Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Session 1 4 Imm
Session 1 4 Imm
Uploaded by
badboy99.tkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Session 1 4 Imm
Session 1 4 Imm
Uploaded by
badboy99.tkCopyright:
Available Formats
International
INTER
NATIO
Marketing
NAL
MARK
Management Dr
ETING
Gautam
MANA
Dutta
GEME
BE, MBA,
NT
PhD (IIT)
Gautam Dutta
BE, MBA, PhD (IIT)
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Objective of the course
Gain perspectives of international marketing; how is it
different from domestic marketing?
Familiarity with the environmental issues of marketing
beyond national boundaries.
Understand the entry modes for international markets
Expand knowledge about global marketing information
system and research
Analyse international marketing mix decisions
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Session Plan:
15 Sessions of 120 Minutes Each
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Framework
The Concept of International Marketing (1)
The International Marketing Environment(2)
Assessing Opportunity & Selection of Markets (2)
Global Market Entry Strategy (3)
Product & Branding Decision for International Markets (2)
Pricing Decisions for International Markets (1)
International Distribution Decisions (1)
Promotional Decisions for International Markets(1)
Research In International Marketing(1)
International Marketing: Strategic Aspects (1)
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Text Book : Global Marketing Management.
Svend Hollensen
Selected Reading on International Marketing
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Selected Readings on International
Marketing
Copyright Gautam Dutta
READINGS
MODULE 1:The Concept of International Marketing
• Globalization of Markets. Theodore Levitt
• Managing in a borderless world by Kenichi Ohmae
MODULE 2 & 3The International Marketing Environment
• An integrative framework for cross cultural consumer behaviour by Luna and
Gupta
MODULE 4 & 5 : Assessing Opportunity & Selection of Markets
• Market selection for international expansion by Sema, Eckman and Hyllegard
• Guide line for export market research by Cavusgil
MODULE 6 & 7 : Internationalization Theories & Entry Choices
• Selecting overseas markets and entry modes: two decision processes or one?
By Koch
• The mechanism of internationalization by Johansson and Valne
• Theory of internationalization and their impact of market entry by Jeryl
Whitelock
• Theory Development within International Market Entry Mode - An Assessment
by Flemming Cumberland
• An Eclectic Theory of the Choice of International Entry Mode Author(s): Charles
W. L. Hill, Peter Hwang, W. Chan Kim
Copyright Gautam Dutta
READINGS
MODULE 8 & 9: Product and Branding Decision for International Markets
• International product positioning by Johansson and Thorelli
• The International Dimension of Branding: Strategic Considerations and Decisions
MODULE 10: Pricing Decisions for International Markets
• International pricing decisions: A diagnostic approach by Samli
• The importance of price in international business development
MODULE 11: International Distribution Decisions
• Distribution in Japan; problem and changes by Michael R. Czinkota
• International manufacturing and location designs: balancing configuration and co ordination
aspects.
MODULE 12: Promotional Decisions for International Markets
1. Standardization versus adaptation of international advertising strategies: Towards a framework
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Evaluation
• Quiz (Two) (at the end of 7th and 14th module) 15%
• Case Presentation and discussion 15%
• Assignments 30%
• End term examination 40%
Copyright Gautam Dutta
GROUP WORKS
Case Analysis: 9 cases
Assignment: 9 (Each group will select one out of the list
on first come first serve basis )
Submission of assignment
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Submission of Assignments
Date:
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Elements of Marketing –
Customer Value
V = Benefit / Price
V = Value
B = Perceived Benefits – Perceived Costs
P = Price
Copyright Gautam Dutta
The Three Principles of Marketing
CUSTOMER VALUE
DIFFERENTIATION FOCUS
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Copyright Gautam Dutta
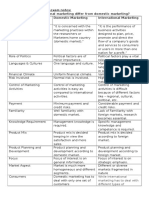
Marketing beyond national border
Company Domestic market Sales in foreign
market(%)
Nokia 99
Audi
68
Clarion , Japan 48
Apple 41
E bay 35
Papa John’s 1
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Motives
Proactive motive : Reactive motive:
• Profit and growth goals • Competitive pressure
• Managerial urge • Domestic market saturated
• Technology competence • Overproduction
• Foreign market • Extend sales of seasonal
opportunities product
• Economies of scale • Proximity to international
customer.
• Tax benefits
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Marketing internationally is continued
1. Greater purchasing power among peoples of the world
2 Technological advances bringing the world “closer together” such
as satellite TV, wide reaching print media, fax, phone systems,
the Internet, faster and cheaper modes of travel, etc.
3. Increasing commonalities of wants, needs, preferences
4.Higher fixed costs of doing business, thus requiring large
customer bases to achieve economies of scale and scope
5.Decrease of trade barriers and feelings of intense nationalism
6.Increasingly common and quality infrastructures and channels of
distribution
7.Regional trading areas with large internal markets
8.More uniform product standards
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Internationalization of marketing activities
basic marketing
multidomestic marketing
international marketing
global marketing
glocal marketing
Copyright Gautam Dutta
The Multinational Phase: World War II - 1970
Marketing were not very much developed
Due the sheer need of the people, products were
marketed.
The STP as tool came at the fag end of 1950. The 4P
of Macarthy came early in early 1960. Product
positioning in the perceptual map became popular
only in late 1960 onwards. From 1960-1970.
Multinational marketing was popular where products
and promotions have local adaptations and they
are produced in different countries of world under
the close observation and control of headquarters.
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Global Phase: From 1970
The global phase saw much more standardization of
product with much more integration of activities
across the countries of the world.
Robert Buzzell’s (1968) article “Can You Standardize
Multinational Marketing ” Theodor Levit’s (1983) “The
Globalization of Market” arguing that markets across
the world are growing more homogenous set the
pace.
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Marketing characteristics Product pricing distribution Advt,
design promotion
Physical environment
packaging
Stage of eco dev
Cultural factor
Industry condition
Stages of PLC/competition
Marketing institutions
Legal restriction
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Global Marketing ?
Local & domestic International marketing & Multi national
marketing strive to marketing strive to maximize marketing
maximize marketing activities in terms of
activities exclusively in primarily Secondarily
terms of
Adaptation to domestic Standardization across Adaptation to country
situation countries specific need
Tailoring to the need Homogenization Tailoring to the need
Difference within the Similarity across the Difference within
country countries each country
Concentration within Activity concentration Activity Diffusion
national territory
Dependence Dependence on home Independence of
country home country
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Global Marketing ?
Global marketing strive to Glocal marketing strive to optimize
maximize marketing activities marketing activities with balance and
exclusively in terms of harmony in terms of
Standardization across Standardization vs Adaptation to
countries country specific need
Homogenization Homogenization vs Tailoring to the
need
Similarity across the countries Similarity vs Difference across the
countries
Activity diffusion Activity concentration vs Activity
Diffusion
Dependence on countries of Dependence on home country vs
specific interest Independence of home country
Synchronization Synchronization vs Flexibility
Integration Integration vs Separation
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Existence of Multi-domestic market.
Japanese customers are fastidious and examine
products carefully before purchase whereas
Americans are impulsive and more or less responds
to in store promotion techniques.
Japanese prefers rice and dried fish in breakfast but the
European prefers ham, cheese, coffee
Tea is the standard drink of Chinese dinner while low
alcohol content beer is common for the Swedish
dinner while drinking beer with food is a strange thing
for the French people.
Thin soled shoes are preferred by the stylish
Mediterranean people but thin soled shoed are not
liked by the Americans.
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Country borders are not important segment limit
Gaps in lifestyle ,tastes, behaviors are narrowing
across the globe
Business customers are increasingly having central
purchasing function.
As customers are traveling across countries and are
exposed to the best products, recognizing ability
of best products, brands, are increasing.
As per Prahalad and Hamel (corporate imagination
and expeditionary marketing, 1991, HBR) new
product lead and change preference. (Indian
breakfast are changing fast)
With increasing global communication and
affluences, many multi domestic product markets
are giving away to global products. Affluence lead
to a desire of variety.
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Global market participation Vs Marketing continuum
To have a global level of market participation requires
significant global market share, a reasonable balance
between the business’s geographic spread and the
market’s spread and presence in globally strategic
country markets.
High global market share is important but not the
sufficient for global market participation. a global
business need to have its geographic distribution of
revenues in reasonable balance with that of the
worldwide market.
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Marketing Program Standardization
Product design,
Product positioning,
Brand name,
Packaging,
Retail price,
Basic advertising message,
Creative expression,
Sales promotion,
Media allocation,
Role of sales force,
Management of sales force,
Role of middlemen,
Type of retail outlets,
Customer service
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Global Market Participation: Requirements?
Transferable business model
The model needs to be transferable in different countries
with more or less same effectiveness.
Business model need to change the customer behavior in
other countries.
The transferability makes the journey from country to
country easy or other wise business model that requires
adaptations finds globalization difficult (Model difficult to
export
E.g. Benetton Vs Marks & Spencer
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Leverageable competitive advantage
1. Customer market dominance
Xerox , Virgin group
2. Product/ service advantage
Minor Items:
Major Items:
:
3. Value Chain Advantage:
3M and American express
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Leverageable competitive advantage
Asset/Resources
Partner Advantage
Scale and scope advantage
World car industry. Most car companies use similar
engine and gear boxes across their entire product
ranges so that different model have similar engine
and gear boxes. This generates cost savings
Copyright Gautam Dutta
3. Participation in the lead countries
Position in the lead country is the surrogate for
excellence in quality, innovativeness.
Japan: consumer electronics
Germany: industrial control equipments
India : Computer software
Copyright Gautam Dutta
1. In general, standardization is more practical in markets that are
economically alike.
2 Standardization strategy is more effective if worldwide customers,
not countries, are the basis of identifying the segment(s) to serve .
3 The greater the similarity in the markets in terms of customer
behavior and lifestyle, the higher the degree of standardization.
4 The higher the cultural compatibility of the product across the host
countries, the greater the degree of standardization.
5. The greater the degree of similarity in a firm’s competitive positions
in different markets, the higher the degree of standardization
6 . Industrial and high technology products are more suitable for
standardization than consumer products,
Copyright Gautam Dutta
7. Standardization is more appropriate when the home market positioning
strategy is meaningful in the host market.
8. The greater the difference in physical, political, and legal environments
between home and host countries, the lower the degree of
standardization.
9 The more similar the marketing infrastructure in the home and host
countries, the higher the degree of standardization .
10 Companies in which key managers share a common world view, as
well as a common view of the critical tasks flowing from the
strategy, are more effective in implementing a standardization
strategy.
11. The greater the strategic consensus among parent- subsidiary
managers on key standardization issues, the more effective the
implementation of standardization strategy.
12 The greater the centralization of authority for setting policies and
allocating resources, the more effective the implementation of
standardization strategy
Copyright Gautam Dutta
HIGH
PHARMACEUTICALS
MICRO CHIPS
FORCES
MILITARY
AUTOMOBILE AIRCRAFT
BULK
CHEMICALS TELECOMMUNICATION
GLOBALISATION
EQUIPMENT
CIVIL TELECOMMUNICATION
AIRCRAFT SERVICES
PACKAGED FOODS
RETAIL BANKING
LOW FOOD RETAILING
LOW LOCALISATION FORCES HIGH
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Global Marketing : Controllability
Foreign environment
(uncontrollable)
Political/legal 1 Economic
forces forces
Domestic environment
(uncontrollable) 2
7
Competitive
Political/
structure Competitive
legal (controllable)
Cultural forces Forces
forces
Environmental
Product Price
uncontrollable
country market A
7 3
Channels of Promotion Environmental
distribution uncontrollable
6
country
market B
Geography Level of
and Economic climate Technology
Environmental
Infrastructure uncontrollable
4 country
5 market C
Structure of
distribution
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Organizational Orientation
EPRG Concept
Ethnocentric
Polycentric
Regiocentric
Geocentric
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Strategic Orientation: EPRG Schema
Generally, four distinctive approaches dominate strategic thinking:
1. Ethnocentric or Domestic Marketing Extension Concept:
Home country marketing practices will succeed elsewhere
without adaptation; however, international marketing is
viewed as secondary to domestic operations
2. Polycentric or Multi-Domestic Marketing Concept:
Opposite of ethnocentrism
Management of these firms place importance
on international operations as a source for profits
Management believes that each country is unique and
allows each to develop own marketing strategies locally
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Strategic Orientation: EPRG Schema
Generally, four distinctive approaches dominate strategic thinking:
3. Regiocentric:
Sees the world as one market and develops a standardized
marketing strategy for the entire world
4. Geocentric:
Regiocentric and Geocentric are synonymous with a Global
Marketing Orientation where a uniform, standardized
marketing strategy is used for several countries, countries in
a region, or the entire world
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Self Reference Criteria
Self Reference Criteria (SRC):
Represents viewing rest of the world from the
perspective of home market.
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Avoiding the Self Reference Criterion
To
To avoid
avoid the
the SRC,
SRC, the
the following
following steps
steps are
are suggested:
suggested:
1: Define the business problem or goal in home-country cultural traits,
habits, or norms
2: Define the business problem or goal in foreign-country cultural
traits, habits, or norms. Make no value judgments
3: Isolate the SRC Influence in the problem and examine it carefully to
see how it complicates the problem
4: Redefine the problem without the SRC influence and solve for the
optimum business goal situation.
Copyright Gautam Dutta
The FITA Global Trade Portal, is the
source for international import export trade leads, events,
and
links to 8,000 international trade (export import) related W
ebsites
. Premier International B2B Trade
Portal with the most complete
foreign trade, import and export
information!
(www,foreign trade.com)
•Premier International B2B Trade
Portal with the most complete
foreign trade, import and export
information!
The world leader in global business
intelligence
Copyright Gautam Dutta
www.mckinsey
quarterly
.com
www.ama.org
www.trbi.co.uk
Copyright Gautam Dutta
www.ictsd.org
development and environment concerns
in the context of international trade.
www.ala.org/library
www.worldbank.org/
data/databytopic/
class.xls
Copyright Gautam Dutta
Copyright Gautam Dutta
You might also like
- Session 5 - International MarketingDocument27 pagesSession 5 - International MarketingGaming Theater33% (3)
- ACC 411 - Excersice Chapter 1Document2 pagesACC 411 - Excersice Chapter 1AlDassakiNo ratings yet
- International Marketing C1Document24 pagesInternational Marketing C1phiht224022cNo ratings yet
- Introduction & EPRGDocument9 pagesIntroduction & EPRGsujeetleopardNo ratings yet
- UCV Session 1 Introduction IMDocument29 pagesUCV Session 1 Introduction IMLuis GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Updated) IM 1 - MergedDocument271 pages(Updated) IM 1 - MergedHưng Lê QuangNo ratings yet
- International Marketing EnvironmentDocument29 pagesInternational Marketing EnvironmentsujeetleopardNo ratings yet
- (Updated) IM 1Document20 pages(Updated) IM 1Như Lê QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- (Updated) IM 1Document18 pages(Updated) IM 1Hoanh Nguyễn Thị TuyếtNo ratings yet
- Global MarketingDocument30 pagesGlobal Marketingchandni kundelNo ratings yet
- International Marketing Handout 2022 P1Document48 pagesInternational Marketing Handout 2022 P1Ngân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Globalization ConceptsDocument79 pagesGlobalization ConceptsKhalid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter One IM ImprovedDocument86 pagesChapter One IM ImprovedDebeli BokaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii - Product and Branding Decisions Approaches To International PricingDocument210 pagesUnit Iii - Product and Branding Decisions Approaches To International PricingÀďhïšh HåŕïšhNo ratings yet
- International Marketing MBA IV SEMDocument129 pagesInternational Marketing MBA IV SEMAll In OneNo ratings yet
- Session 9 International Strategy New - 6377790b17033Document66 pagesSession 9 International Strategy New - 6377790b17033champika de alwisNo ratings yet
- International Marketing 01 - IntroductionDocument38 pagesInternational Marketing 01 - IntroductionhinaNo ratings yet
- International MarketingDocument59 pagesInternational MarketingRahul Singh100% (3)
- Introduction To International Business/MarketingDocument51 pagesIntroduction To International Business/MarketingSanthosh Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Presentation: Course Name: International Business Course Code: Ibs 363Document18 pagesWelcome To Our Presentation: Course Name: International Business Course Code: Ibs 363Smith DavidNo ratings yet
- Global Marketing Chapter 1-2Document36 pagesGlobal Marketing Chapter 1-2Iyus Darmawan PYNo ratings yet
- Bba Glo Mark.Document90 pagesBba Glo Mark.aniketpandey923No ratings yet
- International MarketingDocument20 pagesInternational Marketingزينب سيدNo ratings yet
- International Marketing Reading Materials For MBA 1 2020Document80 pagesInternational Marketing Reading Materials For MBA 1 2020Kasiira HatimuNo ratings yet
- Global MarketingDocument8 pagesGlobal MarketingShogunate TokugawaNo ratings yet
- International Marketing and Strategy MixDocument34 pagesInternational Marketing and Strategy Mixrastogi paragNo ratings yet
- International MarketingDocument23 pagesInternational MarketingDaniela TalmaciuNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Int. MktingDocument15 pagesBasic Concepts of Int. MktingAmit DuhanNo ratings yet
- Chap1-CateoraDocument24 pagesChap1-CateoraSabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Class 2 2023Document51 pagesClass 2 2023Sheyla MilenaNo ratings yet
- International Business NotesDocument101 pagesInternational Business NotesJAGRITI AWASTHINo ratings yet
- From Single Brand To Global Brand: Multi Local Global MaketingDocument11 pagesFrom Single Brand To Global Brand: Multi Local Global Maketingsanddy69No ratings yet
- 4 International Strategic Management ADocument111 pages4 International Strategic Management AKiran RimalNo ratings yet
- Ba Marketing Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesBa Marketing Lecture NotesErkin YavuzNo ratings yet
- Supriya Reflection PaperDocument7 pagesSupriya Reflection PaperSupriya sNo ratings yet
- Global Markets and FDIDocument21 pagesGlobal Markets and FDIReemaNo ratings yet
- Session 1 and 2 SlidesDocument61 pagesSession 1 and 2 SlidesNeluka vishuddhiNo ratings yet
- International MarketingDocument28 pagesInternational Marketingharsh kumarNo ratings yet
- IMM Scheme of ValuationDocument12 pagesIMM Scheme of Valuationpullarao kotaNo ratings yet
- Gemsun Marketing With Notes0Document6 pagesGemsun Marketing With Notes0Calixta SoberNo ratings yet
- Tata Case StudyDocument94 pagesTata Case StudyTarun_Jain_716100% (2)
- Introduction To International MarketingDocument53 pagesIntroduction To International MarketingshailuNo ratings yet
- IMT 01 - Understanding Intl MarketingDocument17 pagesIMT 01 - Understanding Intl MarketingNurul Afsar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 01 Present 1 en Nature of Marketing of FEA 41Document41 pages01 Present 1 en Nature of Marketing of FEA 41Olha KolomiietsNo ratings yet
- Chap1 (Debbie)Document21 pagesChap1 (Debbie)Maciel García FuentesNo ratings yet
- Global MarketingDocument23 pagesGlobal MarketingBgmi HackersNo ratings yet
- Use of Assets Challenges Global BusinessDocument6 pagesUse of Assets Challenges Global BusinessAby MathewNo ratings yet
- GlobalmarketingDocument15 pagesGlobalmarketingTeesha shahNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document8 pagesModule 1AdityaNo ratings yet
- IB 10 MarketingDocument44 pagesIB 10 Marketingquytt21407No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document36 pagesUnit 1Rishit KumarNo ratings yet
- IBM in MarketingDocument5 pagesIBM in MarketingCaroline MoforNo ratings yet
- Mba Fa Iv Sem 404 Major Decision of International MarketingDocument15 pagesMba Fa Iv Sem 404 Major Decision of International MarketingŠöbíķá RáņčíNo ratings yet
- Maneesh KR TarunDocument9 pagesManeesh KR Tarungoel_anshipu87No ratings yet
- Complete MBA NotesDocument9 pagesComplete MBA NotesSadaf NazneenNo ratings yet
- Mba GMDocument275 pagesMba GMAnuj ShroffNo ratings yet
- International Advertising: Definition of International MarketingDocument2 pagesInternational Advertising: Definition of International MarketingAfad KhanNo ratings yet
- Tata Research ReportDocument94 pagesTata Research ReportChandra Shekar CNo ratings yet
- Dealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)From EverandDealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)No ratings yet
- Nippon Paint (India) PVT - Ltd. BangaloreDocument31 pagesNippon Paint (India) PVT - Ltd. BangaloreP K Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Pembukuan BarangDocument478 pagesPembukuan BarangAKMAL THAYEBNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EnterprisesDocument14 pagesChapter 2 EnterprisesAngelita Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Sertifikat ISO 9001-2015 Sentralindo Teguh GemilangDocument2 pagesSertifikat ISO 9001-2015 Sentralindo Teguh GemilangChd LagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Za PrijevodDocument30 pagesChapter3 Za PrijevodKerim MuharembegovicNo ratings yet
- Shannon's Demon, Parrando's ParadoxDocument4 pagesShannon's Demon, Parrando's ParadoxjohnthomastNo ratings yet
- 0422云途物流海外企业画册 (TH)Document18 pages0422云途物流海外企业画册 (TH)Khanh TranNo ratings yet
- Customer Experience Programme: Net Promoter Score (NPS) Overview - Year To Date (September)Document3 pagesCustomer Experience Programme: Net Promoter Score (NPS) Overview - Year To Date (September)Usman FarooqNo ratings yet
- Revised Guidelines For The Entrepreneurial Profile Assignment - March 2021Document3 pagesRevised Guidelines For The Entrepreneurial Profile Assignment - March 2021NikhilNo ratings yet
- TENDER SOR MR 00b854Document137 pagesTENDER SOR MR 00b854Soumitra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Process Turtle - QMRDocument16 pagesProcess Turtle - QMRRavi javaliNo ratings yet
- Longenecker19e PPT Ch01 FinalDocument37 pagesLongenecker19e PPT Ch01 FinalAhmad Al-RusasiNo ratings yet
- The Cash Flow Curve in StartupsDocument2 pagesThe Cash Flow Curve in StartupsjomarioalaNo ratings yet
- Apply 5s ProcedureDocument35 pagesApply 5s ProcedureBiniam Hunegnaw BitewNo ratings yet
- 1876119754bst Sure Shot QuestionsDocument63 pages1876119754bst Sure Shot QuestionsMaxNo ratings yet
- The Interrelationship Between Culture, Capital Structure, and Performance: Evidence From European RetailersDocument7 pagesThe Interrelationship Between Culture, Capital Structure, and Performance: Evidence From European RetailersNgọc Minh PhúNo ratings yet
- F2 - Mock - QDocument14 pagesF2 - Mock - Qjekiyas228No ratings yet
- Review About Kpi & Okr, Change Management, and Mece Principles Management Trainee 2023Document3 pagesReview About Kpi & Okr, Change Management, and Mece Principles Management Trainee 2023Owing 28No ratings yet
- DAFZ Auditors List - 24 03 22Document4 pagesDAFZ Auditors List - 24 03 22TehseenNo ratings yet
- WVSU QP 01 F06 Risk Registry Sheet Blank DocumentDocument2 pagesWVSU QP 01 F06 Risk Registry Sheet Blank DocumentMAE ANGELESNo ratings yet
- 4 Ways Cloud ERP Can Boost Your Bottom LineDocument2 pages4 Ways Cloud ERP Can Boost Your Bottom LineDexNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument29 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Product Life Cycle ManagementSaravanan SaroNo ratings yet
- The Stakeholder Approach To Business, Society and EthicsDocument32 pagesThe Stakeholder Approach To Business, Society and EthicsKY KooNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Procurement ManagementDocument41 pagesModule 2 Procurement ManagementOkita SoujiNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument666 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFchandraNo ratings yet
- Constant Increasing and Decreasing - Cost IndustryDocument3 pagesConstant Increasing and Decreasing - Cost IndustrySiti Suhaili Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Automotive-Spice en Man3 Project-ManagementDocument15 pagesWhitepaper Automotive-Spice en Man3 Project-Managementnicky engineerNo ratings yet
- Jit Key ElementDocument35 pagesJit Key ElementshfqshaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Sensitivity Analysis GraphicalDocument7 pagesChapter 05 Sensitivity Analysis Graphicaldalrine rajanNo ratings yet