Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsEnergy
Energy
Uploaded by
Jhanavi GeraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- SET-NET Pericyclic ReactionsDocument61 pagesSET-NET Pericyclic ReactionsBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Forms and Sources of EnergyDocument60 pagesForms and Sources of EnergyCindy Mae MacamayNo ratings yet
- Energy & Form's of Energy: Presented By: Lulav Saeed Gulistan Yusif Supervised By: Mss. SallyDocument15 pagesEnergy & Form's of Energy: Presented By: Lulav Saeed Gulistan Yusif Supervised By: Mss. SallyLulav BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy: Presented By: S. Harry 5/02/2021Document16 pagesConservation of Energy: Presented By: S. Harry 5/02/2021Errol WebsterNo ratings yet
- Types and Forms of EnergyDocument10 pagesTypes and Forms of EnergyUday Shankar100% (1)
- Energy Revise Term3Document27 pagesEnergy Revise Term3thahappy0221No ratings yet
- Nces-Unit 1Document64 pagesNces-Unit 1rock starNo ratings yet
- Energy and It's Types.Document17 pagesEnergy and It's Types.usmansherdinNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 W4 - EnergyDocument37 pagesSCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 W4 - EnergyRex AlcistoNo ratings yet
- WK 1notesDocument6 pagesWK 1notesfngumNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy: Class - VDocument37 pagesSources of Energy: Class - Vmad_sudrocksNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy PowerpointDocument27 pagesConservation of Energy Powerpointapi-266026638No ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT Science Q3 W4 EnergyDocument28 pagesGrade 5 PPT Science Q3 W4 EnergyMarilyn Estrada DullasNo ratings yet
- P6 PAL Science L11 Forms and Uses of Energy-1Document24 pagesP6 PAL Science L11 Forms and Uses of Energy-1XuaN XuanNo ratings yet
- Energy-Forms and ChangesDocument17 pagesEnergy-Forms and ChangesantoniodellisantiNo ratings yet
- Physics EnergyDocument11 pagesPhysics EnergyahanatajnimNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Bentuk EnergiDocument25 pagesBentuk Bentuk Energisebastian harveyNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Forms of EnergyDocument27 pagesPhysics 12 Forms of Energyd4872krNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument16 pagesEnergyEllieNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Sources of EnergyDocument48 pagesTopic 6 Sources of EnergyNur AmalinaNo ratings yet
- Energy PresentationDocument41 pagesEnergy PresentationAron Roland Anthony CidNo ratings yet
- Energy FormsDocument41 pagesEnergy FormsHamza MujahidNo ratings yet
- The Classification of Different Types of Energy DipitDocument12 pagesThe Classification of Different Types of Energy Dipitvineet_knwrNo ratings yet
- What Is EnergyDocument12 pagesWhat Is Energyapi-379952307No ratings yet
- Energy Forms PPTDocument16 pagesEnergy Forms PPTEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Types of Energy Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesTypes of Energy Potential EnergySalwa SadiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Energy FinalDocument30 pagesLesson 2-Energy FinalJonathanNo ratings yet
- Energy: Forms and Changes: BBBBBBBBBBDocument41 pagesEnergy: Forms and Changes: BBBBBBBBBBSam AwanNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy Sources 1 NewDocument38 pagesAlternative Energy Sources 1 Newnasir siyarNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy Sources 1 NewDocument38 pagesAlternative Energy Sources 1 Newnasir siyarNo ratings yet
- What Is Energy: Ansunlight Makes Our DaytimeDocument16 pagesWhat Is Energy: Ansunlight Makes Our DaytimeMuhamad Afif100% (2)
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument20 pagesEnergy Forms and ChangesMonica JavierNo ratings yet
- Concept 3.1Document8 pagesConcept 3.1Abdellateef AlalfyNo ratings yet
- Report ToyadoDocument21 pagesReport ToyadoPrincess MagpatocNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument28 pagesEnergy吕洁儿No ratings yet
- Types and Forms of EnergyDocument16 pagesTypes and Forms of EnergyMary Angelie Lobiano Grecia100% (2)
- Typesandformsofenergy 1Document16 pagesTypesandformsofenergy 1MarvinNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument42 pagesEnergy Forms and Changesflory mae gudiaNo ratings yet
- Energy: Stores of Energy & Energy TransferDocument13 pagesEnergy: Stores of Energy & Energy TransferBaranee NathenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Slides PDFDocument69 pagesChapter 4 Slides PDFcmcdonald3597No ratings yet
- Metabilism and EnergyDocument40 pagesMetabilism and EnergyKisra MahdereNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument44 pagesEnergy Forms and Changesdoudouthekiller100% (1)
- ReviewerDocument9 pagesReviewerHxlcyon ElleNo ratings yet
- Forms of Energy: RmsofenergyDocument19 pagesForms of Energy: RmsofenergyAly S TerNo ratings yet
- Energy: Forms and ChangesDocument43 pagesEnergy: Forms and ChangesDian WestbyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energy 2ºfDocument8 pagesChemical Energy 2ºfIván CrespoNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion: Dr. Mohamed ElsamahyDocument42 pagesEnergy Conversion: Dr. Mohamed ElsamahyHossamKamalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EnergyDocument44 pagesMechanical Energyrichele rectoNo ratings yet
- الجزء الأولDocument31 pagesالجزء الأولMustafa MandourNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Energy Study Guide AnswersDocument8 pages8th Grade Energy Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Chapter 1a Biochemistry and Organization of CellsDocument38 pagesChapter 1a Biochemistry and Organization of CellsSyahirah FazialNo ratings yet
- Heat EnergyDocument5 pagesHeat Energysana.incubationNo ratings yet
- 2 7 Atp-AdpDocument27 pages2 7 Atp-Adpıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument7 pagesScienceAletheia BlatzNo ratings yet
- What Will Hit the Ground First? | Children's Physics of EnergyFrom EverandWhat Will Hit the Ground First? | Children's Physics of EnergyNo ratings yet
- The Powerful World of Energy with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Powerful World of Energy with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Courtesy: Waec Uploaded byDocument41 pagesChemistry: Courtesy: Waec Uploaded byAkpevweoghene Kelvin IdogunNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Practice Test: Test 1 - Material From Chapters 2-4Document11 pagesSelf-Assessment Practice Test: Test 1 - Material From Chapters 2-4Sumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Exp Nana 1Document7 pagesExp Nana 1ellymanisNo ratings yet
- Teaching Electrophilic Aromatic Substitu PDFDocument3 pagesTeaching Electrophilic Aromatic Substitu PDFYummyNo ratings yet
- Group 7 2023 PROJECT THESISDocument21 pagesGroup 7 2023 PROJECT THESISkelvinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 2015-16Document37 pagesBiochemistry 2015-16Anogh SivaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent To: Erpenbach Et AlDocument6 pagesUnited States Patent To: Erpenbach Et AlDian Agung SatyanagaraNo ratings yet
- Cba Chem Syllabus Final Version f1-f2Document35 pagesCba Chem Syllabus Final Version f1-f2richardNo ratings yet
- Journal of Chromatography A Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1016 - J.chroma.2017.05.035) Nestola, Marco Schmidt, Torsten C. - Determination of Mineral Oil Aromatic Hydrocarbons (MOAH) in Edible Oils and FDocument21 pagesJournal of Chromatography A Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1016 - J.chroma.2017.05.035) Nestola, Marco Schmidt, Torsten C. - Determination of Mineral Oil Aromatic Hydrocarbons (MOAH) in Edible Oils and FayukurnNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Chemical Periodicity (Paper-01) WYDocument16 pagesThe Periodic Table Chemical Periodicity (Paper-01) WYgreedy AsunaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Technology of Explosives Vol 3 Urbanski TextDocument729 pagesChemistry and Technology of Explosives Vol 3 Urbanski TextCleberson ValadaresNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument18 pagesChemical EquilibriumSohila A. MabroukNo ratings yet
- Allen Guided Revision Organic ChemistryDocument74 pagesAllen Guided Revision Organic ChemistrymemepepedankNo ratings yet
- Previous 10 Year Question Paper PocDocument21 pagesPrevious 10 Year Question Paper Pocjoel gNo ratings yet
- BELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F5Document8 pagesBELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F5Chee Jin TangNo ratings yet
- Code Chemistry Course DetailsDocument41 pagesCode Chemistry Course DetailsNauman MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reations and Equations: Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-18Document54 pagesChemical Reations and Equations: Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-18Shanthosh .sNo ratings yet
- Determining Percent Yield in A Chemical Reaction LabDocument2 pagesDetermining Percent Yield in A Chemical Reaction Labapi-307565882No ratings yet
- Lab Stoichiometry Iron With Copper II SulfateDocument5 pagesLab Stoichiometry Iron With Copper II Sulfateapi-249441006No ratings yet
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides NEETDocument10 pagesAlkyl and Aryl Halides NEETJagrav GargNo ratings yet
- HSE - Combining HAZOP With Dynamic Simulation-Applications For Safety EducationDocument8 pagesHSE - Combining HAZOP With Dynamic Simulation-Applications For Safety EducationLandryNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Reactions of Organic Chem - Alkanes PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet On Reactions of Organic Chem - Alkanes PDFpretzNo ratings yet
- Astronomy - 01 06 2018 PDFDocument80 pagesAstronomy - 01 06 2018 PDFKelum BuddhikaNo ratings yet
- Corrosive Sulphur and DBDS in Transformer Oil: Risk Assessments and Mitigation Actions On Power Transformers and Reactors - Utility ExperienceDocument7 pagesCorrosive Sulphur and DBDS in Transformer Oil: Risk Assessments and Mitigation Actions On Power Transformers and Reactors - Utility ExperienceWaqqar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Angew Chem Int Ed - 2005 - Blackmond - Reaction Progress Kinetic Analysis A Powerful Methodology For Mechanistic StudiesDocument19 pagesAngew Chem Int Ed - 2005 - Blackmond - Reaction Progress Kinetic Analysis A Powerful Methodology For Mechanistic StudiesFilipi ChalitaNo ratings yet
- PETE 311 Lab 3 MemoDocument3 pagesPETE 311 Lab 3 MemoTyler MroskoNo ratings yet
- CHM 231 Ca 2019-2020Document4 pagesCHM 231 Ca 2019-2020idriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 2 Microscopic World I - LQ - PDFDocument22 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 2 Microscopic World I - LQ - PDFSiu Hon ChengNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: (Physical Chemistry)Document26 pagesChemical Kinetics: (Physical Chemistry)keshavNo ratings yet
Energy
Energy
Uploaded by
Jhanavi Gera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views18 pagesOriginal Title
8._Energy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views18 pagesEnergy
Energy
Uploaded by
Jhanavi GeraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
Energy
Nature of Energy
• You use energy when you:
• hit a softball.
• lift your book bag.
• compress a spring.
Nature of Energy
Living organisms need energy for
growth and movement.
Nature of Energy
• Energy can be defined as the ability to do work.
• If an object does work means the object uses energy.
• Because of the direct connection between energy and
work, energy is measured in the same unit as work:
joules (J).
• In addition to using energy to do work, objects gain
energy because work is being done on them.
Forms of Energy
The five main forms of energy
are:
• Heat
• Chemical
• Electromagnetic
• Nuclear
• Mechanical
Thermal/Heat Energy
• A special form of kinetic energy
• Energy of moving or vibrating molecules
• The faster the molecules vibrate the hotter
they become
• When heat is produced we have thermal
energy.
Thermal/Heat Energy
• Volcanoes can be a natural source of thermal energy.
When we use the heat of the earth it is called
geothermal energy.
Chemical Energy
• Stored in chemical bonds holding the atoms of
compounds together
• Food, wood, batteries, fossil fuels
Chemical Energy
• When a chemical reaction takes place energy is used.
• If energy is pulled in from the surrounding area during
a chemical reaction, the area gets cold and the
reaction is endothermic.
• Commercial ice packs for injuries work this way.
Chemical Energy
• When a chemical
reaction takes place
and releases energy
it can increase the
temperature. We call
this an exothermic
reaction.
Chemical Energy
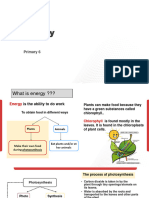
Plants can make their own
energy through a process
called photosynthesis.
They are the bases for a
food chain. All other living
things that cannot carry
on photosynthesis
depend on plants for their
energy.
Energy Transformation
• In photosynthesis radiant or light energy from
the sun is changed to chemical energy in the
leaf.
Chemical Energy
• Other living things can get energy from eating plants
or eating things that eat plants.
Chemical Energy
• The energy we eat is stored as potential chemical energy until we
need it. When we use the energy through an activity then it becomes
kinetic mechanical energy.
Chemical Energy
• Plants make food through the process of photosynthesis. When we
use the energy from the chemical energy we store we break it
down through a process called respiration. These are opposite
energy reactions.
Nuclear Energy
• Energy stored in the nuclei
of atoms
• Released by fission, the
splitting of nuclei of heavy
atoms
• Released by fusion-the
combining of nuclei of light
atoms
Mechanical Energy
• Most familiar-involved with moving objects;
atoms are moving and pushing each other
• Sound is an example-occurs when atoms in
a media vibrate in a direction outward from
the sound source. Sometimes, sound is
classified as its own energy source.
Mechanical Energy
• When we move or work we are using mechanical
energy.
You might also like
- SET-NET Pericyclic ReactionsDocument61 pagesSET-NET Pericyclic ReactionsBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Forms and Sources of EnergyDocument60 pagesForms and Sources of EnergyCindy Mae MacamayNo ratings yet
- Energy & Form's of Energy: Presented By: Lulav Saeed Gulistan Yusif Supervised By: Mss. SallyDocument15 pagesEnergy & Form's of Energy: Presented By: Lulav Saeed Gulistan Yusif Supervised By: Mss. SallyLulav BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy: Presented By: S. Harry 5/02/2021Document16 pagesConservation of Energy: Presented By: S. Harry 5/02/2021Errol WebsterNo ratings yet
- Types and Forms of EnergyDocument10 pagesTypes and Forms of EnergyUday Shankar100% (1)
- Energy Revise Term3Document27 pagesEnergy Revise Term3thahappy0221No ratings yet
- Nces-Unit 1Document64 pagesNces-Unit 1rock starNo ratings yet
- Energy and It's Types.Document17 pagesEnergy and It's Types.usmansherdinNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 W4 - EnergyDocument37 pagesSCIENCE 6 PPT Q3 W4 - EnergyRex AlcistoNo ratings yet
- WK 1notesDocument6 pagesWK 1notesfngumNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy: Class - VDocument37 pagesSources of Energy: Class - Vmad_sudrocksNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy PowerpointDocument27 pagesConservation of Energy Powerpointapi-266026638No ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT Science Q3 W4 EnergyDocument28 pagesGrade 5 PPT Science Q3 W4 EnergyMarilyn Estrada DullasNo ratings yet
- P6 PAL Science L11 Forms and Uses of Energy-1Document24 pagesP6 PAL Science L11 Forms and Uses of Energy-1XuaN XuanNo ratings yet
- Energy-Forms and ChangesDocument17 pagesEnergy-Forms and ChangesantoniodellisantiNo ratings yet
- Physics EnergyDocument11 pagesPhysics EnergyahanatajnimNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Bentuk EnergiDocument25 pagesBentuk Bentuk Energisebastian harveyNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Forms of EnergyDocument27 pagesPhysics 12 Forms of Energyd4872krNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument16 pagesEnergyEllieNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Sources of EnergyDocument48 pagesTopic 6 Sources of EnergyNur AmalinaNo ratings yet
- Energy PresentationDocument41 pagesEnergy PresentationAron Roland Anthony CidNo ratings yet
- Energy FormsDocument41 pagesEnergy FormsHamza MujahidNo ratings yet
- The Classification of Different Types of Energy DipitDocument12 pagesThe Classification of Different Types of Energy Dipitvineet_knwrNo ratings yet
- What Is EnergyDocument12 pagesWhat Is Energyapi-379952307No ratings yet
- Energy Forms PPTDocument16 pagesEnergy Forms PPTEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Types of Energy Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesTypes of Energy Potential EnergySalwa SadiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Energy FinalDocument30 pagesLesson 2-Energy FinalJonathanNo ratings yet
- Energy: Forms and Changes: BBBBBBBBBBDocument41 pagesEnergy: Forms and Changes: BBBBBBBBBBSam AwanNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy Sources 1 NewDocument38 pagesAlternative Energy Sources 1 Newnasir siyarNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy Sources 1 NewDocument38 pagesAlternative Energy Sources 1 Newnasir siyarNo ratings yet
- What Is Energy: Ansunlight Makes Our DaytimeDocument16 pagesWhat Is Energy: Ansunlight Makes Our DaytimeMuhamad Afif100% (2)
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument20 pagesEnergy Forms and ChangesMonica JavierNo ratings yet
- Concept 3.1Document8 pagesConcept 3.1Abdellateef AlalfyNo ratings yet
- Report ToyadoDocument21 pagesReport ToyadoPrincess MagpatocNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument28 pagesEnergy吕洁儿No ratings yet
- Types and Forms of EnergyDocument16 pagesTypes and Forms of EnergyMary Angelie Lobiano Grecia100% (2)
- Typesandformsofenergy 1Document16 pagesTypesandformsofenergy 1MarvinNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument42 pagesEnergy Forms and Changesflory mae gudiaNo ratings yet
- Energy: Stores of Energy & Energy TransferDocument13 pagesEnergy: Stores of Energy & Energy TransferBaranee NathenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Slides PDFDocument69 pagesChapter 4 Slides PDFcmcdonald3597No ratings yet
- Metabilism and EnergyDocument40 pagesMetabilism and EnergyKisra MahdereNo ratings yet
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument44 pagesEnergy Forms and Changesdoudouthekiller100% (1)
- ReviewerDocument9 pagesReviewerHxlcyon ElleNo ratings yet
- Forms of Energy: RmsofenergyDocument19 pagesForms of Energy: RmsofenergyAly S TerNo ratings yet
- Energy: Forms and ChangesDocument43 pagesEnergy: Forms and ChangesDian WestbyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energy 2ºfDocument8 pagesChemical Energy 2ºfIván CrespoNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion: Dr. Mohamed ElsamahyDocument42 pagesEnergy Conversion: Dr. Mohamed ElsamahyHossamKamalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EnergyDocument44 pagesMechanical Energyrichele rectoNo ratings yet
- الجزء الأولDocument31 pagesالجزء الأولMustafa MandourNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Energy Study Guide AnswersDocument8 pages8th Grade Energy Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Chapter 1a Biochemistry and Organization of CellsDocument38 pagesChapter 1a Biochemistry and Organization of CellsSyahirah FazialNo ratings yet
- Heat EnergyDocument5 pagesHeat Energysana.incubationNo ratings yet
- 2 7 Atp-AdpDocument27 pages2 7 Atp-Adpıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument7 pagesScienceAletheia BlatzNo ratings yet
- What Will Hit the Ground First? | Children's Physics of EnergyFrom EverandWhat Will Hit the Ground First? | Children's Physics of EnergyNo ratings yet
- The Powerful World of Energy with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Powerful World of Energy with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Courtesy: Waec Uploaded byDocument41 pagesChemistry: Courtesy: Waec Uploaded byAkpevweoghene Kelvin IdogunNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Practice Test: Test 1 - Material From Chapters 2-4Document11 pagesSelf-Assessment Practice Test: Test 1 - Material From Chapters 2-4Sumaira AliNo ratings yet
- Exp Nana 1Document7 pagesExp Nana 1ellymanisNo ratings yet
- Teaching Electrophilic Aromatic Substitu PDFDocument3 pagesTeaching Electrophilic Aromatic Substitu PDFYummyNo ratings yet
- Group 7 2023 PROJECT THESISDocument21 pagesGroup 7 2023 PROJECT THESISkelvinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 2015-16Document37 pagesBiochemistry 2015-16Anogh SivaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent To: Erpenbach Et AlDocument6 pagesUnited States Patent To: Erpenbach Et AlDian Agung SatyanagaraNo ratings yet
- Cba Chem Syllabus Final Version f1-f2Document35 pagesCba Chem Syllabus Final Version f1-f2richardNo ratings yet
- Journal of Chromatography A Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1016 - J.chroma.2017.05.035) Nestola, Marco Schmidt, Torsten C. - Determination of Mineral Oil Aromatic Hydrocarbons (MOAH) in Edible Oils and FDocument21 pagesJournal of Chromatography A Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1016 - J.chroma.2017.05.035) Nestola, Marco Schmidt, Torsten C. - Determination of Mineral Oil Aromatic Hydrocarbons (MOAH) in Edible Oils and FayukurnNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Chemical Periodicity (Paper-01) WYDocument16 pagesThe Periodic Table Chemical Periodicity (Paper-01) WYgreedy AsunaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Technology of Explosives Vol 3 Urbanski TextDocument729 pagesChemistry and Technology of Explosives Vol 3 Urbanski TextCleberson ValadaresNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument18 pagesChemical EquilibriumSohila A. MabroukNo ratings yet
- Allen Guided Revision Organic ChemistryDocument74 pagesAllen Guided Revision Organic ChemistrymemepepedankNo ratings yet
- Previous 10 Year Question Paper PocDocument21 pagesPrevious 10 Year Question Paper Pocjoel gNo ratings yet
- BELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F5Document8 pagesBELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F5Chee Jin TangNo ratings yet
- Code Chemistry Course DetailsDocument41 pagesCode Chemistry Course DetailsNauman MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reations and Equations: Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-18Document54 pagesChemical Reations and Equations: Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-18Shanthosh .sNo ratings yet
- Determining Percent Yield in A Chemical Reaction LabDocument2 pagesDetermining Percent Yield in A Chemical Reaction Labapi-307565882No ratings yet
- Lab Stoichiometry Iron With Copper II SulfateDocument5 pagesLab Stoichiometry Iron With Copper II Sulfateapi-249441006No ratings yet
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides NEETDocument10 pagesAlkyl and Aryl Halides NEETJagrav GargNo ratings yet
- HSE - Combining HAZOP With Dynamic Simulation-Applications For Safety EducationDocument8 pagesHSE - Combining HAZOP With Dynamic Simulation-Applications For Safety EducationLandryNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Reactions of Organic Chem - Alkanes PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet On Reactions of Organic Chem - Alkanes PDFpretzNo ratings yet
- Astronomy - 01 06 2018 PDFDocument80 pagesAstronomy - 01 06 2018 PDFKelum BuddhikaNo ratings yet
- Corrosive Sulphur and DBDS in Transformer Oil: Risk Assessments and Mitigation Actions On Power Transformers and Reactors - Utility ExperienceDocument7 pagesCorrosive Sulphur and DBDS in Transformer Oil: Risk Assessments and Mitigation Actions On Power Transformers and Reactors - Utility ExperienceWaqqar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Angew Chem Int Ed - 2005 - Blackmond - Reaction Progress Kinetic Analysis A Powerful Methodology For Mechanistic StudiesDocument19 pagesAngew Chem Int Ed - 2005 - Blackmond - Reaction Progress Kinetic Analysis A Powerful Methodology For Mechanistic StudiesFilipi ChalitaNo ratings yet
- PETE 311 Lab 3 MemoDocument3 pagesPETE 311 Lab 3 MemoTyler MroskoNo ratings yet
- CHM 231 Ca 2019-2020Document4 pagesCHM 231 Ca 2019-2020idriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 2 Microscopic World I - LQ - PDFDocument22 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 2 Microscopic World I - LQ - PDFSiu Hon ChengNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: (Physical Chemistry)Document26 pagesChemical Kinetics: (Physical Chemistry)keshavNo ratings yet