis Is FloodingDocument20 pagesPap 19 Port Louis Is Floodingdev2 Lol100% (1)
- OSC2 Abstracts BookDocument263 pagesOSC2 Abstracts BookSanjayAroraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Water Quality Para. - Cont.Document23 pagesChemical Water Quality Para. - Cont.Charan DeepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Nicole Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Infrastructure Coating Materials On Storm-Water Quality Review and Experimental StudyDocument12 pagesImpact of Infrastructure Coating Materials On Storm-Water Quality Review and Experimental StudyFairmont Ind Quality DivisionNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper.. Atmosphere (Composition, Structure & Temperature), Macalolot Krizia..FlemingDocument2 pagesReaction Paper.. Atmosphere (Composition, Structure & Temperature), Macalolot Krizia..FlemingBhebzkie Fernz Macszkie100% (1)
- Manitoba Flood Outlook Report - February 2023Document30 pagesManitoba Flood Outlook Report - February 2023ChrisDcaNo ratings yet
- Development of 8-Lane Vadodara - Mumbai ExpresswayDocument16 pagesDevelopment of 8-Lane Vadodara - Mumbai ExpresswayNaman JainNo ratings yet
- REFLECTION MAPPING UPSC PRELIMS 2023 FROM KBsIAS MAPPING NOTES 2023Document13 pagesREFLECTION MAPPING UPSC PRELIMS 2023 FROM KBsIAS MAPPING NOTES 2023Suraj GaneshNo ratings yet
- Environmental Sociology 1Document5 pagesEnvironmental Sociology 1Siva Ganga SivaNo ratings yet
- Joint Water Purification Pilot Program Pilot Study of Advanced Treatment Processes To Recycle JWPCP Secondary EffluentDocument383 pagesJoint Water Purification Pilot Program Pilot Study of Advanced Treatment Processes To Recycle JWPCP Secondary EffluentNguyễn ThảoNo ratings yet
- BiorockDocument8 pagesBiorockRahayu SuranNo ratings yet
- 6 Wastewater Treatment Systems Week 6Document46 pages6 Wastewater Treatment Systems Week 6Divyashini MohanNo ratings yet
- Meaning Nature, Scope and Imporatance of StudyDocument9 pagesMeaning Nature, Scope and Imporatance of Studyshrey narulaNo ratings yet
- Ecology and Ecosystem - En.arDocument8 pagesEcology and Ecosystem - En.arMohammad ShormanNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument48 pagesFinalmanish jatNo ratings yet
- Advance Waste Water TreatmentDocument4 pagesAdvance Waste Water TreatmentEr Govind Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam (NSCI 111 - People & The Earth's Ecosystem)Document10 pagesMidterm Exam (NSCI 111 - People & The Earth's Ecosystem)Jov Soyom100% (1)
- The Rio Declaration On Environment and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesThe Rio Declaration On Environment and Developmentanshul0714No ratings yet
- Galle City Lowcarbon PresentationDocument23 pagesGalle City Lowcarbon PresentationPradeep EhanNo ratings yet
- Flood Forecasting Model Using Empirical Method For A Small Catchment AreaDocument8 pagesFlood Forecasting Model Using Empirical Method For A Small Catchment AreaSamuel HariandyaNo ratings yet
- ENS43 Chapter5 WaterManagementandConservationDocument67 pagesENS43 Chapter5 WaterManagementandConservationcdo LJORNo ratings yet
- Water Conservation in KeralaDocument10 pagesWater Conservation in KeralaVivek N ShajiNo ratings yet
- 3150 FM Bwew0083Document2 pages3150 FM Bwew0083Bishop Ojonuguwa AmehNo ratings yet
- On DesertificationDocument18 pagesOn DesertificationParthNo ratings yet
- Aquafix, Inc. Winter 2009 NewsletterDocument2 pagesAquafix, Inc. Winter 2009 NewsletterKevin Ripp, "The Bug Man"No ratings yet
- Manpower Forecast 21033-21034Document2 pagesManpower Forecast 21033-21034sabih344No ratings yet
- MIME Drinking Water Quality Standards 2004 enDocument20 pagesMIME Drinking Water Quality Standards 2004 enKang arechNo ratings yet
- ESS Model IADocument3 pagesESS Model IAAnonymous DrSwwoNo ratings yet