Professional Documents
Culture Documents
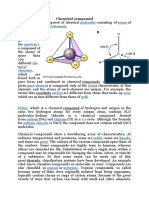
Viscose Rayon Fiber
Viscose Rayon Fiber
Uploaded by
Ruddro Islam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views20 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views20 pagesViscose Rayon Fiber
Viscose Rayon Fiber
Uploaded by
Ruddro IslamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
Textile Fiber II (Tex-229)
4. Viscose rayon fiber
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 1
Introduction
● Viscose is the naturally regenerated cellulosic fibre.
● can be made from naturally occurring cellulosic based material.
Such as cotton, linters, wood pulp.
● It can be found in cotton like end uses as well as silk like end uses .
● In 1924, a committee formed by the U.S. Department of Commerce
and various commercial associations decided upon the name
"rayon" for "Artificial Silk".
● It was called "rayon" for one of two reasons: either because of its
brightness and similarities in structure with cotton (sun = ray, on =
cotton).
● The name Viscose was derived from the word “viscous” which
means sticky spinning solution out of which “Rayon” was
manufactured.
● Thus the innovative cellulosic derivative has taken the present name
of “Viscose rayon”
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 2
Characteristics of viscose
● Highly absorbent
● Soft and comfortable
● Easy to dye
● Drapes well
● Versatile
● It does not shrink when heated
● It is bio degradable
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 3
Flow chart of Viscose fiber production
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 4
Purification of Cellulose
● Trees are cut into pieces.
● These pieces are cooked with a solution of calcium
bisulphate [Ca (HSO3)2] under pressure for 14 Hrs.
● The lignin material present in the wood is converted
into sulphonated compound. This sulphonated
compound is soluble in water.
● After cooking wood with calciurn bisulphate large
amount of water is added. When cellulose pulp floats
on water it is then sucked.
● Then this sucked slurry of cellulose is treated with
bleaching agent. Which is finally converted into
paperboards or sheets.
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 5
Conditioning
● Cellulose sheets/paperboards are kept in a
room at a definite temperature and
humidity for a sufficient time.
● When they absorb a definite amount of
moisture from the air by storing the sheets
under controlled conditions
● it is possible to take a known weight of
cellulose for manufacturing of viscose
rayon.
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 6
Steeping and Pressing
● In this process, white sheets of board containing 90-94% pure
cellulose are soaked in a 17.5 % caustic soda for one to four hours.
This process is known as steeping or mercerizing.
● The boards become greatly swollen and the hemicellulose dissolves
in the caustic soda.
● Here cellulose is simultaneously converted into soda cellulose. The
excess caustic soda liquor along with dissolved hemi cellulose is
removed by pressing.
● This then transferred to shredding machine for the next operation.
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 7
Shredding & Ageing
● The soda cellulose is mechanically shredded to make
the cellulose easier to process.
● This shredded cellulose is often referred to as “white
crumb”.
● After shredding, the crumbs are aged. Ageing is done to
improve the spinning qualities of the solutions.
● The crumbs delivered by shredding process are stored
in a galvanized vessel with a lid for about 48 hours at
230C.
● Through the oxidation with atmospheric oxygen,
degradative changes set in.
● Some depolymerisation occurs, and degree of
polymerization falls from 1000 to 300 (350 in some
cases) in this process.
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 8
Churning/Xanthation
● This process is also called as Xanthation or Sulpholising.
● After ageing process crumbs of-soda cellulose are transferred to
rotating airtight hexagonal churners (mixers).
● Carbon disulphide is added to the mixer and churned together for
3Hrs. by rotating the mixer at a slow speed i.e. 2rpm.
● In this process soda cellulose xanthate is formed and color of the
product changes from white to light yellow to deep blue and then to
reddish orange.
● After churning is over vacuum is applied to remove the ill smelling
vapours of carbon disulphide from the mixer.
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 9
Dissolving/Mixing
● In the mixers the sodium cellulose xanthate is
stirred with dilute caustic soda solution for four to
five hours, the vessel being cooled. The xanthate
dissolves to a clear-brown, viscous liquid similar
in appearance to honey.
● The soda cellulose Xanthate dissolves to give a
clear brown thick liquor, which is called as
viscose.
● Filtration is also done to remove undissolved
portion from the wood pulp. During stirring air gets
entrapped in the solution. Hence degassing is
also carried out to remove entrapped air.
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 10
Ripening
● Viscose solutions require to be ripened to give
a solution having the best spinning qualities.
● The viscose solution is stored for 2 to 5 days at
10-18oC and during storage it ripens.
● Viscosity of the solution initially decreases and
then rises to get original value.
● Ripened solution is again filtered to remove
undissolved materials that might disrupt the
spinning process or cause defects in the rayon
filament.
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 11
Spinning
● The spinning solution is kept at 40-450C, sodium sulphate coagulates
or precipitates the dissolved sodium cellulose Xanthate
● Sulphuric acid converts Xanthate into cellulose glucose and gives
softness and pliability to the filament.
● In spinning process ripened viscose solution is forced by compressed
air to spinning frame.
● From spinning frame it is distributed to different spinning units. And
spinning solutions is discharged from nozzles to a spinning bath.
● As a number of filaments emerge from the spinneret they are taken
together to an eye at the surface of the spinning bath and then guided
to two rollers.
● Spinning bath contains chemicals which are represented in Table 1
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 12
Reactions involved
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 13
Chemical reactions for viscose production
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 14
Chemical Structure :
● Chemical structure is like as cotton. i.e
cellulose , but the polymer chain are
much shorter.
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 15
Identification
Microscopic view : 2. Cross-Sectional View
⮚ Irregular with a serrated
1.Longitudinal View: outline
🠶 Normal type fairly dense ⮚ Oval or round
longitudinal striations or
fine line
🠶 Special type-may be
smooth and Structure less
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 16
Physical properties of viscose as compared to cotton
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 17
Chemical properties of viscose
● Acids like H2SO4, HCL breaks the cellulose to
hydrocellulose.
● Oxidising agents like Na(OCL)2, bleaching
powder, K2Cr2O7,KMnO4, form oxycellulose.
● Cold acid solution for a short time do not attack
viscose
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 18
End uses
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 19
Thanks to all
08/08/2021 SEU, DTE 20
You might also like
- Test Module 1 Apologia General ScienceDocument2 pagesTest Module 1 Apologia General ScienceMelissa Brent Furman75% (4)
- The Breakup CureDocument168 pagesThe Breakup CureMladen Muskinja100% (2)
- Solvent Dyeing PDFDocument23 pagesSolvent Dyeing PDFDhrubo Adhikary100% (1)
- What Is Colloidal SilicaDocument5 pagesWhat Is Colloidal SilicaJmt IndiaNo ratings yet
- Report On Rayon FibresDocument7 pagesReport On Rayon FibresMomin ShahNo ratings yet
- A Guide to the Wet Plate Process of Photography - Camera Series Vol. XVIII. - A Selection of Classic Articles on Development, Fixing, Chemicals andFrom EverandA Guide to the Wet Plate Process of Photography - Camera Series Vol. XVIII. - A Selection of Classic Articles on Development, Fixing, Chemicals andNo ratings yet
- Tex-201 (2.1) Regenerated Cellulosic Fibres (S-5)Document65 pagesTex-201 (2.1) Regenerated Cellulosic Fibres (S-5)helloNo ratings yet
- Regenerated Cellulose Fibers Viscose: Farzana Faiza Lecturer, AUSTDocument12 pagesRegenerated Cellulose Fibers Viscose: Farzana Faiza Lecturer, AUSTMustafiz RahmanNo ratings yet
- Viscose RayonDocument30 pagesViscose Rayonnaimur.7566No ratings yet
- Properties of ViscoseDocument2 pagesProperties of Viscosesureshparekh023No ratings yet
- Rayon DyeingDocument26 pagesRayon Dyeingtkr163100% (1)
- Viscose Rayon NotesDocument11 pagesViscose Rayon NotesAnkur Vaidya100% (1)
- Regenerated FibresDocument31 pagesRegenerated Fibreszxy_cbe100% (1)
- Textilelearner - Blogspot.ca-Rayon Fiber Characteristics of Rayon Fiber Manufacturing Process of Viscose Rayon End Uses of RayoDocument4 pagesTextilelearner - Blogspot.ca-Rayon Fiber Characteristics of Rayon Fiber Manufacturing Process of Viscose Rayon End Uses of Rayolyouf100% (1)
- Viscose RayonDocument3 pagesViscose Rayonmaya_muthNo ratings yet
- Cellulose Plastics: by Lakhan SinghDocument17 pagesCellulose Plastics: by Lakhan SinghlakhancipetNo ratings yet
- Viscose Fiber Production ProcessDocument6 pagesViscose Fiber Production Processadityasirawale100% (1)
- Regular Rayon (Or Viscose) Is The Most Widely Produced Form of Rayon. This Method of RayonDocument11 pagesRegular Rayon (Or Viscose) Is The Most Widely Produced Form of Rayon. This Method of RayonManda Ramesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 IIDocument34 pagesLecture 3 IINadeeka TisseraNo ratings yet
- What Is Rayon? Describe The Basic Principle of Viscose Process To Produce RayonDocument2 pagesWhat Is Rayon? Describe The Basic Principle of Viscose Process To Produce RayonMOJAHID HASAN Fall 19No ratings yet
- خط الصناعةDocument14 pagesخط الصناعةمحمد السعيديNo ratings yet
- Cassava Resins Outline 111Document7 pagesCassava Resins Outline 111Jenilyn Castro GallegoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectParthiv MandalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 SPONGE AND MICROCELLULAR RUBBER LecturerDocument41 pagesCHAPTER 2 SPONGE AND MICROCELLULAR RUBBER LecturerMuhd BazliNo ratings yet
- Man-Made Fibres GLDocument5 pagesMan-Made Fibres GLLinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Gun CottonDocument8 pagesGun CottonwahnobeldfNo ratings yet
- Preperation of Rayon ThreadsDocument16 pagesPreperation of Rayon ThreadsjyothisreemurthyNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYgatherbouttechNo ratings yet
- Viscose FiberDocument19 pagesViscose FiberSourabh Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Spinning Process and Synthetic FibersDocument48 pagesSpinning Process and Synthetic FibersSivaganesh babuNo ratings yet
- Chem Project RAYON THREADDocument15 pagesChem Project RAYON THREADdeath cupidNo ratings yet
- LYOCELLDocument5 pagesLYOCELLKingson_786100% (1)
- Apn 4 05 01Document2 pagesApn 4 05 01fperezbrNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Rubber PDFDocument8 pagesSynthetic Rubber PDFmjunaidNo ratings yet
- Latex Compounds: Dunlop Latices For Dipping & MouldingDocument8 pagesLatex Compounds: Dunlop Latices For Dipping & MouldingThushara RavindraNo ratings yet
- RayonDocument9 pagesRayonRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Making Rayon FiberDocument15 pagesMaking Rayon FibernatarajantexNo ratings yet
- Glass ManufacturingDocument26 pagesGlass ManufacturingJoana Laxela CalmaNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatmen T and Disposal: MSV - N180478 Ashok - N180282Document18 pagesSludge Treatmen T and Disposal: MSV - N180478 Ashok - N180282saiganeshmadasuNo ratings yet
- 4.3 SingeingDocument18 pages4.3 SingeingManoja SamarasingheNo ratings yet
- Tech Report - Sheet Glass ManufacturingDocument25 pagesTech Report - Sheet Glass ManufacturingSom777100% (1)
- Cellulose Ethers: Technical Overview and Product GuideDocument8 pagesCellulose Ethers: Technical Overview and Product GuideIdo RevelNo ratings yet
- AffanDocument9 pagesAffanAshnab Zahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Growing Paints On Trees: Quelle/Publication: Ausgabe/Issue: Seite/Page: European Coatings Journal 12/2005 36Document8 pagesGrowing Paints On Trees: Quelle/Publication: Ausgabe/Issue: Seite/Page: European Coatings Journal 12/2005 36Ahmad Ma'rupNo ratings yet
- Cellulose Ethers: 2006 Wiley-Vch Verlag GMBH & Co. Kgaa, WeinheimDocument18 pagesCellulose Ethers: 2006 Wiley-Vch Verlag GMBH & Co. Kgaa, WeinheimjaimeNo ratings yet
- Final Reports Re Yash IDocument49 pagesFinal Reports Re Yash IsreyashidipanjanaNo ratings yet
- Abstarct:: What Is Modal: DefinitionDocument5 pagesAbstarct:: What Is Modal: DefinitionYashNo ratings yet
- Cellulose Based CoatingsDocument8 pagesCellulose Based CoatingsJHuvieCLaireNo ratings yet
- Advanced Ship Building Materials Lesson 2Document36 pagesAdvanced Ship Building Materials Lesson 2Chanaka DilshanNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemistry - Is Matter Around Us Pure - Notes & Video LinkDocument8 pages9 Chemistry - Is Matter Around Us Pure - Notes & Video LinkYash TripathiNo ratings yet
- Abdi Be (Copy)Document8 pagesAbdi Be (Copy)Milkias SolomonNo ratings yet
- Elastomeric Impression Material..Document57 pagesElastomeric Impression Material..asha docNo ratings yet
- Dental MaterialsDocument10 pagesDental MaterialsAL-ABATCHI -10No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistrygatherbouttechNo ratings yet
- Rayon: Purvisha NadkarniDocument20 pagesRayon: Purvisha NadkarniChristopherGunawanNo ratings yet
- Natural RubberDocument7 pagesNatural RubberFrancis AdrianNo ratings yet
- Lecture Glass IndustryDocument41 pagesLecture Glass IndustryUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Scouring AgentDocument8 pagesScouring AgenthtfinechemNo ratings yet
- Paper N PulpDocument20 pagesPaper N Pulpashnasaifudeen7No ratings yet
- Glass Recycling Process: By: Charo Mel TabloDocument42 pagesGlass Recycling Process: By: Charo Mel TabloCharo Mel TabloNo ratings yet
- Baff Iguana Project ReportDocument22 pagesBaff Iguana Project ReportCharukaNo ratings yet
- The Art of Paper-Making: A Practical Handbook of the Manufacture of Paper from Rags, Esparto, Straw, and Other Fibrous Materials, Including the Manufacture of Pulp from Wood FibreFrom EverandThe Art of Paper-Making: A Practical Handbook of the Manufacture of Paper from Rags, Esparto, Straw, and Other Fibrous Materials, Including the Manufacture of Pulp from Wood FibreNo ratings yet
- Central Air Conditioning: Systems and Applications: November 2019Document21 pagesCentral Air Conditioning: Systems and Applications: November 2019Ruddro IslamNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Plant 1Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Plant 1Ruddro IslamNo ratings yet
- Ruddrosurveyreport 1Document14 pagesRuddrosurveyreport 1Ruddro IslamNo ratings yet
- Survey On Color Preferences (Responses)Document259 pagesSurvey On Color Preferences (Responses)Ruddro IslamNo ratings yet
- Survey On Color PreferencesDocument67 pagesSurvey On Color PreferencesRuddro IslamNo ratings yet
- CV 2024050501004450Document2 pagesCV 2024050501004450Ruddro IslamNo ratings yet
- CV 2024050500595131Document2 pagesCV 2024050500595131Ruddro IslamNo ratings yet
- Received 451402035704594Document6 pagesReceived 451402035704594Ruddro IslamNo ratings yet
- 4.sisgp Eligible Master Programmes 2024 2025-UaDocument74 pages4.sisgp Eligible Master Programmes 2024 2025-UaRuddro IslamNo ratings yet
- P Block ChemistryDocument7 pagesP Block ChemistryNcnagesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Interest Rates (Note)Document18 pagesThe Structure of Interest Rates (Note)Hoi Mun100% (1)
- Open Edge Switch Specification v0 5 2 PDFDocument25 pagesOpen Edge Switch Specification v0 5 2 PDFNaser KhoshbakhtNo ratings yet
- 3 Way Electrical Control Valve: TYPE 7562EDocument13 pages3 Way Electrical Control Valve: TYPE 7562EAhmed EmamNo ratings yet
- Story of Siachen-1Document28 pagesStory of Siachen-1Henish KananiNo ratings yet
- Unitarity Constraints in The Two Higgs Doublet ModelDocument5 pagesUnitarity Constraints in The Two Higgs Doublet ModelAndres Castillo RNo ratings yet
- ID26Document21 pagesID26Ashish BaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- Final Week For Brewers To Enter AIBADocument2 pagesFinal Week For Brewers To Enter AIBAWrightsPRNo ratings yet
- J28475 Galnorth Presentation Royal BafokengDocument17 pagesJ28475 Galnorth Presentation Royal BafokengLeeLowersNo ratings yet
- FIG74Document4 pagesFIG74Moez KarouiNo ratings yet
- M Tech SP ADSD Model Question PaperDocument2 pagesM Tech SP ADSD Model Question Papersafu_117No ratings yet
- SERVICIO Ir2530 - 2525Document370 pagesSERVICIO Ir2530 - 2525solser digitalNo ratings yet
- Sikadur®-42 MP Slow - PDSDocument7 pagesSikadur®-42 MP Slow - PDSkamran abbasiNo ratings yet
- Insulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument40 pagesInsulin Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes MellitusEDWIN WIJAYANo ratings yet
- Military Gear Suppliers Expo Attendees.Document32 pagesMilitary Gear Suppliers Expo Attendees.Waf EtanoNo ratings yet
- Branches of Aerodynamics: Conservation LawsDocument2 pagesBranches of Aerodynamics: Conservation LawsKarthiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemical Equilibria of Aqueous Solutions: Che 401: Analytical ChemistryScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: CalfactantDocument1 pageDrug Study: CalfactantAngelokeizer GavinoNo ratings yet
- Narrative Letter Additional AdditionalDocument3 pagesNarrative Letter Additional AdditionalIUSECAPSLOCKNo ratings yet
- Computer Application Unit 1Document9 pagesComputer Application Unit 1Yubraj Chaudhary100% (1)
- Briggs&Stratton Series 450Document24 pagesBriggs&Stratton Series 450djvscribdNo ratings yet
- Ppgj-Pro-Cal-184 Hot Oil Transfer Pump (P-1001 A&b)Document8 pagesPpgj-Pro-Cal-184 Hot Oil Transfer Pump (P-1001 A&b)Tifano KhristiyantoNo ratings yet
- Design of Rigid Pavement CC Road With M25Document5 pagesDesign of Rigid Pavement CC Road With M25pravincs_007No ratings yet
- Systems Biology Approaches To Development Beyond Bioinformatics: Nonlinear Mechanistic Models Using Plant SystemsDocument14 pagesSystems Biology Approaches To Development Beyond Bioinformatics: Nonlinear Mechanistic Models Using Plant SystemsaparnaNo ratings yet
- Radiology in A Trench Coat PDFDocument238 pagesRadiology in A Trench Coat PDFAnantha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Genital Prolapse: Clinical FeaturesDocument29 pagesGenital Prolapse: Clinical FeaturesMerlin AshlyNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Blis 6Document4 pagesBlis 6Syed KabirNo ratings yet