Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsPreposition
Preposition
Uploaded by
Axel Joy AlonPREPOSITION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- List of Different Types of Prepositions With ExamplesDocument15 pagesList of Different Types of Prepositions With ExamplessurajiNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech BDocument7 pagesParts of Speech BCh Bilal AslamNo ratings yet
- English 1 (Structure) : Mulai MateriDocument138 pagesEnglish 1 (Structure) : Mulai MateriMorganNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument31 pagesPronounJoyce Ann CascayanNo ratings yet
- Anthony The Preposition Boy HeheheDocument21 pagesAnthony The Preposition Boy HeheheNeshele Ann ApostolNo ratings yet
- 3rdQEnglish 10 Week 7Document62 pages3rdQEnglish 10 Week 7arshpogi123No ratings yet
- Anthony The Preposition Boy HeheheDocument23 pagesAnthony The Preposition Boy HeheheNeshele Ann Apostol SulpotNo ratings yet
- Have Fun With Prepositions!!Document18 pagesHave Fun With Prepositions!!Calida Royce D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- PEL 174 Comprehension and Communication Skills in English Lecture BookDocument64 pagesPEL 174 Comprehension and Communication Skills in English Lecture BookOmprakash Singh DhoniNo ratings yet
- Фонетика емтиханDocument4 pagesФонетика емтиханАйжан СактапбергеноваNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 1Document9 pagesParts of Speech 1lhajNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument14 pagesPart of SpeechMuthohar FalahNo ratings yet
- XI1 - Preposition - Haidar Askarul HaqDocument3 pagesXI1 - Preposition - Haidar Askarul HaqHAIDAR ASKARUL HAQNo ratings yet
- PrepositionDocument11 pagesPrepositionWong Jia MingNo ratings yet
- The Parts of Speech: By: Syeda Rifa AnjumDocument39 pagesThe Parts of Speech: By: Syeda Rifa AnjumaNo ratings yet
- El3 Group 2Document28 pagesEl3 Group 2Shemiah GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Part of Speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adjective)Document39 pagesWeek 2 - Part of Speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adjective)Anisa LarasNo ratings yet
- What Is A PrepositionDocument15 pagesWhat Is A PrepositionGeneva SinontaoNo ratings yet
- Modul 8Document8 pagesModul 8Anisya Nada L.H.No ratings yet
- English QuipperDocument29 pagesEnglish QuipperErnie B LabradorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 5Document15 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 5Rj MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 5Document15 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 5Rj MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Preposition: What Is A Preposition?Document13 pagesPreposition: What Is A Preposition?Sam YanNo ratings yet
- TSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Document29 pagesTSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Miziana Suhana Binti Saboo IPGKPINo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument15 pagesPrepositionsdimuthuchathuranga630No ratings yet
- Pronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519Document102 pagesPronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519vivek singhNo ratings yet
- Tugas Artikel AdverbsDocument11 pagesTugas Artikel AdverbsZul ZulpikalNo ratings yet
- PrepositionDocument10 pagesPrepositionNur AsiaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Cheat Sheet To Use With BellworkDocument8 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet To Use With Bellworksaed ahmad100% (1)
- Prespositions and Stative VerbsDocument17 pagesPrespositions and Stative VerbsRodolfo Rudy AguirreNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument6 pagesPrepositionsjaviercossiocalderon2502No ratings yet
- University of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Document47 pagesUniversity of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Sajad HayderNo ratings yet
- Basics of English Grammar-Lecture 2Document13 pagesBasics of English Grammar-Lecture 2Mirza HaseebNo ratings yet
- Preposition and Its TypesDocument10 pagesPreposition and Its TypesShazi Khan100% (1)
- Normalizacao - MinosDocument17 pagesNormalizacao - MinosMinos Moises Curcundes NavaiaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech For AllDocument43 pagesParts of Speech For AllMuhammad TariqNo ratings yet
- Phrasal VerbsDocument24 pagesPhrasal VerbsJoseth PedrazaNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument19 pagesPrepositionsadhvan33No ratings yet
- Quiz IzzDocument42 pagesQuiz Izzsaid.arofatNo ratings yet
- Intro To IS 105 - Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesIntro To IS 105 - Parts of SpeechEki OmallaoNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and Preposition - Team IDocument12 pagesConjunction and Preposition - Team IIqbal RafiNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions Prepositions Interjections Inversionw5Document24 pagesConjunctions Prepositions Interjections Inversionw5Anh-7A-18 Đặng Thu NgaNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF SPEECH-matetDocument9 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH-matetPEMS Ivan Theodore P LopezNo ratings yet
- Noun, Pronoun, AdjectiveDocument24 pagesNoun, Pronoun, AdjectiveZhiHui TayeNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - PREPOSTIONSDocument36 pagesGroup 6 - PREPOSTIONSBarbie DollNo ratings yet
- The Parts of SpeechDocument28 pagesThe Parts of SpeechRita astriyaniNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes Spoken English, Let's Enjoy Learning EnglishDocument21 pagesGrammar Notes Spoken English, Let's Enjoy Learning Englishwww.efrenmaria010600No ratings yet
- Assingment 10Document8 pagesAssingment 10issakamusah649No ratings yet
- Preposition PresentationDocument42 pagesPreposition PresentationWaqas Akram100% (3)
- PrepositionsDocument14 pagesPrepositionsNavyasree GolusulaNo ratings yet
- The Flower in The Vase Is A PeonyDocument8 pagesThe Flower in The Vase Is A PeonySheilah Mae PadallaNo ratings yet
- ADVERBDocument8 pagesADVERBDANES CLAUEI GUHITINGNo ratings yet
- Parts of The SpeechDocument7 pagesParts of The SpeechJessica MereyNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - PrepositionsDocument15 pagesGroup 2 - PrepositionsViaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument39 pagesParts of SpeechRida AkramNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocument42 pagesParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDFirda JinanNo ratings yet
- PREPOSITION TypesDocument13 pagesPREPOSITION TypesRonesa OmarNo ratings yet
- The Parts of Speech: Miss AriniDocument31 pagesThe Parts of Speech: Miss AriniMochamed HasyimNo ratings yet
- Degrees of ComparisionDocument22 pagesDegrees of ComparisionPothukuchi Krishna MohanNo ratings yet
- Use of English Continuidad. 18-24 Mayo AKDocument3 pagesUse of English Continuidad. 18-24 Mayo AKLucía RiveroNo ratings yet
- GCSE French Grammar Booklet by Saraherowland and OllieMFLDocument27 pagesGCSE French Grammar Booklet by Saraherowland and OllieMFLDharm GajjarNo ratings yet
- The 'Get' MasterclassDocument17 pagesThe 'Get' MasterclassGatluak Thalow KuethNo ratings yet
- Unit10. Lexis. Characteristics of Word Formation in English. Prefixation, Suffixation and Compounding.Document5 pagesUnit10. Lexis. Characteristics of Word Formation in English. Prefixation, Suffixation and Compounding.Miriam Reinoso SánchezNo ratings yet
- PrepositionDocument8 pagesPrepositionDebabrat SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Mastering JCE English 2nd EdDocument274 pagesMastering JCE English 2nd Edlapozodestiny4No ratings yet
- 01 13 Page English Foundation FinalDocument13 pages01 13 Page English Foundation Finalmunirjon123No ratings yet
- INTERCHANGE 2 - QUIZ UNITS 5 & 6 - Revisión Del IntentoDocument5 pagesINTERCHANGE 2 - QUIZ UNITS 5 & 6 - Revisión Del IntentoJorge GrajalesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document16 pagesLecture 2kundyz083No ratings yet
- A1-C2 Data EnglishprofileDocument1,004 pagesA1-C2 Data Englishprofilefumarov0930No ratings yet
- English I - Nouns - QuizizzDocument6 pagesEnglish I - Nouns - QuizizzRukhma SajidNo ratings yet
- Contents - 4 High Note 4Document1 pageContents - 4 High Note 4t.mohd.hamdanNo ratings yet
- Personalized ExerciseDocument12 pagesPersonalized ExercisePhan OanhNo ratings yet
- English3 Q4 W2Document19 pagesEnglish3 Q4 W2Marie RavsNo ratings yet
- Modul Advanced Grammar FixDocument57 pagesModul Advanced Grammar FixSsyfaaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesParts of SpeechnaswaauliaaaaNo ratings yet
- Nouns 1Document3 pagesNouns 1mostarjelicaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 PhraseDocument18 pagesGroup 1 PhraseMoh. Ridho FauzanNo ratings yet
- Materi Asking For and Giving DirectionDocument4 pagesMateri Asking For and Giving Directionwinersarif666No ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs-103Document2 pagesIrregular Verbs-103nguyenquangNo ratings yet
- Great Thinkers b2+ Vocabulary Unit 6+ ExercisesDocument2 pagesGreat Thinkers b2+ Vocabulary Unit 6+ ExercisesRaquelNo ratings yet
- Grammar Examination Answer Key (Third Term)Document8 pagesGrammar Examination Answer Key (Third Term)steve LNo ratings yet
- 2600 - Idioms and Phrases FinalDocument353 pages2600 - Idioms and Phrases Finaltadvikunik5No ratings yet
- Quiz On Modal VerbsDocument9 pagesQuiz On Modal VerbsRaheel Abbas100% (1)
- Phrase Versus ClauseDocument4 pagesPhrase Versus Clausegoldennyeche080No ratings yet
- Grammar GNS 101 - 045314Document23 pagesGrammar GNS 101 - 045314Juicy LipsNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Review PracticeDocument2 pagesParts of Speech Review PracticeismailhazlaouiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar (Direct and Indirect Speech)Document13 pagesEnglish Grammar (Direct and Indirect Speech)aditya prabhakarNo ratings yet
Preposition
Preposition
Uploaded by
Axel Joy Alon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views35 pagesPREPOSITION
Original Title
preposition
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPREPOSITION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views35 pagesPreposition
Preposition
Uploaded by
Axel Joy AlonPREPOSITION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 35
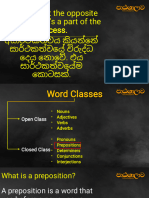
PREPOSITION
A preposition is a word or group of
words used before a noun,
pronoun, or noun phrase to show
direction, time, place, location,
spatial relationships, or to
introduce an object.
Some examples of prepositions are
words like “in”, “at”, “on”, “of”, “to”,
etc.
1. I am heading to Bacolod City.
I am heading to Bacolod City.
2. Participants have gone out of the lake.
Participants have gone out of the lake.
Types of
Preposition
Types of
Prepositions Simple Preposition
Simple prepositions are the short words
used to determine a relation between
nouns, pronouns or even to join parts of
a clause or sentence.
Some examples of simple prepositions are
on, in, off, over, at, to, by, above, near, with,
for, but, behind, from, beside, during, down,
and under.
1. The kitty is sitting on the chair.
The kitty is sitting on the chair.
2. I was fascinated by his talent.
I was fascinated by his talent.
Types of
Prepositions Double Preposition
Double preposition is a word that is
made by the combination of two simple
prepositions made into one word to
make a whole new word.
Some examples of double prepositions are in
between, from within, out of, inside of, up to,
onto, upon, into, from behind, outside of,
within, and without.
1. The snake has gone out of control.
The snake has gone out of control.
2. The monkey climbed onto the poles.
The monkey climbed onto the poles.
Types of
Prepositions Compound Preposition
Compound preposition is a preposition
that has two or more prepositional words.
They are written by joining the
preposition words in a sentence before the
pronoun, noun, adjective, and adverb.
Some examples of compound prepositions are on
behalf of, according to, in addition to, aside from,
with a view to, in the middle of, from beneath, in
front of, across from, in place of, in regard to, in
spite of.
1. Meryll dressed according to the dress code.
Meryll dressed according to the dress code.
2. He has a shop across the street.
He has a shop across the street.
Difference of Double and Compound Preposition
Double preposition is a mix of two
basic prepositions made into a single
word while compound preposition is a
blend of a preposition and a non-
preposition.
Types of
Prepositions Participle Preposition
Participle preposition (also called
participial preposition) is a participle
that is use as preposition and it is a verb
ending with ‘-ing’, ‘-en’, or ‘-ed’,
Some examples of participle prepositions are
considering, touching, following, failing, accepting,
saving, respected, given, gone, taken, provided, etc.
1. He was sad, given the fact he secured fewer
marks.
He was sad, given the fact he secured fewer marks.
2. The puppy kept following me through the market.
The puppy kept following me through the market.
Types of
Prepositions Disguised Preposition
Disguised preposition is a preposition
that is not directly used or implemented
in a sentence but is mentioned
indirectly.
Some examples of disguised prepositions
are “a” and “o”
1. He usually wakes up at 6 o’clock (of the
clock).
He usually wakes up at 6 o’clock (of the clock).
2. Rena went a shore (onshore).
Rena went a shore (onshore).
Types of
Prepositions Detached Preposition
Detached preposition refers to a
preposition which has been
detached and moved to the ending
of a statement.
Examples:
1. Whom are you waiting for?
Whom are you waiting for?
2. Are you staring at me?
Are you staring at me?
Types of
Prepositions Time Preposition
Time preposition indicates the
connection of time between noun
and the remaining words of the
sentence.
Types of
Prepositions Time Preposition
For years, months, seasons, centuries
and times of day, use preposition in:
• I first met John in 2015.
I first met John in 2015.
• It is always cold in January.
It is always cold in January.
Types of
Prepositions Time Preposition
For days, dates and specific holiday
days, use preposition on:
• We go to school on Mondays, but not on Sundays.
We go to school on Mondays, but not on Sundays.
• Buy me a present on my birthday.
Buy me a present on my birthday.
Types of
Prepositions Time Preposition
For times, indicators of exception
and festivals, use preposition at:
• I work faster at night.
I work faster at night.
• Her shift finished at 7pm.
Her shift finished at 7pm.
Some examples of time prepositions are
on, at, in, from, to, ago, before, till, for,
since, until, by.
1. She began exercising at 10 a.m.
She began exercising at 10 a.m.
2. Edrian has been unwell since Friday.
Edrian has been unwell since Friday.
Types of
Prepositions Place Preposition
Place preposition depicts the
correlation of place amongst nouns
and the rest of the sentence. Most
common place prepositions are “on”,
“in”, and “at”.
Types of
Prepositions Place Preposition
• On is used when referring to something
with a surface.
• In is used when referring to something that
is inside or within confined boundaries.
• At is used when referring to something at a
specific point.
1. The ball is in the box.
2. The ball is on the box.
3. The ball is under the box.
4. The ball is next to the box.
1. The ball is behind the box.
2. The ball is in front of the box.
3. The ball is between the two boxes.
Types of
Prepositions Movement Preposition
Movement preposition describes
how something or someone moves
from one place to another.
Most commonly used movement
preposition is “to” which usually serves
to highlight that there is movement
towards a specific destination.
1. He has gone on vacation to France.
He has gone on vacation to France.
2. I will go to bed when I am Tired.
I will go to bed when I am Tired.
Types of
Prepositions Thing Preposition
Thing preposition establish a causal
relation amongst nouns and other
components of the statement.
Some examples of thing prepositions are
of, for, by, with, about, etc.
1. This report is about prepositions.
This report is about prepositions.
2. Kyant is dancing with his friends.
Kyant is dancing with his friends.
Types of
Prepositions Phrasal Preposition
Phrasal preposition is a simple
preposition preceded by a word
from another category, such as an
adverb, adjective, or conjunction.
Some examples of phrasal prepositions are
according to, aside from, next to, ahead of,
because of, out of, along with, in spite of, etc.
1. They, along with their kids, went to
Atlanta.
They, along with their kids, went to Atlanta.
2. I am heading out of town.
I am heading out of town.
How to Recognize a Preposition
• Prepositions are almost always
short words, with the majority
having less than six letters.
• One technique people use to
identify a preposition is to
think of a preposition as
anywhere a mouse can go.
Above, below, next to, between,
beyond, through, by, with…
Exercises for you!
1. The bone was _______ the dog.
The bone was for the dog.
2. We are going on vacation _______ August.
We are going on vacation in August.
3. Please put the vase ________ the table.
Please put the vase on the table.
4. I received a present ________ Janet.
I received a present from Janet.
5. School begins ________ Monday.
School begins on Monday.
Thank
you for
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- List of Different Types of Prepositions With ExamplesDocument15 pagesList of Different Types of Prepositions With ExamplessurajiNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech BDocument7 pagesParts of Speech BCh Bilal AslamNo ratings yet
- English 1 (Structure) : Mulai MateriDocument138 pagesEnglish 1 (Structure) : Mulai MateriMorganNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument31 pagesPronounJoyce Ann CascayanNo ratings yet
- Anthony The Preposition Boy HeheheDocument21 pagesAnthony The Preposition Boy HeheheNeshele Ann ApostolNo ratings yet
- 3rdQEnglish 10 Week 7Document62 pages3rdQEnglish 10 Week 7arshpogi123No ratings yet
- Anthony The Preposition Boy HeheheDocument23 pagesAnthony The Preposition Boy HeheheNeshele Ann Apostol SulpotNo ratings yet
- Have Fun With Prepositions!!Document18 pagesHave Fun With Prepositions!!Calida Royce D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- PEL 174 Comprehension and Communication Skills in English Lecture BookDocument64 pagesPEL 174 Comprehension and Communication Skills in English Lecture BookOmprakash Singh DhoniNo ratings yet
- Фонетика емтиханDocument4 pagesФонетика емтиханАйжан СактапбергеноваNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 1Document9 pagesParts of Speech 1lhajNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument14 pagesPart of SpeechMuthohar FalahNo ratings yet
- XI1 - Preposition - Haidar Askarul HaqDocument3 pagesXI1 - Preposition - Haidar Askarul HaqHAIDAR ASKARUL HAQNo ratings yet
- PrepositionDocument11 pagesPrepositionWong Jia MingNo ratings yet
- The Parts of Speech: By: Syeda Rifa AnjumDocument39 pagesThe Parts of Speech: By: Syeda Rifa AnjumaNo ratings yet
- El3 Group 2Document28 pagesEl3 Group 2Shemiah GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Part of Speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adjective)Document39 pagesWeek 2 - Part of Speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adjective)Anisa LarasNo ratings yet
- What Is A PrepositionDocument15 pagesWhat Is A PrepositionGeneva SinontaoNo ratings yet
- Modul 8Document8 pagesModul 8Anisya Nada L.H.No ratings yet
- English QuipperDocument29 pagesEnglish QuipperErnie B LabradorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 5Document15 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 5Rj MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 5Document15 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 5Rj MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Preposition: What Is A Preposition?Document13 pagesPreposition: What Is A Preposition?Sam YanNo ratings yet
- TSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Document29 pagesTSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Miziana Suhana Binti Saboo IPGKPINo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument15 pagesPrepositionsdimuthuchathuranga630No ratings yet
- Pronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519Document102 pagesPronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519vivek singhNo ratings yet
- Tugas Artikel AdverbsDocument11 pagesTugas Artikel AdverbsZul ZulpikalNo ratings yet
- PrepositionDocument10 pagesPrepositionNur AsiaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Cheat Sheet To Use With BellworkDocument8 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet To Use With Bellworksaed ahmad100% (1)
- Prespositions and Stative VerbsDocument17 pagesPrespositions and Stative VerbsRodolfo Rudy AguirreNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument6 pagesPrepositionsjaviercossiocalderon2502No ratings yet
- University of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Document47 pagesUniversity of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Sajad HayderNo ratings yet
- Basics of English Grammar-Lecture 2Document13 pagesBasics of English Grammar-Lecture 2Mirza HaseebNo ratings yet
- Preposition and Its TypesDocument10 pagesPreposition and Its TypesShazi Khan100% (1)
- Normalizacao - MinosDocument17 pagesNormalizacao - MinosMinos Moises Curcundes NavaiaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech For AllDocument43 pagesParts of Speech For AllMuhammad TariqNo ratings yet
- Phrasal VerbsDocument24 pagesPhrasal VerbsJoseth PedrazaNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument19 pagesPrepositionsadhvan33No ratings yet
- Quiz IzzDocument42 pagesQuiz Izzsaid.arofatNo ratings yet
- Intro To IS 105 - Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesIntro To IS 105 - Parts of SpeechEki OmallaoNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and Preposition - Team IDocument12 pagesConjunction and Preposition - Team IIqbal RafiNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions Prepositions Interjections Inversionw5Document24 pagesConjunctions Prepositions Interjections Inversionw5Anh-7A-18 Đặng Thu NgaNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF SPEECH-matetDocument9 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH-matetPEMS Ivan Theodore P LopezNo ratings yet
- Noun, Pronoun, AdjectiveDocument24 pagesNoun, Pronoun, AdjectiveZhiHui TayeNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - PREPOSTIONSDocument36 pagesGroup 6 - PREPOSTIONSBarbie DollNo ratings yet
- The Parts of SpeechDocument28 pagesThe Parts of SpeechRita astriyaniNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes Spoken English, Let's Enjoy Learning EnglishDocument21 pagesGrammar Notes Spoken English, Let's Enjoy Learning Englishwww.efrenmaria010600No ratings yet
- Assingment 10Document8 pagesAssingment 10issakamusah649No ratings yet
- Preposition PresentationDocument42 pagesPreposition PresentationWaqas Akram100% (3)
- PrepositionsDocument14 pagesPrepositionsNavyasree GolusulaNo ratings yet
- The Flower in The Vase Is A PeonyDocument8 pagesThe Flower in The Vase Is A PeonySheilah Mae PadallaNo ratings yet
- ADVERBDocument8 pagesADVERBDANES CLAUEI GUHITINGNo ratings yet
- Parts of The SpeechDocument7 pagesParts of The SpeechJessica MereyNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - PrepositionsDocument15 pagesGroup 2 - PrepositionsViaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument39 pagesParts of SpeechRida AkramNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDocument42 pagesParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDFirda JinanNo ratings yet
- PREPOSITION TypesDocument13 pagesPREPOSITION TypesRonesa OmarNo ratings yet
- The Parts of Speech: Miss AriniDocument31 pagesThe Parts of Speech: Miss AriniMochamed HasyimNo ratings yet
- Degrees of ComparisionDocument22 pagesDegrees of ComparisionPothukuchi Krishna MohanNo ratings yet
- Use of English Continuidad. 18-24 Mayo AKDocument3 pagesUse of English Continuidad. 18-24 Mayo AKLucía RiveroNo ratings yet
- GCSE French Grammar Booklet by Saraherowland and OllieMFLDocument27 pagesGCSE French Grammar Booklet by Saraherowland and OllieMFLDharm GajjarNo ratings yet
- The 'Get' MasterclassDocument17 pagesThe 'Get' MasterclassGatluak Thalow KuethNo ratings yet
- Unit10. Lexis. Characteristics of Word Formation in English. Prefixation, Suffixation and Compounding.Document5 pagesUnit10. Lexis. Characteristics of Word Formation in English. Prefixation, Suffixation and Compounding.Miriam Reinoso SánchezNo ratings yet
- PrepositionDocument8 pagesPrepositionDebabrat SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Mastering JCE English 2nd EdDocument274 pagesMastering JCE English 2nd Edlapozodestiny4No ratings yet
- 01 13 Page English Foundation FinalDocument13 pages01 13 Page English Foundation Finalmunirjon123No ratings yet
- INTERCHANGE 2 - QUIZ UNITS 5 & 6 - Revisión Del IntentoDocument5 pagesINTERCHANGE 2 - QUIZ UNITS 5 & 6 - Revisión Del IntentoJorge GrajalesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document16 pagesLecture 2kundyz083No ratings yet
- A1-C2 Data EnglishprofileDocument1,004 pagesA1-C2 Data Englishprofilefumarov0930No ratings yet
- English I - Nouns - QuizizzDocument6 pagesEnglish I - Nouns - QuizizzRukhma SajidNo ratings yet
- Contents - 4 High Note 4Document1 pageContents - 4 High Note 4t.mohd.hamdanNo ratings yet
- Personalized ExerciseDocument12 pagesPersonalized ExercisePhan OanhNo ratings yet
- English3 Q4 W2Document19 pagesEnglish3 Q4 W2Marie RavsNo ratings yet
- Modul Advanced Grammar FixDocument57 pagesModul Advanced Grammar FixSsyfaaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesParts of SpeechnaswaauliaaaaNo ratings yet
- Nouns 1Document3 pagesNouns 1mostarjelicaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 PhraseDocument18 pagesGroup 1 PhraseMoh. Ridho FauzanNo ratings yet
- Materi Asking For and Giving DirectionDocument4 pagesMateri Asking For and Giving Directionwinersarif666No ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs-103Document2 pagesIrregular Verbs-103nguyenquangNo ratings yet
- Great Thinkers b2+ Vocabulary Unit 6+ ExercisesDocument2 pagesGreat Thinkers b2+ Vocabulary Unit 6+ ExercisesRaquelNo ratings yet
- Grammar Examination Answer Key (Third Term)Document8 pagesGrammar Examination Answer Key (Third Term)steve LNo ratings yet
- 2600 - Idioms and Phrases FinalDocument353 pages2600 - Idioms and Phrases Finaltadvikunik5No ratings yet
- Quiz On Modal VerbsDocument9 pagesQuiz On Modal VerbsRaheel Abbas100% (1)
- Phrase Versus ClauseDocument4 pagesPhrase Versus Clausegoldennyeche080No ratings yet
- Grammar GNS 101 - 045314Document23 pagesGrammar GNS 101 - 045314Juicy LipsNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Review PracticeDocument2 pagesParts of Speech Review PracticeismailhazlaouiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar (Direct and Indirect Speech)Document13 pagesEnglish Grammar (Direct and Indirect Speech)aditya prabhakarNo ratings yet