Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsCH 3
CH 3
Uploaded by
Prathamesh NaraleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Basic Training Manual Updated 09-05-14Document68 pagesBasic Training Manual Updated 09-05-14PamelaJacksonNo ratings yet
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayFrom EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- One Sim Card ManualDocument16 pagesOne Sim Card ManualUkah FranklinNo ratings yet
- MMS (Multi Media Messaging)Document4 pagesMMS (Multi Media Messaging)bkbenjyNo ratings yet
- Kannel Open Source Sms Gateway UserGuideDocument158 pagesKannel Open Source Sms Gateway UserGuidekdorairajsgNo ratings yet
- CN Notes Unit 5Document13 pagesCN Notes Unit 5Shreya MankarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Network TrendsDocument17 pagesModule 3 - Network TrendsShipra ShaliniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Mobile Network ArchitectureDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - Mobile Network Architecturemanar ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Core To 4G Mobile Communications: Luis Eduardo Sánchez de LoeraDocument26 pagesThe Core To 4G Mobile Communications: Luis Eduardo Sánchez de LoeraEduardo S de LoeraNo ratings yet
- Mod Overlay DesignDocument33 pagesMod Overlay DesignDevarajNo ratings yet
- Presenting By:: Santosh Chenna 116A1D5815Document33 pagesPresenting By:: Santosh Chenna 116A1D5815kavithachennaNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11e-Qos and Comparison of Wifi and UmtsDocument25 pagesIEEE 802.11e-Qos and Comparison of Wifi and Umtsswathi sriniNo ratings yet
- WCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 1Document40 pagesWCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 1Sushíl kanikeNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document12 pagesLec 4xp4bwxnmbkNo ratings yet
- MC MOD 6Document83 pagesMC MOD 6wilaxin634No ratings yet
- Long Term EvolutionDocument32 pagesLong Term Evolutionmkrao_kiranNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 MobileCommunication ShortDocument43 pagesLecture5 MobileCommunication Shortreza danteNo ratings yet
- 17EC81 Module 1 NotesDocument48 pages17EC81 Module 1 NotesHarshitha LNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile Radio CommunicationDocument4 pagesEvolution of Mobile Radio CommunicationmanjuNo ratings yet
- 4G Mobile TechnologyDocument19 pages4G Mobile TechnologyHani TaHaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Cellular NetworksDocument21 pagesChapter 5-Cellular NetworksHuseinNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture INGGRISDocument6 pagesGSM Architecture INGGRISJesika Oktavia1110No ratings yet
- BY Upasana GaikwadDocument30 pagesBY Upasana GaikwadRenu YadavNo ratings yet
- 4G TechnologyDocument21 pages4G TechnologyvigneshknNo ratings yet
- UmtsDocument23 pagesUmtsMitz PaminNo ratings yet
- 3GPP Technologies Evolution From GSM To 5G 1706397791Document7 pages3GPP Technologies Evolution From GSM To 5G 1706397791stNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile Communication: 1G (First Generation Mobile System)Document10 pagesEvolution of Mobile Communication: 1G (First Generation Mobile System)ARUNKUMAR SNo ratings yet
- Generations of Mobile TechDocument12 pagesGenerations of Mobile Techseema fatimaNo ratings yet
- Wcdma (Umts) Tdcdma Cdma2000 Wcdma (Docomo) Td-Scdma Mobiles Bluetooth Homerf/Swap Wap GPRS, HSCSD Edge Camel, inDocument6 pagesWcdma (Umts) Tdcdma Cdma2000 Wcdma (Docomo) Td-Scdma Mobiles Bluetooth Homerf/Swap Wap GPRS, HSCSD Edge Camel, invipin171986No ratings yet
- If6i-Wmn-Unit 3 NotesDocument15 pagesIf6i-Wmn-Unit 3 Notes514 Vaibhavi PawarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Presentation On Telecommunication SystemDocument15 pagesIndustrial Training Presentation On Telecommunication SystemsajalNo ratings yet
- New LTEDocument33 pagesNew LTEVikash YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter#6 Emerging Telecon TechnologiesDocument30 pagesChapter#6 Emerging Telecon TechnologiesYaqoob AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Mobile ComputingDocument178 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Mobile Computinggoraniya reenaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 4 Generation Wireless Networks: Presented by Huiqi ZhangDocument32 pagesIntroduction To 4 Generation Wireless Networks: Presented by Huiqi ZhangAsaadNo ratings yet
- Basic Mobile CommunicationDocument41 pagesBasic Mobile CommunicationParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Module - 1: Drawbacks of IGDocument53 pagesModule - 1: Drawbacks of IGgokulaNo ratings yet
- MCN-Unit-1 - Cellular Concepts - NotesDocument32 pagesMCN-Unit-1 - Cellular Concepts - Notesamey vermaNo ratings yet
- What Is 3GDocument15 pagesWhat Is 3GShampad AyanNo ratings yet
- Module - 1: by Arunabha Ghosh, Jan Zhang, Jefferey Andrews, Riaz MohammedDocument176 pagesModule - 1: by Arunabha Ghosh, Jan Zhang, Jefferey Andrews, Riaz MohammedHarinath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Wap 1Document7 pagesWap 1Sunil PillaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture CellularTechnologies Part2Document78 pagesLecture CellularTechnologies Part2DanishNo ratings yet
- 3G NetworksDocument9 pages3G Networkschenjerai chabaraNo ratings yet
- Mobile Internet Applications RTD 704 /7Document26 pagesMobile Internet Applications RTD 704 /7Isa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture Notes - Wire & Wireless CommunicationDocument22 pages1st Lecture Notes - Wire & Wireless CommunicationJordan-James OlivoNo ratings yet
- Image Encryption Using 2D Chaotic Ma Presented by Nazish KhalidDocument39 pagesImage Encryption Using 2D Chaotic Ma Presented by Nazish KhalidNazish KhalidNo ratings yet
- Modern Communication SystemsDocument27 pagesModern Communication SystemsVicky SinghNo ratings yet
- Iclterpop Section 1Document33 pagesIclterpop Section 1Witto PereNo ratings yet
- 3G Technology in The Wireless Communications: AbstractDocument4 pages3G Technology in The Wireless Communications: AbstractpkmukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 4G NotesDocument7 pages4G NoteskavithachennaNo ratings yet
- Third-Generation Mobile Phones: Digital Voice and DataDocument5 pagesThird-Generation Mobile Phones: Digital Voice and DataShanky KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 AMCS - Week 1 LectureDocument13 pagesUnit 1 AMCS - Week 1 LectureMANASA P (RA2011004010071)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless TechnologyDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Wireless TechnologyOlasupo OkunaiyaNo ratings yet
- 4G Technology: Presented by Varun JayakumarDocument26 pages4G Technology: Presented by Varun JayakumarVarun JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Practical 6 Introducing 4G Technology: BackgroundDocument7 pagesPractical 6 Introducing 4G Technology: BackgroundIshant GohilNo ratings yet
- 3G VS WifiDocument22 pages3G VS WifiAleemuddin Mohd AbdulNo ratings yet
- Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology, Management & GramothanDocument22 pagesSwami Keshvanand Institute of Technology, Management & GramothanSonam BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WCDMA Fundamentals NokiaDocument106 pagesIntroduction To WCDMA Fundamentals NokiaSadasivan Ep100% (2)
- 3G and 4G: From: R.ROHITH (07S41A0533)Document11 pages3G and 4G: From: R.ROHITH (07S41A0533)Pranay RajNo ratings yet
- Networking 2023 - ModDocument114 pagesNetworking 2023 - Modmalindabissoon312No ratings yet
- Generations of Wireless Mobile Systems: Comparison of Channel Capacity For Different Channel TypesDocument2 pagesGenerations of Wireless Mobile Systems: Comparison of Channel Capacity For Different Channel TypesFranch Maverick Arellano LorillaNo ratings yet
- WCC Mod - 2Document12 pagesWCC Mod - 2Robin MishraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: There Are Four Main Types of Wireless NetworksDocument15 pagesWireless Networks: There Are Four Main Types of Wireless NetworksSyed ShahidNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Standard: Muhammad Ali Raza AnjumDocument45 pagesBluetooth Standard: Muhammad Ali Raza AnjumAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- 04 Telephone DiagnosticsDocument19 pages04 Telephone DiagnosticsSalisburNo ratings yet
- RFI Content Delivery PlatformDocument5 pagesRFI Content Delivery PlatformDakshata Vamsi TalasilaNo ratings yet
- 4G Wireless TechnologyDocument22 pages4G Wireless TechnologyAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes - Networking and Internet For IBPS Bank ExamDocument4 pagesComputer Notes - Networking and Internet For IBPS Bank ExamakshitaNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece Vjec 1Document29 pagesDepartment of Ece Vjec 1Surangma ParasharNo ratings yet
- Courses Subject Codes 1. B.A. TAMIL (2008-2009) I YEARDocument48 pagesCourses Subject Codes 1. B.A. TAMIL (2008-2009) I YEARMAdhuNo ratings yet
- An Improved SMS User Interface System To PDFDocument145 pagesAn Improved SMS User Interface System To PDFBwayo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- MCQ On IT 2Document8 pagesMCQ On IT 2udai_chakraborty5511No ratings yet
- MSC Computer Science Syllabus 2012 OnwardsDocument42 pagesMSC Computer Science Syllabus 2012 OnwardsJothi KumarNo ratings yet
- Moviles NokiaDocument27 pagesMoviles Nokiaapi-4528173No ratings yet
- Config Nokia 6600Document3 pagesConfig Nokia 6600Justine ItugotNo ratings yet
- Mobile Testing Interview Question & AnswerDocument10 pagesMobile Testing Interview Question & Answerramakant tyagi100% (1)
- Mobile UsabilityDocument67 pagesMobile Usabilityapi-3859663No ratings yet
- Abbreviations: Class VIII: Ascii Bios DBA ERP GIF HTML I/O JS Mbps Mips PDF FTP VPN Wlan SDDDocument2 pagesAbbreviations: Class VIII: Ascii Bios DBA ERP GIF HTML I/O JS Mbps Mips PDF FTP VPN Wlan SDDShakeelAhmedNo ratings yet
- Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli - 620 024. Master of Computer Application (M.C.A) - Course Structure Under CBCSDocument54 pagesBharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli - 620 024. Master of Computer Application (M.C.A) - Course Structure Under CBCSB. Srini VasanNo ratings yet
- Setting GPRS Semua OperatorDocument2 pagesSetting GPRS Semua OperatorSeptianAryoNo ratings yet
- Mobile Ip & Wap NotesDocument17 pagesMobile Ip & Wap NotesMelissa HobbsNo ratings yet
- Telecom Sector in BangladeshDocument92 pagesTelecom Sector in BangladeshNasir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of AirtelDocument93 pagesMarketing Strategies of AirtelSami ZamaNo ratings yet
- Wireless - Merits & DemeritsDocument10 pagesWireless - Merits & DemeritsAnirudhan RaviNo ratings yet
- Mobile Application Thesis PhilippinesDocument4 pagesMobile Application Thesis Philippinesfjnev0hc100% (2)
- Records Transferred Start Filerfno End Filerfno: Updation Status (From: To: User: 3/21/2011Document17 pagesRecords Transferred Start Filerfno End Filerfno: Updation Status (From: To: User: 3/21/2011ramesh2745No ratings yet
- WAP 450 Data Sheet (2) 1Document2 pagesWAP 450 Data Sheet (2) 1rebin1988No ratings yet
- Videocon MobilesDocument14 pagesVideocon MobilesAvinash MohanNo ratings yet
- RBT System ARBT Subject PDFDocument33 pagesRBT System ARBT Subject PDFbaraharbNo ratings yet
CH 3
CH 3
Uploaded by
Prathamesh Narale0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views49 pagesOriginal Title
ch-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views49 pagesCH 3
CH 3
Uploaded by
Prathamesh NaraleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 49
Wireless Application Protocol(WAP)
• Wireless Application Protocol or WAP is a set
of communication protocols based on the
concept of the World Wide Web (WWW
• WAP is a protocol designed for micro-
browsers, and it enables the mobile devices to
transmit information over the Internet.
• It has ability to create web applications for
mobile devices.
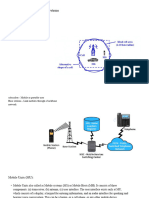
Working of Wireless Application Protocol or WAP
Model
• WAP model comprises of 3-Levels that
are : Client, Gateway and Origin Server.
• The WAP user agent sends a request via
mobile to WAP gateway by using encoded
WAP protocol i.e. called as encoding request.
• The encoding request is translated through
WAP gateway and is further forwarded in the
form of HTTP request to the server side where
scripts are available.
• Response from the scripts and content is
picked up as requested response, through
HTTP and is forwarded to the WAP gateway
once again.
• The required HTTP response is then forwarded
in decode format to the client protocol stack as
the final response for the initial request made
by client.
• Advantages : Wireless Application Protocol
• Fast technology.
• Open source-Free.
• Can be implemented on multiple platform.
• Independent of network standard.
• Higher controlling options.
• Applications : Wireless Application Protocol
• E-mails access.
• Weather forecasting.
• Flight information.
• Movie & cinema information.
• Traffic updates.
• Disadvantages : Wireless Application Protocol
• Fast Technology.
• Less Secured.
• User interface(UI) is small.
• Less availability.
• (WAP) Gateway
• The Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
gateway is part of a protocol for protected use
of the Internet.
• In WAP, requests to access a website are sent
through a WAP gateway for security purposes.
WML
• WML stands for Wireless Markup Language
• WML is an application of XML
• WML is the markup language defined in the
WAP specification.
• WAP sites are written in WML, while web sites
are written in HTML.
• WML is very similar to HTML. Both of them
use tags and are written in plain text format.
• WML files have the extension ".wml".
Features of WML:
• Supports for text and images
• Support for user input
• International support
IMT 2000
• IMT-2000 Stands for International Mobile
Telecommunications-2000.
The goal of International Mobile
Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) is to
support data transmission rates of up to 2 Mbps
for fixed stations(permanently fixed) and 384
Kbps for mobile stations.
• Note that the “2000” in the term “International
Mobile Telecommunications-2000” refers to
the transmission speed (approximately 2000
Kbps)
Features:
• It is used for all radio environments.
• It supports both packet switched and circuit
switched data transmission.
• It offers high spectrum efficiency.
• It support wide range of telecommunication
services like voice , data, multimedia and
internet.
• IMT 2000 Architecture:
• Figure shows the IMT 2000 Architecture.
• The ITU standardize 5 group of 3G for radio
access technology.
• IMT-DS:
• It is used the direct spread technology.
• It is also called Wideband CDMA.
• It is part of Third Generation Partnership
Project(3GPP)
• IMT-TC:
• It uses Time Code Technology.
• It further divided into 2 standards TDD and
TD-SCDMA.
• IMT-MC:
• It uses Multi Carrier Technology.
• CDMA is multi carrier technology and it is part
of 3GPP2.
• IMT-SC:
• It uses Single Carrier Technology.
• It is enhancement of US TDMA System.
• IMT-FT:
• It uses Frequency Time Technology.
• It is enhancement version of the digital
cordless telephone standards DECT.
• Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
(WCDMA)
• is a type of cellular technology that was developed
as a third-generation (3G) mobile communications
standard.
• It is based on the Code Division Multiple Access
(CDMA) technologies that were developed in the
1980s,
• it provides higher data rates than previous versions
of CDMA.
• . The first version of the WCDMA standard
was released in 1998
• The development of WCDMA began in the
late 1990s, and the first WCDMA networks
were launched in Japan in 2001.
• WCDMA is also known as Universal Mobile
Telecommunications System (UMTS), which is
the third generation (3G) mobile
telecommunications standard developed by
the International Telecommunication Union
(ITU).
• Advantage:
• Energy-efficient data transfers
• Better battery life for IoT devices
• High-speed information exchange
• Delivery of small packets of information to a
destination
• Purpose-built for cell phones and industrial
modems
• Disadvantage:
• One drawback is that it requires a more
complex and expensive infrastructure to
support its wideband frequency bands.
• Additionally, WCDMA has been replaced by
newer, faster mobile technologies such as 4G
and 5G.
• The Universal Mobile Telecommunications
System (UMTS)
• (UMTS) is defined as the third-generation (3G)
mobile network built on the global GSM
standard, compatible with data transfer up to
2 Megabits per second.
Features
• UMTS is a component of IMT-2000 developed
by 3GPP(Third Generation Partnership
Project).
• It uses wideband code division multiple access
(W-CDMA) air interface.
• It provides transmission of text, digitized
voice, video and multimedia.
• It provides high bandwidth(The maximum
amount of data transmitted over an internet
connection in a given amount of time.) to
mobile operators.
• It gives a high data rate of 2Mbps. It is also
known as Freedom of Mobile Multimedia
Access (FOMA).
• UMTS is popularly known as a third-
generation (3G) cellular network. It was seen
as a better cellular technology for data transfer
than its predecessor, the GSM technology.
• How Does UMTS Work?
• A mobile network of the UMTS can be divided
into three major parts –
• user equipment,
• the access network, and
• the core network.
• These parts are linked and work together to
transfer data through the UMTS mobile
network.
• 1) The user equipment
• The user equipment is divided into the mobile
station, which is the device itself and the SIM
card, which describes the U-SIM or universal
subscriber identity module.
• The mobile station cannot transmit signals
without the U-SIM.
• The U-SIM performs three main functions,
which include:
• Holding of a subscriber’s identity
• Performing authentication algorithms
• Storing authentication and encryption keys
• 2) The access network
• The access network consists of towers to
which the mobile station connects. These
towers are known as Node B.
• There can be one or more Node Bs depending
on the size of the network.
• Another essential component of the access
network is the radio network controller
(RNC). It processes the data gotten from Node
B connected to it.
• The Node B and RNC composite structure is
known as UMTS terrestrial radio access
network (UTRAN).
• RNC also acts as an admission controller.
• For instance, if a mobile station (e.g., a phone)
wants to transmit through a voice call, and a
particular Node B is congested with other
connected devices, the RNC gives it a new
CDMA code to connect it to an available Node
B.
• 3. The core network
• This is the backbone network. It consists of a
circuit-switched (CS) domain and packet-
switched (PS) domain.
• The circuit-switched domain is the part of the
network responsible for voice calls, while the
packet-switched domain is responsible for
carrying the packet data.
Applications
• Streaming and downloading of videos and audio
YouTube
Social media (or Web 2.0) companies
Internet of Things (IoT)
Mobile e-commerce
Fast internet and intranet
Mobile entertainment (gaming)
Emails and multimedia messages
Video conferences
• When was 4G introduced?
• The fourth generation of mobile technology was
introduced in 2010 in order to meet out the need for
faster speed and better connectivity.
• Airtel was the first company to have launched 4G services
using TD-LTE technology in Kolkata in 2012.
• It was followed by the launch of 4G in Bangalore, Pune,
Chandigarh, Mohali and Panchkula.
• Later, 4G services in India was launched by Aircel,
Vodafone and RJIO.
• What are the features of 4g?
• The features of 4G are :
• Better download speed
• Extremely high voice quality.
• Easy access to Internet, IM, social networks,
streaming media, video calling.
• Higher bandwidth.
• Much faster than 3G
• What are the different Network Standards of
4G?
• There are multiple 4G mobile technology
standards used by different cellular providers
namely,
• LTE (pre – 4G),
• LTE-Advanced(4.5G),
• Note – LTE stands for Long Term Evolution (LTE).
• LTE and VOLTE are new technologies that are
quickly being adopted worldwide.
• What is LTE?
• LTE is a high-speed mobile data technology
that has been developed together by the 3GPP.
• It is based on existing 3G networks
• it supports much higher data rates compared to
those supported by 2G.
• Benefits of LTE
• Improved Coverage
• Additional Security
• Better Network Management
• Improved Services
• What is VOLTE?
• VOLTE stands for Voice over LTE and it is a form
of Voice Over Internet Protocol or VoIP.
• It combines the 2G GPRS technology with
higher data rates that are being used in 3G
networks.
• This has allowed phone calls to be carried
through a data connection instead of the
traditional circuit-switched one.
• What are the differences between LTE and
VOLTE?
• LTE only supports data. This technology is purely
data-based, which means that it is not designed
to handle calls and other types of services.
• VOLTE, on the other hand, can be used for both
calls and data. It does this by combining the
capabilities of 2G GPRS networks with 3G or 4G
LTE networks.
• LTE-Advanced Pro, often referred to as 4.5G or
4.9G, is an intermediate step between 4G LTE
(Long-Term Evolution) and 5G technologies.
• It is designed to enhance the capabilities of
LTE networks, providing improved
performance, increased capacity, and
additional features to meet the growing
demands of mobile communication.
• 4.5G is an intermediate step between 4G and 5G
mobile networks.
• It is an enhancement of 4G LTE technology that
provides faster data speeds and improved network
capacity.
• 4.5G is also known as LTE Advanced Pro or 4G+. It
offers higher data rates, better coverage, and
improved performance compared to 4G, but it is
not as advanced as 5G in terms of speed and
latency.
• applications of 4g
• A user can access a database of street, building, large city etc
• 4G will provide user services at all times, even if the user is
off-site.
• LTE advanced
• 3GPP long term
• It will provide a good opportunity to people anywhere in the
world to continue their education online in a cost-effective
manner, best technology till date
• Camera in traffic light
• Mobile WiMAX
• 4G car
You might also like
- Basic Training Manual Updated 09-05-14Document68 pagesBasic Training Manual Updated 09-05-14PamelaJacksonNo ratings yet
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayFrom EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- One Sim Card ManualDocument16 pagesOne Sim Card ManualUkah FranklinNo ratings yet
- MMS (Multi Media Messaging)Document4 pagesMMS (Multi Media Messaging)bkbenjyNo ratings yet
- Kannel Open Source Sms Gateway UserGuideDocument158 pagesKannel Open Source Sms Gateway UserGuidekdorairajsgNo ratings yet
- CN Notes Unit 5Document13 pagesCN Notes Unit 5Shreya MankarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Network TrendsDocument17 pagesModule 3 - Network TrendsShipra ShaliniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Mobile Network ArchitectureDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - Mobile Network Architecturemanar ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Core To 4G Mobile Communications: Luis Eduardo Sánchez de LoeraDocument26 pagesThe Core To 4G Mobile Communications: Luis Eduardo Sánchez de LoeraEduardo S de LoeraNo ratings yet
- Mod Overlay DesignDocument33 pagesMod Overlay DesignDevarajNo ratings yet
- Presenting By:: Santosh Chenna 116A1D5815Document33 pagesPresenting By:: Santosh Chenna 116A1D5815kavithachennaNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11e-Qos and Comparison of Wifi and UmtsDocument25 pagesIEEE 802.11e-Qos and Comparison of Wifi and Umtsswathi sriniNo ratings yet
- WCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 1Document40 pagesWCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 1Sushíl kanikeNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document12 pagesLec 4xp4bwxnmbkNo ratings yet
- MC MOD 6Document83 pagesMC MOD 6wilaxin634No ratings yet
- Long Term EvolutionDocument32 pagesLong Term Evolutionmkrao_kiranNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 MobileCommunication ShortDocument43 pagesLecture5 MobileCommunication Shortreza danteNo ratings yet
- 17EC81 Module 1 NotesDocument48 pages17EC81 Module 1 NotesHarshitha LNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile Radio CommunicationDocument4 pagesEvolution of Mobile Radio CommunicationmanjuNo ratings yet
- 4G Mobile TechnologyDocument19 pages4G Mobile TechnologyHani TaHaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Cellular NetworksDocument21 pagesChapter 5-Cellular NetworksHuseinNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture INGGRISDocument6 pagesGSM Architecture INGGRISJesika Oktavia1110No ratings yet
- BY Upasana GaikwadDocument30 pagesBY Upasana GaikwadRenu YadavNo ratings yet
- 4G TechnologyDocument21 pages4G TechnologyvigneshknNo ratings yet
- UmtsDocument23 pagesUmtsMitz PaminNo ratings yet
- 3GPP Technologies Evolution From GSM To 5G 1706397791Document7 pages3GPP Technologies Evolution From GSM To 5G 1706397791stNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile Communication: 1G (First Generation Mobile System)Document10 pagesEvolution of Mobile Communication: 1G (First Generation Mobile System)ARUNKUMAR SNo ratings yet
- Generations of Mobile TechDocument12 pagesGenerations of Mobile Techseema fatimaNo ratings yet
- Wcdma (Umts) Tdcdma Cdma2000 Wcdma (Docomo) Td-Scdma Mobiles Bluetooth Homerf/Swap Wap GPRS, HSCSD Edge Camel, inDocument6 pagesWcdma (Umts) Tdcdma Cdma2000 Wcdma (Docomo) Td-Scdma Mobiles Bluetooth Homerf/Swap Wap GPRS, HSCSD Edge Camel, invipin171986No ratings yet
- If6i-Wmn-Unit 3 NotesDocument15 pagesIf6i-Wmn-Unit 3 Notes514 Vaibhavi PawarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Presentation On Telecommunication SystemDocument15 pagesIndustrial Training Presentation On Telecommunication SystemsajalNo ratings yet
- New LTEDocument33 pagesNew LTEVikash YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter#6 Emerging Telecon TechnologiesDocument30 pagesChapter#6 Emerging Telecon TechnologiesYaqoob AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Mobile ComputingDocument178 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Mobile Computinggoraniya reenaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 4 Generation Wireless Networks: Presented by Huiqi ZhangDocument32 pagesIntroduction To 4 Generation Wireless Networks: Presented by Huiqi ZhangAsaadNo ratings yet
- Basic Mobile CommunicationDocument41 pagesBasic Mobile CommunicationParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Module - 1: Drawbacks of IGDocument53 pagesModule - 1: Drawbacks of IGgokulaNo ratings yet
- MCN-Unit-1 - Cellular Concepts - NotesDocument32 pagesMCN-Unit-1 - Cellular Concepts - Notesamey vermaNo ratings yet
- What Is 3GDocument15 pagesWhat Is 3GShampad AyanNo ratings yet
- Module - 1: by Arunabha Ghosh, Jan Zhang, Jefferey Andrews, Riaz MohammedDocument176 pagesModule - 1: by Arunabha Ghosh, Jan Zhang, Jefferey Andrews, Riaz MohammedHarinath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Wap 1Document7 pagesWap 1Sunil PillaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture CellularTechnologies Part2Document78 pagesLecture CellularTechnologies Part2DanishNo ratings yet
- 3G NetworksDocument9 pages3G Networkschenjerai chabaraNo ratings yet
- Mobile Internet Applications RTD 704 /7Document26 pagesMobile Internet Applications RTD 704 /7Isa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture Notes - Wire & Wireless CommunicationDocument22 pages1st Lecture Notes - Wire & Wireless CommunicationJordan-James OlivoNo ratings yet
- Image Encryption Using 2D Chaotic Ma Presented by Nazish KhalidDocument39 pagesImage Encryption Using 2D Chaotic Ma Presented by Nazish KhalidNazish KhalidNo ratings yet
- Modern Communication SystemsDocument27 pagesModern Communication SystemsVicky SinghNo ratings yet
- Iclterpop Section 1Document33 pagesIclterpop Section 1Witto PereNo ratings yet
- 3G Technology in The Wireless Communications: AbstractDocument4 pages3G Technology in The Wireless Communications: AbstractpkmukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 4G NotesDocument7 pages4G NoteskavithachennaNo ratings yet
- Third-Generation Mobile Phones: Digital Voice and DataDocument5 pagesThird-Generation Mobile Phones: Digital Voice and DataShanky KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 AMCS - Week 1 LectureDocument13 pagesUnit 1 AMCS - Week 1 LectureMANASA P (RA2011004010071)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless TechnologyDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Wireless TechnologyOlasupo OkunaiyaNo ratings yet
- 4G Technology: Presented by Varun JayakumarDocument26 pages4G Technology: Presented by Varun JayakumarVarun JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Practical 6 Introducing 4G Technology: BackgroundDocument7 pagesPractical 6 Introducing 4G Technology: BackgroundIshant GohilNo ratings yet
- 3G VS WifiDocument22 pages3G VS WifiAleemuddin Mohd AbdulNo ratings yet
- Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology, Management & GramothanDocument22 pagesSwami Keshvanand Institute of Technology, Management & GramothanSonam BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WCDMA Fundamentals NokiaDocument106 pagesIntroduction To WCDMA Fundamentals NokiaSadasivan Ep100% (2)
- 3G and 4G: From: R.ROHITH (07S41A0533)Document11 pages3G and 4G: From: R.ROHITH (07S41A0533)Pranay RajNo ratings yet
- Networking 2023 - ModDocument114 pagesNetworking 2023 - Modmalindabissoon312No ratings yet
- Generations of Wireless Mobile Systems: Comparison of Channel Capacity For Different Channel TypesDocument2 pagesGenerations of Wireless Mobile Systems: Comparison of Channel Capacity For Different Channel TypesFranch Maverick Arellano LorillaNo ratings yet
- WCC Mod - 2Document12 pagesWCC Mod - 2Robin MishraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: There Are Four Main Types of Wireless NetworksDocument15 pagesWireless Networks: There Are Four Main Types of Wireless NetworksSyed ShahidNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Standard: Muhammad Ali Raza AnjumDocument45 pagesBluetooth Standard: Muhammad Ali Raza AnjumAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- 04 Telephone DiagnosticsDocument19 pages04 Telephone DiagnosticsSalisburNo ratings yet
- RFI Content Delivery PlatformDocument5 pagesRFI Content Delivery PlatformDakshata Vamsi TalasilaNo ratings yet
- 4G Wireless TechnologyDocument22 pages4G Wireless TechnologyAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes - Networking and Internet For IBPS Bank ExamDocument4 pagesComputer Notes - Networking and Internet For IBPS Bank ExamakshitaNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece Vjec 1Document29 pagesDepartment of Ece Vjec 1Surangma ParasharNo ratings yet
- Courses Subject Codes 1. B.A. TAMIL (2008-2009) I YEARDocument48 pagesCourses Subject Codes 1. B.A. TAMIL (2008-2009) I YEARMAdhuNo ratings yet
- An Improved SMS User Interface System To PDFDocument145 pagesAn Improved SMS User Interface System To PDFBwayo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- MCQ On IT 2Document8 pagesMCQ On IT 2udai_chakraborty5511No ratings yet
- MSC Computer Science Syllabus 2012 OnwardsDocument42 pagesMSC Computer Science Syllabus 2012 OnwardsJothi KumarNo ratings yet
- Moviles NokiaDocument27 pagesMoviles Nokiaapi-4528173No ratings yet
- Config Nokia 6600Document3 pagesConfig Nokia 6600Justine ItugotNo ratings yet
- Mobile Testing Interview Question & AnswerDocument10 pagesMobile Testing Interview Question & Answerramakant tyagi100% (1)
- Mobile UsabilityDocument67 pagesMobile Usabilityapi-3859663No ratings yet
- Abbreviations: Class VIII: Ascii Bios DBA ERP GIF HTML I/O JS Mbps Mips PDF FTP VPN Wlan SDDDocument2 pagesAbbreviations: Class VIII: Ascii Bios DBA ERP GIF HTML I/O JS Mbps Mips PDF FTP VPN Wlan SDDShakeelAhmedNo ratings yet
- Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli - 620 024. Master of Computer Application (M.C.A) - Course Structure Under CBCSDocument54 pagesBharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli - 620 024. Master of Computer Application (M.C.A) - Course Structure Under CBCSB. Srini VasanNo ratings yet
- Setting GPRS Semua OperatorDocument2 pagesSetting GPRS Semua OperatorSeptianAryoNo ratings yet
- Mobile Ip & Wap NotesDocument17 pagesMobile Ip & Wap NotesMelissa HobbsNo ratings yet
- Telecom Sector in BangladeshDocument92 pagesTelecom Sector in BangladeshNasir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of AirtelDocument93 pagesMarketing Strategies of AirtelSami ZamaNo ratings yet
- Wireless - Merits & DemeritsDocument10 pagesWireless - Merits & DemeritsAnirudhan RaviNo ratings yet
- Mobile Application Thesis PhilippinesDocument4 pagesMobile Application Thesis Philippinesfjnev0hc100% (2)
- Records Transferred Start Filerfno End Filerfno: Updation Status (From: To: User: 3/21/2011Document17 pagesRecords Transferred Start Filerfno End Filerfno: Updation Status (From: To: User: 3/21/2011ramesh2745No ratings yet
- WAP 450 Data Sheet (2) 1Document2 pagesWAP 450 Data Sheet (2) 1rebin1988No ratings yet
- Videocon MobilesDocument14 pagesVideocon MobilesAvinash MohanNo ratings yet
- RBT System ARBT Subject PDFDocument33 pagesRBT System ARBT Subject PDFbaraharbNo ratings yet