Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presented by Johndrick
Presented by Johndrick
Uploaded by
2022-1029640 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesOriginal Title
PRESENTED BY JOHNDRICK
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesPresented by Johndrick
Presented by Johndrick
Uploaded by
2022-102964Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
PRESENTED BY:
JOHNDRICK ROHAN B. ARBOLEDA
JERALD CORPIN
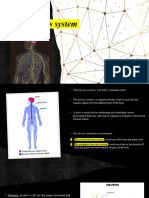
NEURON
• Neurons are nerve cells that send messages all
over your body to allow you to do everything from
breathing to talking, eating, walking, and thinking.
Until recently, most neuroscientists (scientists who
study the brain) thought we were born with all the
neurons we were ever going to have.
PARTS OF A NEURON AND THEIR
FUNCTION
Types of Neuron
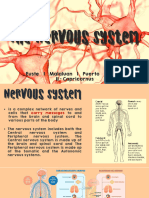
Neurons, or nerve cells, are the fundamental units of the nervous system
responsible for transmitting information. There are several types of neurons
based on their structure and function. The three main types are:
• Sensory Neurons (Afferent Neurons): These neurons transmit signals
from sensory organs (such as eyes, ears, skin) to the central nervous
system (brain and spinal cord). They play a crucial role in conveying
information about the external environment to the brain.
• Interneurons (Association Neurons): Found within the central nervous
system, interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons. They integrate
and interpret the signals received from sensory neurons, and they also
communicate with motor neurons to generate appropriate responses.
Interneurons are essential for processing information and forming
complex neural pathways.
• Motor Neurons (Efferent Neurons): Motor neurons transmit signals
from the central nervous system to muscles and glands. They are
responsible for carrying out the body's responses to sensory input. Motor
neurons play a key role in controlling muscle contractions and other
motor functions.
Additionally, neurons can be categorized based on their structure:
1.
Unipolar Neurons: These neurons have a single process extending from the cell body, which then splits into two branches. Unipolar neurons are typically found in invertebrates.
2.
Bipolar Neurons: These neurons have two processes extending from the cell body—an axon and a dendrite. Bipolar neurons are commonly found in sensory organs like the retina of the eye and the olfactory epithelium in the nose.
3.
Multipolar Neurons: These neurons have multiple processes extending from the cell body, including one axon and multiple dendrites. Most neurons in the human nervous system are multipolar, and they play various roles in
information processing and transmission.
NERVE CELL STRUCTURE
• CELL BODY : Two major components – Nucleus and Cytoplasm
• CYTOPLASM : Contains microscopic organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes,
lysomes, and golgi complexes.
• Primary function is to metabolize protein for maintenance, growth and viability
of the cell.
• CELL BODIES : Not only utilize and convert outside glucose to generate energy,
but also manufacture their own protein
• This protein is conducted through microtubules through the axons.
You might also like
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Coordinated Functions Nervoys SDocument3 pagesCoordinated Functions Nervoys SGwency Ross Alvarez (Gwen)No ratings yet
- Unit Five - Human Biology and Health Ppt-RevisedDocument342 pagesUnit Five - Human Biology and Health Ppt-Revisedsamuelgorfu58No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument42 pagesNervous Systemlashes stylesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (Student Version) PDFDocument65 pagesNervous System (Student Version) PDFAlex HigginsNo ratings yet
- Psicología The NeuronDocument10 pagesPsicología The NeuronDamianLauANo ratings yet
- Neurons 15032022 022019pmDocument9 pagesNeurons 15032022 022019pmayan khanNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous Systemsahiniahamed2No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemGracielle Angelyka PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Anfis System NeurologiDocument51 pagesAnfis System Neurologianon_822636748No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological SystemDocument38 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological SystemBrantNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Q3 Week 3 Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesG10 Science Q3 Week 3 Nervous Systemhimotoumaruchan009No ratings yet
- PPT1Document50 pagesPPT1Kudo KuchikiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - 2Document13 pagesNervous System - 2fumiko.cruzNo ratings yet
- Science Sofie 10 3 RevDocument11 pagesScience Sofie 10 3 Revjinxtapperhat07No ratings yet
- Nscelec4-Week 15Document23 pagesNscelec4-Week 15Jeune Kristine OngNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Altered Cognitive-Perceptual Patterns: Clients With Neuroligic DisordersDocument96 pagesAltered Cognitive-Perceptual Patterns: Clients With Neuroligic DisordersJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Nervous SystemDavid ToledoNo ratings yet
- A2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 1 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanDocument10 pagesA2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 1 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanAwais BodlaNo ratings yet
- LP 1.2 in PhysioBio PsychologyDocument11 pagesLP 1.2 in PhysioBio PsychologyWayne GodioNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (B.SC Nursing 1st Year)Document92 pagesNervous System (B.SC Nursing 1st Year)swainnibedita63No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Biology For EngineersDocument16 pagesUnit 3 Biology For Engineers20me006No ratings yet
- Biological Foundation of Human BehaviorDocument32 pagesBiological Foundation of Human Behaviorjonaxx enthusiastNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CNS 1Document50 pagesIntroduction To CNS 1Sefrinmi AyodejiNo ratings yet
- NervesDocument26 pagesNerveskentNo ratings yet
- Neuron and Glial CellsDocument25 pagesNeuron and Glial Cellsfakhar aliNo ratings yet
- 9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMDocument24 pages9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Psychology For Nurses 2 The Brain Vs The Mind: DR Gihan SalemDocument32 pagesPsychology For Nurses 2 The Brain Vs The Mind: DR Gihan SalemWeji ShNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemNorleen Rose S. AguilarNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychology Summary BookletDocument12 pagesNeuropsychology Summary Bookletapi-642709499No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Nervous System Part 1Document62 pagesUnit 3 Nervous System Part 1Shehzad Haider100% (1)
- Nervous TissuesDocument13 pagesNervous TissuesSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Psychology AssignmentDocument5 pagesPsychology AssignmentAmrutha ChandranNo ratings yet
- 10th STD 15. Nervous SystemDocument35 pages10th STD 15. Nervous Systemnasheethahmedschool2No ratings yet
- How Your Brain WorksDocument7 pagesHow Your Brain WorksMRITZNo ratings yet
- Lab 16 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesLab 16 The Nervous Systemrhycelayon304No ratings yet
- 3 Types of Muscle of TissueDocument5 pages3 Types of Muscle of TissueMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 - The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesLecture4 - The Nervous SystemVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesThe Nervous SystemNoar RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesNervous SystemkenNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document29 pagesModule 2rohitrajww4No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument31 pagesThe Nervous SystemceneveNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Q3 Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesG10 Science Q3 Nervous SystemEvadine LeeNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous Systemrafay56776No ratings yet
- The Human Nervous Syste1Document10 pagesThe Human Nervous Syste1taytay321No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemLeon MarkoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxDocument36 pages4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxZaara RashéidNo ratings yet
- BIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaDocument6 pagesBIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaCassandraNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023Document94 pagesUNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023ndamanomhataabisai7No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 8 - Nervous System20230027475No ratings yet
- Types of NeuronsDocument4 pagesTypes of NeuronsDeirdreNo ratings yet
- IEU Psik 2Document88 pagesIEU Psik 2İdilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Document64 pagesAnatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Batot EvaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesNervous Systemdty2257202010031No ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- Arsi University College of Health Sciences Department of MedicineDocument127 pagesArsi University College of Health Sciences Department of MedicineWorku KifleNo ratings yet
- Food AdulterationDocument25 pagesFood AdulterationHemlata SoniNo ratings yet
- Rao2021 Article UnintentionalWeightLossWhatRadDocument15 pagesRao2021 Article UnintentionalWeightLossWhatRadAndres F AristizabalNo ratings yet
- Tissue Salts 2Document13 pagesTissue Salts 2Roshin Sudesh100% (1)
- HTN PPT - YasDocument18 pagesHTN PPT - YasCiaNo ratings yet
- Lakshmi Lalaji Dissertation FinalDocument71 pagesLakshmi Lalaji Dissertation Finalshalini75No ratings yet
- List of The Hospital Empanelled With DDA (June 2021)Document24 pagesList of The Hospital Empanelled With DDA (June 2021)ygkrchNo ratings yet
- Case Investigation Form: (For COVID-19 Vaccine AEFI)Document12 pagesCase Investigation Form: (For COVID-19 Vaccine AEFI)Jake RamirezNo ratings yet
- CA 2 CDN Review Notes 2Document21 pagesCA 2 CDN Review Notes 2Andrew Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Oxford University Press Esc Handbook of Cardiovascular Rehabilitation 0198849303Document225 pagesOxford University Press Esc Handbook of Cardiovascular Rehabilitation 0198849303ArmandoCamaraNinoNo ratings yet
- Q2 - A.Y. 21 22 - G2 - TOS and Periodical ExamDocument6 pagesQ2 - A.Y. 21 22 - G2 - TOS and Periodical ExamSher SherwinNo ratings yet
- "A Nursing Process On Ovarian Cancer": Pres. Diosdado Macapagal Blvd. Metropolitan Park, Pasay CityDocument21 pages"A Nursing Process On Ovarian Cancer": Pres. Diosdado Macapagal Blvd. Metropolitan Park, Pasay Citysaint_ronald8No ratings yet
- Introduction To Population Genetics 8-AndersenDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Population Genetics 8-AndersenmikshaNo ratings yet
- American EskimosDocument21 pagesAmerican EskimosJorie RocoNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument34 pagesSpina Bifidaapi-271779479No ratings yet
- 5 - HayashiItsuki 2012 TeenageSmokingWhatAre SmokingHealthEffectsPDocument38 pages5 - HayashiItsuki 2012 TeenageSmokingWhatAre SmokingHealthEffectsPlobont nataliaNo ratings yet
- Incident Accident RegisterDocument2 pagesIncident Accident RegisterMuruganNo ratings yet
- Louisiana SDM Screening and Response Assessment 10-17-2011Document22 pagesLouisiana SDM Screening and Response Assessment 10-17-2011Rick ThomaNo ratings yet
- Diease LossDocument10 pagesDiease LossGeetha EconomistNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Anthracis: - MorfologiDocument3 pagesBacillus Anthracis: - MorfologiCiendy ShintyaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet TGX-2209: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument16 pagesSafety Data Sheet TGX-2209: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingV U P RaoNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Molecular DockingDocument19 pagesAntidiabetic Molecular DockingChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument3 pagesResearch Proposalshivangi pushkarnaNo ratings yet
- A One Health Approach To Tackle Cryptosporidiosis: ReviewDocument14 pagesA One Health Approach To Tackle Cryptosporidiosis: ReviewAslam MuhammadNo ratings yet
- ICMIDocument4 pagesICMIKim MingyuNo ratings yet
- JASMIN, Kisha Jane P.Document2 pagesJASMIN, Kisha Jane P.Kisha Jane JasminNo ratings yet
- Tropical Haematology and Blood Transfusion PDFDocument77 pagesTropical Haematology and Blood Transfusion PDFZiauddin AzimiNo ratings yet
- Travel MedicineDocument31 pagesTravel Medicineanshari dwi nugrahaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Class 10th (KPK)Document23 pagesBiology: Class 10th (KPK)Muhammad Owais FayazNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram ExaminationDocument13 pagesElectrocardiogram ExaminationayunisallehNo ratings yet