Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsChapter 009
Chapter 009
Uploaded by
dsmith289b
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Final - UFP Skills For Sci Eng - Lab Assessment 2 Instructions 2022-23Document10 pagesFinal - UFP Skills For Sci Eng - Lab Assessment 2 Instructions 2022-23MaharshiGohelNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis PDFDocument286 pagesFunctional Analysis PDFbmandarNo ratings yet
- Stryker X8000 Xenon Light Source Service ManualDocument71 pagesStryker X8000 Xenon Light Source Service Manualrafael gonzalez80% (5)
- Nervous System 1Document13 pagesNervous System 1wasim akhtarNo ratings yet
- SHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022Document16 pagesSHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022kailaskrishnaushusNo ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch16 eDocument9 pagesRev Notes ch16 eEdgar LeungNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Excitable TissueDocument117 pagesExcitable Tissueur.yared21No ratings yet
- The Human Nervous System A2Document33 pagesThe Human Nervous System A2Melody PamireNo ratings yet
- Neural TissueDocument9 pagesNeural TissueJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Nervous SystemDocument117 pagesUnit 11 Nervous SystemChandan Shah100% (1)
- Human Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Nervous SystemUmair BasheerNo ratings yet
- PSY-105 Chapter # 03: Neuro Science and BehaviorDocument9 pagesPSY-105 Chapter # 03: Neuro Science and BehaviorSabbir AhammedNo ratings yet
- ICSE Biology Notes Nervous System For 20 PDFDocument25 pagesICSE Biology Notes Nervous System For 20 PDFMmt RdcNo ratings yet
- Neuron Is The Scientific Name For A Nerve CellDocument10 pagesNeuron Is The Scientific Name For A Nerve Cellirene_bayubaycuteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 22 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- MC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSDocument7 pagesMC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Class 10Document35 pagesNervous System Class 10Just JaenNo ratings yet
- Histology 7 Nerve TissueDocument82 pagesHistology 7 Nerve TissueAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 7 The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCH 7 The Nervous Systemapi-267543553No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document51 pagesUnit 5JAYANT CH (RA2111004010265)No ratings yet
- Unit 5-Immune SystemDocument51 pagesUnit 5-Immune SystemAnih Kishor (RA1911002010062)No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument5 pagesCerebrumShiella Barroga LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Oxford X Cognitive NeuroscienceDocument73 pagesOxford X Cognitive Neurosciencedudong borjaNo ratings yet
- Updated Science 8Document172 pagesUpdated Science 8Manha abdellahNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Khaleel Alyahya, PHD, Med King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelyaDocument31 pagesNervous System: Khaleel Alyahya, PHD, Med King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelyaSalem AlshahraniNo ratings yet
- Physiology For AnesthesiaDocument115 pagesPhysiology For AnesthesiaBahredin AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Human Regulatory SystemDocument37 pagesHuman Regulatory SystemRudolfNo ratings yet
- 2017 Nervous System - YdcDocument104 pages2017 Nervous System - YdcayssNo ratings yet
- Botan's Cns and The Brain 2023Document115 pagesBotan's Cns and The Brain 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesControl and CoordinationShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class X Nervous System NotesDocument20 pagesICSE Class X Nervous System Notesprogrammer.ron.akNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument55 pagesNervous SystemJhemDelfinNo ratings yet
- Note 1 Nervous CoDocument8 pagesNote 1 Nervous ComalshiNo ratings yet
- CH 07 Lecture PresentationDocument25 pagesCH 07 Lecture PresentationMESI JAYVEE F.No ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- Science Sofie 10 3 RevDocument11 pagesScience Sofie 10 3 Revjinxtapperhat07No ratings yet
- 5 The Nervous SystemDocument72 pages5 The Nervous SystemNardos TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: by Dr. K. Sumangala BhatDocument37 pagesNervous System: by Dr. K. Sumangala BhatanushkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1wakaopakao2No ratings yet
- Science 8 PDFDocument172 pagesScience 8 PDFaftab khanNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafDocument31 pagesKonsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafdiandraNo ratings yet
- Nervous System LecDocument26 pagesNervous System LecLuningning Nobleza100% (3)
- Med Surg NotesDocument65 pagesMed Surg NotesAthena ShylaNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document26 pagesWeek 5Avril Ros ReyesNo ratings yet
- Describe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous Systemsiska yantiNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Nervous TissueDocument28 pagesLab 9 Nervous TissueSarwar JafarNo ratings yet
- Samenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 B&CDocument3 pagesSamenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 B&CMarlijn Ter MorsNo ratings yet
- StimuliDocument9 pagesStimuliJAZEEL ASLAMI PANDIKKADNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAnonymous 3OKQDoiJNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument59 pagesCentral Nervous SystemChew Yee SoonNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Nervous System 2021Document64 pages1.introduction To Nervous System 2021Erdem AltunNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Assigment About NeurologyDocument5 pagesAssigment About NeurologyYola NoviyanaNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationDocument107 pagesPoints To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationRagheNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Review Summary NoteDocument117 pagesBiology F4 Review Summary NoteSocdal AbdiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesNervous Systemagyapongruth731No ratings yet
- Homework Fifth Grade Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesHomework Fifth Grade Nervous Systemmed.visionschoolNo ratings yet
- Key Terms: Coordination & Response The Nervous System in MammalsDocument8 pagesKey Terms: Coordination & Response The Nervous System in MammalsheyyoNo ratings yet
- Neural Control & Coordination Part 1 OfflineDocument45 pagesNeural Control & Coordination Part 1 Offlinedivyaasreekumar3No ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue - UpdatedDocument129 pagesNervous Tissue - UpdatedPojangNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- AC Tank Type Test TRFRMR by HAEFELYDocument20 pagesAC Tank Type Test TRFRMR by HAEFELYmadhukarreddy2811No ratings yet
- Ganga Raya Bhandari Analysis Report PDFDocument37 pagesGanga Raya Bhandari Analysis Report PDFsantosh sahNo ratings yet
- Calculus MATH 192 - Lec 1Document10 pagesCalculus MATH 192 - Lec 1ahmadomar89No ratings yet
- ch16 Lecture 8e GOODDocument105 pagesch16 Lecture 8e GOODJana Mae Catot AcabalNo ratings yet
- CEP Assignmnet Number 2 Network AnalysisDocument3 pagesCEP Assignmnet Number 2 Network AnalysisHussain MustafaNo ratings yet
- Vibration ExampleDocument27 pagesVibration ExamplekosarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Physicists: Volker Hohmann Institute of Physics University of Oldenburg, GermanyDocument90 pagesNumerical Methods For Physicists: Volker Hohmann Institute of Physics University of Oldenburg, GermanyAdeyemiNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument51 pagesTransformerMuhammad Husnain RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Math S Practice Paper - 1 QPDocument7 pagesMath S Practice Paper - 1 QPmanviprivateaccNo ratings yet
- FSI-851 (Ion Smoke Detector)Document2 pagesFSI-851 (Ion Smoke Detector)Umair A. MoqeetNo ratings yet
- A Non-Premixed Combustion Model Based On Flame STRDocument59 pagesA Non-Premixed Combustion Model Based On Flame STRCarlos AlarconNo ratings yet
- National Public School WhitefieldDocument2 pagesNational Public School WhitefieldSameera KurhekarNo ratings yet
- Physics: AnswersDocument23 pagesPhysics: AnswersKrishna ChoureyNo ratings yet
- Cpp-Alkyl HalideDocument5 pagesCpp-Alkyl Halidekrishnagamer565No ratings yet
- Midas Civil Application in Box Girder LRT 3Document48 pagesMidas Civil Application in Box Girder LRT 3milkcNo ratings yet
- ZG QCW Handheld Laser WelderDocument6 pagesZG QCW Handheld Laser Welderultra2boxNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components of MHPDocument10 pagesElectrical Components of MHPDiyath VindulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Welded Connections: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manual, 14 EdDocument10 pagesChapter 5 - Welded Connections: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manual, 14 EdINNOBUNo7No ratings yet
- D 6477 - 02 Rdy0nzctmdjbDocument4 pagesD 6477 - 02 Rdy0nzctmdjbJuan GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 6-Estimation of Soot Content in Engine OilDocument2 pages6-Estimation of Soot Content in Engine Oilmahesh8760No ratings yet
- Viscosity - WikipediaDocument35 pagesViscosity - WikipediaHamza MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Pouring Time CalculationDocument5 pagesPouring Time CalculationKaarthicNatarajan100% (1)
- Moodle Updated-2Document200 pagesMoodle Updated-2srlohitkriishnaaNo ratings yet
- Pump System Design PDFDocument21 pagesPump System Design PDFP Priya100% (1)
- Dwnload Full College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3rd Edition Knight Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3rd Edition Knight Test Bank PDFthomasmurphy013t100% (20)
- AS Chemistry Revision Seminar 9701Document32 pagesAS Chemistry Revision Seminar 9701Jhoshna MuniandyNo ratings yet
- COE 105 Chapter3 KinematicsDocument9 pagesCOE 105 Chapter3 Kinematicsjethrocunanan04No ratings yet
Chapter 009
Chapter 009
Uploaded by
dsmith2890 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views40 pagesb
Original Title
Chapter_009
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentb
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views40 pagesChapter 009
Chapter 009
Uploaded by
dsmith289b
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 40
Chapter 9
Nervous System
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Lesson 9.1: Nervous System
Learning Objectives (1 of 2)
1. List the organs and divisions of the nervous system and
describe the generalized functions of the system as a
whole.
2. Identify the major types of cells in the nervous system
and discuss the functions of each.
3. Identify the anatomical components of a reflex arc and
explain its function.
4. Explain the mechanisms of transmission of a nerve
impulse along a nerve fiber and across a synapse.
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 2
Lesson 9.1: Nervous System
Learning Objectives (2 of 2)
5. Identify the major anatomical components of
the brain and spinal cord and briefly comment
on the functions of each.
6. Compare and contrast cranial and spinal
nerves.
7. Discuss the anatomical and functional
characteristics of the two divisions of the
autonomic nervous system.
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 3
Organization of the Nervous
System
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
All nerves
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 4
Cells of the Nervous System
(1 of 2)
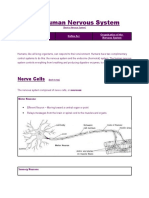
Neurons
Neuron structure: Each neuron consists of three main parts
• Cell body of neuron
• Dendrites: Branching projections that conduct impulses to cell body
of neuron
• Axon: Elongated projection that conducts impulses away from cell
body of neuron
Types of neurons: Classified according to function
• Sensory (afferent) neurons: Conduct impulses to the spinal cord and
brain
• Motor (efferent) neurons: Conduct impulses away from brain and
spinal cord to muscles and glands
• Interneurons: Conduct impulses from sensory neurons to motor
neurons or among a network of interneurons; also known as central
or connecting neurons
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 5
Neuron
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 6
Cells of the Nervous System
(2 of 2)
Glia (neuroglia)
Support cells, bringing the cells of nervous tissue together
structurally and functionally
Three main types of glial cells of the CNS
• Astrocytes: Star-shaped cells that anchor small blood
vessels to neurons
• Microglia: Small cells that move in inflamed brain tissue
carrying on phagocytosis
• Oligodendrocytes: Form myelin sheaths on axons in the CNS
Schwann cells form myelin sheaths on axons of the PNS
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 7
Central Glia
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 8
Nerves and Tracts
Nerve: Bundle of peripheral axons
Tract: Bundle of central axons
White matter: Tissue composed primarily of myelinated axons
(nerves or tracts)
Gray matter: Tissue composed primarily of cell bodies and
unmyelinated fibers
Nerve coverings: Fibrous connective tissue
Endoneurium: Surrounds individual fibers within a nerve
Perineurium: Surrounds a group (fascicle) of nerve fibers
Epineurium: Surrounds the entire nerve
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 9
The Nerve
Courtesy Dr. Richard Kessel, Professor of Biological Sciences, University of Iowa,
Iowa City.
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 10
Nerve Signals
Reflex arcs
Nerve impulses are conducted from receptors
to effectors over neuron pathways or reflex arcs;
conduction by a reflex arc results in a reflex
(i.e., contraction by a muscle or secretion
by a gland)
The simplest reflex arcs are two-neuron arcs, consisting of
sensory neurons synapsing in the spinal cord with motor
neurons
Three-neuron arcs consist of sensory neurons synapsing
in the spinal cord with interneurons that synapse with
motor neurons (Figure 9-5)
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 11
Knee-Jerk Reflex
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 12
Nerve Impulse (1 of 4)
Definition of a nerve impulse
Self-propagating wave of electrical disturbance that
travels along the surface of a neuron membrane (also
called action potential)
Mechanism of a nerve impulse
At rest, the neuron's membrane is slightly positive on
the outside—polarized—from a slight excess of
sodium ions (Na+) on the outside
A stimulus triggers the opening of Na+ channels in the
plasma membrane of the neuron
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 13
Nerve Impulse (2 of 4)
Mechanism of a nerve impulse
Inward movement of Na+ depolarizes the membrane
by making the inside more positive than the outside at
the stimulated point; this depolarization is a nerve
impulse (action potential)
The stimulated section of membrane immediately
repolarizes, but by that time, the depolarization has
already triggered the next section of membrane to
depolarize, thus propagating a wave of electrical
disturbances (depolarizations) all the way down the
membrane
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 14
Nerve Signals (3 of 4)
The synapse: The place where impulses are transmitted
from one neuron to another (the postsynaptic neuron)
(Figure 9-8)
Synapse made of three structures
Synaptic knob
Synaptic cleft
Plasma membrane
Neurotransmitters
Bind to specific receptor molecules in the membrane of a
postsynaptic neuron, opening ion channels and thereby
stimulating impulse conduction by the membrane
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 15
Nerve Signals (4 of 4)
Neurotransmitters: Chemicals by which neurons
communicate
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Catecholamines: Norepinephrine, dopamine, and
serotonin
Endorphins
Enkephalins
Nitric oxide (NO)
Other compounds
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 16
Components of a Synapse
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 17
Central Nervous System
Divisions of the brain
Brainstem
• Medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain
Cerebellum
Diencephalon
• Hypothalamus, thalamus, and pineal gland
Cerebrum
Spinal cord
Coverings and fluid spaces
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 18
Major Regions of the
Central Nervous System
From Vidic B, Suarez FR: Photographic atlas of the human body, St
Louis, 1984, Mosby.
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 19
Brainstem
Consists of three parts of brain, named in ascending
order
Medulla oblongata
Pons
Midbrain
Structure
White matter with bits of gray matter scattered through it
Functions
All three parts of brainstem conduct impulses to the higher
parts of the brain
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 20
Cerebellum
Structure
Second largest part of the human brain
Gray matter outer layer is thin but highly folded, forming a large
surface area for processing information
Arbor vitae: Internal, treelike network of white matter tracts
Functions
Helps control muscle contractions to produce coordinated
movements for maintaining balance, moving smoothly, and
sustaining normal postures
Variety of additional coordinating effects, assisting the cerebrum
and other regions of the brain
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 21
Diencephalon (1 of 2)
Hypothalamus
Consists mainly of the posterior pituitary gland, pituitary stalk,
and gray matter
Acts as the major center for controlling the ANS; therefore, it
helps control the functioning of most internal organs
Controls hormone secretion by anterior and posterior pituitary
glands; therefore, it indirectly helps control hormone secretion by
most other endocrine glands
Contains centers for controlling body temperature, appetite,
wakefulness, and pleasure
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 22
Diencephalon (2 of 2)
Thalamus
Dumbbell-shaped mass of gray matter extending toward each
cerebral hemisphere
Relays sensory impulses to cerebral cortex sensory areas
In some way produces the emotions of pleasantness or
unpleasantness associated with sensations
Pineal gland (pineal body)
Small body resembling a pine nut behind the thalamus
Adjusts output of “time-keeping hormone” melatonin in response
to changing levels of external light (sunlight and moonlight)
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 23
Cerebrum
Largest part of the human brain
Outer layers of gray matter are the cerebral cortex; made up
of lobes; composed mainly of dendrites and cell bodies of
neurons
Interior of the cerebrum composed mainly of white matter
Tracts: Nerve fibers arranged in bundles
Basal nuclei: Islands of gray matter regulate automatic
movements and posture
Functions of the cerebrum
Mental processes of all types, including sensations,
consciousness, memory, and voluntary control of movements
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 24
The Cerebrum
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 25
Spinal Cord
Columns of white matter, composed of bundles of
myelinated nerve fibers, form the outer portion of the H-
shaped core of the spinal cord; bundles of axons called
tracts
Interior composed of gray matter made up mainly of
neuron dendrites and cell bodies
Spinal cord tracts provide two-way conduction paths:
Ascending and descending
Spinal cord functions as the primary center for all spinal
cord reflexes; sensory tracts conduct impulses to the
brain, and motor tracts conduct impulses from the brain
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 26
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 27
Coverings and Fluid Spaces of the
Brain and Spinal Cord
Coverings
Cranial bones and vertebrae
Cerebral and spinal meninges
• Dura mater
• Pia mater
• Arachnoid mater
Fluid spaces
Subarachnoid spaces of meninges
Central canal inside cord
Ventricles in brain
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 28
Spinal Cord and Its Coverings
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 29
Peripheral Nervous System
Cranial nerves
Twelve pairs: Attached to undersurface of the brain
Connect brain with the neck and structures in the thorax
and abdomen
Spinal nerves
Thirty-one pairs: Contain dendrites of sensory neurons and
axons of motor neurons
Conduct impulses necessary for sensations and voluntary
movements
Dermatome: Skin surface area supplied by a single cranial
or spinal nerve
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 30
Cranial Nerves
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 31
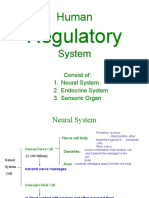
Autonomic Nervous System
Functional anatomy
Autonomic conduction paths
Sympathetic division
Parasympathetic division
Autonomic neurotransmitters
Autonomic nervous system as a whole
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 32
Functional Anatomy
Consists of motor neurons that conduct impulses from the CNS to
cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glandular epithelial tissue;
regulates the body’s automatic or involuntary functions
Preganglionic autonomic neurons
Conduct impulses from spinal cord or brainstem to an autonomic
ganglion
Postganglionic neurons
Conduct from autonomic ganglia to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and
glandular epithelial tissue
Autonomic or visceral effectors
Tissues to which autonomic neurons conduct impulses
Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 33
Innervation of Major Target Organs
by the Autonomic Nervous System
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 34
Autonomic Conduction Paths
Consist of two-neuron relays (i.e., preganglionic
neurons from the CNS to autonomic ganglia,
synapses, postganglionic neurons from ganglia
to visceral effectors)
In contrast, somatic motor neurons conduct all
the way from the CNS to somatic effectors with
no intervening synapses
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 35
Sympathetic Division (1 of 2)
Structure
Dendrites and cell bodies of sympathetic preganglionic
neurons are located in the gray matter of the thoracic and
upper lumbar segments of the spinal cord
Axons leave the spinal cord in the anterior roots of spinal
nerves, extend to sympathetic or collateral ganglia, and
synapse with several postganglionic neurons whose axons
extend to spinal or autonomic nerves to terminate in
visceral effectors
A chain of sympathetic ganglia is in front of and at each
side of the spinal column
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 36
Sympathetic Division (2 of 2)
Functions
Serves as the emergency or stress system,
controlling visceral effectors during strenuous
exercise and when strong emotions (anger, fear, hate,
or anxiety) are triggered
Group of changes induced by sympathetic control is
called the fight-or-flight response
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 37
Parasympathetic Division
Structure
Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons
• Have dendrites and cell bodies in the gray matter of the brainstem
and the sacral segments of the spinal cord
• Terminate in parasympathetic ganglia located in the head and the
thoracic and abdominal cavities close to visceral effectors
• Each parasympathetic preganglionic neuron synapses with
postganglionic neurons to only one effector
Functions
Dominates control of many visceral effectors under normal,
everyday conditions
Counterbalances sympathetic function
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 38
Autonomic Neurotransmitters
Cholinergic fibers
Preganglionic axons of parasympathetic and sympathetic
systems and parasympathetic postganglionic axons
release acetylcholine
Adrenergic fibers
Axons of sympathetic postganglionic neurons release
norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 39
Autonomic Nervous System as a
Whole
Regulates the body’s automatic functions in ways that
maintain or quickly restore homeostasis
Many visceral effectors are doubly innervated (i.e., they
receive fibers from parasympathetic and sympathetic
divisions and are influenced in opposite ways by the two
divisions)
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 40
You might also like
- Final - UFP Skills For Sci Eng - Lab Assessment 2 Instructions 2022-23Document10 pagesFinal - UFP Skills For Sci Eng - Lab Assessment 2 Instructions 2022-23MaharshiGohelNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis PDFDocument286 pagesFunctional Analysis PDFbmandarNo ratings yet
- Stryker X8000 Xenon Light Source Service ManualDocument71 pagesStryker X8000 Xenon Light Source Service Manualrafael gonzalez80% (5)
- Nervous System 1Document13 pagesNervous System 1wasim akhtarNo ratings yet
- SHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022Document16 pagesSHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022kailaskrishnaushusNo ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch16 eDocument9 pagesRev Notes ch16 eEdgar LeungNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Excitable TissueDocument117 pagesExcitable Tissueur.yared21No ratings yet
- The Human Nervous System A2Document33 pagesThe Human Nervous System A2Melody PamireNo ratings yet
- Neural TissueDocument9 pagesNeural TissueJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Nervous SystemDocument117 pagesUnit 11 Nervous SystemChandan Shah100% (1)
- Human Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Nervous SystemUmair BasheerNo ratings yet
- PSY-105 Chapter # 03: Neuro Science and BehaviorDocument9 pagesPSY-105 Chapter # 03: Neuro Science and BehaviorSabbir AhammedNo ratings yet
- ICSE Biology Notes Nervous System For 20 PDFDocument25 pagesICSE Biology Notes Nervous System For 20 PDFMmt RdcNo ratings yet
- Neuron Is The Scientific Name For A Nerve CellDocument10 pagesNeuron Is The Scientific Name For A Nerve Cellirene_bayubaycuteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 22 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- MC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSDocument7 pagesMC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Class 10Document35 pagesNervous System Class 10Just JaenNo ratings yet
- Histology 7 Nerve TissueDocument82 pagesHistology 7 Nerve TissueAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 7 The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCH 7 The Nervous Systemapi-267543553No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document51 pagesUnit 5JAYANT CH (RA2111004010265)No ratings yet
- Unit 5-Immune SystemDocument51 pagesUnit 5-Immune SystemAnih Kishor (RA1911002010062)No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument5 pagesCerebrumShiella Barroga LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Oxford X Cognitive NeuroscienceDocument73 pagesOxford X Cognitive Neurosciencedudong borjaNo ratings yet
- Updated Science 8Document172 pagesUpdated Science 8Manha abdellahNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Khaleel Alyahya, PHD, Med King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelyaDocument31 pagesNervous System: Khaleel Alyahya, PHD, Med King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelyaSalem AlshahraniNo ratings yet
- Physiology For AnesthesiaDocument115 pagesPhysiology For AnesthesiaBahredin AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Human Regulatory SystemDocument37 pagesHuman Regulatory SystemRudolfNo ratings yet
- 2017 Nervous System - YdcDocument104 pages2017 Nervous System - YdcayssNo ratings yet
- Botan's Cns and The Brain 2023Document115 pagesBotan's Cns and The Brain 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesControl and CoordinationShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class X Nervous System NotesDocument20 pagesICSE Class X Nervous System Notesprogrammer.ron.akNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument55 pagesNervous SystemJhemDelfinNo ratings yet
- Note 1 Nervous CoDocument8 pagesNote 1 Nervous ComalshiNo ratings yet
- CH 07 Lecture PresentationDocument25 pagesCH 07 Lecture PresentationMESI JAYVEE F.No ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- Science Sofie 10 3 RevDocument11 pagesScience Sofie 10 3 Revjinxtapperhat07No ratings yet
- 5 The Nervous SystemDocument72 pages5 The Nervous SystemNardos TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: by Dr. K. Sumangala BhatDocument37 pagesNervous System: by Dr. K. Sumangala BhatanushkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1wakaopakao2No ratings yet
- Science 8 PDFDocument172 pagesScience 8 PDFaftab khanNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafDocument31 pagesKonsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafdiandraNo ratings yet
- Nervous System LecDocument26 pagesNervous System LecLuningning Nobleza100% (3)
- Med Surg NotesDocument65 pagesMed Surg NotesAthena ShylaNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document26 pagesWeek 5Avril Ros ReyesNo ratings yet
- Describe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous Systemsiska yantiNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Nervous TissueDocument28 pagesLab 9 Nervous TissueSarwar JafarNo ratings yet
- Samenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 B&CDocument3 pagesSamenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 B&CMarlijn Ter MorsNo ratings yet
- StimuliDocument9 pagesStimuliJAZEEL ASLAMI PANDIKKADNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAnonymous 3OKQDoiJNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument59 pagesCentral Nervous SystemChew Yee SoonNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Nervous System 2021Document64 pages1.introduction To Nervous System 2021Erdem AltunNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Assigment About NeurologyDocument5 pagesAssigment About NeurologyYola NoviyanaNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationDocument107 pagesPoints To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationRagheNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Review Summary NoteDocument117 pagesBiology F4 Review Summary NoteSocdal AbdiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesNervous Systemagyapongruth731No ratings yet
- Homework Fifth Grade Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesHomework Fifth Grade Nervous Systemmed.visionschoolNo ratings yet
- Key Terms: Coordination & Response The Nervous System in MammalsDocument8 pagesKey Terms: Coordination & Response The Nervous System in MammalsheyyoNo ratings yet
- Neural Control & Coordination Part 1 OfflineDocument45 pagesNeural Control & Coordination Part 1 Offlinedivyaasreekumar3No ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue - UpdatedDocument129 pagesNervous Tissue - UpdatedPojangNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- AC Tank Type Test TRFRMR by HAEFELYDocument20 pagesAC Tank Type Test TRFRMR by HAEFELYmadhukarreddy2811No ratings yet
- Ganga Raya Bhandari Analysis Report PDFDocument37 pagesGanga Raya Bhandari Analysis Report PDFsantosh sahNo ratings yet
- Calculus MATH 192 - Lec 1Document10 pagesCalculus MATH 192 - Lec 1ahmadomar89No ratings yet
- ch16 Lecture 8e GOODDocument105 pagesch16 Lecture 8e GOODJana Mae Catot AcabalNo ratings yet
- CEP Assignmnet Number 2 Network AnalysisDocument3 pagesCEP Assignmnet Number 2 Network AnalysisHussain MustafaNo ratings yet
- Vibration ExampleDocument27 pagesVibration ExamplekosarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Physicists: Volker Hohmann Institute of Physics University of Oldenburg, GermanyDocument90 pagesNumerical Methods For Physicists: Volker Hohmann Institute of Physics University of Oldenburg, GermanyAdeyemiNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument51 pagesTransformerMuhammad Husnain RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Math S Practice Paper - 1 QPDocument7 pagesMath S Practice Paper - 1 QPmanviprivateaccNo ratings yet
- FSI-851 (Ion Smoke Detector)Document2 pagesFSI-851 (Ion Smoke Detector)Umair A. MoqeetNo ratings yet
- A Non-Premixed Combustion Model Based On Flame STRDocument59 pagesA Non-Premixed Combustion Model Based On Flame STRCarlos AlarconNo ratings yet
- National Public School WhitefieldDocument2 pagesNational Public School WhitefieldSameera KurhekarNo ratings yet
- Physics: AnswersDocument23 pagesPhysics: AnswersKrishna ChoureyNo ratings yet
- Cpp-Alkyl HalideDocument5 pagesCpp-Alkyl Halidekrishnagamer565No ratings yet
- Midas Civil Application in Box Girder LRT 3Document48 pagesMidas Civil Application in Box Girder LRT 3milkcNo ratings yet
- ZG QCW Handheld Laser WelderDocument6 pagesZG QCW Handheld Laser Welderultra2boxNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components of MHPDocument10 pagesElectrical Components of MHPDiyath VindulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Welded Connections: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manual, 14 EdDocument10 pagesChapter 5 - Welded Connections: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manual, 14 EdINNOBUNo7No ratings yet
- D 6477 - 02 Rdy0nzctmdjbDocument4 pagesD 6477 - 02 Rdy0nzctmdjbJuan GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 6-Estimation of Soot Content in Engine OilDocument2 pages6-Estimation of Soot Content in Engine Oilmahesh8760No ratings yet
- Viscosity - WikipediaDocument35 pagesViscosity - WikipediaHamza MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Pouring Time CalculationDocument5 pagesPouring Time CalculationKaarthicNatarajan100% (1)
- Moodle Updated-2Document200 pagesMoodle Updated-2srlohitkriishnaaNo ratings yet
- Pump System Design PDFDocument21 pagesPump System Design PDFP Priya100% (1)
- Dwnload Full College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3rd Edition Knight Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3rd Edition Knight Test Bank PDFthomasmurphy013t100% (20)
- AS Chemistry Revision Seminar 9701Document32 pagesAS Chemistry Revision Seminar 9701Jhoshna MuniandyNo ratings yet
- COE 105 Chapter3 KinematicsDocument9 pagesCOE 105 Chapter3 Kinematicsjethrocunanan04No ratings yet