Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2 - Ecosystem
Unit 2 - Ecosystem
Uploaded by
Diya Sarkar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesOriginal Title
Unit 2- Ecosystem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesUnit 2 - Ecosystem
Unit 2 - Ecosystem
Uploaded by
Diya SarkarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
What is an ECOSYSTEM?
• An ecosystem can be defined as a biological environment consisting of
all the organisms living in a particular area interacting with each other,
as well as with all the nonliving, physical components of the
environment, such as air, soil, water, and sunlight, exchanging energy
and matter.
• The study of ecosystems is called ecology. The term ecology was coined
in 1869 (by Ernst Haeckel) much before the term ecosystem.
Structure
• Biotic components, or biotic factors, can be described as any living component that
affects another organism or shapes the ecosystem.
• Producers, otherwise known as autotrophs, convert energy (through the
process of photosynthesis) into food.
• Consumers, otherwise known as heterotrophs, depend upon producers (and
occasionally other consumers) for food.
• Decomposers, otherwise known as detritivores, break down chemicals from
producers and consumers into simpler form which can be reused.
• Abiotic Components –
• The abiotic components are air, water, salts, light, temperature, nutrients etc.
• Nutrients such as N, P and Ca, necessary for the growth of living organisms are
accumulated in the biomass and the abiotic components like the soil.
Functions of an Ecosystem
• Primary Production • Soil Formation and Erosion Control
• Nutrient Cycling • Pollination and Seed Dispersal
• Pest Control
• Biodiversity Support
• Recreation and Cultural Services
• Climate Regulation
• Provision of Natural Resources
• Water Cycle Regulation
Nutrient Cycling
• Nutrient cycling is a cyclic process that encompasses the movement of nutrients from the
physical environment to living organisms and back to the environment. Nutrients are
present on the earth where they are recycled, transformed into different forms and
reutilized.
• It is required for the transformation of nutrients from one form to another so that it can
be readily utilized by different organisms, e.g. plants cannot take atmospheric nitrogen
and it has to be fixed and converted to ammonium and nitrate for uptake.
• Nutrient cycles keep the ecosystem in equilibrium and help in storing nutrients for future
uptake
• Transfer of nutrients from one place to another for utilization, e.g. air to soil or water
Ecological Concepts
TROPHIC LEVELS- Trophic levels can be defined as the feeding position in a food
chain such as primary producers, herbivore, primary carnivore etc., Organisms
within an ecosystem can be categorized into different trophic levels based on their
primary sources of nutrition and their roles as producers or consumers.
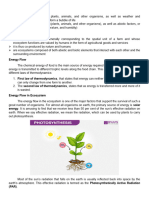
ENERGY FLOW- Energy flow in an ecosystem refers to the transfer and
transformation of energy through various trophic levels, starting from producers
(autotrophs) and moving up through consumers (heterotrophs). It represents the
movement of energy from one organism to another as organisms interact through
feeding relationships. Energy flow is vital for sustaining life within an ecosystem. It
supports the growth, reproduction, and activities of organisms, enabling them to
carry out essential life functions.
FOOD CHAIN - A food chain is a linear sequence that represents the transfer of
energy and nutrients between different organisms in an ecosystem. It illustrates
the feeding relationships and flow of energy from one organism to another, starting
with a primary producer and progressing through various consumers up to the top
predator. Each step in the food chain is known as a trophic level.
FOOD WEB - A food web is a more complex representation of the feeding
relationships within an ecosystem compared to a simple food chain. It is a graphical
model that depicts the interconnection of multiple food chains, showing the various
pathways through which energy and nutrients flow among different organisms.
Food chain vs Food Web
ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS- Ecological pyramids, also known as energy pyramids or
trophic pyramids, are graphical representations of the flow of energy, biomass, or
numbers of organisms through the different trophic levels of an ecosystem.
*Pyramid of Energy *Pyramid of Biomass *Pyramid of Numbers
ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION
• Ecological succession refers to the process of change and development in the
species composition and structure of an ecological community over time. It
describes the gradual transition of plant and animal communities in an
ecosystem following a disturbance, such as a natural disaster, fire, or the
abandonment of agricultural land. Ecological succession is driven by a
combination of biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors, including
changes in soil composition, availability of resources, climate conditions, and
interactions between species.
You might also like
- Lesson 2 - EcosystemDocument28 pagesLesson 2 - EcosystemJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Biome CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesBiome CharacteristicsTolu 'Fridgey' KuforijiNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Earth HistoryDocument410 pagesBiodiversity and Earth HistoryFelipe Andres Morales Vicencio75% (4)
- Art Integration ActivityDocument22 pagesArt Integration ActivityHarishkumaran VNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Program On CH - 1: EcosystemDocument71 pagesE-Learning Program On CH - 1: EcosystemRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 2Document38 pagesEnvironmental Science 2Calzada DanielaNo ratings yet
- Types, Features, Structure, and Function of Ecosystem (Terrestrial/aquatic)Document24 pagesTypes, Features, Structure, and Function of Ecosystem (Terrestrial/aquatic)Bhavvyam BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument14 pagesEcologyHaritha HaridasNo ratings yet
- PPt. 1-EVS. Intro. 4feb.Document27 pagesPPt. 1-EVS. Intro. 4feb.tisir87933No ratings yet
- Module 5Document14 pagesModule 5Melody GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ECOSYSTEMDocument54 pagesModule 3 ECOSYSTEMSHRAVAN JEEVAL B ANo ratings yet
- Ecology and EcosystemDocument42 pagesEcology and EcosystemGunjan Adhikari Kathayat100% (1)
- CH 3 EcosystemDocument68 pagesCH 3 EcosystemfqwjbfdjkwNo ratings yet
- ESDM Unit I BSs EcosystemsDocument87 pagesESDM Unit I BSs EcosystemsMuthuraman ArNo ratings yet
- Ecological Concepts and Principles: TTH 5 - 6:30 PM 7 - 8:30 PM 2 Semester AY: 2018 - 2019Document76 pagesEcological Concepts and Principles: TTH 5 - 6:30 PM 7 - 8:30 PM 2 Semester AY: 2018 - 2019Reggie PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Q4. L5 Interactions of OrganismDocument30 pagesQ4. L5 Interactions of OrganismMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument28 pagesEcosystemAkshitaNo ratings yet
- EVS - Unit 1 - EcosystemsDocument21 pagesEVS - Unit 1 - EcosystemsADITYA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Biology CH # 7 Man and His Environment Class X Revised 23-24Document13 pagesBiology CH # 7 Man and His Environment Class X Revised 23-24mustufamudassir43No ratings yet
- 0 Environmental Systems, EcosystemDocument21 pages0 Environmental Systems, EcosystemitzmeabeerNo ratings yet
- Eco Systems, m2Document34 pagesEco Systems, m2kukkuNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science ProjectDocument34 pagesEnvironmental Science ProjectAshwini Kishor KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Lesson 1Document24 pagesBioenergetics Lesson 1azwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument28 pagesEcosystemakhilesh.dabarase02No ratings yet
- EnvironmentalDocument49 pagesEnvironmentalsaksham kumarNo ratings yet
- BIO111 EcologyDocument35 pagesBIO111 Ecologytoyosi owoseniNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 ESDocument85 pagesUnit-2 ESyashwanth.mamilla07No ratings yet
- Unit 1...Document36 pagesUnit 1...N.S Achyuth AnandNo ratings yet
- HWDocument6 pagesHWabm12diamond.lozada.quineNo ratings yet
- 7 Ecology ChecklistDocument5 pages7 Ecology Checklistu19majli0No ratings yet
- Environment and Ecology Notes Unit 2Document25 pagesEnvironment and Ecology Notes Unit 2divyanshu potaliyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Earth As A SystemDocument22 pagesLesson 2 - Earth As A SystemJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Ecosytem (Structure and Function - Food Chain. Food Web, Energy Flow)Document37 pagesUNIT-2 Ecosytem (Structure and Function - Food Chain. Food Web, Energy Flow)adityapandey83406No ratings yet
- Ecology NotesDocument41 pagesEcology Notesmayos2027No ratings yet
- Introduction To Ecology: Place of Living and Logos'Document33 pagesIntroduction To Ecology: Place of Living and Logos'Prakriti GoelNo ratings yet
- Handout ECOSYSTEMDocument3 pagesHandout ECOSYSTEMHubert BernardNo ratings yet
- Agri NotesDocument7 pagesAgri NotesMikaella GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Environment EcologyDocument66 pages2021 Environment EcologyAWS DEVELOPERNo ratings yet
- People and The Earths Ecosystem CoverageDocument49 pagesPeople and The Earths Ecosystem CoverageChristen Honely DadangNo ratings yet
- EnviSci Lesson 2 The Environment and OrganismsDocument38 pagesEnviSci Lesson 2 The Environment and OrganismsJohn Kyle SorimaNo ratings yet
- EVS Unit-1bDocument42 pagesEVS Unit-1bAkshay GoyalNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From and Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument4 pagesMaterial Downloaded From and Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksInderpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Environment and Society Nature, Modern Science and TechnologyDocument18 pagesEnvironment and Society Nature, Modern Science and TechnologyAllex WafulaNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 EcologyDocument46 pagesUnit 10 Ecologyadaney963No ratings yet
- Est MicroprojectDocument8 pagesEst Microprojectjayeshbaviskar9501No ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Ecosystem: Srivatsan 19BFS053Document11 pagesStructure and Functions of Ecosystem: Srivatsan 19BFS05319BFS053 Srivatsan SridharNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument226 pagesEcologyRaheel MustafaNo ratings yet
- Education NotesDocument17 pagesEducation NotesshereenyaminNo ratings yet
- Esdm Mod 2Document102 pagesEsdm Mod 2sanjithr619No ratings yet
- MATERI KULIAH Ekologi Tanaman 2011Document134 pagesMATERI KULIAH Ekologi Tanaman 2011Elsa Ade Komala100% (1)
- Energy Flow and Nutrient CyclingDocument39 pagesEnergy Flow and Nutrient CyclingAshley JohnsNo ratings yet
- GEOL 1 Module 7Document10 pagesGEOL 1 Module 7abelardopaloyojrNo ratings yet
- Chapter I EcosystemDocument37 pagesChapter I EcosystemChennaiSuperkingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Components of EcosystemDocument24 pagesChapter2 Components of EcosystemvenjosagadbuhayNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - EcosystemDocument73 pagesGroup 4 - EcosystemAshley Sofia BooNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument36 pagesEcosystemR. JhansiraniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Environemt & EcosystemDocument43 pagesUnit 1 - Environemt & EcosystemViswanathan NatrayasamyNo ratings yet
- EVS Module 3Document37 pagesEVS Module 3Yolo GuyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science & Disaster ManagementDocument99 pagesEnvironmental Science & Disaster ManagementJyothis T SNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Environmental Systems, EcosystemDocument18 pages2.2 Environmental Systems, EcosystemSadi Mohammad HridoyNo ratings yet
- FINAL - Lecture 2 - Ecology - in - Science (Printed)Document66 pagesFINAL - Lecture 2 - Ecology - in - Science (Printed)mon patrick pradoNo ratings yet
- Exploring the Ecological Dynamics : Interactions Between Fish and Birds in Aquatic EcosystemsFrom EverandExploring the Ecological Dynamics : Interactions Between Fish and Birds in Aquatic EcosystemsNo ratings yet
- Nvmen Vol 51Document551 pagesNvmen Vol 51Esotericist MinorNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument18 pagesBio ProjectVivek Prasad93% (14)
- Emergency Ordinance No 195 - 2005Document42 pagesEmergency Ordinance No 195 - 2005iubaNo ratings yet
- What Is An EcosystemDocument2 pagesWhat Is An EcosystemAhmad Raza100% (1)
- General Studies Project CBSE Class 11Document8 pagesGeneral Studies Project CBSE Class 11Viom KapurNo ratings yet
- Esdm Mod 2Document102 pagesEsdm Mod 2sanjithr619No ratings yet
- Pre. Compass 2023 Environment Rau S IasDocument209 pagesPre. Compass 2023 Environment Rau S IasADESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Sciences MYP 2 SA Unit 5 Criterion ADocument7 pagesSciences MYP 2 SA Unit 5 Criterion AEsma YildizNo ratings yet
- What Is Environmental Awareness?Document8 pagesWhat Is Environmental Awareness?Jennilyn AlbeosNo ratings yet
- Block - Aaa - Gelect3 Midterm Assessment 1b Chapter 6 EcosystemsDocument3 pagesBlock - Aaa - Gelect3 Midterm Assessment 1b Chapter 6 EcosystemsMhartin OrsalNo ratings yet
- CAMPAÑA INGLESdocxDocument7 pagesCAMPAÑA INGLESdocxyhonatan leonNo ratings yet
- Biblio Himalaya FloraDocument280 pagesBiblio Himalaya FloraMadhan RajNo ratings yet
- Routes and Roots Navigating Caribbean and Pacific Island LiteraturesDocument353 pagesRoutes and Roots Navigating Caribbean and Pacific Island LiteraturesPotiki100% (1)
- Global Sustainability: Toward Definition: Environmental Management January 1987Document8 pagesGlobal Sustainability: Toward Definition: Environmental Management January 1987AR RafiNo ratings yet
- DeltasWetlands Program 2024 FinDocument6 pagesDeltasWetlands Program 2024 FinMarian IaniNo ratings yet
- Competition As A Social Process: Sociology Project OnDocument21 pagesCompetition As A Social Process: Sociology Project OnChoudhary Shadab phalwanNo ratings yet
- Sericea LespedezaDocument1 pageSericea Lespedezaapi-506709715No ratings yet
- Truffle GuideDocument2 pagesTruffle GuidetaadvNo ratings yet
- City in AWild GardenDocument220 pagesCity in AWild GardenSinduja RNo ratings yet
- (2013) Joseph - Resilience As Embedded Neoliberalism. A Governmentality ApproachDocument16 pages(2013) Joseph - Resilience As Embedded Neoliberalism. A Governmentality ApproachCarlos Araneda-UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law: Chanakya National Law University, PatnaDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Law: Chanakya National Law University, PatnaVaishnavi Prakash100% (1)
- Environmental Science Your World Your Turn Chapter 4 NotesDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Science Your World Your Turn Chapter 4 NotesTaylorRayKaneNo ratings yet
- Examining "Borrowed Theory" in Original vs. New Disciplines Via Text MiningDocument35 pagesExamining "Borrowed Theory" in Original vs. New Disciplines Via Text MiningStephen DowningNo ratings yet
- On Thom Hartmann and The Last Hours of Ancient SunlightDocument8 pagesOn Thom Hartmann and The Last Hours of Ancient SunlightDanut ViciuNo ratings yet
- Daniel Weiss: Education G.P.A. 3.2/4.0Document2 pagesDaniel Weiss: Education G.P.A. 3.2/4.0api-638692198No ratings yet
- Biodiversity and The Healthy SocietyDocument16 pagesBiodiversity and The Healthy SocietyDaisy Marie A. RoselNo ratings yet
- Giant Hogweed BrochureDocument2 pagesGiant Hogweed BrochureThe Livingston County NewsNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms in The Environt and Microbial BiotechnologyDocument33 pagesMicroorganisms in The Environt and Microbial Biotechnologytaty jatyNo ratings yet